Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cell Reviewer
Cell Reviewer
Uploaded by
Kaireen Oz0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views4 pagesMitochondria produce ATP from oxygen and glucose inside cells. Microfilaments form an internal framework. Membrane proteins receive hormones and transport molecules into cells. Diffusion moves molecules down concentration gradients, while active transport uses ATP to move molecules against gradients. The plasma membrane is selectively permeable and holds cells together. Mitochondria and ribosomes synthesize proteins and other molecules.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentMitochondria produce ATP from oxygen and glucose inside cells. Microfilaments form an internal framework. Membrane proteins receive hormones and transport molecules into cells. Diffusion moves molecules down concentration gradients, while active transport uses ATP to move molecules against gradients. The plasma membrane is selectively permeable and holds cells together. Mitochondria and ribosomes synthesize proteins and other molecules.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views4 pagesCell Reviewer
Cell Reviewer
Uploaded by
Kaireen OzMitochondria produce ATP from oxygen and glucose inside cells. Microfilaments form an internal framework. Membrane proteins receive hormones and transport molecules into cells. Diffusion moves molecules down concentration gradients, while active transport uses ATP to move molecules against gradients. The plasma membrane is selectively permeable and holds cells together. Mitochondria and ribosomes synthesize proteins and other molecules.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 4
Mitochondria - where glucose or an amino acid bind
- Produces ATP from oxygen to to a receptor protein on the plasma
glucose membrane, which then moves the
Microfilaments is inside the cell molecule into the cell without the
Membrane protein expenditure of energy
- To receive amino acid-based Diffusion
hormones that cannot pass through - the movement of ions and molecules
plasma membrane away from regions where they are in
Lysosome high concentration towards regions
- Contains acidic environment where they are in lower
(ENZYME) that is capable of concentration.
digesting wide variety of molecules Endocytosis
Active transport - the plasma membrane engulfs the
- Uses energy (ATP) to move a substance and moves it through the
molecule against its concentration membrane.
- the use of energy from ATP to move - phagocytosis and pinocytosis
ions and small molecules against - A cell ingests bacteria.
their concentration gradient. Integral protein in the PM
PLASMA MEMBRANE - is to form channels to allow for the
- The plasma membranes of adjacent passage of ions.
cells are held together by Answer is B: the inside of a cell is negative
desmosomes. while the exterior side of the
- It contains receptors for specific mem brane is positive. This difference
signaling molecules. in charge constitutes a difference in
- It is selectively permeable. electrical potential (or voltage), known
The sodium-potassium pump as the resting membrane potential. An
- mechanism that ensures that there is action potential is generated when the
a higher concentration of sodium membrane is stimulated and the
ions in the extracellular fluid than in potential reversed.
the intracellular fluid Osmosis
PHOSPOLIPIDS - diffusion of water through a
- to present a barrier to the passage of membrane
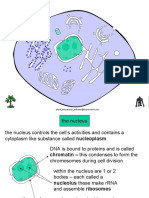
water-soluble molecules. cell nucleus
- a cell contains molecules that have a - contains chromosomes which are
hydrophobic end and a hydrophilic composed of molecules of DNA.
end DNA
- Phosphate is the HYDROPHILIC - is composed of units called
- Lipid is the Hydrophobic nucleotides which consist of a sugar
- polar head and non-polar tail (deoxy ribose) attached to a
RIBOSOME phosphoric acid group (PO 3 OH)
- Synthesize protein and one of four bases.
ER Chromosomes
- Synthesize fatty acid, phospholipid - contain the code for the sequence of
and cholesterol amino acids used to construct
Facilitated diffusion different proteins
- movement along a concentration codon
gradient assisted by protein carrier - adenine, guanine, cytosine &
molecules. thymine
- refers to the role of the protein . mRNA “transcribes”
carriers. - this code then moves from the
- protein channels or molecules nucleus to a ribosome in the
cytoplasm where it is
“translated” intravenous solutions allows red
- the protein is assembled by joining blood cells to retain their normal size
the required amino acids in the and disc-like shape.
