Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Report 7 - Calorimetry (
Report 7 - Calorimetry (
Uploaded by
Georges MaaloufOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Report 7 - Calorimetry (
Report 7 - Calorimetry (
Uploaded by
Georges MaaloufCopyright:
Available Formats
Report : General Chemistry Faculty of Science
Experiment title : CALORIMETRY
Prepared by :
Jason Hyakal
Bettina lakandy
Georges Al Maalouf
Teacher :
Grade /20 OBSERVATION :
USEK ©2016-2017 CHE 270 1/5
Report : General Chemistry Faculty of Science
I. Objective
1. Determine the specific heat capacity of calorimeter.
2. Thermometric titration between NaCl and HCL
1
II. Results and Calculation
A. Determination of the water value μ of the calorimeter
Value (in g) of the water weight m1 50.72g
Value of the temperature t’1 (°C) 22.5 C0 0.5
Value (in g) of the water weight m2 50.17g
Value of the temperature t2 (°C) 60.3 C0
0.5
Value of the temperature tf (°C) 40.2 C0
1
Calculation of the water value of the calorimeter
The expression of the heat Q gained by the cold water and the calorimeter:
Q=(µ+m)×Cs×ΔT
Q=(µ+50.72)×4.18×(40.2-22.5)
Q=(µ+50.72)×73.986
The expression of the heat Q lost by the heat water and the calorimeter:
Q= m×Cs×ΔT
Q=50.17×4.184×-20.1
3
Q=-4219.216 J
Using the fact that Q gained = Q lost:
|Q gained|=|Q lost|
Q=(µ+50.72)×73.986=4219.216
4219.216
(µ+50.72)= 73.986 =57.07
µ=57.07-50.72=6.35g
USEK ©2016-2017 CHE 270 2/5
Report : General Chemistry Faculty of Science
B- Titration of HCl by NaOH
B1- Volumetric titration
Titration Reaction NaOH + HCL → H2O+ NaCl
0.5
The equivalence volume : 7.8ml 0.5
Normality of HCl : N=C×Z
For a solution of HCL Z is equal to the number of
H+ =1
1
N=C×1
N=C= 0.078N
Molar concentration of HCl :
At the equivalence and according to the stoichiometry
of the reaction :
ca×va cb×vb 0.5
= 1
1
cb×vb 0.1×7.8
Ca= = =0.078mol.L-1
va 10
Error Calculation : ΔCa ΔCb ΔVa ΔVb
= Cb + + Vb
ΔCa Va
ΔCa 0.02 2×0.06
=0+ 10 + =0.0178
0.078 7.8
1.5
ΔCa=0.0178×0.078=1.356×10−3 mol.L-1
Ca=0.078±1.356×10−3 mol.L-1
B2- Colorimetric titration
Titration Reaction NaOH + HCL → H2O+ NaCl
0.5
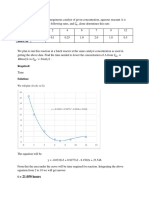
Titration Curve
USEK ©2016-2017 CHE 270 3/5
Report : General Chemistry Faculty of Science
Chart Title
27.4
27.2
27
tempreature (c0)
26.8
26.6
26.4
26.2
26
25.8
25.6
25.4
0.0 2.0 4.0 6.0 8.0 10.0 12.0 14.0 16.0 18.0
volume (ml)
TITLE: curve showing the variation of the temperature in function of the volume of the base
added
The equivalence volume : This titration is a thermometric titration using the
following method were we draw to 2 line following the
trend and the perpendicular that pass by the
0.5
intersection point give the volume which id equal to
7.8ml
Normality of HCl : N=C×Z
For a solution of HCL Z is equal to the number of
H+ =1
1
N=C×1
N=C= 0.078N
Molar concentration of HCl :
At the equivalence and according to the stoichiometry
of the reaction :
ca×va cb×vb 0.5
= 1
1
cb×vb 0.1×7.8
Ca= = =0.078mol.L-1
va 10
Molar enthalpy of the reaction : Using the fact that at constant pressure the enthalpy of
the reaction is equal to the amount of heat.
q
ΔH=n.
