Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Specimen (IAL) MS
Specimen (IAL) MS
Uploaded by
Karim OwnCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Freud Bose CorrespondenceDocument17 pagesFreud Bose CorrespondenceSiddhi JangidNo ratings yet
- Edexcel As A Level Physics Answers (2015)Document34 pagesEdexcel As A Level Physics Answers (2015)AbdulRahman Mustafa50% (4)
- Solution To 2010 VJC Prelim H2 Paper 3Document10 pagesSolution To 2010 VJC Prelim H2 Paper 3cjcsucksNo ratings yet
- Drug-Induced Diseases PDFDocument1,135 pagesDrug-Induced Diseases PDFGiang Vớ Vẩn100% (1)
- Current, Charge, Potential Difference & Power 1 MS PDFDocument7 pagesCurrent, Charge, Potential Difference & Power 1 MS PDFAnt LiveNo ratings yet
- Answers & Solutions: For For For For For JEE (MAIN) - 2021 (Online) Phase-4Document23 pagesAnswers & Solutions: For For For For For JEE (MAIN) - 2021 (Online) Phase-4Insta GramNo ratings yet
- Skema Permarkahan Kertas 3 No. 1 Answer MarkDocument5 pagesSkema Permarkahan Kertas 3 No. 1 Answer MarkHajar Aja NurNo ratings yet
- 9792 PHYSICS: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2013 SeriesDocument6 pages9792 PHYSICS: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2013 SeriesKelvin SerimweNo ratings yet
- Practice Test NeetDocument23 pagesPractice Test NeetnileshkumarmudraprajapatiNo ratings yet
- NEET 2024 Provisional Key Answer HAYATH'S IIT & NEET ACADEMYDocument36 pagesNEET 2024 Provisional Key Answer HAYATH'S IIT & NEET ACADEMYMohammed Obaid MohiuddinNo ratings yet
- Statics & Resolving Forces 2 MSDocument8 pagesStatics & Resolving Forces 2 MSelsieNo ratings yet
- 1486536129GATE ECE Answerkey PDFDocument13 pages1486536129GATE ECE Answerkey PDFVivek KushwahNo ratings yet
- Trial Pahang Answers For Physics Paper 1 Trial 2010Document16 pagesTrial Pahang Answers For Physics Paper 1 Trial 2010lilysuhanyNo ratings yet
- Mid Year 2022 (Scheme)Document8 pagesMid Year 2022 (Scheme)LOOK HAO YU MoeNo ratings yet
- Test Series For Neet-2020Document15 pagesTest Series For Neet-2020kavyareddyNo ratings yet
- Sample Assessment Material 2018: Mark SchemeDocument15 pagesSample Assessment Material 2018: Mark Scheme謝利米No ratings yet
- Answer and Solutions - JEE - Main 2023 - PH 1 - 25 01 2023 - Morning - Shift 1 PDFDocument25 pagesAnswer and Solutions - JEE - Main 2023 - PH 1 - 25 01 2023 - Morning - Shift 1 PDFinduja c mNo ratings yet
- Esophageal DiseaseDocument36 pagesEsophageal DiseaseSaurabh RokadeNo ratings yet
- 647b2f370b281a001874498e - ## - City Test Paper 01 - 21 May 2023 (PDF Only)Document19 pages647b2f370b281a001874498e - ## - City Test Paper 01 - 21 May 2023 (PDF Only)Satyam AgrawalNo ratings yet
- ECE 322 MRKNG SCHMDocument7 pagesECE 322 MRKNG SCHMNicholas OyieNo ratings yet
- NEET 2024 Provisional Key AnswerDocument36 pagesNEET 2024 Provisional Key Answerjaspindervirdi7No ratings yet
- Vedantu - JEE Main Simulator: 1. in A Circuit Consisting of A Capacitance and A Generator With Alternating Emf EDocument53 pagesVedantu - JEE Main Simulator: 1. in A Circuit Consisting of A Capacitance and A Generator With Alternating Emf EPandu KpNo ratings yet
- January 2022 (IAL) MSDocument8 pagesJanuary 2022 (IAL) MSKalkidan EstifanosNo ratings yet
- Anc Ment 638412758974269347Document30 pagesAnc Ment 638412758974269347Trishir AlvaNo ratings yet
- Marking Scheme Physics Trial SPM SBP 2016 Paper 3Document6 pagesMarking Scheme Physics Trial SPM SBP 2016 Paper 3Anonymous UypCttWNo ratings yet
