Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 viewsMecanismo de Accao Antibiotico
Mecanismo de Accao Antibiotico
Uploaded by
cassimo2009Penicillin was originally discovered in the 1920s and proved effective against many bacteria. However, bacterial resistance to penicillin has developed through several mechanisms, including production of beta-lactamase enzymes that break down the penicillin molecule. Today, natural penicillins like penicillin G (given intravenously) and penicillin V (given orally) remain effective against streptococci, meningococci, pneumococci, and other gram-positive bacteria. However, most Staphylococcus aureus are now resistant to penicillin.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Antibiotics - Compleate ClassificationDocument2 pagesAntibiotics - Compleate ClassificationNeal Gupta83% (12)
- AntiCancer Drugs MCQsDocument25 pagesAntiCancer Drugs MCQssk91% (11)
- Endocrinology - Polyuria - SOAP Note - Jeanette GoguenDocument3 pagesEndocrinology - Polyuria - SOAP Note - Jeanette GoguenFrancieudo SampaioNo ratings yet
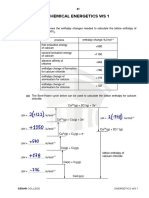
- Energetics AnswersDocument28 pagesEnergetics AnswersZafar IqbalNo ratings yet
- List of The PhobiaDocument8 pagesList of The PhobiaRjvm Net Ca FeNo ratings yet
- Reviewer PcolDocument3 pagesReviewer PcolMycaela Archivido De AlvaNo ratings yet
- AntibioticsDocument9 pagesAntibioticsJanie-Vi GorospeNo ratings yet
- Anti Bit OcsDocument6 pagesAnti Bit OcsAlexa TimNo ratings yet
- AntibioticsDocument4 pagesAntibioticsJan Leanne OrbigosoNo ratings yet
- Beta-Lactam Antibiotics & Other Cell Wall Synthesis InhibitorsDocument29 pagesBeta-Lactam Antibiotics & Other Cell Wall Synthesis InhibitorsRen PastelNo ratings yet
- 2.2.1 - Cell Wall Inhibitors-Introduction - Oct2012-Oct 2019Document30 pages2.2.1 - Cell Wall Inhibitors-Introduction - Oct2012-Oct 2019Frank Dany M'endormir MebeliNo ratings yet
- Antibiotic Classification & Mechanism - Basic Science - OrthobulletsDocument9 pagesAntibiotic Classification & Mechanism - Basic Science - OrthobulletsHossam Elden Helmy HaridyNo ratings yet
- Antibiotics: Microbial Control Antimicrobial AgentsDocument25 pagesAntibiotics: Microbial Control Antimicrobial AgentsMohammed Moutasim AyoubNo ratings yet
- AntibioticsDocument5 pagesAntibioticsLaureece Salm ApduhanNo ratings yet
- Antiboitic - PHA-308Document14 pagesAntiboitic - PHA-308Nowfal Hasan SiamNo ratings yet
- Antibiotics GuideDocument33 pagesAntibiotics Guidej7qs46h8wrNo ratings yet
- Bacteriostatic Agents: Drugs Which Bind To The 50s Ribosomal UnitDocument3 pagesBacteriostatic Agents: Drugs Which Bind To The 50s Ribosomal UnitJoshua Trinidad100% (1)
- Antibioticsummary DiagramDocument1 pageAntibioticsummary DiagramkarenmstamNo ratings yet
- Chemotherapy NotesDocument9 pagesChemotherapy Notesnileshkumarhjoshi942No ratings yet
- Penicillin 140625060421 Phpapp01Document22 pagesPenicillin 140625060421 Phpapp01newtamil 2021No ratings yet
- Mark Miguel P. Latras, RPHDocument11 pagesMark Miguel P. Latras, RPHLOLOLONo ratings yet
- Antibiotic KatsungDocument13 pagesAntibiotic KatsungJeffrey SutedjaNo ratings yet
- Antimicrobal Drugs #Dental 1Document30 pagesAntimicrobal Drugs #Dental 1ggNo ratings yet
- Antibiotics CologyDocument31 pagesAntibiotics CologyManthan ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Anti MicrobialDocument55 pagesAnti MicrobialNdayisaba CorneilleNo ratings yet
