Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ANATOMY
ANATOMY
Uploaded by
Fawzi Jarkin0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views6 pagesThis document contains a student's answers to anatomy homework questions. It discusses various bones and joints in the human body, including examples of gomphosis joints, markings on bone slides, specific names for parts of the radius bone, joints that contain articular discs, functions of the vertebral column, differences between cervical and thoracic vertebrae, and the definition of a tectorial membrane. The student provides detailed responses to each question drawing from various sources to demonstrate their knowledge of human anatomy.
Original Description:
Original Title
ANATOMY-converted
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document contains a student's answers to anatomy homework questions. It discusses various bones and joints in the human body, including examples of gomphosis joints, markings on bone slides, specific names for parts of the radius bone, joints that contain articular discs, functions of the vertebral column, differences between cervical and thoracic vertebrae, and the definition of a tectorial membrane. The student provides detailed responses to each question drawing from various sources to demonstrate their knowledge of human anatomy.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views6 pagesANATOMY
ANATOMY
Uploaded by
Fawzi JarkinThis document contains a student's answers to anatomy homework questions. It discusses various bones and joints in the human body, including examples of gomphosis joints, markings on bone slides, specific names for parts of the radius bone, joints that contain articular discs, functions of the vertebral column, differences between cervical and thoracic vertebrae, and the definition of a tectorial membrane. The student provides detailed responses to each question drawing from various sources to demonstrate their knowledge of human anatomy.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 6
Student: Fawzi Jarkin
Student id: 142237
Anatomy Homework
Q#1) Give two examples of gomphosis in the human
body
A#1) A gomphosis is a joint between the root of a tooth
and the socket in the maxilla or mandible.
(Temporomandibular joint)
Examples 1:- socket in the mandible
2:- socket in the maxilla
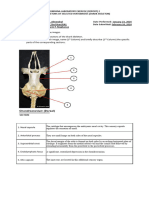
Q#2) Give one example of each bone marking and
formation according to the slide #29
A#2) The knee joint is a hinge type synovial joint, which
mainly allows for flexion and extension (and a small
degree of medial and lateral rotation). It is formed by
articulations between the patella, femur and tibia.
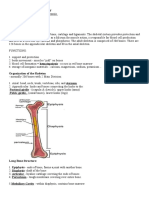
Q#3) Choose one bone and provide specific names
The radius is a long bone in the forearm. It lies laterally
and parallel to ulna, the second of the forearm bones.
The radius pivots around the ulna to produce movement
at the proximal and distal radio-ulnar joints.
Student: Fawzi Jarkin
Student id: 142237
The radius articulates in four places:
Elbow joint – Partly formed by an articulation between
the head of the radius, and the capitulum of the
humerus.
Proximal radioulnar joint – An articulation between the
radial head, and the radial notch of the ulna.
Wrist joint – An articulation between the distal end of
the radius and the carpal bones.
Distal radioulnar joint – An articulation between the
ulnar notch and the head of the ulna.
In this article, we shall look at the bony landmarks and
osteological features of the radius.
Proximal Region of the Radius
The proximal end of the radius articulates in both the
elbow and proximal radioulnar joints.
Student: Fawzi Jarkin
Student id: 142237
Important bony landmarks include the head, neck and
radial tuberosity:
Head of radius – A disk shaped structure, with a concave
articulating surface. It is thicker medially, where it takes
part in the proximal radioulnar joint.
Neck – A narrow area of bone, which lies between the
radial head and radial tuberosity.
Radial tuberosity – A bony projection, which serves as
the place of attachment of the biceps brachii muscle.
Q#4)Which joints includes articular disc?
A#4) An articular disk separates the fossa and articular
surface of the head of the mandible.
Examples 1:- sternoclavicular joint
2- synovial joints-knee joint(the disc can
provide shock absorption and cushioning between the
bones)
3- temporomandibular joint of the lower jaw
4-ulnocarpal (inner forearm bone and wrist)
Student: Fawzi Jarkin
Student id: 142237
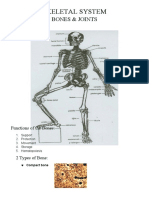
Q#5) What are the functions of the vertebral column
The vertebral column has four main functions:
• Protection – encloses and protects the spinal cord
within the spinal canal.
