Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Amines
Amines
Uploaded by
GAMEPORIUMOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Amines
Amines
Uploaded by
GAMEPORIUMCopyright:
Available Formats
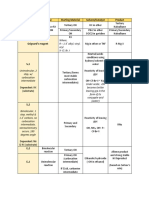
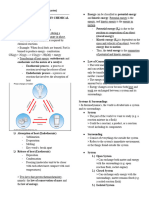
Mechanism Name Reagent Solvent/Catalyst Product
a. Nitrobenzene
a. Benzene a. HNO3/H2SO4
Reduction of (intermediate)
SE
Nitrobenzene
b. Nitrobenzene b. H2/Pd
b. Aniline
a. RCN
a. NaCN
(intermediate)
a. RX
Reduction of
SN2 b. LiAlH4 (strong
Nitriles b. Primary amine
b. RCN RA) in
(+1 more
ether/H2O
carbon always)
a. SOCl2 or DCC
(activate -OH
a. RCOOH or to make it a
other goof leaving
derivatives group despite a. RCON
Reduction of
(acid halides, its acidity)
Amides acid anhydrides) /NH3 (base) b. RCNH2
b. RCON b. LiAlH4 (strong
RA) in
ether/H2O
SNAcyl
NH3 Primary amine
Alkylation (all Reactive, thus can Difficult to form
SN2 begins with RX continue to react NaOH with just NH3
then forms the à) RNH2 Secondary amine
R2NH Tertiary amine
R3N Quarternary amine
Axide (-N3)
LiAlH4 in
Primary amine
Overalkylation is ether/H2O
prevented
a. Carbinolamine
and Imine
a. Aldehyde or
a. NH3 intermediate
Ketone
Reductive b. H2/Ni b. Aldehyde:
b. Carbinolamine
Amination orNaBH4 primary
and Imine
(Weak RA) amine/Ketone:
intermediate
secondary
amine
You might also like
- Project Report On Lithium Ion Battery Manufacturing UnitDocument9 pagesProject Report On Lithium Ion Battery Manufacturing UnitEIRI Board of Consultants and Publishers100% (1)
- Flange 10 & 12 InchDocument2 pagesFlange 10 & 12 InchreniNo ratings yet
- Corrosion Technology: Cathodic and Anodic ProtectionDocument36 pagesCorrosion Technology: Cathodic and Anodic Protectionsohrab25100% (1)
- Synthetic Routes (A Level) - Reaction Pathways Aliphatic CompoundsDocument6 pagesSynthetic Routes (A Level) - Reaction Pathways Aliphatic CompoundsJunior GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Alkane: Preparation of Alkanes (6-Methods)Document20 pagesAlkane: Preparation of Alkanes (6-Methods)siddansh100% (1)
- Organic Chemistry Synthesis IedxcelDocument10 pagesOrganic Chemistry Synthesis IedxcelAliya Rahman100% (2)
- GMP GR: Reaction Chart For AlkanesDocument3 pagesGMP GR: Reaction Chart For AlkanesManoj DesaiNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Fiitjee Flowcharts PDFDocument12 pagesOrganic Chemistry Fiitjee Flowcharts PDFTanishq VermaNo ratings yet
- HaloalkanesDocument1 pageHaloalkanesSahil MenghaniNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2024-04-16 at 22.57.21Document6 pagesScreenshot 2024-04-16 at 22.57.21fpjbrqfyktNo ratings yet
- Amide RxnsDocument1 pageAmide Rxnsapi-465421809No ratings yet
- Amines: 2.1 Structure 2.2 Chemical Properties 2.3 PreparationsDocument6 pagesAmines: 2.1 Structure 2.2 Chemical Properties 2.3 PreparationsSarah FeyNo ratings yet
- Chapter: Amines Top Concepts: Ni, PT or PD 2 2 2 2 Ni, PT or PD 2 2 2 2Document12 pagesChapter: Amines Top Concepts: Ni, PT or PD 2 2 2 2 Ni, PT or PD 2 2 2 2Navya NitashNo ratings yet
- HaloalkanesDocument2 pagesHaloalkanesGAMEPORIUMNo ratings yet
- CH 19 Problem Answers (All)Document26 pagesCH 19 Problem Answers (All)sorinavramescuNo ratings yet
- ABC 1 (Theory Exercise)Document17 pagesABC 1 (Theory Exercise)Mayank GoyalNo ratings yet
- AminesDocument24 pagesAminesRajdeep Singh RahiNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Reaction Summary SheetDocument30 pagesOrganic Chemistry Reaction Summary SheetKylo RenNo ratings yet
- L7 Amines and Amino AcidsDocument16 pagesL7 Amines and Amino AcidsCheng FuNo ratings yet
- Amines 1Document21 pagesAmines 1Gowri ShankarNo ratings yet
- Oxidation, Reduction, HydrolysisDocument19 pagesOxidation, Reduction, HydrolysisTEJA SINGHNo ratings yet
- ShortNotes-6. Aldehyde and Ketone - 22128886Document6 pagesShortNotes-6. Aldehyde and Ketone - 22128886PranavNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry ReactionDocument3 pagesOrganic Chemistry ReactionGAMEPORIUMNo ratings yet
