Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Faculty Business Management 2023 Session 1 - Pra-D 230717 130249
Faculty Business Management 2023 Session 1 - Pra-D 230717 130249
Uploaded by
Khairul AdibOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Faculty Business Management 2023 Session 1 - Pra-D 230717 130249
Faculty Business Management 2023 Session 1 - Pra-D 230717 130249
Uploaded by
Khairul AdibCopyright:
Available Formats
CONFIDENTIAL BA/FEB 2023/ECO162/104
UNIVERSITI TEKNOLOGI MARA
FINAL EXAMINATION
COURSE MICROECONOMICS
COURSE CODE ECO162/104
EXAMINATION FEBRUARY 2023
TIME 3 HOURS
INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
1. This question paper consists of two (2) parts: PART A (20 Questions)
PART B (4 Questions)
2. Answer ALL questions from ALL two (2) parts:
i. Answer PART A in the Objective Answer Sheet.
ii. Answer PART B in the Answer Booklet. Start each answer on a new page.
3. Do not bring any material into the examination room unless permission is given by the invigilator.
Please check to make sure that this examination pack consists of:
i. the Question Paper
ii. an Answer Booklet -provided by the Faculty
iii. an Objective Answer Sheet - provided by the Faculty
5. Answer ALL questions in English.
DO NOT TURN THIS PAGE UNTIL YOU ARE TOLD TO DO SO
This examination paper consists of 11 printed pages
© Hak Cipta Universiti Teknologi MARA CONFIDENTIAL
CONFIDENTIAL 2 BA/FEB 2023/ECO162/104
PART A
Multiple-choice Questions
QUESTION 1
The most fundamental economic problem is
A security.
B the fact that Malaysia buys more goods from foreigners than we sell to foreigners.
C wealth.
D scarcity.
(2 marks)
QUESTION 2
Which of the following is the microeconomic issue?
A the reasons for a decline in average prices.
B the reasons why Ali buys pineapple juice.
C the cause of why total employment may decrease.
D the effect of the government budget deficit on inflation.
(2 marks)
QUESTION 3
When one decision is made, the next best alternative not selected is called
A economic resource.
B opportunity cost.
C scarcity.
D production.
(2 marks)
QUESTION 4
The law of demand shows a relation between the .
A quantity demanded and quantity supplied of a commodity.
B income and quantity demanded of the commodity.
C price and quantity demanded of a commodity.
D income and price of a commodity.
(2 marks)
© Hak Cipta Universiti Teknologi MARA CONFIDENTIAL
CONFIDENTIAL 3 BA/FEB 2023/ECO162/104
QUESTION 5
If the market supply curve for a product shift rightwards, what is the best possible
explanation for this shift?
A Increase in the price of raw materials.
B Introduction of a tax on that product by the government.
C Introduction of a new technique that makes the production of that commodity cheaper.
D An advertising campaign that is successful in promoting the product.
(2 marks)
QUESTION 6
Which of the following is not a determinant of the demand for good J?
A The income of consumers who buy good J.
B The cost of labour used to produce good J.
C The price of good Y, a complement to J.
D The number of buyers of good J.
(2 marks)
QUESTION 7
Assume that there are two commodities. A positive coefficient of cross-elasticity of demand
indicates that the two commodities are .
A essential goods.
B complementary goods.
C substitute goods.
D inferior goods.
(2 marks)
QUESTION 8
Price elasticity of demand is influenced by the following, except
A improvement in production method.
B time period.
C habit of the buyer.
D level of income.
(2 marks)
© Hak Cipta Universiti Teknologi MARA CONFIDENTIAL
CONFIDENTIAL 4 BA/FEB 2023/ECO162/104
QUESTION 9
If a 7% decrease in the price of Good W results in a decrease of 5% in the quantity supplied
of Good W, then it can be concluded that the supply is
A elastic.
B inelastic.
C unitary elastic.
D infinite.
(2 marks)
QUESTION 10
If the price elasticity of supply for a leather purse is 0.65 and the price increases by 3%, then
the quantity supplied for the leather purse will
A increase by 1.95%.
B decrease by 1.95%.
C increase by 0.217%.
D decrease by 0.217%.
(2 marks)
QUESTION 11
A sales tax on cigarettes imposed by the government will make the supply curve shift
and the price to .
A rightwards; increase.