- 5 6179243493991386840Document20 pages5 6179243493991386840Anil KumarNo ratings yet
- FTS Code A Paper PDFDocument3 pagesFTS Code A Paper PDFSaurabh GoyalNo ratings yet
- NeSS Assignments For Beginners Fourier SeriesDocument3 pagesNeSS Assignments For Beginners Fourier SeriesEshan GuptaNo ratings yet
- Marking Scheme Physics Trial SPM SBP 2016 Paper 3 PDFDocument6 pagesMarking Scheme Physics Trial SPM SBP 2016 Paper 3 PDFkingNo ratings yet
- PHY2016Document3 pagesPHY2016Advita AgarwalNo ratings yet
- 2nd Internal Test BSC 2024Document3 pages2nd Internal Test BSC 2024lp eelceeNo ratings yet
- JEE Main 2020 Question Paper With Solution 08 Jan 2020 Shift 1 Memory BasedDocument34 pagesJEE Main 2020 Question Paper With Solution 08 Jan 2020 Shift 1 Memory BasedmisostudyNo ratings yet
- 2023 NEET PhysicsDocument19 pages2023 NEET PhysicsFAIZAN RATHERNo ratings yet
- Complete Syllabus Test - 04: CST-04 Code-A Test Date 01-04-2020Document13 pagesComplete Syllabus Test - 04: CST-04 Code-A Test Date 01-04-2020Ankush BhuniaNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument5 pagesPhysicsDeng SyiemliehNo ratings yet
- Ap Review Chapter 5 Answer Key at The End of DocDocument26 pagesAp Review Chapter 5 Answer Key at The End of Doc조민성No ratings yet
- Code-A: Regd. Office: Aakash Tower, 8, Pusa Road, New Delhi-110005 PH.: 011-47623456Document15 pagesCode-A: Regd. Office: Aakash Tower, 8, Pusa Road, New Delhi-110005 PH.: 011-47623456rhevaNo ratings yet
- F MGL Sut at V U GS: Engineering Mathematics UFMFJ9-30-1 Worksheet 1: DimensionsDocument26 pagesF MGL Sut at V U GS: Engineering Mathematics UFMFJ9-30-1 Worksheet 1: Dimensionsmohammad jamalNo ratings yet
- Physics I Phys 1001 - 2022Document6 pagesPhysics I Phys 1001 - 2022xilag49210No ratings yet
- SolutionDocument3 pagesSolutionAnadi RanjanNo ratings yet
- Nov 04 p4msDocument6 pagesNov 04 p4ms1mathew1No ratings yet
- Resolving & Moments MSDocument6 pagesResolving & Moments MSleesha.sahaNo ratings yet
- Question 994390Document4 pagesQuestion 994390xelivo8277No ratings yet
- Physics - II (Backlog) Phys 2001Document2 pagesPhysics - II (Backlog) Phys 2001Vikash KumarNo ratings yet
- 12th PhysicsDocument4 pages12th Physicsरविंद्र महाराज गोडसेNo ratings yet
- Milestone Test - 00 - Test PaperDocument19 pagesMilestone Test - 00 - Test Paperheloindai5No ratings yet
- Questions & Answers: For For For For For JEE (MAIN) - 2020 (Online) Phase-2Document12 pagesQuestions & Answers: For For For For For JEE (MAIN) - 2020 (Online) Phase-2Manila NandaNo ratings yet
- Ece, Ee, Bme Ph201 Physics - I r18Document5 pagesEce, Ee, Bme Ph201 Physics - I r18dsreNo ratings yet
- 13.1 Deformation of Solids CIE IAL Physics MS Theory UnlockedDocument4 pages13.1 Deformation of Solids CIE IAL Physics MS Theory Unlockedmaze.putumaNo ratings yet
- Cse It Me Ce Ph101 Physics - I 18Document4 pagesCse It Me Ce Ph101 Physics - I 18dsreNo ratings yet
- Physics Class Xii Sample Paper 01 For 2019 20 1Document6 pagesPhysics Class Xii Sample Paper 01 For 2019 20 1dick kumarNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Atomic Structure Test Mark Scheme: Allow No. of Nucleons / Amount of P & NDocument3 pages1.1 Atomic Structure Test Mark Scheme: Allow No. of Nucleons / Amount of P & NalexisNo ratings yet
- JEE Main 4 2021 Paper PDFDocument12 pagesJEE Main 4 2021 Paper PDFBiswadeep GiriNo ratings yet
