Professional Documents
Culture Documents
What Is Computer Memory and Storage
What Is Computer Memory and Storage
Uploaded by
Alisha KhalidOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
What Is Computer Memory and Storage
What Is Computer Memory and Storage
Uploaded by
Alisha KhalidCopyright:
Available Formats
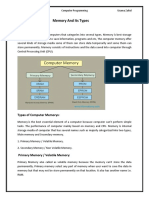
What is Computer Memory?
The essential component of the computer is its Memory. It is assembled on the motherboard as it
is a storage device used for storing data and instructions for performing a task on the system.
A memory is used to store data and instructions. It is the storage space in a computer,
where data is to be processed and all the instructions are stored that are required for
processing. In simple words, it works just like a human brain where we can store
memories.
Storage devices are hardware devices that are capable of storing and fetching data. Hard
drives or optical discs are an example of such storage devices.
Without memory, the computer can't perform a single task.
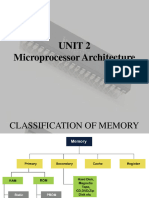
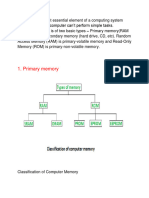
Types of Computer Memory
There are two types of memories:
1. Primary Memory
2. Secondary Memory
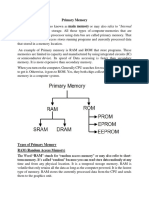
1. Primary Memory (Main Memory)
It is also referred to as Main Memory. It is volatile. The reason behind is, Primary memory holds
only those data and instructions on which the computer is currently working that is it does not
store the data permanently.
It also stores the operating system and data required to run the computer.
It is a limited capacity memory and data or information is lost when power is switched
off. Primary Memory is generally constructed with a semiconductor device.
Registers are much faster than these memories but it is faster than secondary memory.
It contains all the data and instructions that are required to be processed.
It is further divided into two subcategories RAM and ROM.
1.1. RAM (Random Access Memory)
It is Random Access Memory because of the random selection of memory locations. It performs
both read and writes operations on memory. It stores data temporarily.
If power failures happen in the system during memory access then you will lose your data
permanently. So, RAM is a volatile memory.
RAM categorized into following types:
1. SRAM
2. DRAM
1.1.1. SRAM (Static Random Access Memory)
It holds data in a static form, that is, as long as the memory has the power as the dynamic RAM,
it is not needed to refresh it again and again.
Static RAM provides faster access to data and is more expensive than DRAM as each cell
must contain multiple transistors.
SRAM does not use capacitors.
SRAM is also highly recommended for use in PCs, peripheral equipment, printers, LCD
screens, hard disk buffers, router buffers and buffers in CDROM / CDRW drives.
1.1.2. DRAM (Dynamic Random Access Memory)
It is a type of random-access memory used in computing devices. It is made up of capacitors and
transistors.
This type of memory uses separate capacitors or transistors to stores each bit of data and
it has two states of value in one bit called 0 and 1.
As compared with other RAM's it is less expensive.
Data were written by DRAM at the byte-level.
In DRAM, data is written at the byte-level and it reads data at the multiple-byte page
level.
DRAM requires less power than other RAMs.
1.2. ROM (Read Only Memory)
ROM offers huge types of standards to save data as it is a permanent memory location. But it
works with the read-only operation. whenever power failure occurs during the ROM memory
work in computers then no data lose happens.
It is Used where the programming requires no change and also in embedded systems or.
It is Used in peripheral devices and calculators.
The ROM is divided into the following three categories:
a. PROM (Programmable read-only memory)
b. EPROM (Erasable Programmable read only memory)
c. EEPROM (Electrically erasable programmable read only memory)
1.1.1. PROM (programmable read-only memory)
Developers created a type of ROM known as programmable read-only memory (PROM) because
Creating ROM chips from scratch are time-consuming and very expensive.
It can be coded by the user. Once coded, the data and instructions in it cannot be changed.
It is used to store permanent data in digital electronic devices.
It can be bought at a low cost as compared to other RAMs.
1.2.2. EPROM (Erasable Programmable read only memory)
This is the type of memory that can be reprogrammed. We can erase data from it and reprogram
it that is erase all the previous data by using high voltage Ultraviolet light.
It is required to erase each cell in EPROM.
1.2.3. EEPROM (Electrically erasable programmable read only memory)
The data can be erased and reprogrammed by applying an electric charge. There is no need for
ultraviolet light and we can erase only portions of the chip.
It was a replacement for PROM and EPROM chips and later it is used for computer's
BIOS.
