Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Umbilical Cord
Umbilical Cord
Uploaded by
Nezuko0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views3 pagesUmbilical cord
Original Title
UMBILICAL-CORD
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentUmbilical cord
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views3 pagesUmbilical Cord
Umbilical Cord
Uploaded by
NezukoUmbilical cord
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
1
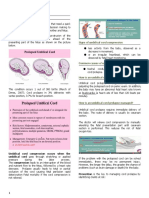
UMBILICAL CORD PROBLEM MOST COMMON UMBILICAL CORD ISSUES THAT
CAN INTERFERE WITH THE HEALTH OF THE
WHAT ARE SIGNS OF UMBILICAL CORD BABY
PROBLEMS?
UMBILICAL CORD COMPRESSION
An umbilical cord may become compressed or
damaged before or during childbirth. One common umbilical cord problem is
due to compression. Compression
Common signs of umbilical cord occurs when pressure partially or
problems include an irregular fetal completely stops the flow of blood
heartbeat and decreased or low fetal through the umbilical cord. Babies can
movement survive short periods of umbilical cord
Umbilical cord problems can be a compression, but if an adequate flow of
serious threat to the child’s health and blood to the baby is not re-established,
should be carefully monitored and the baby may suffer serious birth
treated as necessary. injuries. As we covered in the previous
The vein delivers blood full of nutrients sections, this condition is dangerous
and oxygen to the baby, while the because babies need nutrients and
arteries remove deoxygenated blood oxygen to remain healthy during
and waste from the baby back to the development
placenta Sign of umbilical cord compression may
After the baby is born, the umbilical include less activity from the baby,
cord is clamped and cut. There are no observed as a decrease in movement,
nerves within an umbilical cord, so this or an irregular heartbeat, which can be
is not painful for the baby or for the observed by fetal heart monitoring.
mother. Within a couple of weeks, the Common causes of umbilical cord
clamped stump of the umbilical cord compression include: nuchal cords. True
will eventually fall off, leaving a behind knots, and umbilical cord prolapsed
the baby’s belly button.
Umbilical cord compressed NUCHAL CORD
Nuchal cords
Nuchal cord is the medical term when
True knots
an umbilical cord becomes wrapped
Umbilical cord prolapsed
once or more times around the baby’s
Short umbilical cords
neck within the womb. Nuchal cord
Vasa previa
with one loop of cord around the baby’s
Umbilical cord infection
neck may occur in approximately 20%
of deliveries.
Nuchal cord is usually caused by the
baby’s movement through a loop of the
umbilical cord. Nuchal cord may be
detectable by electronic fetal heart
monitoring. Certain patterns of the
2
baby’s heart, like variable Polyhydramnios (excessive amniotic
decelerations” of the heart rate, are fluid)
often associated with nuchal cord. Malpresentation of fetus (breech
Nuchal cord may sometimes be presentation)
visualized on color Doppler ultrasound.
HOW IS AN UMBILICAL CORD PROLAPSE
DIAGNOSED
Umbilical cord prolapse is diagnosed by
seeing or palpating the prolapsed cord
on pelvic exam. In addition, the baby
may have an abnormal fetal heart rate
known as bradycardia (a heart rate of
less than 120 beats per minute)
HOW IS AN UMBILICAL CORD PROLAPSE
MANAGED?
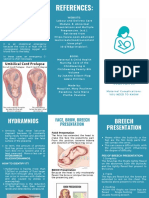
UMBILICAL CORD PROLAPSED
Umbilical cord prolapse is an acute
Before or during birth, the umbilical obstetric emergency that requires
cord can drop through the open cervix immediate delivery of the baby. The
into the vagina ahead of the baby. This route of delivery is usually by caesarean
complication, called umbilical cord section. The doctor will relieve cord
prolapsed, must be dealt with compression by manually elevating the
immediately so the fetus doesn’t put fetal presentation part until caesarean
pressure on the cord, cutting off oxygen section is performed. This reduces the
WHAT IS UMBILICAL CORD PROLAPSED? risk of fetal oxygen loss.
If the problem with the prolapsed cord
This condition occurs when the can be solved immediately, there may
umbilical cord drops (prolapsed) be no permanent injury. However, the
between the fetal presenting part and longer the delay, the greater the chance
the cervix into the vagina. Umbilical of problems (such as brain damage or
cord prolapse occurs prior to or during death) for the baby.
delivery of the baby. The overall
incidence is reported at 0.16%-0.18% or
approximately one in every 300 births.
COMON CAUSES UMBILICAL CORD PROLAPSE
INCLUDE:
Premature rupture of membranes
Pretern labor
Multiple gestation pregnancies (twins,
triplets, etc.).
3
WHAT HAPPENS IF THERE IS A KNOT IN THE
UMBILICAL CORD?