- Ans&Sol JEE (Main) - 2024 Ph-1 (30-01-2024) EveningDocument17 pagesAns&Sol JEE (Main) - 2024 Ph-1 (30-01-2024) EveningJINESH JAINNo ratings yet
- Class 11 JEE Based Unit and Dimensions TestDocument2 pagesClass 11 JEE Based Unit and Dimensions TestANUJ KALRANo ratings yet
- Question 1163433Document6 pagesQuestion 1163433ParthNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Physical Sciences Term 3 Experiment-1Document5 pagesGrade 10 Physical Sciences Term 3 Experiment-1braceface0abmNo ratings yet
- Guess PaperDocument8 pagesGuess Paperadtydv007No ratings yet
- Universiti Kuala Lumpur: Final ExaminationDocument7 pagesUniversiti Kuala Lumpur: Final ExaminationMuhd AkmalNo ratings yet
- Skema p3 f4 Pat 2017Document12 pagesSkema p3 f4 Pat 2017tengkusuhaidaNo ratings yet
- Me Som IesDocument75 pagesMe Som IesSanket ManeNo ratings yet
- Moments, Monodromy, and Perversity. (AM-159): A Diophantine Perspective. (AM-159)From EverandMoments, Monodromy, and Perversity. (AM-159): A Diophantine Perspective. (AM-159)No ratings yet
- Difference Between Dyes and PigmentsDocument5 pagesDifference Between Dyes and PigmentsHameedullah Ansari100% (1)
- Joy Trust Fear Surprise Sadness Disgust Anger AnticipationDocument4 pagesJoy Trust Fear Surprise Sadness Disgust Anger AnticipationsatyakaamsNo ratings yet
- Acronyms and Its Meaning: S/N Acronyms Stand For Explainationa & Meaning Examples TLVDocument2 pagesAcronyms and Its Meaning: S/N Acronyms Stand For Explainationa & Meaning Examples TLVshamroz khanNo ratings yet
- ASIYADocument3 pagesASIYASOFIKUL HUUSAINNo ratings yet
- Learn Solar PPT On MC4 ConnectorDocument17 pagesLearn Solar PPT On MC4 ConnectorPARBATINo ratings yet
- Enfield Saheli: Funding NEWSDocument5 pagesEnfield Saheli: Funding NEWSenfieldclubhouseNo ratings yet
- The Science Behind AspirinDocument14 pagesThe Science Behind AspirindipetNo ratings yet
- Methods of Measuring Plaque PH: Assignment in CariologyDocument6 pagesMethods of Measuring Plaque PH: Assignment in Cariologydr_shakir-sudanNo ratings yet
- Certificate of Compliance CSA For Fluke 113 - 114 - 115-116-117Document2 pagesCertificate of Compliance CSA For Fluke 113 - 114 - 115-116-117CHARLES BARRAZA100% (1)
- Embedded Controlled Drip Irrigation SystemDocument5 pagesEmbedded Controlled Drip Irrigation SystemInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNo ratings yet
- 6 Fem3343 M6 - Prinsip Dan Nilai Etika 27mac18Document38 pages6 Fem3343 M6 - Prinsip Dan Nilai Etika 27mac18Ron ChongNo ratings yet
- Sore ThroatDocument10 pagesSore Throatapi-551073862No ratings yet
- Claim BillDocument5 pagesClaim BillVimala VimuNo ratings yet
- 2022 Tucson Plug in Hybrid Emergency Response Quick Reference GuideDocument2 pages2022 Tucson Plug in Hybrid Emergency Response Quick Reference GuideForum PompieriiNo ratings yet
- Evelyn Glennie (Responses) PDFDocument8 pagesEvelyn Glennie (Responses) PDFRohit JhambNo ratings yet
- Heart DiseaseDocument88 pagesHeart DiseaseBruce Lawrence MadeirosNo ratings yet
- Exercise Induced Neuroplasticity - Rogge 2018Document38 pagesExercise Induced Neuroplasticity - Rogge 2018Juani Cantellanos0% (1)
- Presentation HPLCDocument81 pagesPresentation HPLCSangram KendreNo ratings yet
- AIA Future Builder FAQsDocument3 pagesAIA Future Builder FAQsjulianraphaelrazonNo ratings yet
- Thermostats,: Type KPDocument12 pagesThermostats,: Type KPEvandro Jva compressoresNo ratings yet
- CompressorDocument33 pagesCompressorfvaefaNo ratings yet