Configurations parameters are stored by using EEPROM. In modern computers, they
replaced BIOS CMOS memory.
It is required that data to be written or erased by EEPROM one byte at a time.
2. Secondary Memory
The secondary memory is non-volatile, persistent and not immediately accessible by a computer
or processor. By using the secondary memory, we can store, retrieve, and transmit the data and
information.
The secondary memory is basically divided into two parts: Magnetic and Optical Memory.
2.1. Magnetic Memory
The examples of magnetic memory are: floppy diskette, hard disk, tape drive, etc.
2.2. Optical Memory
The examples of optical memory are: CD-ROMs, DVDs, Virtual optical devices, RDX, Flash
drives, etc.
You might also like
- Computer Memory TypesDocument9 pagesComputer Memory TypesJEETENDRANo ratings yet
- RCA Transistor Manual 1964Document387 pagesRCA Transistor Manual 1964Alejandro AGDvintageNo ratings yet
- XI CSC Computer Chapter 1 1 of 6Document9 pagesXI CSC Computer Chapter 1 1 of 6Tanay PhadeNo ratings yet
- CMTS Handout 4Document6 pagesCMTS Handout 4Tolosa TafeseNo ratings yet
- 2.BCI Unit2 R19Document16 pages2.BCI Unit2 R19chariNo ratings yet
- Storage DevicesDocument11 pagesStorage DevicesHuma aliNo ratings yet
- Ict Assignment# 01Document7 pagesIct Assignment# 01ibrarNo ratings yet
- Ece Unit 3 Memories PDFDocument7 pagesEce Unit 3 Memories PDFCHINMAY AGRAWALNo ratings yet
- Names: Rafal Hassan Ali, Supervised By: Sadiq H. Abdulhussain Goulshin Adnan Fadhil, Edia Nail Saeed, Zainab Haidar HafedDocument9 pagesNames: Rafal Hassan Ali, Supervised By: Sadiq H. Abdulhussain Goulshin Adnan Fadhil, Edia Nail Saeed, Zainab Haidar Hafedرفل حسن عليNo ratings yet
- Computer Memor1Document12 pagesComputer Memor1kschauhan8007No ratings yet
- Memory Unit - 5 Coa PDFDocument18 pagesMemory Unit - 5 Coa PDFArun KrishNo ratings yet
- Memory: Mohana S.H, Usmrfg College, Kuvempu UniversityDocument6 pagesMemory: Mohana S.H, Usmrfg College, Kuvempu UniversityMohana KurubaNo ratings yet
- Types of MemoryDocument5 pagesTypes of MemoryANIRUDDHA SAHANo ratings yet
- Computer Memory: Engr. Nuzhat MadinaDocument20 pagesComputer Memory: Engr. Nuzhat Madinadua tanveerNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document15 pagesUnit 2Smit AnjanaNo ratings yet
- BCE Unit 1 Part 3Document42 pagesBCE Unit 1 Part 3AbhiraNo ratings yet
- CSC113 AssignmentDocument3 pagesCSC113 AssignmentAlphus DavidNo ratings yet
- CFOS Unit II by - ErrorDocument22 pagesCFOS Unit II by - ErrorminatiummalikNo ratings yet
- Unit - III Concept of Memory PDFDocument13 pagesUnit - III Concept of Memory PDFxsaaNo ratings yet
- Computer PresentationDocument14 pagesComputer PresentationAayush Niroula OfficialNo ratings yet
- Memory and Its Types: Types of Computer MemorysDocument3 pagesMemory and Its Types: Types of Computer MemorysFahad kamranNo ratings yet
- Memory and It's TypesDocument4 pagesMemory and It's TypesAkshay KumarNo ratings yet
- " Types of Memories ": # Manav SharmaDocument16 pages" Types of Memories ": # Manav SharmaYogi SahuNo ratings yet
- BBA SEM II Memory System by Dr. Rakesh RanjanDocument7 pagesBBA SEM II Memory System by Dr. Rakesh RanjanVaibhav TripathiNo ratings yet
- Types of Ram and RomDocument10 pagesTypes of Ram and RomhussainNo ratings yet
- Digital Ram & RomDocument4 pagesDigital Ram & Romanilgahlawat1987No ratings yet
- Memory." and Primary Storage. All Those Types of Computer Memories That AreDocument6 pagesMemory." and Primary Storage. All Those Types of Computer Memories That Aregargib07No ratings yet
- ITM MbaDocument93 pagesITM MbaPrince kumarNo ratings yet