- Class 12 - AminesDocument34 pagesClass 12 - AminesRidhi AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Summary of Reactions chm2120Document4 pagesSummary of Reactions chm2120sabrinasameja75No ratings yet
- Amine SynthDocument1 pageAmine Synthapi-465421809No ratings yet
- Xii OrganicDocument25 pagesXii OrganicArindam GoswamiNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER21 Amines and Their DerivativesDocument36 pagesCHAPTER21 Amines and Their DerivativesRiyanto WidodoNo ratings yet
- Oxidation ReductionnewDocument16 pagesOxidation ReductionnewanjalilalshaNo ratings yet
- Alkanes Alkenes AlkynesDocument2 pagesAlkanes Alkenes AlkynesGAMEPORIUMNo ratings yet
- REDUCING AND OXIDISING AGENTS IN ORGANIC CHMISTRY (Chemistry - Today - February - 2018)Document2 pagesREDUCING AND OXIDISING AGENTS IN ORGANIC CHMISTRY (Chemistry - Today - February - 2018)Pushpa ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Nitrile RxnsDocument1 pageNitrile Rxnsapi-465421809No ratings yet
- 12 Chemistry Notes ch13 Amines-1Document8 pages12 Chemistry Notes ch13 Amines-1mv7602456No ratings yet
- BenzeneDocument2 pagesBenzeneGAMEPORIUMNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbon: GMP GRDocument30 pagesHydrocarbon: GMP GRVinod AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Reagent ListDocument5 pagesReagent ListAditya VermaNo ratings yet
- Kelas Kimiawi Gugus Rumus Rumus Struktural Awalan Akhiran ContohDocument6 pagesKelas Kimiawi Gugus Rumus Rumus Struktural Awalan Akhiran ContohRizky RaditNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 13 Amines NotesDocument10 pagesClass 12 Chemistry Chapter 13 Amines Notescharusrirajkumar27No ratings yet
- HydrocarbonsDocument76 pagesHydrocarbonsAyush KumarNo ratings yet
- 3.13 Revision Guide Amino Acids Proteins and Dna Aqa 1Document9 pages3.13 Revision Guide Amino Acids Proteins and Dna Aqa 1Rutba SafdarNo ratings yet
- CHEM1090 Final - Module 2Document10 pagesCHEM1090 Final - Module 2Dani R.No ratings yet
- 6 2 5 Revision Guides Organic SynthesisDocument5 pages6 2 5 Revision Guides Organic SynthesisAddan AddanNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class-12 Chemistry Quick Revision Notes Chapter-13: Amines AminesDocument8 pagesCBSE Class-12 Chemistry Quick Revision Notes Chapter-13: Amines AminesAryan MeenaNo ratings yet
- Orgo 2 Cheat SheetDocument1 pageOrgo 2 Cheat SheetMartha DejaNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbon 1-Jeemain - Guru PDFDocument16 pagesHydrocarbon 1-Jeemain - Guru PDFPIYUSH MADANNo ratings yet
- AMINESDocument7 pagesAMINESpathakgourav0302No ratings yet
- 12th Board Sprint-Amines (15.12.2020)Document62 pages12th Board Sprint-Amines (15.12.2020)Harsh ShahNo ratings yet
- Orgarnic Chemistry Functional Group TestDocument9 pagesOrgarnic Chemistry Functional Group TestShourya veer singhNo ratings yet
- 3.14 Revision Guide Organic Synthesis AqaDocument7 pages3.14 Revision Guide Organic Synthesis AqaRutba SafdarNo ratings yet
- Preparation: (1) Reduction MethodDocument9 pagesPreparation: (1) Reduction MethodSsNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbons Jeemain - GuruDocument76 pagesHydrocarbons Jeemain - Guruchaewon10271No ratings yet
- Reducing AgentDocument15 pagesReducing Agentpranshul jadonNo ratings yet
- Reactive Intermediates - LecturesDocument24 pagesReactive Intermediates - Lecturesapi-3771395100% (1)
- CHEM1920 Lecture 17v2Document29 pagesCHEM1920 Lecture 17v2Mr SpaciousNo ratings yet
- Amines Ic19770Document6 pagesAmines Ic19770Satendra KumarNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbon (12th)Document22 pagesHydrocarbon (12th)Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- Named ReactionsDocument5 pagesNamed Reactionsgoodvp05No ratings yet
- Aromatic Compounds: 1.1 Some Useful Names 1.2 Structure 1.3 Characteristic Chemistry 1.4 Benzene ReactionsDocument6 pagesAromatic Compounds: 1.1 Some Useful Names 1.2 Structure 1.3 Characteristic Chemistry 1.4 Benzene ReactionsSarah FeyNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbons: Ella EH EH ÉDocument19 pagesHydrocarbons: Ella EH EH ÉIsabella LopezNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbon 13 THDocument20 pagesHydrocarbon 13 THRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- Reduction, Oxidation - Hydrolysis Theory PDFDocument14 pagesReduction, Oxidation - Hydrolysis Theory PDFGOURISH AGRAWALNo ratings yet