- E Mannual Temperate Fruits 1Document44 pagesE Mannual Temperate Fruits 1gamerrr.mahiNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Request Form - TemplateDocument2 pagesLaboratory Request Form - TemplateShafiq Azam RumiNo ratings yet
- Exercise 1. You Have Been Given A Form Which Shows The Details of Technical Jobs Carried OutDocument2 pagesExercise 1. You Have Been Given A Form Which Shows The Details of Technical Jobs Carried OutNgo Gia Huy (K15 HCM)No ratings yet
- K-008 ( 20001) - Fuel System - A30000 Fuel Piping ## K-008 ( 20001)Document2 pagesK-008 ( 20001) - Fuel System - A30000 Fuel Piping ## K-008 ( 20001)Martin LindbergNo ratings yet
- Activated Carbon From BambooDocument19 pagesActivated Carbon From BambooErik WeeksNo ratings yet
- LV Panel ReportDocument71 pagesLV Panel ReportMudassirNo ratings yet
- Timber GrowthDocument17 pagesTimber GrowthAbdul Sukur Kamsir100% (3)
Specimen (IAL) MS
Specimen (IAL) MS
Uploaded by
Karim OwnOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Specimen (IAL) MS
Specimen (IAL) MS
Uploaded by
Karim OwnCopyright:
Available Formats
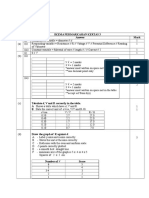
Unit 6: Practical Skills in Physics II - Mark scheme
Question Answer Mark
number
1(a) 2.860 (1) 1
1(b) 2.858 cm (four sig figs. Allow ecf from (a)) (1) 1
1(c) 4πr 3 3
Use of V (1)
3
m
Use of (1)
V
Density = 8.020 g cm-3 must be to 4 SF allow ecf from (b) (1)
Example of calculation
4π1.429 3 cm 3
V = 12.223 cm3
3
98.00g
= = 8.018 g cm-3
12.223cm 3
1(d) Calculates % uncertainty in diameter from (b) (1) 2
% uncertainty in density = 0.4 (accept 0.42 or 0.37 if half-
range is used) (1)
Example of calculation
Uncertainty in diameter = 2.858-2.854 = 0.004
% uncertainty in diameter = 0.004/2.858 × 100 = 0.14%
% uncertainty in volume and density = 3 × 0.14 = 0.42
Total for Question 1 7
Pearson Edexcel International Advanced Subsidiary/Advanced Level in Physics 173
Sample Assessment Materials – Issue 1 – September 2017 © Pearson Education Limited 2017
Question Answer Mark
number
2(a) metre rule shown vertical with set square on floor (1) 1
2(b)(i) The resolution of the stopwatch is 0.01 seconds (1) 2
But there is a human reaction time when starting and stopping
the stopwatch (1)
2(b)(ii) v = 0.59 m s-1 (1) 1
Example of calculation
2h
v= = 2 × 0.885/3.0
t
v = 0.59 m s-1
2(b)(iii) Calculates value of momentum (1) 1
Example of calculation
P = 0.96 kg × 0.59 m s-1 = 0.57 kg m s-1
2(c)(i) Momentum = 0.88 kg m s-1 (1) 1
Example of calculation
p = 0.030 × 9.81 × 3.0
= 0.88 kg m s-1
2(c)(ii) External forces acting 1
Or friction acting (1)
Total for Question 2 7
174 Pearson Edexcel International Advanced Subsidiary/Advanced Level in Physics
Sample Assessment Materials – Issue 1 – September 2017 © Pearson Education Limited 2017
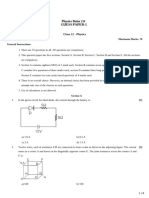
Question Answer Mark
number
3(a) Circuit showing power supply unit (psu), heater, ammeter in 5
series and voltmeter in parallel with heater (1)
Measure the p.d., current and mass of block (and heater) (1)
Measure initial and final temperature and corresponding time
interval (1)
Use of E = VIt (1)
Use of c= ΔE/m Δθ (1)
Example of circuit
3(b) Not all energy from the heater is supplied to the block 2
Or some energy transferred to/from surroundings (1)
energy transfer to cancels/equals energy transfer from the
surroundings (by using same temperature difference
below/above surroundings) (1)
Total for Question 3 7