- Computer Memory: Is An Essential Element of A Computer. Without Its Memory, A Computer Is of HardlyDocument3 pagesComputer Memory: Is An Essential Element of A Computer. Without Its Memory, A Computer Is of HardlyArap ChitoNo ratings yet
- Primary or Main MemoryDocument6 pagesPrimary or Main MemoryChiranjib MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Computer MemoryDocument8 pagesComputer MemoryTakudzwa TapaNo ratings yet
- Memory ICS NotesDocument33 pagesMemory ICS NotesKafeel KhanNo ratings yet
- Memory and Its TypesDocument36 pagesMemory and Its TypesAaruni100% (1)
- Types of Main Memory: 1-Read-Write or Random Access Memory (RAM)Document4 pagesTypes of Main Memory: 1-Read-Write or Random Access Memory (RAM)Sarmad Salih Jawad AlkodaryNo ratings yet
- Selection - Memory - DR Monika - 22.03.23Document8 pagesSelection - Memory - DR Monika - 22.03.23Prof.Monika JainNo ratings yet
- Computer Memory: Types of RamDocument3 pagesComputer Memory: Types of RamJose Ric Catarus Bataluna Jr.No ratings yet
- Internal and External Devices of ComputerDocument53 pagesInternal and External Devices of ComputerSayoojNo ratings yet
- Explain in Detail Memory Classification. (Summer-2016, Summer-2015)Document19 pagesExplain in Detail Memory Classification. (Summer-2016, Summer-2015)yashuNo ratings yet
- Data StorageDocument9 pagesData Storage2027dpatel.studentNo ratings yet
- Storage DevicesDocument4 pagesStorage Devicesarmygamer0007No ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document12 pagesChapter 4Awash Zilong SharmaNo ratings yet
- Computer MemoryDocument5 pagesComputer MemorySophiya PrabinNo ratings yet
- Ram RomDocument6 pagesRam RomTaimoor GillNo ratings yet
- Basic Memory Operation: Static RAM, SRAM: An SRAM Is More Expensive and Less Dense Than DRAM. It Uses ADocument3 pagesBasic Memory Operation: Static RAM, SRAM: An SRAM Is More Expensive and Less Dense Than DRAM. It Uses AmadesrrrrNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document14 pagesChapter 4Awash Zilong SharmaNo ratings yet
- Memory DevicesDocument19 pagesMemory DevicesMst. Najnin SultanaNo ratings yet
- Q1: Define and Differentiate Between RAM and ROM. RAMDocument4 pagesQ1: Define and Differentiate Between RAM and ROM. RAMA. JadoonNo ratings yet
- Primary and Secondary MemoryDocument3 pagesPrimary and Secondary Memoryp100% (1)
- Unit 3 NotesDocument14 pagesUnit 3 Notesesasc.swayamNo ratings yet
- Ram and RomDocument3 pagesRam and RomMEENA J RCBSNo ratings yet
- Global College of Science and Technology: Continuous Assessment:2 (CA 2) A Report On Computer MemoryDocument5 pagesGlobal College of Science and Technology: Continuous Assessment:2 (CA 2) A Report On Computer MemoryarghajitrayNo ratings yet
- Here Is An Example of A Machine With 1GB of RAMDocument6 pagesHere Is An Example of A Machine With 1GB of RAMaguslizarNo ratings yet
- Computer Memory and ChipslDocument21 pagesComputer Memory and ChipslMardy LanuzaNo ratings yet
- Chap 4 Storage Devices - 9thDocument11 pagesChap 4 Storage Devices - 9thZubair FaiziNo ratings yet
- Computer ProficiencyDocument165 pagesComputer ProficiencyMani RaiNo ratings yet
- Types of Computer: It Is A Midsize Multi-Processing System Capable of Supporting Up To 250 Users SimultaneouslyDocument5 pagesTypes of Computer: It Is A Midsize Multi-Processing System Capable of Supporting Up To 250 Users SimultaneouslyMunim RajpootNo ratings yet
- Syallabus of Mid Term ExamDocument10 pagesSyallabus of Mid Term Exammuhammadahmadonstrike8No ratings yet
- RAM and RomDocument4 pagesRAM and Rommanoj22490No ratings yet
- PlayStation 2 Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #12From EverandPlayStation 2 Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #12No ratings yet