- Genchem ReviewerDocument26 pagesGenchem ReviewerGAMEPORIUMNo ratings yet
- Valence ElectronsDocument3 pagesValence ElectronsGAMEPORIUMNo ratings yet
- GENCHEM 2 4th QuarterDocument10 pagesGENCHEM 2 4th QuarterGAMEPORIUMNo ratings yet
- Gen ChemDocument12 pagesGen ChemGAMEPORIUMNo ratings yet
- MS Office 2019 Pro Plus Installation Guide and ActivationDocument5 pagesMS Office 2019 Pro Plus Installation Guide and ActivationGAMEPORIUMNo ratings yet
- African LiteratureDocument17 pagesAfrican LiteratureGAMEPORIUMNo ratings yet
- Cooling Tower 3.4Document5 pagesCooling Tower 3.4Anita Dwi LestariNo ratings yet
- Technical Data Sheet: Resichem 506 AluprimeDocument2 pagesTechnical Data Sheet: Resichem 506 AluprimeTechnicalproducts 02 Indo Riau PerkasaNo ratings yet
- Serkyd s38x60Document1 pageSerkyd s38x60I Love MusicNo ratings yet
- 11 Alcohols Phenols and EthersDocument6 pages11 Alcohols Phenols and EthersVansh VaibhavNo ratings yet
- Direct Shear TestDocument13 pagesDirect Shear Testskyxiaochen0% (2)
- 4.1 Foundation SettlementDocument49 pages4.1 Foundation SettlementRadifan HalifNo ratings yet
- MSD Unit 3 PPT-R1Document46 pagesMSD Unit 3 PPT-R1Vikas RathodNo ratings yet
- ImpedanciaDocument17 pagesImpedanciapaulinaNo ratings yet
- Foreva TFCDocument2 pagesForeva TFCAmel RADJEFNo ratings yet
- NIOEC SP 70 54 (1) 1 Instrument.Document161 pagesNIOEC SP 70 54 (1) 1 Instrument.MahdiNo ratings yet
- Synthesis and Characterization of Natural Pesticides From Custard Apple SeedsDocument5 pagesSynthesis and Characterization of Natural Pesticides From Custard Apple SeedsInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Nutrition Vol10 No3 1178-1195Document18 pagesNutrition Vol10 No3 1178-1195Rayyhana ShopNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Option F: Food Dyes and PigmentsDocument2 pagesChemistry Option F: Food Dyes and PigmentsstudydaemonNo ratings yet
- Báo Cáo Phân Tích Việc Sử Dụng Mỹ Phẩm Tại Việt Nam - Shared by WorldLine TechnologyDocument38 pagesBáo Cáo Phân Tích Việc Sử Dụng Mỹ Phẩm Tại Việt Nam - Shared by WorldLine TechnologymytutuongleNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Activity 09C Part IIDocument1 pageLaboratory Activity 09C Part IIkelly_wu_5No ratings yet
- Module 3Document29 pagesModule 3Beatrice AlejeNo ratings yet
- Graded Recitation ChemistryDocument46 pagesGraded Recitation ChemistrypopNo ratings yet
- Chem Lab Report 1-Lauren SalemDocument8 pagesChem Lab Report 1-Lauren SalemLauren SalemNo ratings yet
- Multiport Valve Brochures SinglePage enDocument12 pagesMultiport Valve Brochures SinglePage enTrung Van BaNo ratings yet
- Titrimetric 2023 BP PLDocument24 pagesTitrimetric 2023 BP PLfojirof555No ratings yet
- Organic - 2Document97 pagesOrganic - 2Creative ThinkerNo ratings yet
- Guía para Seleccionar Columnas HPLCDocument52 pagesGuía para Seleccionar Columnas HPLCDiana Lilibet Sánchez MontesNo ratings yet
- Observing Microorganisms Under The MicroscopeDocument17 pagesObserving Microorganisms Under The MicroscopeLe HungNo ratings yet
- PKa Values 2Document3 pagesPKa Values 2Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- Zinc CitrateDocument1 pageZinc CitrateKasidit SornchaiNo ratings yet
- Deterioration of Luminescence Efficiency of ZNS Phosphors Due To Surface Oxidation by Thermal Decomposition of Ammonium DichromateDocument4 pagesDeterioration of Luminescence Efficiency of ZNS Phosphors Due To Surface Oxidation by Thermal Decomposition of Ammonium DichromateShivaNatarajNo ratings yet
- Formulation Optimatization of Unreinforced and Lignin Nanoparticle-Reinforced Phenolic Foams Using An Analisys of Variance ApproachDocument8 pagesFormulation Optimatization of Unreinforced and Lignin Nanoparticle-Reinforced Phenolic Foams Using An Analisys of Variance ApproachjvchiqueNo ratings yet