- Antibiotics Quick ReviewDocument5 pagesAntibiotics Quick Reviewpranjl100% (5)
- Chapter 12Document2 pagesChapter 12alkhudri.muharraniNo ratings yet
- Antibiotics in Periodontal DiseaseDocument57 pagesAntibiotics in Periodontal DiseaseReshmaaRajendranNo ratings yet
- ANTITUBERCULOUSDocument11 pagesANTITUBERCULOUSScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology - pphm203 Unit 2Document113 pagesPharmacology - pphm203 Unit 2Ãqûã FîggâNo ratings yet
- Antimicrobial Drugs: Powerpoint Presentations Prepared by Bradley W. Christian, Mclennan Community CollegeDocument35 pagesAntimicrobial Drugs: Powerpoint Presentations Prepared by Bradley W. Christian, Mclennan Community CollegeTiffany Jane Huertas100% (1)
- Overview of by Mechanism 2Document16 pagesOverview of by Mechanism 2daven100% (1)
- CephalosDocument15 pagesCephaloskimanh phạmNo ratings yet
- 2 Antimicrobials and Mode of Action - 5 - 8 - 2014rshe - SuskaDocument14 pages2 Antimicrobials and Mode of Action - 5 - 8 - 2014rshe - SuskaIvan AguilarNo ratings yet
- AB Lect2Document38 pagesAB Lect2Ivani Amelia CitraNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Solved Past PapersDocument10 pagesPharmacology Solved Past Papersfatima aghaNo ratings yet
- A018, Pranali Waghode, AntibioticsDocument4 pagesA018, Pranali Waghode, AntibioticsPranali WaghodeNo ratings yet
- Antibiotics: Classification (Based On Mechanism of Action)Document35 pagesAntibiotics: Classification (Based On Mechanism of Action)Mohol DasNo ratings yet
- Antibiotics, The Basics: Classification of Veterinary AntibioticsDocument2 pagesAntibiotics, The Basics: Classification of Veterinary Antibioticsgalihja100% (1)
- PharmacyDocument16 pagesPharmacyJow RamosNo ratings yet
- Antibiotics Handout ReferenceDocument3 pagesAntibiotics Handout Referencebl9nkverseNo ratings yet
- Antibiotics: A. AntibacterialDocument39 pagesAntibiotics: A. AntibacterialCaster Paul ManuelNo ratings yet
- Anti Tubercular DrugsDocument63 pagesAnti Tubercular DrugsYasir KhanNo ratings yet
- AB StaphDocument18 pagesAB StaphandrearosescarNo ratings yet
- Antimicrobial Chemotherapy IDocument30 pagesAntimicrobial Chemotherapy Inighat khanNo ratings yet
- PencillinDocument50 pagesPencillinPrasad SangishettyNo ratings yet
- Target AB Ke BakteriDocument1 pageTarget AB Ke Bakterimazz.rianNo ratings yet
- Antimicrobial Agents: Beta - Lactam CompoundsDocument6 pagesAntimicrobial Agents: Beta - Lactam CompoundsalejandraNo ratings yet
- AntibacterialDocument18 pagesAntibacterialRafia Rayana btbcNo ratings yet
- Basic Principles of Chemotherapy: S. Parasuraman, M.Pharm., PH.D., Senior Lecturer, Faculty of Pharmacy, AIMST UniversityDocument46 pagesBasic Principles of Chemotherapy: S. Parasuraman, M.Pharm., PH.D., Senior Lecturer, Faculty of Pharmacy, AIMST UniversityRohan LAlNo ratings yet
- Klasifikasi Dan Mekanisme ABDocument8 pagesKlasifikasi Dan Mekanisme ABDeboyjackNo ratings yet
- Chemotherapy Question 1Document6 pagesChemotherapy Question 1Vaishali PrasharNo ratings yet
- Antibacterial AgentsDocument44 pagesAntibacterial Agentsbelindasithole965No ratings yet
- Amr SeminarDocument48 pagesAmr SeminarSwijalNo ratings yet
- USMLE Step 3 Lecture Notes 2017-2018Document74 pagesUSMLE Step 3 Lecture Notes 2017-2018kaelenNo ratings yet