B rightwards; decrease.
C leftwards; increase.
D leftwards; decrease.
(2 marks)
QUESTION 12
Suppose there is a shortage of football match tickets, we can predict that
A the price of football match tickets has dropped.
B the quantity of football match tickets sold and purchased are the same.
C the price of football match tickets will rise.
D the quantity demanded of football match tickets is less than the quantity supplied.
(2 marks)
© Hak Cipta Universiti Teknologi MARA CONFIDENTIAL
CONFIDENTIAL 5 BA/FEB 2023/ECO162/104
QUESTION 13
Assume that the equilibrium price for a good is RM5.00. If government set up RM10.00 as
the new price, then
A a shortage will happen and the price remains at RM5.00.
B a surplus will happen and the price remains at RM5.00.
C a shortage will happen and the price rises toward RM 10.00.
D a surplus will happen and the price rises toward RM10.00.
(2 marks)
QUESTION 14
Hoarding is an activity that tends to occur when
A price is set higher than the equilibrium price.
B the price ceiling is set by the government.
C the price floor is set by the government.
D no price regulation is set by the market.
(2 marks)
QUESTION 15
The short run is a time period in which
A all factors of production are fixed.
B the total output is fixed.
C at least one input is fixed.
D all factors of production are variable.
(2 marks)
QUESTION 16
Which of the following items is an implicit cost to a firm?
A Utility bills.
B The time during the weekend spent by the owner on his or her firm.
C Cost of hiring an external trainer.
D Total fixed cost.
(2 marks)
© Hak Cipta Universiti Teknologi MARA CONFIDENTIAL
CONFIDENTIAL 6 BA/FEB 2023/ECO162/104
QUESTION 17
Which of the following is a characteristic of perfect competition?
A Barrier to entry.
B Produces homogenous products.
C Price maker.
D One seller in the whole industry.
(2 marks)
QUESTION 18
Which of the following conditions is necessary for a monopolist to practice effective price
discrimination?
A Produce standardized products.
B May have different price elasticity of demand.
C Must be in perfect market.
D The demand curve should be horizontal.
(2 marks)
QUESTION 19
The demand curve of monopolistic competition is due to the existence of
A more elastic; product differentiation.
B more elastic; homogenous products.
C less elastic; complementary goods.
D less elastic; advertisement expenditure.
(2 marks)
QUESTION 20
According to the assumption of the kinked demand curve, when one oligopolistic firm
increases its price, other oligopolistic firms will
A increase their prices as well.
B not follow but maintain the same prices as before.
C increase advertising expenditures.
D exit from the industry.
(2 marks)
© Hak Cipta Universiti Teknologi MARA CONFIDENTIAL
CONFIDENTIAL 7 BA/FEB 2023/ECO162/104
PARTB
Short Answer Questions
QUESTION 1
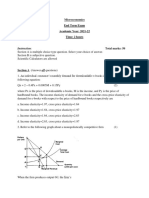
The following diagram shows the production possibilities curve of a hypothetical country at a
given time.
20 7S 80 90 WO
Torts of steel
a) Based on the diagram above, answer the following questions:
i) Calculate the opportunity cost of producing the first 45 tons of wheat.
(2 marks)
ii) Describe what point G indicates.
(2 marks)
iii) What type of opportunity cost is the economy experiencing.
(1 mark)
b) The following table shows the market demand and supply schedules for chicken in town
A per month.
Price (RM/kg) Market Demand (kg) Market Supply (kg)
8.00 16000 2000
8.50 14000 4000
9.00 12000 7000
9.50 10000 10000
10.00 8000 13000
10.50 6000 15000
i) Calculate the price elasticity of demand when the price of chicken increases from
RM8.00 to RM9.50. State the degree of price elasticity of demand.
(2 marks)
© Hak Cipta Universiti Teknologi MARA CONFIDENTIAL
CONFIDENTIAL 8 BA/FEB 2023/ECO162/104
ii) Is the supply of chicken elastic or inelastic when price of chicken increases from RM8.50
to RM10.00. Show the calculation.
(2 marks)
iii) Explain three (3) factors that determine the price elasticity of supply for chicken.
(3 marks)
iv) The demand of good W increases from 100 to 200 when the price of chicken increase from
RM9.00 to RM10.00. Calculate the cross-elasticity of demand and state the relationship
between chicken and good W.
