Professional Documents
Culture Documents
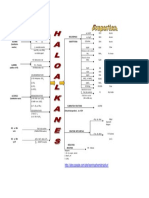
Haloalkanes
Haloalkanes
Uploaded by
GAMEPORIUMOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Haloalkanes
Haloalkanes
Uploaded by
GAMEPORIUMCopyright:
Available Formats
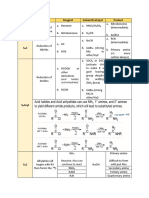
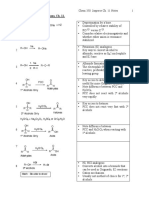
Mechanism Name Starting Material Solvent/Catalyst Product
Tertiary
Sn1 Tertiary OH HX in ether
Synthesize RX Haloalkane
with -OH Primary/Secondary PBr2 in ether Primary/Secondary
Sn2
OH SOCl2 in pyridine Haloalkane
RX
Where,
Grignard’s reagent R – 1-3* alkyl, vinyl, Mg in ether or THF R-Mg-X
aryl
X- Cl, Br, I
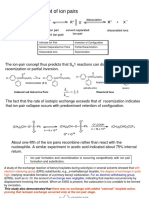
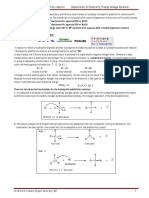
Neutral/acidic
conditions using
hydroxyl solvent or
Sn1 water
Unimolecular, 2 Reactivity of leaving
Tertiary (forms
step, w/ grp:
most stable
carbocation RNu
carbocation
intermediate OH<Cl<Br<I ~ H2O
intermediates)
Under acidic, -OH
Dependent: RX becomes better
(substrate) leaving grp in the
form of its
conjugate acid
(water)
Sn2
Bimolecular, 1
step, methyl &
1-2* carbons, no Reactivity of leaving
carbocation grp:
Primary and
intermediate, RNu
Secondary
stereochemistry OH, NH2, OR< F<
occurs, 180 Cl<Br<I
degrees angle
Dependent: Nü
& RX (substrate)
En2 Bimolecular
Tertiary OH
reaction Alkene product
Primary OH and strong stable
(carbocation Ethanolic hydroxide HX biproduct
En1 Unimolecular intermediate) (-OH in ethanol)
reaction (based on Zaitsev’s
If E1cB, carbanion rule)
intermediate
You might also like
- Service Manual: © MARCH 2016, Mercury Marine. All Rights Reserved. 90-8M0107213Document94 pagesService Manual: © MARCH 2016, Mercury Marine. All Rights Reserved. 90-8M0107213fabianoNo ratings yet
- GMP GR: Reaction Chart For AlkanesDocument3 pagesGMP GR: Reaction Chart For AlkanesManoj DesaiNo ratings yet
- Reagent Function Notes: Any/all 2° R-LDocument10 pagesReagent Function Notes: Any/all 2° R-Lbluebeary22No ratings yet
- SN1 SN2 E1 E2 Cheat SheetDocument1 pageSN1 SN2 E1 E2 Cheat SheetMyshaM099No ratings yet
- Botany LAB MANGO AND LEAVESDocument15 pagesBotany LAB MANGO AND LEAVESEPHRAIM JOASH ABEJO GAGANTINGNo ratings yet
- Summary of Reactions chm2120Document4 pagesSummary of Reactions chm2120sabrinasameja75No ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Fiitjee Flowcharts PDFDocument12 pagesOrganic Chemistry Fiitjee Flowcharts PDFTanishq VermaNo ratings yet
- HaloalkanesDocument1 pageHaloalkanesSahil MenghaniNo ratings yet
- SN1Document31 pagesSN1Niza Yusnita AprianiNo ratings yet
- Reagent Function Notes/Limitations: Very Reactive, Cannot Be UsedDocument3 pagesReagent Function Notes/Limitations: Very Reactive, Cannot Be UsedAnna LeeNo ratings yet
- Xii OrganicDocument25 pagesXii OrganicArindam GoswamiNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbon 13 THDocument20 pagesHydrocarbon 13 THRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbon (12th)Document22 pagesHydrocarbon (12th)Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- Plij Gib Me BookDocument16 pagesPlij Gib Me BookDarsheel AmbasthaNo ratings yet