1.5
Q=m×Cs×ΔT
Q=6.35×(27.3-25.6)=10.795J
nNaOH=C×V=0.1×7.8=0.78mol
USEK ©2016-2017 CHE 270 4/5
Report : General Chemistry Faculty of Science
q 10.795 j kj
ΔH=n = =13.839mol =0.013mol
0.78
III. Discussion and Comparison of the volumetric and calorimetric titration
In this experiment we used the law of thermodynamics as well the diffusion to determine the
specific heat capacity of a calorimeter
1. Putting 50g of cold water 22.5C0 in the calorimeter first.
2. We adding another 50 g of hot water 60C0.
3. This will create a temperature difference between the cold water and the calorimeter
form one side and the hot water.
4. An equilibrium temperature will be obtained after some minute equal to 40C0.
5. Using the fact that the system will achieve an equilibrium meaning that the heat lost
by the jot water is gained by the cold water and the calorimeter.
6. Qlost=Qgained will allow us to calculate the specific heat capacity of the calorimeter
6.35g
7. the second part of the experiment involve a thermometric titration between HCL and 2
NaOH
8. the data allowed us to represent graphicly the variation of the temperature in function
of the added volume of NaOH.
9. We calculated the equivalence volume 7.8ml using these data as well the HCL
concentration 0.078±1.356×10−3 mol.L-1
10. Since the pressure is constant so the enthalpy of the reaction is equal to the quantity
kj
of heat we calculated ΔH=0.013mol so the objective of the session is achivied.
11. Overall this session allowed us to test thermal energy transfer between 2 bodies
having different temperatures.
IV. Bibliographic research
1. https://www.americanpharmaceuticalreview.com
2. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6780066/
3. https://www.medicalexpo.com
4. https://www.news-medical.net/life-sciences/Differential-Scanning-Calorimetry-of-
1
Pharmaceuticals.aspx
5. https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/medicine-and-dentistry/direct-calorimetry
USEK ©2016-2017 CHE 270 5/5
You might also like
- Piovan WTC Thw9Document48 pagesPiovan WTC Thw9T desNo ratings yet
- Coursebook Answers: Self-Assessment QuestionsDocument2 pagesCoursebook Answers: Self-Assessment QuestionslizNo ratings yet
- Ullia Nurul - 11.7.6 OtkDocument8 pagesUllia Nurul - 11.7.6 OtkUllia Ismala0% (1)
- Preparation and Standard NaOHDocument2 pagesPreparation and Standard NaOHEliise JungNo ratings yet
- Asupu Nano BubblesDocument10 pagesAsupu Nano BubblesAgung50% (2)
- 02 - Trích IChO 31st - DAP ANDocument15 pages02 - Trích IChO 31st - DAP ANTạ Đình TrungNo ratings yet
- Iodine LabDocument4 pagesIodine LabHuang ViviNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Report (Final)Document5 pagesChemistry Report (Final)Georges MaaloufNo ratings yet
- Batch Reactor ExpDocument12 pagesBatch Reactor ExpJack AndreasNo ratings yet
- Annotated Solution 2019 USNCO Local Exam: 1 SolutionsDocument13 pagesAnnotated Solution 2019 USNCO Local Exam: 1 SolutionsMeli SilabanNo ratings yet
- Expl SodaAsh TitrationXXDocument4 pagesExpl SodaAsh TitrationXXRolen Simcha Castillo SamsNo ratings yet
- A00830666 - Lab Report - BatchDocument13 pagesA00830666 - Lab Report - BatchJocelyn garcia gonzalezNo ratings yet
- Che61 At11Document9 pagesChe61 At11Michael Alex MabaoNo ratings yet
- Benzoic - Acid ExperimentDocument7 pagesBenzoic - Acid ExperimentShivani SinghNo ratings yet
- NCHE312Document11 pagesNCHE312Charmaine MoyoNo ratings yet