(2 marks)
v) Assume that the income elasticity of good H is -2.5. What does it mean?
(1 mark)
© Hak Cipta Universiti Teknologi MARA CONFIDENTIAL
CONFIDENTIAL 9 BA/FEB 2023/ECO162/104
QUESTION 2
The table below shows the market demand and supply schedules for avocado juice in
Indonesia.
Price (RM/unit) Quantity Demanded (Unit) Quantity Supplied (Unit)
10 5,000 500
20 4,200 1,000
30 3,100 1,600
40 2,000 2,000
50 1,500 3,200
60 500 4,400
a) Sketch the market equilibrium of avocado juice market. State the equilibrium price
and quantity of avocado juice.
(3 marks)
b) What will happen if the government fixed the price of avocado juice at RM30? State the
price control and determine how much its shortage or surplus?
(2 marks)
c) Show the price control that is implemented by the government in a diagram you have
drawn in a). State two (2) disadvantages of the price control.
(3 marks)
d) In a separate diagram, show and explain the effects of an increase in technology on the
production of avocado juice.
(3 marks)
e) State two (2) factors that would increase the supply of avocado juice and two (2) factors
that would increase the demand of avocado juice.
(4 marks)
© Hak Cipta Universiti Teknologi MARA CONFIDENTIAL
CONFIDENTIAL 10 BA/FEB 2023/ECO162/104
QUESTION 3
The following is the production and cost schedule of a firm in the short run.
Labour Total Cost Average Marginal Average Total Marginal
Cost Cost Variable Product Product
(RM) (RM) (RM) Cost (RM) (unit) (unit)
0 100 - - - 0 -
1 170 6
2 220 13
3 260 22
4 310 29
5 370 34
a) Complete the above table production and cost schedule.
(4 marks)
b) In one diagram, show the relationship between average cost, average variable cost and
marginal cost.
(2 marks)
c) How much is the firm's average fixed cost (AFC) at 22 units output level?
(2 marks)
d) At what quantity of labour usage does the law of diminishing returns start to set in? Justify
your answer.
(2 marks)
e) State two (2) sources of economies of scale.
(1 mark)
© Hak Cipta Universiti Teknologi MARA CONFIDENTIAL
CONFIDENTIAL 11 BA/FEB 2023/ECO162/104
QUESTION 4
Table below shows the long run data for a company known as Dreamerz Bhd. The cost,
price and quantity of Good K produced by Dreamerz Bhd are given below.
Price Quantity Total Total Marginal Average Marginal
(RM) demanded Cost Revenue Revenue Cost Cost
(Units) (RM) (RM) (RM) (RM) (RM)
12 0 10
11 1 14
10 2 16
9 3 23
8 4 30
7 5 48
6 6 60
5 7 75
a) Calculate the firm's total revenue, marginal revenue, marginal cost and average cost.
(4 marks)
b) Determine the equilibrium price and quantity of the firm.
(3 marks)
c) At the equilibrium output, state the amount of profit made by the firm. Name the type of
profit the firm is making.
(4 marks)
d) In what type of market structure is the above firm operating? State two (2) characteristics
of this firm.
(3 marks)
e) Draw a diagram to show the firm's long run equilibrium. Label the output level, price level
and shade the area of profit earned.
(3 marks)
f) What is meant by mutual interdependence?