- Chapter Four Major Organic ReactionsDocument63 pagesChapter Four Major Organic ReactionsdagmawiNo ratings yet
- AminesDocument2 pagesAminesGAMEPORIUMNo ratings yet
- Alkyl Halides, Alcohol and PhenolDocument9 pagesAlkyl Halides, Alcohol and PhenolSTUDY.No ratings yet
- SN1, SN2, E1 and E2 Reactions in OCDocument60 pagesSN1, SN2, E1 and E2 Reactions in OCHimanshu SharmaNo ratings yet
- HydrocarbonDocument36 pagesHydrocarbonUsha SherkhaneNo ratings yet
- Mind Map (Hydrocarbons)Document3 pagesMind Map (Hydrocarbons)Meenakshi NairNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry - Chemistry of Life and Beyond ..: SynthesisDocument71 pagesOrganic Chemistry - Chemistry of Life and Beyond ..: Synthesiskrystel pyneeNo ratings yet
- Org Chem Lec m8 AlkylhalidesDocument5 pagesOrg Chem Lec m8 AlkylhalidesAbigail P. ARANGGANo ratings yet
- New CHY3201 Chapter 7 Nucleophilic Substitution On Saturated CarbonsDocument44 pagesNew CHY3201 Chapter 7 Nucleophilic Substitution On Saturated Carbons222418No ratings yet
- Hydrocarbon: GMP GRDocument30 pagesHydrocarbon: GMP GRVinod AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Chapter7 Sn1 E1 E2 Sn2Document37 pagesChapter7 Sn1 E1 E2 Sn2Ariy DedeNo ratings yet
- OCI Lecture4-5Document19 pagesOCI Lecture4-5Baga DagaNo ratings yet
- Summary of Chapter 7 HaloalkanesDocument3 pagesSummary of Chapter 7 Haloalkanesfaris zainuddinNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbon: Target Iit Jee 2017 Xii (VS+VR)Document36 pagesHydrocarbon: Target Iit Jee 2017 Xii (VS+VR)Aariya KumariNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbon: Ashwani Tyagi Sir (Code: ATJEE)Document22 pagesHydrocarbon: Ashwani Tyagi Sir (Code: ATJEE)Prince DigvijayNo ratings yet
- Alcohols Phenols Carboxylic AcidsDocument5 pagesAlcohols Phenols Carboxylic AcidsAnanya AryaNo ratings yet
- Mind Map HaloallkanesDocument3 pagesMind Map HaloallkanesNURUL HIDAYAH BINTI SAIFUL ANUAR MoeNo ratings yet
- Winstein: Concept of Ion Pairs: Contact or Tight Ion PairDocument14 pagesWinstein: Concept of Ion Pairs: Contact or Tight Ion PairAnil Kumar100% (1)
- Alcohol SummaryDocument2 pagesAlcohol Summarymikumo81No ratings yet
- 14Document10 pages14Hasen umerNo ratings yet
- Ch11 Self-Study PDFDocument22 pagesCh11 Self-Study PDFRida Naila MangiNo ratings yet
- 5L ReductionsDocument20 pages5L ReductionsCarlos Javier Orellana OrtizNo ratings yet
- SynrxnsDocument48 pagesSynrxnsRonak MantriNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Concept MapDocument55 pagesChemistry Concept MapKaia GuarteNo ratings yet
- KOF-mekanisme ReaksiDocument64 pagesKOF-mekanisme ReaksiAudry YuniarNo ratings yet
- Reactions of Alkyl Halides: A. Nucleophilic Substitution (S RXN)Document25 pagesReactions of Alkyl Halides: A. Nucleophilic Substitution (S RXN)cikguhafidzuddinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document189 pagesChapter 7Eshita SharmaNo ratings yet
- Neetkakajee - Name ReactionDocument5 pagesNeetkakajee - Name Reactionkaifazad10No ratings yet
- 6carboxylic AcidsDocument1 page6carboxylic AcidssharmimiameerasanadyNo ratings yet