appropriate sequence Protein
Mitosis - molecules in the cell membrane that
- is the process by which a somatic serve as receptors or binding sites
cell divides to produce two cells with for hormones or other chemical
identical DNA. messengers
- then during mitosis, the two peroxisomes
chromatids separate and move into - A cell whose job is to detoxify
the two daughter cells harmful or poisonous substances
Meiosis such as alcohol would have many
- occurs only in the gonads. This - uses molecular oxygen to convert
process results in four daughter and detoxify harmful substances
cells. Human cells have two copies such as alcohol and free radicals
of each of 23 chromosomes, one Microvilli is for absorption
copy being inherited from the father - tiny finger-like projections that
and the other copy from the mother. increase the surface are of the cell
The gametes need to have only one for quicker absorption
copy of each of the 23 interphase, prophase, metaphase,
chromosomes, so that when the anaphase, telophase
sperm fuses with the ovum, the Cilia
“diploid” number of 46 (two copies of - Whiplike cellular extensions that
each chromosome) is restored. move substances along the cell
Nucleolus surface are called
- site where ribosome assemble prior Gene
to their migration into the cytoplasm - DNA segment that carries
transfer RNA information for building one protein
- molecule that carries an amino acid or polypeptide chain
to the ribosome for incorporation into Membrane Conjunctions
a protein • Tight junctions are areas where the
- molecule that contains anticodons membranes of adjacent cells fuse together.
Cytoskeleton This creates an impermeable leak proof
- forms an internal framework inside cellular sheet and prevents substances from
the cell and is made of microtubules, passing between the cells. Tight junctions are
intermediate filaments, and found in epithelia lining fluid containing
microfilaments cavities, such as the small intestine.
Filtration • Desmosomes are areas where fine protein
- do not involve the movement of filaments extend between two adjacent cells
molecules from an area of greater and are anchored in button-like thickenings of
concentration to an area of lower the cell membranes called plaque. This type
concentration of junction holds adjacent cells together very
dehydrated patient firmly and is found in areas where cellular
- hypotonic intravenous drip sheets are subjected to considerable
- it is solution that contains fewer mechanical stress, such as the skin. Within
solutes than the cell each cell, the plaques on one side are
- Isotonic solutions have the same connected to plaques on the opposite side by
solute and water concentrations as thicker protein filaments that act to internally
the cell. Isotonic solutions cause no anchor the plaques in place.
visible changes in cells since there is • Gap junctions consist of hollow protein
not an area more highly cylinders, called connexons, which extend
concentrated. The use of isotonic completely through the plasma membrane of
neighboring cells and meet and join together again. A nuclear membrane then forms
in the extracellular space. This creates a around each chromatin mass, the spindle
continuous channel for the passage of breaks down and disappears,
substances between the interiors of the two
adjacent cells. Gap junctions, which promote The rough endoplasmic reticulum (ER):
intercellular communication, are found - is studded with ribosomes b. makes
between the cardiac muscle cells in the proteins on its ribosomes
heart. The smooth ER:
Translation - lacks ribosomes on its surface
- during protein synthesis, of - functions in lipid metabolism, drug
assembling proteins by decoding the and pesticide detoxification
information in messenger RNA Five molecules in PLASMA MEMBRANE
centrioles 1. Lipid molecules (phospholipids) provide
- rod-shaped bodies that lie at right the medium in which protein molecules
angles to each other and internally float, form the basic fabric of the
are made up of fine microtubing membrane, and are relatively
Interphase impermeable to most water-soluble
- period of the cell cycle when the cell molecules.
grows and performs its metabolic 2. Cholesterol molecules have a stabilizing
activities effect and help to keep the membrane
- DNA replication fluid.
anaphase 3. Protein molecules are responsible for
- phase of cell division during which the most specialized functions of the
the chromatids are pulled apart and membrane. They act as enzymes, serve
move to the opposite ends of the cell as receptors or binding sites for
Prophase hormones and other chemical
- cancer drug interferes with the messengers, act as carriers that bind to
development of mitotic spindle fibers substances and move them through the
during cell division cell membrane, and form pores through
• Prophase- chromatin threads coil and which water and small molecules can
shorten so that visible bar-like bodies, called move.
chromosomes, appear. Each chromosome is 4. Carbohydrate molecules add an
made up of two strands, called chromatids, identification tag to mark protein
which are held together by a centromere. molecules, and make the cell membrane
Additionally, the centrioles separate and move a fuzzy, sticky, sugar-rich area.
toward opposite sides of the cell, directing the 5. Glycoprotein molecules determine blood
assembly of the mitotic spindle (composed of type; act as receptors that certain
microtubules) between them as they move. bacteria, viruses, or their toxins can bind
• 2. Metaphase chromosomes cluster and to; and play a role in cell-to-cell
align in the center of the spindle, midway interactions
between the centrioles, forming a straight line STEPS OF PROTEIN SYSTESIZE
of chromosomes. 1. Uncoiling of DNA the DNA segment or
• Anaphase the centromere split and the gene that specifies one polypeptide or
chromosomes move slowly apart toward protein uncoils.