(2 marks)
END OF QUESTION PAPER
© Hak Cipta Universiti Teknologi MARA CONFIDENTIAL
You might also like
- Eco 101 Question and Answer PDFDocument28 pagesEco 101 Question and Answer PDFOlawale100% (3)
- Set 1 MID TERM TEST ECO162 MAC23-1Document8 pagesSet 1 MID TERM TEST ECO162 MAC23-1Nurus Sahirah67% (3)
- Appeal To Authority: A Failure of TrustDocument19 pagesAppeal To Authority: A Failure of Trustclapujugas100% (3)
- ZZZZDocument14 pagesZZZZMustofa Nur HayatNo ratings yet
- Bombardier Aerospace 20140716 Business Aircraft Market Forecast - 2014 33Document43 pagesBombardier Aerospace 20140716 Business Aircraft Market Forecast - 2014 33asbadgNo ratings yet
- Economics Exam Jan 10Document8 pagesEconomics Exam Jan 10Tam DoNo ratings yet
- Final Examination March-Aug 2022 (Set 1)Document12 pagesFinal Examination March-Aug 2022 (Set 1)RUSDI CHODENGNo ratings yet
- ECO162 (Feb 2022)Document12 pagesECO162 (Feb 2022)2023825868No ratings yet
- Course Name: Microeconomics Course Code: PEC1133 Duration: 1 HOUR (6.00 PM - 7.00 PM)Document7 pagesCourse Name: Microeconomics Course Code: PEC1133 Duration: 1 HOUR (6.00 PM - 7.00 PM)Amir BasirNo ratings yet
- Eco162 104 PDFDocument10 pagesEco162 104 PDFMark Victor Valerian IINo ratings yet
- BB 107 Supplementary Exam Summer 2020 Q (Set A) (Online)Document6 pagesBB 107 Supplementary Exam Summer 2020 Q (Set A) (Online)Brewell CoNo ratings yet
- MicroeconomicsDocument8 pagesMicroeconomicsfifieshafika100% (1)
- Universiti Teknologi Mara Final Examination: Confidential BM/JAN 201 2/ECOI 62/104Document11 pagesUniversiti Teknologi Mara Final Examination: Confidential BM/JAN 201 2/ECOI 62/104Mark Victor Valerian IINo ratings yet
- Module Name: Module Code: Economics 1A ECON211 Economics 1A ECON211pDocument9 pagesModule Name: Module Code: Economics 1A ECON211 Economics 1A ECON211pReeceNo ratings yet
- Test Sample (Nov2021)Document7 pagesTest Sample (Nov2021)2021492824No ratings yet
- ECO120 Apr 2009Document12 pagesECO120 Apr 2009Azie MahmoodNo ratings yet
- Eco PaperDocument7 pagesEco PaperSainadh Reddy Syamala AP21110010703No ratings yet
- Econ - 22-23 - S6 - Mock Exam - P1Document13 pagesEcon - 22-23 - S6 - Mock Exam - P1title subNo ratings yet
- Soal - UTS Microeconomics - MNJ1X - Kary - Kamis - 28 Okt 2021Document5 pagesSoal - UTS Microeconomics - MNJ1X - Kary - Kamis - 28 Okt 2021Lisa FebrianiNo ratings yet
- Amity BBA 1 ST Sem Assignment ME NEW (3) ASODLDocument9 pagesAmity BBA 1 ST Sem Assignment ME NEW (3) ASODLBhavna JainNo ratings yet
- Universiti Teknologi Mara Final Examination: Confidential BM/OCT 2012/ECO162/104Document11 pagesUniversiti Teknologi Mara Final Examination: Confidential BM/OCT 2012/ECO162/104Anonymous gdA3wqWcPNo ratings yet
- Econ294C QuizDocument13 pagesEcon294C QuizAudrey JacksonNo ratings yet
- 2022 - Final Eco120 - Set 1 QuestionDocument10 pages2022 - Final Eco120 - Set 1 QuestionNur Syaza Athirah ZulkefliNo ratings yet
- ECON 1550 Sem 2 Session 20082009Document12 pagesECON 1550 Sem 2 Session 20082009regoleNo ratings yet
- FCE BINF Question Pool SolvedDocument109 pagesFCE BINF Question Pool SolvedGertaNo ratings yet
- ECON 300 Practice Quiz TwoDocument12 pagesECON 300 Practice Quiz Twosam lissenNo ratings yet
- Principles of Economics 11th Edition Case Test BankDocument32 pagesPrinciples of Economics 11th Edition Case Test Bankhoadieps44ki100% (30)
- Fe Mpme7113Document9 pagesFe Mpme7113Aruvin JothiNo ratings yet
- TECO602 Review Questions - T3 - 2022Document30 pagesTECO602 Review Questions - T3 - 2022Cyan SeaNo ratings yet
- Eco162 104Document12 pagesEco162 104Abdullah RamlyNo ratings yet