- Chapter Four 221212Document24 pagesChapter Four 221212Barnabas YohannesNo ratings yet
- HALOALKENES AND HALO ARENES - Chemistry NotesDocument24 pagesHALOALKENES AND HALO ARENES - Chemistry Notesrahul SNo ratings yet
- Named ReactionsDocument5 pagesNamed Reactionsgoodvp05No ratings yet
- Trans Vicinal: Halogenation DihalidesDocument4 pagesTrans Vicinal: Halogenation DihalidesKarla PereraNo ratings yet
- Barta2001Bis (Acetylacetonato) Zinc (II)Document2 pagesBarta2001Bis (Acetylacetonato) Zinc (II)Horatiu MoldovanNo ratings yet
- Substitution Reactions (Nucleophilic)Document34 pagesSubstitution Reactions (Nucleophilic)DidarulNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 25 Oct 2022Document3 pagesAdobe Scan 25 Oct 2022aashuonly12445No ratings yet
- RXN Mechanism-4rt PartDocument9 pagesRXN Mechanism-4rt PartAASHISH KATUWALNo ratings yet
- CH 11 Handouts (All)Document22 pagesCH 11 Handouts (All)netsanet mesfinNo ratings yet
- Lecture 33 - Nucleophilic Substiution-2 - 27.10.2014Document42 pagesLecture 33 - Nucleophilic Substiution-2 - 27.10.2014Sampada DesaiNo ratings yet
- AminesDocument24 pagesAminesRajdeep Singh RahiNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Reaction Summary SheetDocument30 pagesOrganic Chemistry Reaction Summary SheetKylo RenNo ratings yet
- 3-23 C460 Catalytic Cross-Coupling New LectureDocument10 pages3-23 C460 Catalytic Cross-Coupling New LecturetangduchoangminhNo ratings yet
- Chapter:-Nucleophilic Substitution Reaction Department of Chemistry, Pratap College, AmalnerDocument12 pagesChapter:-Nucleophilic Substitution Reaction Department of Chemistry, Pratap College, Amalnermilindthakare75No ratings yet
- 2018 Review IDocument6 pages2018 Review IsophNo ratings yet
- Lone Pair DelocalizationDocument6 pagesLone Pair DelocalizationGIORGIA MERIEN ILAONo ratings yet
- Alkanes Alkenes AlkynesDocument2 pagesAlkanes Alkenes AlkynesGAMEPORIUMNo ratings yet
- HydrocarbonDocument94 pagesHydrocarbonArshNo ratings yet
- Graphene-based Carbocatalysis: Synthesis, Properties and Applications: Volume 1From EverandGraphene-based Carbocatalysis: Synthesis, Properties and Applications: Volume 1No ratings yet
- Genchem ReviewerDocument26 pagesGenchem ReviewerGAMEPORIUMNo ratings yet
- GENCHEM 2 4th QuarterDocument10 pagesGENCHEM 2 4th QuarterGAMEPORIUMNo ratings yet
- Valence ElectronsDocument3 pagesValence ElectronsGAMEPORIUMNo ratings yet
- Gen ChemDocument12 pagesGen ChemGAMEPORIUMNo ratings yet
- MS Office 2019 Pro Plus Installation Guide and ActivationDocument5 pagesMS Office 2019 Pro Plus Installation Guide and ActivationGAMEPORIUMNo ratings yet
- African LiteratureDocument17 pagesAfrican LiteratureGAMEPORIUMNo ratings yet
- Editorial Status Report - Dr. Y. Thiagarajan - JERRDocument3 pagesEditorial Status Report - Dr. Y. Thiagarajan - JERRThiaga RajanNo ratings yet
- Rps School System: Final Term (2018)Document7 pagesRps School System: Final Term (2018)Zahra AhmedNo ratings yet