opposite ends of the cell. A cleavage furrow 2. Transcription (DNA-directed synthesis
appears over the midline of the spindle and of mRNA) one strand of DNA acts as a
eventually pinches the cytoplasmic mass into template for the synthesis of the
two parts in a process called cytokinesis. complementary mRNA molecule, and
• Telophase- the chromosomes reach opposite there is a transfer of information from
ends of the cell and their movement ends, the DNAʹs base sequence (code) into
and they then uncoil and become chromatin the complementary base sequence of
mRNA (codon).
3. Translation (RNA-directed synthesis of
a polypeptide or protein) involves five
steps. First, mRNA leaves the nucleus
and attaches to ribosomes. Second,
tRNA (anticodon) transports an amino
acid to the mRNA strand and recognizes
a mRNA molecule (codon). Third, the
codon and the anticodon bind. Fourth,
the ribosome moves the mRNA strand
along as each codon is read
sequentially. Finally, as each amino acid
is bound to the next by a polypeptide
bond, its tRNA is released. The
polypeptide or protein chain is released
when the termination (stop) codon is
read.
You might also like
- The Cellular Level of Organization - AnaphyDocument12 pagesThe Cellular Level of Organization - AnaphyJean Rose SalahayNo ratings yet
- BBMS1001 NotesDocument41 pagesBBMS1001 NotesHelen WanNo ratings yet
- Dropping Signals Web Activity PDFDocument1 pageDropping Signals Web Activity PDFKatie FairNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure Function Review PresentationDocument8 pagesCell Structure Function Review PresentationCharles IppolitoNo ratings yet
- HISTO LEC 2 - The CystoplasmDocument7 pagesHISTO LEC 2 - The CystoplasmjkthmsvtchNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology - The Cellular Level of OrganizationDocument11 pagesAnatomy and Physiology - The Cellular Level of OrganizationChristina MarkwartNo ratings yet
- Cell STRUCTURE and Function Worksheet. HomeworkDocument5 pagesCell STRUCTURE and Function Worksheet. HomeworkMichael WrightNo ratings yet
- Ana PhyDocument7 pagesAna Physilva, april joy c.No ratings yet
- Microana Prelim ReviewerDocument17 pagesMicroana Prelim ReviewerjerlerositaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 The Cytoplasm ReviewerDocument13 pagesChapter 2 The Cytoplasm ReviewerKyleBernalÜNo ratings yet
- Microtubules Which Occur On Exposed Membrane SurfacesDocument3 pagesMicrotubules Which Occur On Exposed Membrane Surfacesprettyfriends 05No ratings yet
- II. Chapter 2 (Cytoplasm)Document14 pagesII. Chapter 2 (Cytoplasm)rosalesjirehrNo ratings yet
- H2 BIO Cell Structure NotesDocument15 pagesH2 BIO Cell Structure NotesEdcademiaNo ratings yet
- CELLDocument7 pagesCELLzairazapanta001No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Cell Structures & Their Functions: Certain Molecules To Enter/exit The Cell)Document5 pagesChapter 3 Cell Structures & Their Functions: Certain Molecules To Enter/exit The Cell)Gellyace A.No ratings yet
- Histology Dr. Noelyn Bernal Cytoplasm-September 7,2018: Page - PEREZDocument13 pagesHistology Dr. Noelyn Bernal Cytoplasm-September 7,2018: Page - PEREZA18- Jessa Mae DayagNo ratings yet
- Reviewer (Cells)Document6 pagesReviewer (Cells)Sophia Mae ClavecillaNo ratings yet
- Chap 2 HistoDocument24 pagesChap 2 HistoAbegail Ashley PenoniaNo ratings yet
- Micro HSB Lecture Guide Week 1 - Cell Parenchyma StromaDocument12 pagesMicro HSB Lecture Guide Week 1 - Cell Parenchyma StromajandaniellerasNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document15 pagesModule 2mycamariebeliot0508No ratings yet