- Personal Antibiotics Reference Guide FINALDocument1 pagePersonal Antibiotics Reference Guide FINALAnita SzűcsNo ratings yet
- Chemotherapy ToxicityDocument37 pagesChemotherapy ToxicityCarlos Eduardo Cadu100% (1)
- Med ChemDocument3 pagesMed ChemPranali WaghodeNo ratings yet
- Antibiotic Classification and MechanismsDocument43 pagesAntibiotic Classification and Mechanismsyoza_kidNo ratings yet
- Prefinal Drug ClassDocument4 pagesPrefinal Drug ClassFtm Ashe SariolNo ratings yet
- Supplementary Information: E. ColiDocument4 pagesSupplementary Information: E. ColiListANo ratings yet
- ANTIBIOTICSDocument7 pagesANTIBIOTICSLutfi HakimNo ratings yet
- AntibacterialsDocument2 pagesAntibacterialsakeelNo ratings yet
- Chloe Ting - 2 Weeks Shred Challenge - Free Workout Program PDFDocument1 pageChloe Ting - 2 Weeks Shred Challenge - Free Workout Program PDFvalentina9echeniqueNo ratings yet
- Origin 12 ManualDocument34 pagesOrigin 12 ManualKenshironokenNo ratings yet
- Padampur ReportDocument16 pagesPadampur ReportSaudagar BiswalNo ratings yet
- ProcedureDocument2 pagesProcedureNeni SuryaniNo ratings yet
- Level 7 - Supervisor - Bar SupervisorDocument5 pagesLevel 7 - Supervisor - Bar SupervisorYudi YudiNo ratings yet
- 12 Chemistry Notes ch02 Solutions PDFDocument5 pages12 Chemistry Notes ch02 Solutions PDFSahilGuptaNo ratings yet
- TOS in PE 10Document3 pagesTOS in PE 10Aljon Cainto OperarioNo ratings yet
- CSR Catalog ColorDocument48 pagesCSR Catalog ColorMaritza LopezNo ratings yet
- Specification For Pressure Vessel Plates, Alloy Steel, Chromium-MolybdenumDocument6 pagesSpecification For Pressure Vessel Plates, Alloy Steel, Chromium-MolybdenumAnilNo ratings yet
- Read Online Textbook Applications in Design and Simulation of Sustainable Chemical Processes 1St Edition Dimian A Ebook All Chapter PDFDocument22 pagesRead Online Textbook Applications in Design and Simulation of Sustainable Chemical Processes 1St Edition Dimian A Ebook All Chapter PDFandrew.kraemer929100% (4)
- Diagnostics: Speed Bumps Ahead Prefer Hospitals Over DiagnosticsDocument33 pagesDiagnostics: Speed Bumps Ahead Prefer Hospitals Over DiagnosticsD BasavarajaNo ratings yet
- From The Rest: Read The Passage and Choose The Best Answer For Each Blank. The DolphinDocument3 pagesFrom The Rest: Read The Passage and Choose The Best Answer For Each Blank. The DolphinHa TranNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document5 pagesChapter 5Rena Jocelle NalzaroNo ratings yet
- Ap Stat 1-7 NotesDocument12 pagesAp Stat 1-7 NotesCooper BarthNo ratings yet
- Daniel Padilla Kathryn Bernardo: Barcelona: A Love UntoldDocument10 pagesDaniel Padilla Kathryn Bernardo: Barcelona: A Love UntoldHoney MalabuteNo ratings yet
- PMR v26 I4 158 166 PDFDocument9 pagesPMR v26 I4 158 166 PDFemzzNo ratings yet
- TaucuDocument1 pageTaucuWan ZiehanNo ratings yet
- Mastermind 2 Unit 7 WordlistDocument3 pagesMastermind 2 Unit 7 WordlistRolando Guzman MartinezNo ratings yet
- Mouth CareDocument11 pagesMouth CareKedamObulesu Kedam50% (2)
- Essay On Cigarette SmokingDocument6 pagesEssay On Cigarette Smokingfz5s2avw100% (2)
- 13 - Photosynthesis AQA BookletDocument28 pages13 - Photosynthesis AQA BookletSevilay CaferogluNo ratings yet
- Spiral Similarity: Definitions and BasicsDocument9 pagesSpiral Similarity: Definitions and Basicsmichael scottNo ratings yet