- Chaucer As A HumoristDocument5 pagesChaucer As A HumoristAlisha KhalidNo ratings yet
- The Knight by ChaucerDocument5 pagesThe Knight by ChaucerAlisha KhalidNo ratings yet
- The KiteDocument2 pagesThe KiteAlisha KhalidNo ratings yet
- Italian RenaissanceDocument1 pageItalian RenaissanceAlisha KhalidNo ratings yet
- NMOS FabricationDocument18 pagesNMOS FabricationDhaval Doshi100% (1)
- Junction Field Effect Transistors: Class 7Document47 pagesJunction Field Effect Transistors: Class 7s_subbulakshmi100% (1)
- Transistor Biasing Represents . ConditionsDocument8 pagesTransistor Biasing Represents . ConditionsRaj PatelNo ratings yet
- USBDM CF JMXXCLD V3Document8 pagesUSBDM CF JMXXCLD V3Sergio Johann ComasNo ratings yet
- AXElite Parts NumberDocument35 pagesAXElite Parts NumberAhmed Ali AlaqabeNo ratings yet
- General Purpose Transistors NPN Silicon: LH8050PLT1G Series S-LH8050PLT1G SeriesDocument4 pagesGeneral Purpose Transistors NPN Silicon: LH8050PLT1G Series S-LH8050PLT1G SeriesfrankyNo ratings yet
- Datta Das FET ExplanationDocument2 pagesDatta Das FET ExplanationJulie HaydenNo ratings yet
- UboatDocument6 pagesUboatjuanitruenosNo ratings yet
- 2N3055 NPN Silicon Darlingtons: Absolute Maximum RatingsDocument3 pages2N3055 NPN Silicon Darlingtons: Absolute Maximum RatingszesleyNo ratings yet
- EASA AML Module 4 ElectronicsDocument184 pagesEASA AML Module 4 ElectronicsDinuka WanigasekaraNo ratings yet
- THYRISTOR StudentDocument30 pagesTHYRISTOR StudentgggggNo ratings yet
- High Power Synchronous Buck Converter Delivers Up To 50ADocument2 pagesHigh Power Synchronous Buck Converter Delivers Up To 50ABerat GündoğanNo ratings yet
- Previous Question PapersDocument4 pagesPrevious Question Papersshaker423No ratings yet
- IRF640 Series: N-Channel Power MOSFET (18A, 200volts) DescriptionDocument7 pagesIRF640 Series: N-Channel Power MOSFET (18A, 200volts) DescriptionAlam Macedo OlveraNo ratings yet
- MM74HC161 - MM74HC163 Synchronous Binary Counter With Asynchronous Clear - Synchronous Binary Counter With Synchronous ClearDocument2 pagesMM74HC161 - MM74HC163 Synchronous Binary Counter With Asynchronous Clear - Synchronous Binary Counter With Synchronous Clearr3155No ratings yet
- Transistor C 548 BDocument4 pagesTransistor C 548 BEdson GomesNo ratings yet
- Linear Regulator Fundamentals: 2.4 NMOSDocument9 pagesLinear Regulator Fundamentals: 2.4 NMOSJose Helio PalmaNo ratings yet
- Polycrystalline Si Solar CellDocument9 pagesPolycrystalline Si Solar CellSajid BabuNo ratings yet
- Littelfuse Thyristor Cross ReferenceDocument30 pagesLittelfuse Thyristor Cross ReferenceSinisa KondicNo ratings yet
- Homework 2 SolDocument12 pagesHomework 2 SolAnouarNo ratings yet
- Power-Electronics Power-Transistors NotesDocument37 pagesPower-Electronics Power-Transistors NotesRAJ KUMAR SHIHINo ratings yet
- Bipolar Junction Transistor: ELAC 223/221L Electronics 1Document25 pagesBipolar Junction Transistor: ELAC 223/221L Electronics 1Sepillo RandelNo ratings yet
- Junction LeakageDocument9 pagesJunction LeakageMayank GuptaNo ratings yet
- VLSI Circuit Design Course - OutlineDocument3 pagesVLSI Circuit Design Course - OutlineAL RIZWANNo ratings yet
- Industrial ElectronicsDocument121 pagesIndustrial ElectronicssmagendiranNo ratings yet
- BUB941ZTDocument8 pagesBUB941ZTrun awayNo ratings yet
- EE341 Organic Transistors PresentationDocument19 pagesEE341 Organic Transistors PresentationmigmakeNo ratings yet
- Fabrication of PNP TransistorDocument32 pagesFabrication of PNP TransistorRahul RajNo ratings yet
- COMM 471 - F14 - Midterm - Makeup - Solutions PDFDocument5 pagesCOMM 471 - F14 - Midterm - Makeup - Solutions PDFSandy ZakariaNo ratings yet