- Calor Lat Vap Chopey - Djra Mipg20Document11 pagesCalor Lat Vap Chopey - Djra Mipg20Dan JefteNo ratings yet
- Expt09 2020A1PS0727PDocument2 pagesExpt09 2020A1PS0727PNAVYA GUPTANo ratings yet
- Statement of The Problem: % RecoveryDocument5 pagesStatement of The Problem: % RecoveryAnthon ToledanoNo ratings yet
- Lemper RevisedDocument7 pagesLemper RevisedTitin Setya MuktiNo ratings yet
- Lab 4 - PotentiometryDocument8 pagesLab 4 - PotentiometrychiuNo ratings yet
- Sarmiento Prelim StabDocument7 pagesSarmiento Prelim Stabedward somogodNo ratings yet
- Kinetics (Gjjkkkgty)Document5 pagesKinetics (Gjjkkkgty)Chrysler Kane DepnagNo ratings yet
- Kinetics Worksheet AnswersDocument7 pagesKinetics Worksheet AnswerslinaNo ratings yet
- APPENDIX C ComputationsDocument9 pagesAPPENDIX C ComputationsNicole Anne BorromeoNo ratings yet
- 2009 A Levels P1 (No Worked Soln) and P2Document13 pages2009 A Levels P1 (No Worked Soln) and P2toh tim lamNo ratings yet
- Solution 631049Document3 pagesSolution 631049Gaurav ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Conduct IV I DadDocument7 pagesConduct IV I DadEder E. AguilarNo ratings yet
- 8.1HW Colligative Properties-SolDocument5 pages8.1HW Colligative Properties-SolabcdNo ratings yet
- Final AssessmentDocument10 pagesFinal AssessmentDiogo Tavares de OliveiraNo ratings yet
- Distillation of Multicomponent Alcohol Mixture.: T (C) Vapor Pressure (MMHG) Methanol Ethanol N-Propanol N-ButanolDocument9 pagesDistillation of Multicomponent Alcohol Mixture.: T (C) Vapor Pressure (MMHG) Methanol Ethanol N-Propanol N-Butanolrizky amaliaNo ratings yet
- C Sol Ch-09 SolutionsDocument6 pagesC Sol Ch-09 Solutionsmysoftinfo.incNo ratings yet
- Chemistry The Molecular Nature of Matter and Change 7th Edition Silberberg Solutions Manual 1Document36 pagesChemistry The Molecular Nature of Matter and Change 7th Edition Silberberg Solutions Manual 1josephandersonxqwbynfjzk100% (29)
- Chemistry The Molecular Nature of Matter and Change 7Th Edition Silberberg Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument46 pagesChemistry The Molecular Nature of Matter and Change 7Th Edition Silberberg Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFsusan.robleto221100% (17)
- Chapter 6 Thermochemistry: Energy Flow and Chemical Change: Follow-Up ProblemsDocument30 pagesChapter 6 Thermochemistry: Energy Flow and Chemical Change: Follow-Up ProblemsLarsen Atega AlexanderssonNo ratings yet
- Determination of Partition Coefficient of Iodine in Water and Carbon Tetra ChlorideDocument15 pagesDetermination of Partition Coefficient of Iodine in Water and Carbon Tetra ChlorideNanda SatishNo ratings yet
- Report 4 Group 5 1Document6 pagesReport 4 Group 5 1HƯNG LIÊU MẠNHNo ratings yet
- Binary LiquidsDocument8 pagesBinary LiquidsSuzanne Clariz M. BaltazarNo ratings yet
- Exel Tahanan Gilang RafiDocument26 pagesExel Tahanan Gilang RafiHazemy putraNo ratings yet
- Bui Viet Phuong HW9Document6 pagesBui Viet Phuong HW9Bùi Việt PhươngNo ratings yet
- Pertemuan - 4ATK2 - VAPORIZATION AND COOLING OF MIXTUREDocument9 pagesPertemuan - 4ATK2 - VAPORIZATION AND COOLING OF MIXTUREdonaNo ratings yet
- 2019 USNCO Local Exam: 1 SolutionsDocument18 pages2019 USNCO Local Exam: 1 SolutionsSubha VNo ratings yet
- Semibatch KRD LabDocument7 pagesSemibatch KRD LabPritiNo ratings yet
- MCD4390 Week 10 Tutorial QuestionsDocument5 pagesMCD4390 Week 10 Tutorial QuestionsGabbar100% (1)