- Deogarh Court Boq Garden LightDocument7 pagesDeogarh Court Boq Garden Lighttsadkans59No ratings yet
- A GCE Biology 2805 03 January 2008 Question PaperDocument16 pagesA GCE Biology 2805 03 January 2008 Question PaperVeer RamloghunNo ratings yet
- SL - No Item Name PriceDocument3 pagesSL - No Item Name PriceAmitKumarNo ratings yet
- Target New Factory ProfileDocument3 pagesTarget New Factory ProfileLesly Janeth Banegas LoboNo ratings yet
Mecanismo de Accao Antibiotico
Mecanismo de Accao Antibiotico
Uploaded by
cassimo20090 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views1 pagePenicillin was originally discovered in the 1920s and proved effective against many bacteria. However, bacterial resistance to penicillin has developed through several mechanisms, including production of beta-lactamase enzymes that break down the penicillin molecule. Today, natural penicillins like penicillin G (given intravenously) and penicillin V (given orally) remain effective against streptococci, meningococci, pneumococci, and other gram-positive bacteria. However, most Staphylococcus aureus are now resistant to penicillin.
Original Description:
Original Title
Mecanismo de accao antibiotico
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentPenicillin was originally discovered in the 1920s and proved effective against many bacteria. However, bacterial resistance to penicillin has developed through several mechanisms, including production of beta-lactamase enzymes that break down the penicillin molecule. Today, natural penicillins like penicillin G (given intravenously) and penicillin V (given orally) remain effective against streptococci, meningococci, pneumococci, and other gram-positive bacteria. However, most Staphylococcus aureus are now resistant to penicillin.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views1 pageMecanismo de Accao Antibiotico
Mecanismo de Accao Antibiotico
Uploaded by
cassimo2009Penicillin was originally discovered in the 1920s and proved effective against many bacteria. However, bacterial resistance to penicillin has developed through several mechanisms, including production of beta-lactamase enzymes that break down the penicillin molecule. Today, natural penicillins like penicillin G (given intravenously) and penicillin V (given orally) remain effective against streptococci, meningococci, pneumococci, and other gram-positive bacteria. However, most Staphylococcus aureus are now resistant to penicillin.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
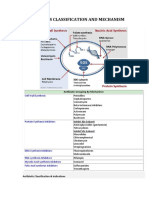
254 CHAPTER 11 Anti-Infectives
Síntese da parede Replicação de ADN (AND-
Celular girase)
Cicloserina
Acido Nalidixico
Vancomicina Flúorquinolonas AND-dependente Polimerase de
Bacitracina ARN
Fosfomicina Rifampin
Penicillinas
Cefalosporinas
Manobactams DNA
Carbapenems
THF A Síntese Proteica
mRNA (50S inibidor)
Metabolismo do
acido fólico Ribossoma Eritromicina
DHF A
Cloranfenicol
Trimetroprim 50 50 50 Clindamicina
Sulfonamidas 30 30 30
Síntese proteica
PABA (30S Inibidor )
Terraciclina
Membrana Celular
Polimixinas Estreptomicina
Gentamicina,
Figura 1. Antimicrobianos: Mecanismo de ação
PABA- Ácido p-aminobenzoico, DHF A – Ácido dihidrofólico, THF A – Ácido tetrahidrofólico
Resistance to Penicillins became available for the treatment of many gram-positive
and gram-negative cocci, anaerobes, and spirochetes.