- 5 - Composition and Functions of Cell Membrane Transport Systems LectureDocument32 pages5 - Composition and Functions of Cell Membrane Transport Systems Lecturegodara28pNo ratings yet
- Midterm 2 Review AnswersDocument35 pagesMidterm 2 Review AnswershamoudyelmouallemNo ratings yet
- 3 Cell Structures FunctionsDocument2 pages3 Cell Structures FunctionsKYLA LORENZ BALUMANo ratings yet
- Cell Membrane and Cell TransportDocument5 pagesCell Membrane and Cell TransportKEITHLYN EIZEL RAMITERRENo ratings yet
- 1.3. Components of The Cell IISubcellular Organelles 070141Document31 pages1.3. Components of The Cell IISubcellular Organelles 070141Angel CaroNo ratings yet
- 1 CytologyDocument86 pages1 CytologyRathana Nguon100% (1)
- Chapter 4 Cell Review AssignmentDocument8 pagesChapter 4 Cell Review Assignmentsarahmohammed801No ratings yet
- MCB CS01 IntroductionToMolecularCellBiology-1Document1 pageMCB CS01 IntroductionToMolecularCellBiology-1MohibNo ratings yet
- PL4 Cell CompartmentsDocument11 pagesPL4 Cell CompartmentsJake GopitaNo ratings yet
- 3 Main Parts of Human CellDocument6 pages3 Main Parts of Human CellNicole Sta AnaNo ratings yet
- Basic Unit of All Living Things: 3 Main RegionsDocument18 pagesBasic Unit of All Living Things: 3 Main RegionsRikki Mae BuenoNo ratings yet
- 05 - Kompart Sorting Protein 1Document33 pages05 - Kompart Sorting Protein 1Haddhi WhibowoNo ratings yet
- Eukaryotic Cells: Chapter 7-2: Cell StructureDocument10 pagesEukaryotic Cells: Chapter 7-2: Cell Structurejmunozbio@yahoo.comNo ratings yet
- Biology Topic 2 NotesDocument12 pagesBiology Topic 2 NotesAasiya SultanaNo ratings yet
- Biology Periodic ReviewerDocument6 pagesBiology Periodic ReviewerLanz NicoleiNo ratings yet
- CELLMOLDocument3 pagesCELLMOLJhon Rey LagosNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles: NucleusDocument4 pagesCell Organelles: NucleusVeronica AlvaradoNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and Function: Structure of The Nuclear EnvelopeDocument40 pagesCell Structure and Function: Structure of The Nuclear EnvelopeKitkat AlorroNo ratings yet
- CellDocument15 pagesCellvijayp2No ratings yet
- Cell Structure and FunctionDocument18 pagesCell Structure and FunctionBeah Marie AlisosoNo ratings yet
- IB Bio Notes MasterDocument45 pagesIB Bio Notes MasterE. GarciaNo ratings yet
- محاضرة 2Document41 pagesمحاضرة 2AbdulNo ratings yet
- Cell Reviewer SeeleysDocument2 pagesCell Reviewer Seeleysmarielle castroNo ratings yet
- Cell StructureDocument35 pagesCell Structure2W10No ratings yet
- Cell OrganellesDocument4 pagesCell OrganellesRokunuz Jahan RudroNo ratings yet
- Ch.5 MembranesDocument25 pagesCh.5 MembranesEmma WisemanNo ratings yet
- CELL-PPT-DR.-LINAO, Updated Aug.2,2020Document103 pagesCELL-PPT-DR.-LINAO, Updated Aug.2,2020Allan Q VenusNo ratings yet
- Compendium Review Cells Part 3Document22 pagesCompendium Review Cells Part 3AmandaSherman100% (2)
- 'Aliah's Microbiology Notes1Document54 pages'Aliah's Microbiology Notes1Luqman Al-Bashir Fauzi100% (1)
- Cell & Intercellular JunctionsDocument35 pagesCell & Intercellular JunctionsDikpal BikramNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles Structure & FunctionDocument4 pagesCell Organelles Structure & FunctionDaniel ChinNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument6 pagesUntitled49 - Kaycee JoaquinNo ratings yet
- The Cell StructureDocument7 pagesThe Cell StructureAbcedef Wyn Grey AbrasadoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document153 pagesLecture 3Miya GordNo ratings yet
- The CellDocument47 pagesThe CellHemloNo ratings yet
- Biology Oral ExamDocument20 pagesBiology Oral ExamLauraNo ratings yet