Most knots don’t cause problems for
our baby. As long as the knot isn’t too
toght, blood flow and nutrients aren’t
restricted. However, a tight knot leaves
your baby without enough oxygen and
puts them at risk for brain damage and
even stillbirth.
TRUE KNOTS
True knots are the medical term for
when the umbilical cord gets twisted
like a rape into a knot. True knots can
form simply by the baby’s movement
within the mother’s womb. Other
causes can include monoamniotic twins
( when twins share the same amniotic
sac). Polyhydramnios (excessive
amounts of amnioticfluis) overly long
umbilical cords, smaller that normal
fetuses, gestational diabetes, and
amniocentesis (a procedure to test the
amniotic fluid). True knots also can
form more often in male fertuses or
when the mother has had several
previous pregnancies.
If a baby’s activity decreases after 37
weeks, that is a common sign of a true
knot. Medical proffesionals should
remain alert for decreased activity and
should test for umbilical cord problems
as needed.
You might also like
- PROBLEMS of THE PASSAGEWAY and PsycheDocument1 pagePROBLEMS of THE PASSAGEWAY and PsycheAirishNo ratings yet
- Cervical CADocument32 pagesCervical CAEvangel Padua100% (2)
- Look Younger, Live LongerDocument5 pagesLook Younger, Live LongersimiliadocNo ratings yet
- Septeper 2015 Recall 200 Sba Mrcog Part 1Document49 pagesSepteper 2015 Recall 200 Sba Mrcog Part 1VINOD GUPTA100% (2)
- Umbilical CordDocument3 pagesUmbilical CordxxandraNo ratings yet
- Cord ProlapseDocument3 pagesCord ProlapseAlphine DalgoNo ratings yet
- Cord ProlapseDocument3 pagesCord ProlapseAlphine DalgoNo ratings yet
- Cord CoilDocument2 pagesCord CoilAlphine DalgoNo ratings yet
- Cord Coil Cord Prolapse Group 4Document31 pagesCord Coil Cord Prolapse Group 4Leah Mae DaguroNo ratings yet
- EctopicDocument4 pagesEctopicAb Staholic BoiiNo ratings yet
- Abnormalities of CordDocument13 pagesAbnormalities of CordtejaNo ratings yet
- Central Nervous System AbnormalitiesDocument56 pagesCentral Nervous System AbnormalitiesApin PokhrelNo ratings yet
- Spina Bbifida: Baguhin, Paul Ceniza, AnneDocument16 pagesSpina Bbifida: Baguhin, Paul Ceniza, AnnePaul Michael BaguhinNo ratings yet
- Umbilical Cord Accidents-1Document16 pagesUmbilical Cord Accidents-1chebetnaomi945No ratings yet
- Problems With The PassagewayDocument43 pagesProblems With The PassagewayMathew Beniga Gaco92% (12)
- Obstetrical EmergenciesDocument61 pagesObstetrical EmergenciesKavya S Mohan100% (3)
- Presented By: Balancar, Robert Jimenez, Jay Lebumfacil, Lani PearlDocument30 pagesPresented By: Balancar, Robert Jimenez, Jay Lebumfacil, Lani PearlAnonymous fGyJwzxTNo ratings yet
- Umblical Cord AbnormalitiesDocument54 pagesUmblical Cord AbnormalitiesKeerti Patel100% (6)
- The Umbilical Cord-1Document27 pagesThe Umbilical Cord-1Ahemigisha JamesNo ratings yet
- Retraction RingDocument5 pagesRetraction RingAna100% (2)
- Problems With The PassengerDocument58 pagesProblems With The PassengerJim NavarroNo ratings yet
- Cord Presentation ProlapseDocument10 pagesCord Presentation ProlapseJHONESSA LAYOSNo ratings yet
- Umbilical Cord ProlapseDocument6 pagesUmbilical Cord ProlapseCeth BeltranNo ratings yet
- 4 Anatomibirth DefectDocument51 pages4 Anatomibirth Defectwahyu ashariNo ratings yet
- Developmental Anomalies of Spinal CordDocument41 pagesDevelopmental Anomalies of Spinal Cordhamza_shoaib99No ratings yet
- Umbilical Cord AccidentsDocument16 pagesUmbilical Cord Accidentschebetnaomi945No ratings yet
- Face PresentationDocument4 pagesFace PresentationRose Ann HajironNo ratings yet
- 4-Fetal LifeDocument11 pages4-Fetal LifeRichard ManuelNo ratings yet
- No. 3 - NCM 109LDocument44 pagesNo. 3 - NCM 109LDalene EvangelioNo ratings yet