Bacterial resistance to penicillin exists secondary to several Table 11-2 lists the indications, doses, and adverse reac-
different bacterial characteristics and/or mechanisms. tions to the most commonly used penicillins. lhe two nat-
First, the penicillins poorly penetrate into the intracellular
ural penicillins used today are benzylpenicillin, also known
space and are therefore ineffective against obligate intracel-
as penicillin G, which can only be given intravenously, and
lular organisms such as Rickettsia or Chlamydia. Nor are penicillin V, which is the oral formulation. Procaine peni-
they effective against gram-negative bacteria because the cillin (Bicillin CR) is penicillin G in combination with a
peptidoglycan wall is not exposed to the antibiotic in gram- local anesthetic (procaine), making it useful for intramus-
negative bacteria. Some gram-negative bacteria also have cular injection. Benzathine benzyl penicillin (Bicillin LA) is
pores in the outer membrane that do not allow passage of a form of penicillin G that is slowly absorbed then hydro-
beta-lactam antibiotics. Other bacteria have efflux pumps lyzed to penicillin G internally. It is used when prolonged
that remove the antibiotic from the periplasmic space. concentrations are required. It is important not to confuse
Some bacteria, such as Mycoplasma, do not make pepti- Bicillin CR and Bicillin LA. Bicillin CR has 1.2 million units
doglycan and are therefore impervious to the mechanism of penicillin G and 1.2 million units of procaine. Bicillin LA
of action of beta-lactam antibiotics. Bacteria that do have has 2.4 million units of penicillin G.17
peptidoglycan can alter the form of peptidoglycan made so Penicillin G remains indicated for infections caused
the beta-lactam antibiotics are ineffective. Finally, bacterial by streptococci, meningococci, enterococci, penicillin-
development of enzymes beta-lactamase or penicillinase susceptible pneumococci, and non–beta-lactamase-
is a common mechanism of resistance. lhese enzymes producing staphylococci. lhis agent also is highly effective
break open the beta-lactam ring of the penicillin molecule against spirochetes such as Treponema pallidum, Clostrid-
and render it inactive.16 ium species, actinomyces, and other gram-positive rods, but
it is inactive against most strains of Staphylococcus aureus.
Natural Penicillins Penicillin V (Veetids), also known as penicillin VK, is
In the late 1920s, natural penicillins were identified, and similar to penicillin G, except it is acid stabile, and penicillin
by 1950, penicillin G was proven to be bactericidal and G is not. Because of its acid stability, penicillin V is the drug
You might also like
- Antibiotics - Compleate ClassificationDocument2 pagesAntibiotics - Compleate ClassificationNeal Gupta83% (12)
- AntiCancer Drugs MCQsDocument25 pagesAntiCancer Drugs MCQssk91% (11)
- Endocrinology - Polyuria - SOAP Note - Jeanette GoguenDocument3 pagesEndocrinology - Polyuria - SOAP Note - Jeanette GoguenFrancieudo SampaioNo ratings yet
- Energetics AnswersDocument28 pagesEnergetics AnswersZafar IqbalNo ratings yet