- Compilation of Problem Set in PchemDocument13 pagesCompilation of Problem Set in PchemAlyza AcolNo ratings yet
- Pset03 SolnDocument17 pagesPset03 SolnazatklcNo ratings yet
- Group 1 - ALEJANO - DEZOLLER - GRATIS - MIXED FLOW REACTOR-4Document8 pagesGroup 1 - ALEJANO - DEZOLLER - GRATIS - MIXED FLOW REACTOR-4John Frix AlejanoNo ratings yet
- Concepts of Thermodynamics (NOC21-ME73) Assignment-8Document8 pagesConcepts of Thermodynamics (NOC21-ME73) Assignment-8Saurabh ManralNo ratings yet
- Crash1 B Ist Year Chapter 8 and 9Document4 pagesCrash1 B Ist Year Chapter 8 and 9hariskaleem150No ratings yet
- University of Sabratha Faculty of Engineering Department of Chemical EngineeringDocument8 pagesUniversity of Sabratha Faculty of Engineering Department of Chemical EngineeringMarNo ratings yet
- Collogative Properties: Vapor Pressure LoweringDocument2 pagesCollogative Properties: Vapor Pressure LoweringKryzler KayeNo ratings yet
- Data Dan Perhitungan P11Document5 pagesData Dan Perhitungan P11Shinta SetyowatiNo ratings yet
- Theory: Sodium Carbonate Is The Salt of A Week Acid, Carbonic Acid (HDocument4 pagesTheory: Sodium Carbonate Is The Salt of A Week Acid, Carbonic Acid (HSadia afrinNo ratings yet
- Lembar PerhitunganDocument12 pagesLembar PerhitunganArie SetieawanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry The Determination of An Unknow PDFDocument8 pagesChemistry The Determination of An Unknow PDFAbdullah Sabry AzzamNo ratings yet
- Chemistry DPP SolutionDocument8 pagesChemistry DPP SolutionabhishekNo ratings yet
- 8.4 and 9.2 Buffers and The Common Ion Effect StudentDocument3 pages8.4 and 9.2 Buffers and The Common Ion Effect StudentMichelle NgNo ratings yet
- Process Flowsheeting With Spreadsheet: Mass and Energy 2: Separation and RecycleDocument17 pagesProcess Flowsheeting With Spreadsheet: Mass and Energy 2: Separation and RecycleHow Bing ShenNo ratings yet
- 2023 JC2 H1 Chem BT MCQ MSDocument7 pages2023 JC2 H1 Chem BT MCQ MSemman tzhNo ratings yet
- Group 1 - ALEJANO - DEZOLLER - GRATIS - MIXED FLOW REACTOR-5Document13 pagesGroup 1 - ALEJANO - DEZOLLER - GRATIS - MIXED FLOW REACTOR-5John Frix AlejanoNo ratings yet
- Conformational AnalysisDocument4 pagesConformational AnalysisJinNo ratings yet
- Topic 17 1 - Equilibrium LawDocument14 pagesTopic 17 1 - Equilibrium LawMichelle EnkhsaikhanNo ratings yet
- Detection of Organic Functional GroupDocument1 pageDetection of Organic Functional Groupchandan3biswasNo ratings yet
- Detection of Acytyl Sallisylic Acid, Caffine and Paracetamol in Clendestine Prepration (Mathura Ki Pudia)Document9 pagesDetection of Acytyl Sallisylic Acid, Caffine and Paracetamol in Clendestine Prepration (Mathura Ki Pudia)PRAKASH TIWARINo ratings yet
- Chemistry - Long Term - Academic CALENDER (2022 & 23) : Velammal Bodhi Campus, PonneriDocument14 pagesChemistry - Long Term - Academic CALENDER (2022 & 23) : Velammal Bodhi Campus, PonneriSPS BALAADITHYA P G12No ratings yet
- Diffusion and Osmosis WorksheetDocument2 pagesDiffusion and Osmosis WorksheetDesmond simpsonNo ratings yet
- JJ Mec - Mep UpdateDocument83 pagesJJ Mec - Mep UpdatesalesNo ratings yet
- Stoichiometry and Mole ConceptDocument4 pagesStoichiometry and Mole Conceptdineshkumar4171100% (1)
- Cross 1977Document13 pagesCross 1977SaviaNo ratings yet
- North South Universty: Lab Report of ENV107Document40 pagesNorth South Universty: Lab Report of ENV107Tanbir. Nahid.No ratings yet