- 2022mar S4 Exam Paper 2 EngDocument13 pages2022mar S4 Exam Paper 2 EngsunnylamyathangNo ratings yet
- PMIC6111 T1 ADocument6 pagesPMIC6111 T1 ANathan VieningsNo ratings yet
- Quiz 1 - Managerial Economics - T322PWB-1Document11 pagesQuiz 1 - Managerial Economics - T322PWB-1Anh TranNo ratings yet
- Pe Final Mocktest - Fow9Document12 pagesPe Final Mocktest - Fow9wwwpa2005No ratings yet
- Module Name: Module Code: Economics 1A ECON211 Economics 1A ECON211pDocument10 pagesModule Name: Module Code: Economics 1A ECON211 Economics 1A ECON211pReeceNo ratings yet
- Army Welfare Education Society PGT Economics PaperDocument6 pagesArmy Welfare Education Society PGT Economics PaperAreebaNo ratings yet
- BAM 040 P2 Long Quiz Answer Key 2Document4 pagesBAM 040 P2 Long Quiz Answer Key 2mkrisnaharq99No ratings yet
- Microeconomics End Term Exam Academic Year: 2021-22 Time: 2 HoursDocument7 pagesMicroeconomics End Term Exam Academic Year: 2021-22 Time: 2 HoursKartik GurmuleNo ratings yet
- Final Exam Eco Sem 2 2010Document10 pagesFinal Exam Eco Sem 2 2010Syazmir ShamsuddinNo ratings yet
- MICROECONOMICS - Revison Notes 2013 S1 Ques Set 2Document6 pagesMICROECONOMICS - Revison Notes 2013 S1 Ques Set 2Imelda WongNo ratings yet
- Post-Mock Revision Set 4 - P1 - QuestionDocument12 pagesPost-Mock Revision Set 4 - P1 - Questiontitle subNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document12 pagesChapter 3mohammed alqurashiNo ratings yet
- Eco120 108 113 107Document11 pagesEco120 108 113 107Amiruddin Zubir100% (1)
- Bbs37 Emi Exam PaperDocument9 pagesBbs37 Emi Exam Paperyulinliu9988No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Part 1Document10 pagesChapter 2 - Part 1dylanNo ratings yet
- KTVMDocument6 pagesKTVM225952233No ratings yet
- Final 2019-2Document13 pagesFinal 2019-2Zaina RameNo ratings yet
- Cambridge O Level: Economics 2281/12Document12 pagesCambridge O Level: Economics 2281/12Akash j shahNo ratings yet
- Faculty - Business Management - 2023 - Session 1 - Pra-Diploma Dan Diploma - Eco211Document16 pagesFaculty - Business Management - 2023 - Session 1 - Pra-Diploma Dan Diploma - Eco2112021202082No ratings yet
- Syjc Economics Sample PaperDocument2 pagesSyjc Economics Sample Paperrishijinay22No ratings yet
- Class C March Eco MCQDocument9 pagesClass C March Eco MCQinternationalmakkhayarNo ratings yet
- UFM ECO102 Mid Semester Test Paper Answer Sheet - Feb 2022 SemesterDocument16 pagesUFM ECO102 Mid Semester Test Paper Answer Sheet - Feb 2022 SemesterKhánh LyNo ratings yet
- Cambridge O Level: Economics 2281/13Document12 pagesCambridge O Level: Economics 2281/13Rima MalkiNo ratings yet
- Micro Mid Term Qestion PaperDocument8 pagesMicro Mid Term Qestion PaperRanjit YadavNo ratings yet
- Economic Analysis For Business DecisionsDocument2 pagesEconomic Analysis For Business DecisionsniranjanbmazireNo ratings yet
- Mid Econ ExamDocument4 pagesMid Econ ExamYeArsema Lij Ermias ShewangizawNo ratings yet
- ECO Test 1Document9 pagesECO Test 1Dilpreet Singh MendirattaNo ratings yet
- BEC1054 - Mid-Term (Take Home Test) - T1 - 20202021 (Q)Document6 pagesBEC1054 - Mid-Term (Take Home Test) - T1 - 20202021 (Q)Sweethaa ArumugamNo ratings yet
- Work Book-Economics-Grade-11 - 12Document31 pagesWork Book-Economics-Grade-11 - 12Abubeker Abdullahi100% (1)
- Ec1002 Za - 2019Document7 pagesEc1002 Za - 2019Noor JassimNo ratings yet