- List of The PhobiaDocument8 pagesList of The PhobiaRjvm Net Ca FeNo ratings yet
- Reviewer PcolDocument3 pagesReviewer PcolMycaela Archivido De AlvaNo ratings yet
- AntibioticsDocument9 pagesAntibioticsJanie-Vi GorospeNo ratings yet
- Anti Bit OcsDocument6 pagesAnti Bit OcsAlexa TimNo ratings yet
- AntibioticsDocument4 pagesAntibioticsJan Leanne OrbigosoNo ratings yet
- Beta-Lactam Antibiotics & Other Cell Wall Synthesis InhibitorsDocument29 pagesBeta-Lactam Antibiotics & Other Cell Wall Synthesis InhibitorsRen PastelNo ratings yet
- 2.2.1 - Cell Wall Inhibitors-Introduction - Oct2012-Oct 2019Document30 pages2.2.1 - Cell Wall Inhibitors-Introduction - Oct2012-Oct 2019Frank Dany M'endormir MebeliNo ratings yet
- Antibiotic Classification & Mechanism - Basic Science - OrthobulletsDocument9 pagesAntibiotic Classification & Mechanism - Basic Science - OrthobulletsHossam Elden Helmy HaridyNo ratings yet
- Antibiotics: Microbial Control Antimicrobial AgentsDocument25 pagesAntibiotics: Microbial Control Antimicrobial AgentsMohammed Moutasim AyoubNo ratings yet
- AntibioticsDocument5 pagesAntibioticsLaureece Salm ApduhanNo ratings yet
- Antiboitic - PHA-308Document14 pagesAntiboitic - PHA-308Nowfal Hasan SiamNo ratings yet
- Antibiotics GuideDocument33 pagesAntibiotics Guidej7qs46h8wrNo ratings yet
- Bacteriostatic Agents: Drugs Which Bind To The 50s Ribosomal UnitDocument3 pagesBacteriostatic Agents: Drugs Which Bind To The 50s Ribosomal UnitJoshua Trinidad100% (1)
- Antibioticsummary DiagramDocument1 pageAntibioticsummary DiagramkarenmstamNo ratings yet
- Chemotherapy NotesDocument9 pagesChemotherapy Notesnileshkumarhjoshi942No ratings yet
- Penicillin 140625060421 Phpapp01Document22 pagesPenicillin 140625060421 Phpapp01newtamil 2021No ratings yet
- Mark Miguel P. Latras, RPHDocument11 pagesMark Miguel P. Latras, RPHLOLOLONo ratings yet
- Antibiotic KatsungDocument13 pagesAntibiotic KatsungJeffrey SutedjaNo ratings yet
- Antimicrobal Drugs #Dental 1Document30 pagesAntimicrobal Drugs #Dental 1ggNo ratings yet
- Antibiotics CologyDocument31 pagesAntibiotics CologyManthan ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Anti MicrobialDocument55 pagesAnti MicrobialNdayisaba CorneilleNo ratings yet
- Antibiotics Quick ReviewDocument5 pagesAntibiotics Quick Reviewpranjl100% (5)
- Chapter 12Document2 pagesChapter 12alkhudri.muharraniNo ratings yet
- Antibiotics in Periodontal DiseaseDocument57 pagesAntibiotics in Periodontal DiseaseReshmaaRajendranNo ratings yet
- ANTITUBERCULOUSDocument11 pagesANTITUBERCULOUSScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology - pphm203 Unit 2Document113 pagesPharmacology - pphm203 Unit 2Ãqûã FîggâNo ratings yet
- Antimicrobial Drugs: Powerpoint Presentations Prepared by Bradley W. Christian, Mclennan Community CollegeDocument35 pagesAntimicrobial Drugs: Powerpoint Presentations Prepared by Bradley W. Christian, Mclennan Community CollegeTiffany Jane Huertas100% (1)
- Overview of by Mechanism 2Document16 pagesOverview of by Mechanism 2daven100% (1)
- CephalosDocument15 pagesCephaloskimanh phạmNo ratings yet