Pearson Edexcel International Advanced Subsidiary/Advanced Level in Physics 175
Sample Assessment Materials – Issue 1 – September 2017 © Pearson Education Limited 2017
Question Answer Mark
number
4(a)(i) 3.5 mm should have the same number of SF as other values in (1) 2
column
There are no repeat readings (1)
4(a)(ii) Any two from 2
Distance between coils (1)
Potential difference (across first coil) power supply (1)
Frequency of ac supply (1)
4(a)(iii) 0.01 V (1) 1
4(a)(iv) Because the final digit fluctuates (1) 1
4(a)(v) Would need to take some repeat readings (1)
Consider how close together in value (1) 2
4(b) There is a value of V when t = 0 (1) 1
4(c) Plot ln V against t (1) 2
Should be a straight-line graph if the relationship is exponential (1)
Total for Question 4 11
176 Pearson Edexcel International Advanced Subsidiary/Advanced Level in Physics
Sample Assessment Materials – Issue 1 – September 2017 © Pearson Education Limited 2017
Question Answer Mark
number
5(a) Record background count (rate) (1) 3
Place thick aluminium/thin lead between source and detector
Or Distance greater than 25 cm between source and detector (1)
Count rate detected above background (1)
5(b) Any two from 2
Point source away from people (1)
Invert source within lead container (1)
Use tongs to handle source (1)
Use tongs to handle lead sheets/ensure source held (1)
5(c)(i) The count is a large number for small distances so percentage errors 1
will be smaller (1)
5(c)(ii) There is a larger variation in count over smaller distances (1) 1
5(d)(i) Calculates count rate per minute or per second or per 30 s (1) 7
Subtract background count (1)
Count rate C1/2 to at least 3SF (1)
Axes labelled for suitable graph and with correct units (1)
Suitable scales (1)
Points plotted (1)
(1)
Line of best fit
Example of table
Time
for C-background C0.5 / C-0.5
d / cm Count count / s C min -1
min-1 min-0.5 /min0.5
5 1163 30 2326 2268 47.62352 0.0210
6 897 30 1794 1736 41.66533 0.0240
7 586 30 1172 1114 33.37664 0.0300
9 793 60 793 735 27.11088 0.0369
11 559 60 559 501 22.38303 0.0447
13 469 60 469 411 20.27313 0.0493
Pearson Edexcel International Advanced Subsidiary/Advanced Level in Physics 177
Sample Assessment Materials – Issue 1 – September 2017 © Pearson Education Limited 2017
5(d)(ii) Use of large triangle to determine gradient (1) 4
k = 280 (allow 260 – 300) (1)
Unit: cm min-0.5 (1)
x (y intercept) = 1.0 cm (allow 0.6 – 1.2) (1)
Example of calculation
(10.0 – 0)/(0.040 – 0.004) = 280 cm min-0.5
Total for Question 5 18
178 Pearson Edexcel International Advanced Subsidiary/Advanced Level in Physics
Sample Assessment Materials – Issue 1 – September 2017 © Pearson Education Limited 2017
You might also like
- Freud Bose CorrespondenceDocument17 pagesFreud Bose CorrespondenceSiddhi JangidNo ratings yet
- Edexcel As A Level Physics Answers (2015)Document34 pagesEdexcel As A Level Physics Answers (2015)AbdulRahman Mustafa50% (4)
- Solution To 2010 VJC Prelim H2 Paper 3Document10 pagesSolution To 2010 VJC Prelim H2 Paper 3cjcsucksNo ratings yet
- Drug-Induced Diseases PDFDocument1,135 pagesDrug-Induced Diseases PDFGiang Vớ Vẩn100% (1)
- Current, Charge, Potential Difference & Power 1 MS PDFDocument7 pagesCurrent, Charge, Potential Difference & Power 1 MS PDFAnt LiveNo ratings yet
- Answers & Solutions: For For For For For JEE (MAIN) - 2021 (Online) Phase-4Document23 pagesAnswers & Solutions: For For For For For JEE (MAIN) - 2021 (Online) Phase-4Insta GramNo ratings yet