- Cord Prolapse: Prepared by Mrs Bini P Samuel Assistant Professor SSRCN, VapiDocument17 pagesCord Prolapse: Prepared by Mrs Bini P Samuel Assistant Professor SSRCN, Vapibinipsamuel25No ratings yet
- Spina BifidaDocument17 pagesSpina Bifidajessy100% (1)
- Chapter 6 and 7Document19 pagesChapter 6 and 7ayylmaoNo ratings yet
- ncm 107 midtermDocument24 pagesncm 107 midtermNURSING WORKSTUFFSNo ratings yet
- Cord ProlapseDocument3 pagesCord ProlapseReyniel Pablo ElumbaNo ratings yet
- NCM 109 Intrapartum Complications ReviewerDocument10 pagesNCM 109 Intrapartum Complications Reviewercrz VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- References:: Maternal and Child HealthDocument2 pagesReferences:: Maternal and Child HealthJulie Marie PavadoraNo ratings yet
- Spinalbifida 121213120324 Phpapp02Document28 pagesSpinalbifida 121213120324 Phpapp02Silvana María Espinoza CuadrosNo ratings yet
- DR Nwankwo's Birth InjuryDocument12 pagesDR Nwankwo's Birth InjurypreciouschichedomNo ratings yet
- Class SssssssDocument34 pagesClass SssssssPrajwal ChhetriNo ratings yet
- Spina BifidaDocument14 pagesSpina BifidaChacha ZakiyaNo ratings yet
- Anomalies of The Placenta and The CordDocument38 pagesAnomalies of The Placenta and The CordDN Sly Litang DumangasNo ratings yet
- Omphalocele: 1 Baskaran NDocument5 pagesOmphalocele: 1 Baskaran Nதாசன் தமிழன்No ratings yet
- Birth AsphyxiaDocument4 pagesBirth AsphyxiaNalin AbeysingheNo ratings yet
- Neuraltube DefectsDocument3 pagesNeuraltube DefectsfdgrgNo ratings yet
- ArzobalDocument2 pagesArzobalAileen S. CaccamNo ratings yet
- Week 8.4 MCNDocument12 pagesWeek 8.4 MCNZxiayieee JeonNo ratings yet
- Vacuum Extraction (Ventouse)Document3 pagesVacuum Extraction (Ventouse)dusty kawiNo ratings yet
- Central Nervous System: Key Points!!! FactsDocument18 pagesCentral Nervous System: Key Points!!! Factsjeron encaboNo ratings yet
- Birth InjuriesDocument9 pagesBirth InjuriesshailaNo ratings yet
- Neural Tube DefectsDocument40 pagesNeural Tube Defectsmdy0xxNo ratings yet
- Spina BifidaDocument33 pagesSpina BifidaRegine Prongoso DagumanpanNo ratings yet
- GD - L08 - Disturbance in Neonatal AdaptationDocument14 pagesGD - L08 - Disturbance in Neonatal AdaptationGarry SoloanNo ratings yet
- Spina BifidaDocument5 pagesSpina BifidaAdiel CalsaNo ratings yet
- Umbilical Cord ProlapseDocument6 pagesUmbilical Cord ProlapseJules Cantal100% (3)
- Congenital Malformation of Nervous System PPT Sesi 1Document22 pagesCongenital Malformation of Nervous System PPT Sesi 1Brandedlovers Onlineshop100% (1)
- Neural Tube Defect: Mrs. Abhilasha Saha Associate Professor-Paediatric Nursing National Medical College, Birgunj, NepalDocument26 pagesNeural Tube Defect: Mrs. Abhilasha Saha Associate Professor-Paediatric Nursing National Medical College, Birgunj, NepalSilvana María Espinoza CuadrosNo ratings yet
- Congenital AbnormalitiesDocument22 pagesCongenital AbnormalitiesNatukunda DianahNo ratings yet
- CPD, Dystocia, Fetal Distress OutputDocument8 pagesCPD, Dystocia, Fetal Distress OutputJohn Dave AbranNo ratings yet
- Module No. Date: Topic:: Cues/Questions/ Keywords Notes Preterm InfantDocument10 pagesModule No. Date: Topic:: Cues/Questions/ Keywords Notes Preterm Infantanon ymousNo ratings yet
- Science Direct Cord CareDocument7 pagesScience Direct Cord CareFatma ElzaytNo ratings yet
- Spina BifidaDocument6 pagesSpina BifidaAdiel Calsa100% (1)
- Vertigo, A Simple Guide to The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandVertigo, A Simple Guide to The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- High Risk PregnancyDocument4 pagesHigh Risk PregnancyNezukoNo ratings yet
- Naspo Gastric Tube Feeding FinalDocument32 pagesNaspo Gastric Tube Feeding FinalNezuko0% (1)
- Chapter 1 3 For Consultation Copy 1Document47 pagesChapter 1 3 For Consultation Copy 1NezukoNo ratings yet