- 2 Antimicrobials and Mode of Action - 5 - 8 - 2014rshe - SuskaDocument14 pages2 Antimicrobials and Mode of Action - 5 - 8 - 2014rshe - SuskaIvan AguilarNo ratings yet
- AB Lect2Document38 pagesAB Lect2Ivani Amelia CitraNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Solved Past PapersDocument10 pagesPharmacology Solved Past Papersfatima aghaNo ratings yet
- A018, Pranali Waghode, AntibioticsDocument4 pagesA018, Pranali Waghode, AntibioticsPranali WaghodeNo ratings yet
- Antibiotics: Classification (Based On Mechanism of Action)Document35 pagesAntibiotics: Classification (Based On Mechanism of Action)Mohol DasNo ratings yet
- Antibiotics, The Basics: Classification of Veterinary AntibioticsDocument2 pagesAntibiotics, The Basics: Classification of Veterinary Antibioticsgalihja100% (1)
- PharmacyDocument16 pagesPharmacyJow RamosNo ratings yet
- Antibiotics Handout ReferenceDocument3 pagesAntibiotics Handout Referencebl9nkverseNo ratings yet
- Antibiotics: A. AntibacterialDocument39 pagesAntibiotics: A. AntibacterialCaster Paul ManuelNo ratings yet
- Anti Tubercular DrugsDocument63 pagesAnti Tubercular DrugsYasir KhanNo ratings yet
- AB StaphDocument18 pagesAB StaphandrearosescarNo ratings yet
- Antimicrobial Chemotherapy IDocument30 pagesAntimicrobial Chemotherapy Inighat khanNo ratings yet
- PencillinDocument50 pagesPencillinPrasad SangishettyNo ratings yet
- Target AB Ke BakteriDocument1 pageTarget AB Ke Bakterimazz.rianNo ratings yet
- Antimicrobial Agents: Beta - Lactam CompoundsDocument6 pagesAntimicrobial Agents: Beta - Lactam CompoundsalejandraNo ratings yet
- AntibacterialDocument18 pagesAntibacterialRafia Rayana btbcNo ratings yet
- Basic Principles of Chemotherapy: S. Parasuraman, M.Pharm., PH.D., Senior Lecturer, Faculty of Pharmacy, AIMST UniversityDocument46 pagesBasic Principles of Chemotherapy: S. Parasuraman, M.Pharm., PH.D., Senior Lecturer, Faculty of Pharmacy, AIMST UniversityRohan LAlNo ratings yet
- Klasifikasi Dan Mekanisme ABDocument8 pagesKlasifikasi Dan Mekanisme ABDeboyjackNo ratings yet
- Chemotherapy Question 1Document6 pagesChemotherapy Question 1Vaishali PrasharNo ratings yet
- Antibacterial AgentsDocument44 pagesAntibacterial Agentsbelindasithole965No ratings yet
- Amr SeminarDocument48 pagesAmr SeminarSwijalNo ratings yet
- USMLE Step 3 Lecture Notes 2017-2018Document74 pagesUSMLE Step 3 Lecture Notes 2017-2018kaelenNo ratings yet
- Personal Antibiotics Reference Guide FINALDocument1 pagePersonal Antibiotics Reference Guide FINALAnita SzűcsNo ratings yet
- Chemotherapy ToxicityDocument37 pagesChemotherapy ToxicityCarlos Eduardo Cadu100% (1)
- Med ChemDocument3 pagesMed ChemPranali WaghodeNo ratings yet
- Antibiotic Classification and MechanismsDocument43 pagesAntibiotic Classification and Mechanismsyoza_kidNo ratings yet
- Prefinal Drug ClassDocument4 pagesPrefinal Drug ClassFtm Ashe SariolNo ratings yet
- Supplementary Information: E. ColiDocument4 pagesSupplementary Information: E. ColiListANo ratings yet
- ANTIBIOTICSDocument7 pagesANTIBIOTICSLutfi HakimNo ratings yet
- AntibacterialsDocument2 pagesAntibacterialsakeelNo ratings yet