- Skema Permarkahan Kertas 3 No. 1 Answer MarkDocument5 pagesSkema Permarkahan Kertas 3 No. 1 Answer MarkHajar Aja NurNo ratings yet
- 9792 PHYSICS: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2013 SeriesDocument6 pages9792 PHYSICS: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2013 SeriesKelvin SerimweNo ratings yet
- Practice Test NeetDocument23 pagesPractice Test NeetnileshkumarmudraprajapatiNo ratings yet
- NEET 2024 Provisional Key Answer HAYATH'S IIT & NEET ACADEMYDocument36 pagesNEET 2024 Provisional Key Answer HAYATH'S IIT & NEET ACADEMYMohammed Obaid MohiuddinNo ratings yet
- Statics & Resolving Forces 2 MSDocument8 pagesStatics & Resolving Forces 2 MSelsieNo ratings yet
- 1486536129GATE ECE Answerkey PDFDocument13 pages1486536129GATE ECE Answerkey PDFVivek KushwahNo ratings yet
- Trial Pahang Answers For Physics Paper 1 Trial 2010Document16 pagesTrial Pahang Answers For Physics Paper 1 Trial 2010lilysuhanyNo ratings yet
- Mid Year 2022 (Scheme)Document8 pagesMid Year 2022 (Scheme)LOOK HAO YU MoeNo ratings yet
- Test Series For Neet-2020Document15 pagesTest Series For Neet-2020kavyareddyNo ratings yet
- Sample Assessment Material 2018: Mark SchemeDocument15 pagesSample Assessment Material 2018: Mark Scheme謝利米No ratings yet
- Answer and Solutions - JEE - Main 2023 - PH 1 - 25 01 2023 - Morning - Shift 1 PDFDocument25 pagesAnswer and Solutions - JEE - Main 2023 - PH 1 - 25 01 2023 - Morning - Shift 1 PDFinduja c mNo ratings yet
- Esophageal DiseaseDocument36 pagesEsophageal DiseaseSaurabh RokadeNo ratings yet
- 647b2f370b281a001874498e - ## - City Test Paper 01 - 21 May 2023 (PDF Only)Document19 pages647b2f370b281a001874498e - ## - City Test Paper 01 - 21 May 2023 (PDF Only)Satyam AgrawalNo ratings yet
- ECE 322 MRKNG SCHMDocument7 pagesECE 322 MRKNG SCHMNicholas OyieNo ratings yet
- NEET 2024 Provisional Key AnswerDocument36 pagesNEET 2024 Provisional Key Answerjaspindervirdi7No ratings yet
- Vedantu - JEE Main Simulator: 1. in A Circuit Consisting of A Capacitance and A Generator With Alternating Emf EDocument53 pagesVedantu - JEE Main Simulator: 1. in A Circuit Consisting of A Capacitance and A Generator With Alternating Emf EPandu KpNo ratings yet
- January 2022 (IAL) MSDocument8 pagesJanuary 2022 (IAL) MSKalkidan EstifanosNo ratings yet
- Anc Ment 638412758974269347Document30 pagesAnc Ment 638412758974269347Trishir AlvaNo ratings yet
- Marking Scheme Physics Trial SPM SBP 2016 Paper 3Document6 pagesMarking Scheme Physics Trial SPM SBP 2016 Paper 3Anonymous UypCttWNo ratings yet
- 5 6179243493991386840Document20 pages5 6179243493991386840Anil KumarNo ratings yet
- FTS Code A Paper PDFDocument3 pagesFTS Code A Paper PDFSaurabh GoyalNo ratings yet
- NeSS Assignments For Beginners Fourier SeriesDocument3 pagesNeSS Assignments For Beginners Fourier SeriesEshan GuptaNo ratings yet
- Marking Scheme Physics Trial SPM SBP 2016 Paper 3 PDFDocument6 pagesMarking Scheme Physics Trial SPM SBP 2016 Paper 3 PDFkingNo ratings yet
- PHY2016Document3 pagesPHY2016Advita AgarwalNo ratings yet
- 2nd Internal Test BSC 2024Document3 pages2nd Internal Test BSC 2024lp eelceeNo ratings yet
- JEE Main 2020 Question Paper With Solution 08 Jan 2020 Shift 1 Memory BasedDocument34 pagesJEE Main 2020 Question Paper With Solution 08 Jan 2020 Shift 1 Memory BasedmisostudyNo ratings yet
- 2023 NEET PhysicsDocument19 pages2023 NEET PhysicsFAIZAN RATHERNo ratings yet