- Hydrogen Perspectives 21st Century Refineries Part2 PDFDocument5 pagesHydrogen Perspectives 21st Century Refineries Part2 PDFOmkarNo ratings yet
- PHY F2 End Term 1Document9 pagesPHY F2 End Term 1Selifa AbutiNo ratings yet
- Digital Unit Plan Template Unit Title: Stoichiometry Name: Yung Chung Content Area: Chemistry Grade Level: 10 GradeDocument5 pagesDigital Unit Plan Template Unit Title: Stoichiometry Name: Yung Chung Content Area: Chemistry Grade Level: 10 Gradeapi-385539760No ratings yet
- Sinfonia - Lifting MagnetDocument10 pagesSinfonia - Lifting Magnetnizam uddinNo ratings yet
- Endogenic Processes Plutonism and VolcanismDocument21 pagesEndogenic Processes Plutonism and VolcanismBen Josiah BayotNo ratings yet
- [Download pdf] Nanomaterials And Nanocomposites Nanostructure Surfaces And Their Applications Selected Proceedings Of The 7Th International Conference Nanotechnology And Nanomaterials Nano2019 27 30 online ebook all chapter pdfDocument43 pages[Download pdf] Nanomaterials And Nanocomposites Nanostructure Surfaces And Their Applications Selected Proceedings Of The 7Th International Conference Nanotechnology And Nanomaterials Nano2019 27 30 online ebook all chapter pdfemma.moon934100% (19)
- Methods For Total Antioxidant Activity Determination A Review 2161 1009.1000106Document10 pagesMethods For Total Antioxidant Activity Determination A Review 2161 1009.1000106Sie ningsihNo ratings yet
- Ash Gravel A Material For Recycling: Rogbeck and J. Hartl NDocument4 pagesAsh Gravel A Material For Recycling: Rogbeck and J. Hartl NGarima GuptaNo ratings yet
- Water Resource Eng. ReportDocument7 pagesWater Resource Eng. ReportRhea PardiñasNo ratings yet
- Intalox® Ultra™ Random Packing - Pushing The EnvelopeDocument4 pagesIntalox® Ultra™ Random Packing - Pushing The Envelope徐孝民No ratings yet
- Lecture 13 (Evaluation of Heat and Mass Transfer Coefficients)Document7 pagesLecture 13 (Evaluation of Heat and Mass Transfer Coefficients)KaleemNo ratings yet
- Lecture5 - Chemical Oxygen Demand PDFDocument40 pagesLecture5 - Chemical Oxygen Demand PDFgagileNo ratings yet
- 2016 Book NewApproachesToBuildingPatholo PDFDocument214 pages2016 Book NewApproachesToBuildingPatholo PDFCarlos Augusto Sanchez RondonNo ratings yet
- Ii) Generation of HV ACDocument33 pagesIi) Generation of HV ACNadiah NasirNo ratings yet
- Dynasonics IS 4000 BrochureDocument8 pagesDynasonics IS 4000 BrochureHarris TLNo ratings yet
- Thermo 2Document12 pagesThermo 2katabayoob11No ratings yet
- Elevator MCQ 20 ItemsDocument4 pagesElevator MCQ 20 ItemsGriffin Garcia50% (4)
- MVC MSDS C 002PL 05 Sodium HypochloriteDocument4 pagesMVC MSDS C 002PL 05 Sodium HypochloriteIan HiguitNo ratings yet
- Examiners' Report/ Principal Examiner Feedback: GCE Physics (6PH02) Paper 01R: Physics at WorkDocument10 pagesExaminers' Report/ Principal Examiner Feedback: GCE Physics (6PH02) Paper 01R: Physics at WorkShyam SharmaNo ratings yet
- Catalase: Hans LuckDocument10 pagesCatalase: Hans LuckNguyễn QuangNo ratings yet








































































![[Download pdf] Nanomaterials And Nanocomposites Nanostructure Surfaces And Their Applications Selected Proceedings Of The 7Th International Conference Nanotechnology And Nanomaterials Nano2019 27 30 online ebook all chapter pdf](https://imgv2-1-f.scribdassets.com/img/document/733006386/149x198/b160c03720/1719940744?v=1)