- Tabatana 2023 ReportDocument15 pagesTabatana 2023 ReportKudakwashe Pride ChirendaNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive With Coil Amc - Air ConditionerDocument2 pagesComprehensive With Coil Amc - Air ConditionerUmesh VirkudNo ratings yet
- 8.protocols For Collecting EvidenceDocument21 pages8.protocols For Collecting EvidenceMugilan KrishnamurthyNo ratings yet
- Part 4 Crop Protection Q ADocument54 pagesPart 4 Crop Protection Q AEleven HopperNo ratings yet
- Using Compound Subject and PredicateDocument8 pagesUsing Compound Subject and PredicateJoan DalilisNo ratings yet
- Your Space 1 Skills Test 10Document2 pagesYour Space 1 Skills Test 10Maxi ComasNo ratings yet
- Orthognathic Surgery Types and Indications: Mousa Ibrahim MousaDocument42 pagesOrthognathic Surgery Types and Indications: Mousa Ibrahim MousahashimalarwliaNo ratings yet
- Hilti Hit Hy 200 With Hit VDocument18 pagesHilti Hit Hy 200 With Hit VRobinReyndersNo ratings yet
- Reverse Unloader Valve Rev0Document1 pageReverse Unloader Valve Rev0JasonNo ratings yet
- Lenovo Ideapad Y700-14ISK: User GuideDocument32 pagesLenovo Ideapad Y700-14ISK: User GuideRudi B. RosidiNo ratings yet
- Quality Control of Sterile Products: (Ms. Riffat)Document21 pagesQuality Control of Sterile Products: (Ms. Riffat)Khan NehalNo ratings yet
- Engineering Data Sheet: 49187073 E 1145842 1 of 1 October 21, 2016 60HzDocument1 pageEngineering Data Sheet: 49187073 E 1145842 1 of 1 October 21, 2016 60HzGustavo VillarrealNo ratings yet
- wph11 01 Rms 20230817Document17 pageswph11 01 Rms 20230817Nirmani RodrigoNo ratings yet
- Emily Gerard Transylvanian SuperstitionsDocument4 pagesEmily Gerard Transylvanian SuperstitionsErzsebet HeghyekNo ratings yet
- RT 200 Midterm Ist TopicDocument34 pagesRT 200 Midterm Ist TopicYola RazoNo ratings yet
- Advanced 250 V Three-Phase BLDC Controller With Embedded STM32 MCUDocument32 pagesAdvanced 250 V Three-Phase BLDC Controller With Embedded STM32 MCUOne SpringNo ratings yet
- Soils OBJ Solved - 070021Document17 pagesSoils OBJ Solved - 070021Antoinette Wiafe100% (1)
- Aviation Indutry in IndiaDocument20 pagesAviation Indutry in IndiayuktimNo ratings yet
- Vocabulary HSC 22 PDFDocument28 pagesVocabulary HSC 22 PDFMadara Uchiha83% (6)
- Tonga Tsunami Before and After Eruption - BBC NewsDocument13 pagesTonga Tsunami Before and After Eruption - BBC Newslae uneNo ratings yet
- Adina ModelisationDocument240 pagesAdina ModelisationSafia SoufiNo ratings yet
- Jap-Motor General v1Document52 pagesJap-Motor General v1Pankaj Poonia100% (1)
- Input Module CP E16Document6 pagesInput Module CP E16Dejan Dunđa JankovNo ratings yet
- Picking Manten Tebu' in The Syncretism of The Cembengan Tradition Perspective of Value Education and Urf'-Lila, Siti, Ning FikDocument10 pagesPicking Manten Tebu' in The Syncretism of The Cembengan Tradition Perspective of Value Education and Urf'-Lila, Siti, Ning FiklilaNo ratings yet
- Transactions Apparatus Systems, Vol - PAS-98, No.1: 97 Ieee Power and Jan/Feb 1979Document13 pagesTransactions Apparatus Systems, Vol - PAS-98, No.1: 97 Ieee Power and Jan/Feb 1979awolNo ratings yet
- AlampatDocument9 pagesAlampatthisischrssmlNo ratings yet