- Complete Syllabus Test - 04: CST-04 Code-A Test Date 01-04-2020Document13 pagesComplete Syllabus Test - 04: CST-04 Code-A Test Date 01-04-2020Ankush BhuniaNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument5 pagesPhysicsDeng SyiemliehNo ratings yet
- Ap Review Chapter 5 Answer Key at The End of DocDocument26 pagesAp Review Chapter 5 Answer Key at The End of Doc조민성No ratings yet
- Code-A: Regd. Office: Aakash Tower, 8, Pusa Road, New Delhi-110005 PH.: 011-47623456Document15 pagesCode-A: Regd. Office: Aakash Tower, 8, Pusa Road, New Delhi-110005 PH.: 011-47623456rhevaNo ratings yet
- F MGL Sut at V U GS: Engineering Mathematics UFMFJ9-30-1 Worksheet 1: DimensionsDocument26 pagesF MGL Sut at V U GS: Engineering Mathematics UFMFJ9-30-1 Worksheet 1: Dimensionsmohammad jamalNo ratings yet
- Physics I Phys 1001 - 2022Document6 pagesPhysics I Phys 1001 - 2022xilag49210No ratings yet
- SolutionDocument3 pagesSolutionAnadi RanjanNo ratings yet
- Nov 04 p4msDocument6 pagesNov 04 p4ms1mathew1No ratings yet
- Resolving & Moments MSDocument6 pagesResolving & Moments MSleesha.sahaNo ratings yet
- Question 994390Document4 pagesQuestion 994390xelivo8277No ratings yet
- Physics - II (Backlog) Phys 2001Document2 pagesPhysics - II (Backlog) Phys 2001Vikash KumarNo ratings yet
- 12th PhysicsDocument4 pages12th Physicsरविंद्र महाराज गोडसेNo ratings yet
- Milestone Test - 00 - Test PaperDocument19 pagesMilestone Test - 00 - Test Paperheloindai5No ratings yet
- Questions & Answers: For For For For For JEE (MAIN) - 2020 (Online) Phase-2Document12 pagesQuestions & Answers: For For For For For JEE (MAIN) - 2020 (Online) Phase-2Manila NandaNo ratings yet
- Ece, Ee, Bme Ph201 Physics - I r18Document5 pagesEce, Ee, Bme Ph201 Physics - I r18dsreNo ratings yet
- 13.1 Deformation of Solids CIE IAL Physics MS Theory UnlockedDocument4 pages13.1 Deformation of Solids CIE IAL Physics MS Theory Unlockedmaze.putumaNo ratings yet
- Cse It Me Ce Ph101 Physics - I 18Document4 pagesCse It Me Ce Ph101 Physics - I 18dsreNo ratings yet
- Physics Class Xii Sample Paper 01 For 2019 20 1Document6 pagesPhysics Class Xii Sample Paper 01 For 2019 20 1dick kumarNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Atomic Structure Test Mark Scheme: Allow No. of Nucleons / Amount of P & NDocument3 pages1.1 Atomic Structure Test Mark Scheme: Allow No. of Nucleons / Amount of P & NalexisNo ratings yet
- JEE Main 4 2021 Paper PDFDocument12 pagesJEE Main 4 2021 Paper PDFBiswadeep GiriNo ratings yet
- Ans&Sol JEE (Main) - 2024 Ph-1 (30-01-2024) EveningDocument17 pagesAns&Sol JEE (Main) - 2024 Ph-1 (30-01-2024) EveningJINESH JAINNo ratings yet
- Class 11 JEE Based Unit and Dimensions TestDocument2 pagesClass 11 JEE Based Unit and Dimensions TestANUJ KALRANo ratings yet
- Question 1163433Document6 pagesQuestion 1163433ParthNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Physical Sciences Term 3 Experiment-1Document5 pagesGrade 10 Physical Sciences Term 3 Experiment-1braceface0abmNo ratings yet
- Guess PaperDocument8 pagesGuess Paperadtydv007No ratings yet
- Universiti Kuala Lumpur: Final ExaminationDocument7 pagesUniversiti Kuala Lumpur: Final ExaminationMuhd AkmalNo ratings yet
- Skema p3 f4 Pat 2017Document12 pagesSkema p3 f4 Pat 2017tengkusuhaidaNo ratings yet
- Me Som IesDocument75 pagesMe Som IesSanket ManeNo ratings yet