- The Trade and Climate Change Nexus: The Urgency and Opportunities for Developing CountriesFrom EverandThe Trade and Climate Change Nexus: The Urgency and Opportunities for Developing CountriesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Economic Insights from Input–Output Tables for Asia and the PacificFrom EverandEconomic Insights from Input–Output Tables for Asia and the PacificNo ratings yet
- Technical and Vocational Education and Training in the Philippines in the Age of Industry 4.0From EverandTechnical and Vocational Education and Training in the Philippines in the Age of Industry 4.0No ratings yet
- Curriculum Vitae: 1 .Personal DataDocument2 pagesCurriculum Vitae: 1 .Personal DataMamadou Gueye100% (1)
- Lecture 2 AERONAUTICAL NOMENCLATUREDocument20 pagesLecture 2 AERONAUTICAL NOMENCLATUREIvan GluhenkiyNo ratings yet
- MAKAUT 2020-2021 ODD Sem Theory Exam Schedule - All B.Tech BSC BCA and MTechDocument84 pagesMAKAUT 2020-2021 ODD Sem Theory Exam Schedule - All B.Tech BSC BCA and MTechArpan DasNo ratings yet
- TMA 1 BA2 Jan 2015 RevisionDocument4 pagesTMA 1 BA2 Jan 2015 RevisionHamshavathini YohoratnamNo ratings yet
- Louisiana Man Gets Charges Dismissed For Using FacebookDocument3 pagesLouisiana Man Gets Charges Dismissed For Using FacebookPR.comNo ratings yet
- Women Leaving Work Because of Family ResponsibilityDocument2 pagesWomen Leaving Work Because of Family ResponsibilityKshamaChopraNo ratings yet
- Proceed FormulationsDocument18 pagesProceed FormulationssudhirchughNo ratings yet
- 31 JCorp L675Document45 pages31 JCorp L675Jaiyesh AshokanNo ratings yet
- PL BT enDocument304 pagesPL BT enOssian89No ratings yet
- (Thaytro - Net) de Thi THPT 2020 Mon Anh de Chinh Thuc Ma de 403Document4 pages(Thaytro - Net) de Thi THPT 2020 Mon Anh de Chinh Thuc Ma de 403longnguyenNo ratings yet
- Ermeto CouplingDocument9 pagesErmeto CouplingRickson Viahul Rayan CNo ratings yet
- Itech Basic Productivity Tools Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesItech Basic Productivity Tools Lesson Planapi-464010392No ratings yet
- Chapter No.1 - Introduction To Personal SellingDocument52 pagesChapter No.1 - Introduction To Personal SellingAyush100% (1)
- Reverso 2Document52 pagesReverso 2Javier Hernández CruzNo ratings yet
- TroubleshootingDocument12 pagesTroubleshootingCraig KalinowskiNo ratings yet
- G.R. No. 93868 - Medenilla VS CSCDocument7 pagesG.R. No. 93868 - Medenilla VS CSCCharmaine Valientes CayabanNo ratings yet
- An Architecture of PLC Ls XBC Dr30e Based Clean Water Controlling SystemDocument11 pagesAn Architecture of PLC Ls XBC Dr30e Based Clean Water Controlling SystemThe Candid MechanicNo ratings yet
- City Limits Magazine, November 2000 IssueDocument52 pagesCity Limits Magazine, November 2000 IssueCity Limits (New York)No ratings yet
- Practice Test 3Document6 pagesPractice Test 3Quỳnh AnhNo ratings yet
- Paper 1: Principles and Practice of AccountingDocument2 pagesPaper 1: Principles and Practice of AccountingrajNo ratings yet
- Commercial Application Form - A-4Document12 pagesCommercial Application Form - A-4sishir mandalNo ratings yet
- Unit 1-At6402 Automotive ChassisDocument39 pagesUnit 1-At6402 Automotive ChassisSathis KumarNo ratings yet
- Math SBA 1Document18 pagesMath SBA 1The First Song Was Titled MemoriesNo ratings yet
- Alhena Eng Rev06Document7 pagesAlhena Eng Rev06Steven BrownNo ratings yet
- Selection of High Efficient Passive Soft Switching Regenerative Snubber For DC-DC Boost ConverterDocument5 pagesSelection of High Efficient Passive Soft Switching Regenerative Snubber For DC-DC Boost ConverterYuvrajsinh ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Manual Frigider SamsungDocument32 pagesManual Frigider Samsungklaudya_teoNo ratings yet
- Deep WorkDocument2 pagesDeep Workbama33% (6)