- Biology Questions 3 by Akudhenga EbenDocument2 pagesBiology Questions 3 by Akudhenga EbenEbenNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure: Rebecca MaynardDocument11 pagesCell Structure: Rebecca Maynardbecki93No ratings yet
- Histo Note, CellDocument9 pagesHisto Note, Cellserainie maiNo ratings yet
- Basic Building Blocks of Life Smallest Living Unit of An OrganismDocument2 pagesBasic Building Blocks of Life Smallest Living Unit of An OrganismkikomagsaysayNo ratings yet
- The Cell Cycle Activity 1Document5 pagesThe Cell Cycle Activity 1sugarxglossNo ratings yet
- Notes Calvin CycleDocument2 pagesNotes Calvin Cycleneelp331No ratings yet
- Fates of PyruvateDocument20 pagesFates of PyruvatedanyalNo ratings yet
- MeiosisDocument9 pagesMeiosisRudzi UdziNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication Prokaryotes EukaryotesDocument38 pagesDNA Replication Prokaryotes EukaryotesSudeep BiswasNo ratings yet
- The Muscle Pump Potential MechanismsDocument5 pagesThe Muscle Pump Potential MechanismsseriousuploaderNo ratings yet
- Apoptosis and Cell Proliferation: Roche Molecular BiochemicalsDocument142 pagesApoptosis and Cell Proliferation: Roche Molecular BiochemicalsIlya BaklanovNo ratings yet
- RnaiDocument13 pagesRnaiIrah Jane BadeNo ratings yet
- Mitosis: Aarifa Hoosein-RiyasatDocument28 pagesMitosis: Aarifa Hoosein-RiyasatAkiela JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Nutri3Document11 pagesJurnal Nutri3Winda SariNo ratings yet
- Sinh Tong Hop Protein MoiDocument25 pagesSinh Tong Hop Protein MoiPhùng Anh DuyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 13 Genes and How They WorkDocument31 pagesLecture 13 Genes and How They WorkPaulNo ratings yet
- 3.2. KARBOHIDRAT II GlikolisisDocument27 pages3.2. KARBOHIDRAT II GlikolisisRikka TakaradaNo ratings yet
- Khan Academy Cellular Division QuestionsDocument3 pagesKhan Academy Cellular Division QuestionsLoraNo ratings yet
- 5.the Genetic CodeDocument8 pages5.the Genetic CodeCharm BatiancilaNo ratings yet
- Dong 2010Document31 pagesDong 2010Samuel Morales NavarroNo ratings yet
- Molecular Genetics TestDocument9 pagesMolecular Genetics TestMelody MunizNo ratings yet
- 114-136 Metabolism Flashcards Kersting PDFDocument1 page114-136 Metabolism Flashcards Kersting PDFRajendra PilludaNo ratings yet
- MODULE 4 Metabolism of Cabohydrate Fats and Proteins Biochem 2nd Sem 2020 2021 1Document19 pagesMODULE 4 Metabolism of Cabohydrate Fats and Proteins Biochem 2nd Sem 2020 2021 1Shaira BayubayNo ratings yet
- Meiosis With Pipe CleanersDocument2 pagesMeiosis With Pipe Cleanersapi-3004364130% (1)
- HHS Public AccessDocument26 pagesHHS Public AccessDr. NasrumminallahNo ratings yet
- 2.4 (Biochemistry) Tca HMP and Uronic Acid PathwayDocument15 pages2.4 (Biochemistry) Tca HMP and Uronic Acid Pathwaylovelots1234100% (1)
- Session No. 1.3. Cell Cycle and Cell DivisionDocument43 pagesSession No. 1.3. Cell Cycle and Cell DivisionShekaina Faith Cuizon LozadaNo ratings yet
- Lect. 49 Histology Review 1Document97 pagesLect. 49 Histology Review 1Mira ThakkarNo ratings yet
- Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts Origin, Function, Imaging, and TherapeuticDocument33 pagesCancer-Associated Fibroblasts Origin, Function, Imaging, and TherapeuticANA PAULANo ratings yet
- Drug TargetDocument35 pagesDrug Targetsri nurlatipahNo ratings yet
- Aerobic and Anaerobic RespirationDocument7 pagesAerobic and Anaerobic RespirationFatmata Haja KamaraNo ratings yet
- HUNTINGTONDocument141 pagesHUNTINGTONcarolinaNo ratings yet
- Aktivasi Sel T LimfositDocument36 pagesAktivasi Sel T LimfositKatou Jeffrey ShigehitoNo ratings yet