- Moments, Monodromy, and Perversity. (AM-159): A Diophantine Perspective. (AM-159)From EverandMoments, Monodromy, and Perversity. (AM-159): A Diophantine Perspective. (AM-159)No ratings yet
- Difference Between Dyes and PigmentsDocument5 pagesDifference Between Dyes and PigmentsHameedullah Ansari100% (1)
- Joy Trust Fear Surprise Sadness Disgust Anger AnticipationDocument4 pagesJoy Trust Fear Surprise Sadness Disgust Anger AnticipationsatyakaamsNo ratings yet
- Acronyms and Its Meaning: S/N Acronyms Stand For Explainationa & Meaning Examples TLVDocument2 pagesAcronyms and Its Meaning: S/N Acronyms Stand For Explainationa & Meaning Examples TLVshamroz khanNo ratings yet
- ASIYADocument3 pagesASIYASOFIKUL HUUSAINNo ratings yet
- Learn Solar PPT On MC4 ConnectorDocument17 pagesLearn Solar PPT On MC4 ConnectorPARBATINo ratings yet
- Enfield Saheli: Funding NEWSDocument5 pagesEnfield Saheli: Funding NEWSenfieldclubhouseNo ratings yet
- The Science Behind AspirinDocument14 pagesThe Science Behind AspirindipetNo ratings yet
- Methods of Measuring Plaque PH: Assignment in CariologyDocument6 pagesMethods of Measuring Plaque PH: Assignment in Cariologydr_shakir-sudanNo ratings yet
- Certificate of Compliance CSA For Fluke 113 - 114 - 115-116-117Document2 pagesCertificate of Compliance CSA For Fluke 113 - 114 - 115-116-117CHARLES BARRAZA100% (1)
- Embedded Controlled Drip Irrigation SystemDocument5 pagesEmbedded Controlled Drip Irrigation SystemInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNo ratings yet
- 6 Fem3343 M6 - Prinsip Dan Nilai Etika 27mac18Document38 pages6 Fem3343 M6 - Prinsip Dan Nilai Etika 27mac18Ron ChongNo ratings yet
- Sore ThroatDocument10 pagesSore Throatapi-551073862No ratings yet
- Claim BillDocument5 pagesClaim BillVimala VimuNo ratings yet
- 2022 Tucson Plug in Hybrid Emergency Response Quick Reference GuideDocument2 pages2022 Tucson Plug in Hybrid Emergency Response Quick Reference GuideForum PompieriiNo ratings yet
- Evelyn Glennie (Responses) PDFDocument8 pagesEvelyn Glennie (Responses) PDFRohit JhambNo ratings yet
- Heart DiseaseDocument88 pagesHeart DiseaseBruce Lawrence MadeirosNo ratings yet
- Exercise Induced Neuroplasticity - Rogge 2018Document38 pagesExercise Induced Neuroplasticity - Rogge 2018Juani Cantellanos0% (1)
- Presentation HPLCDocument81 pagesPresentation HPLCSangram KendreNo ratings yet
- AIA Future Builder FAQsDocument3 pagesAIA Future Builder FAQsjulianraphaelrazonNo ratings yet
- Thermostats,: Type KPDocument12 pagesThermostats,: Type KPEvandro Jva compressoresNo ratings yet
- CompressorDocument33 pagesCompressorfvaefaNo ratings yet
- E Mannual Temperate Fruits 1Document44 pagesE Mannual Temperate Fruits 1gamerrr.mahiNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Request Form - TemplateDocument2 pagesLaboratory Request Form - TemplateShafiq Azam RumiNo ratings yet
- Exercise 1. You Have Been Given A Form Which Shows The Details of Technical Jobs Carried OutDocument2 pagesExercise 1. You Have Been Given A Form Which Shows The Details of Technical Jobs Carried OutNgo Gia Huy (K15 HCM)No ratings yet
- K-008 ( 20001) - Fuel System - A30000 Fuel Piping ## K-008 ( 20001)Document2 pagesK-008 ( 20001) - Fuel System - A30000 Fuel Piping ## K-008 ( 20001)Martin LindbergNo ratings yet
- Activated Carbon From BambooDocument19 pagesActivated Carbon From BambooErik WeeksNo ratings yet
- LV Panel ReportDocument71 pagesLV Panel ReportMudassirNo ratings yet
- Timber GrowthDocument17 pagesTimber GrowthAbdul Sukur Kamsir100% (3)