- Identification of The Target Market 1Document16 pagesIdentification of The Target Market 1NezukoNo ratings yet
- OCDDocument10 pagesOCDkiran mahalNo ratings yet
- Mandaluyong CityDocument4 pagesMandaluyong CityMargaux SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Blunt Trauma AbdomenDocument41 pagesBlunt Trauma AbdomenSanthanu SukumaranNo ratings yet
- NCM 109 Care of Mother and Child at RiskDocument10 pagesNCM 109 Care of Mother and Child at RiskMia Fe Cuaya Lorenzo100% (1)
- NCLEX Study GuideDocument26 pagesNCLEX Study GuideLinda KellyNo ratings yet
- 12 Urinary EliminationDocument21 pages12 Urinary EliminationDarla SaulerNo ratings yet
- Photodynamic TherapyDocument5 pagesPhotodynamic TherapyPranav UpadhyayaNo ratings yet
- Tuberculosis (TB) Blood Test (IGRA) : Minnesota Department of HealthDocument1 pageTuberculosis (TB) Blood Test (IGRA) : Minnesota Department of HealthYeon Ae NaritaNo ratings yet
- NCP Anaphylactic ShockDocument6 pagesNCP Anaphylactic ShockKirstin del CarmenNo ratings yet
- Do Not Resuscitate Order FORDocument3 pagesDo Not Resuscitate Order FORQiew IkiNo ratings yet
- 30073665: Colloids Versus Crystalloids For Fluid Resuscitation in Critically Ill People PDFDocument210 pages30073665: Colloids Versus Crystalloids For Fluid Resuscitation in Critically Ill People PDFAngel VelásquezNo ratings yet
- PTC Slides 2016Document290 pagesPTC Slides 2016graceduma100% (1)
- Health and Wellness Notes 1 EditeDocument13 pagesHealth and Wellness Notes 1 EditeSOCIAL PLACENo ratings yet
- Genetic CounselingDocument12 pagesGenetic CounselingChandraNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology of Thyroid HormonesDocument56 pagesPharmacology of Thyroid HormonesDr.U.P.Rathnakar.MD.DIH.PGDHMNo ratings yet
- Filariasis: Parasitic Disease Roundworms Filarioidea Black Ies Mosquitoes HelminthiasesDocument9 pagesFilariasis: Parasitic Disease Roundworms Filarioidea Black Ies Mosquitoes Helminthiasesadandiba06No ratings yet
- 10 Health Benefits of Physical Fitness: Reduces The Risk of DiseasesDocument4 pages10 Health Benefits of Physical Fitness: Reduces The Risk of DiseasesEDGAR PALOMANo ratings yet
- Upath Ki-67 (30-9) Algorithm RUO 1020164EN - 1Document22 pagesUpath Ki-67 (30-9) Algorithm RUO 1020164EN - 1肥塚泰No ratings yet
- Chronic OsteomyelitisDocument18 pagesChronic OsteomyelitisMar OrdanzaNo ratings yet
- Basics of Anesthesia ReviewerDocument14 pagesBasics of Anesthesia ReviewerJohn Victor B. FelixNo ratings yet
- Filedate - 446download Ebook Rosens Emergency Medicine Concepts and Clinical Practice PDF Full Chapter PDFDocument67 pagesFiledate - 446download Ebook Rosens Emergency Medicine Concepts and Clinical Practice PDF Full Chapter PDFtroy.reader391100% (40)
- Efficacia e Tossicit Della Terapia Farmacologica Per Il Controllo Del Paziente Acutamente Agitato II ParteDocument9 pagesEfficacia e Tossicit Della Terapia Farmacologica Per Il Controllo Del Paziente Acutamente Agitato II ParteVedant Mohan GoyalNo ratings yet
- Myths of Dental Surgery in Patients Receiving Anticoagulant PDFDocument6 pagesMyths of Dental Surgery in Patients Receiving Anticoagulant PDFAlexandra MartinezNo ratings yet
- Cerebral Palsy Case Study Samantha McinerneyDocument11 pagesCerebral Palsy Case Study Samantha Mcinerneyapi-242113272100% (1)
- Hematology 2Document28 pagesHematology 2saad samyNo ratings yet
- Navjyoti Suri 84-Herdwick Street Brampton, ON. L6S 6M1 (647) 287 2618Document4 pagesNavjyoti Suri 84-Herdwick Street Brampton, ON. L6S 6M1 (647) 287 2618api-314566363No ratings yet
- Biomedical Engineering: By: Justin Lau, Kaisen Nakagawa, Preston Iha and Nuuanu Tech ClubDocument10 pagesBiomedical Engineering: By: Justin Lau, Kaisen Nakagawa, Preston Iha and Nuuanu Tech ClubS.m. ChandrashekarNo ratings yet