- Chloe Ting - 2 Weeks Shred Challenge - Free Workout Program PDFDocument1 pageChloe Ting - 2 Weeks Shred Challenge - Free Workout Program PDFvalentina9echeniqueNo ratings yet
- Origin 12 ManualDocument34 pagesOrigin 12 ManualKenshironokenNo ratings yet
- Padampur ReportDocument16 pagesPadampur ReportSaudagar BiswalNo ratings yet
- ProcedureDocument2 pagesProcedureNeni SuryaniNo ratings yet
- Level 7 - Supervisor - Bar SupervisorDocument5 pagesLevel 7 - Supervisor - Bar SupervisorYudi YudiNo ratings yet
- 12 Chemistry Notes ch02 Solutions PDFDocument5 pages12 Chemistry Notes ch02 Solutions PDFSahilGuptaNo ratings yet
- TOS in PE 10Document3 pagesTOS in PE 10Aljon Cainto OperarioNo ratings yet
- CSR Catalog ColorDocument48 pagesCSR Catalog ColorMaritza LopezNo ratings yet
- Specification For Pressure Vessel Plates, Alloy Steel, Chromium-MolybdenumDocument6 pagesSpecification For Pressure Vessel Plates, Alloy Steel, Chromium-MolybdenumAnilNo ratings yet
- Read Online Textbook Applications in Design and Simulation of Sustainable Chemical Processes 1St Edition Dimian A Ebook All Chapter PDFDocument22 pagesRead Online Textbook Applications in Design and Simulation of Sustainable Chemical Processes 1St Edition Dimian A Ebook All Chapter PDFandrew.kraemer929100% (4)
- Diagnostics: Speed Bumps Ahead Prefer Hospitals Over DiagnosticsDocument33 pagesDiagnostics: Speed Bumps Ahead Prefer Hospitals Over DiagnosticsD BasavarajaNo ratings yet
- From The Rest: Read The Passage and Choose The Best Answer For Each Blank. The DolphinDocument3 pagesFrom The Rest: Read The Passage and Choose The Best Answer For Each Blank. The DolphinHa TranNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document5 pagesChapter 5Rena Jocelle NalzaroNo ratings yet
- Ap Stat 1-7 NotesDocument12 pagesAp Stat 1-7 NotesCooper BarthNo ratings yet
- Daniel Padilla Kathryn Bernardo: Barcelona: A Love UntoldDocument10 pagesDaniel Padilla Kathryn Bernardo: Barcelona: A Love UntoldHoney MalabuteNo ratings yet
- PMR v26 I4 158 166 PDFDocument9 pagesPMR v26 I4 158 166 PDFemzzNo ratings yet
- TaucuDocument1 pageTaucuWan ZiehanNo ratings yet
- Mastermind 2 Unit 7 WordlistDocument3 pagesMastermind 2 Unit 7 WordlistRolando Guzman MartinezNo ratings yet
- Mouth CareDocument11 pagesMouth CareKedamObulesu Kedam50% (2)
- Essay On Cigarette SmokingDocument6 pagesEssay On Cigarette Smokingfz5s2avw100% (2)
- 13 - Photosynthesis AQA BookletDocument28 pages13 - Photosynthesis AQA BookletSevilay CaferogluNo ratings yet
- Spiral Similarity: Definitions and BasicsDocument9 pagesSpiral Similarity: Definitions and Basicsmichael scottNo ratings yet
- Deogarh Court Boq Garden LightDocument7 pagesDeogarh Court Boq Garden Lighttsadkans59No ratings yet
- A GCE Biology 2805 03 January 2008 Question PaperDocument16 pagesA GCE Biology 2805 03 January 2008 Question PaperVeer RamloghunNo ratings yet
- SL - No Item Name PriceDocument3 pagesSL - No Item Name PriceAmitKumarNo ratings yet
- Target New Factory ProfileDocument3 pagesTarget New Factory ProfileLesly Janeth Banegas LoboNo ratings yet