• Support – carries the weight of the body above the
pelvis.
• Axis – forms the central axis of the body.
• Movement – has roles in both posture and
movement.
Q#6) What are the differences between the cervical
and thoracic vertebra?
1:- The cervical vertebrae are smaller and more
mobile than their thoracic counterparts, which are
further supported by the rib cage.
2:- The cervical spinal cord also has a larger
diameter, and injuries at the cervical level interrupt
Student: Fawzi Jarkin
Student id: 142237
the sympathetic innervation to major immune
organs
3:- Moreover, the greater vascularity of the cervical
cord increases susceptibility to hemorrhage
following trauma.
4:- Injuries at the cervical level allow for
considerably more spontaneous recovery compared
with injuries at the thoracic level 128
Q#7) What is a tectorial membrane
The tectorial membrane (TM) is one of two acellular
membranes in the cochlea of the inner ear, the other
being the basilar membrane (BM). "Tectorial" in
anatomy means forming a cover. ... Radially the TM
is divided into three zones, the limbal, middle and
marginal zones.
Sources:- Teachmeanatomy.com plus moore book
Student: Fawzi Jarkin
Student id: 142237
You might also like
- Fetal Skull - Madam JustinaDocument11 pagesFetal Skull - Madam JustinaNana Yunus67% (3)
- Customer Relationship Management in Banking Sector-A Case Study of PNBDocument27 pagesCustomer Relationship Management in Banking Sector-A Case Study of PNBmanicoolgal4u100% (1)
- Wolf, Werner and Bernhart, Walter (Ed.) - Description in Literature and Other MediaDocument352 pagesWolf, Werner and Bernhart, Walter (Ed.) - Description in Literature and Other MediaElNegroLiterario100% (3)
- Zoology Act 4Document3 pagesZoology Act 4Marrion PenieroNo ratings yet
- Group2 - BSHM 1 BDocument43 pagesGroup2 - BSHM 1 BSAPILAN DENMARNo ratings yet
- 11 Axial Division of The Skeletal SystemDocument10 pages11 Axial Division of The Skeletal SystemMira Chariza Therese A. - BSN 1- CNo ratings yet
- Act08 The Skeletal System DiscussionDocument8 pagesAct08 The Skeletal System DiscussionSofia A.No ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument62 pagesSkeletal SystemAlyza AlcazarinNo ratings yet
- SkeletalDocument21 pagesSkeletalKeith HiadgeNo ratings yet
- Pharyngeal ArchDocument6 pagesPharyngeal ArchRajsandeep SinghNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy Physiology Chapter 4 Osseous System NotesDocument17 pagesHuman Anatomy Physiology Chapter 4 Osseous System Notesmanku9163No ratings yet
- Midterm Assignment 1Document5 pagesMidterm Assignment 1R Jay LagdaminNo ratings yet
- The Skeletal SystemDocument35 pagesThe Skeletal SystemSamantha EllaineNo ratings yet
- Endoskeleton of Frog (With Diagram) : The Endoskeleton Is Described Under Two Broad HeadsDocument13 pagesEndoskeleton of Frog (With Diagram) : The Endoskeleton Is Described Under Two Broad HeadsMarielle AcojidoNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System: The CraniumDocument7 pagesSkeletal System: The CraniumMohamed MustafeNo ratings yet
- Block 1 Essay Question and Answers (MBBS)Document188 pagesBlock 1 Essay Question and Answers (MBBS)jdfNo ratings yet
- HFBFB Chariza Therese A. Mira BSN 1-C: Page 1 of 8Document8 pagesHFBFB Chariza Therese A. Mira BSN 1-C: Page 1 of 8Mira Chariza Therese A. - BSN 1- CNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument17 pagesSkeletal SystemDEVNo ratings yet
- 4th Report SkeletonDocument14 pages4th Report SkeletonAndi NurhidayahNo ratings yet
- Ear AntomyDocument19 pagesEar Antomyhadeelnazar12No ratings yet
- I. What Are The Different Components of The Skeletal System?Document6 pagesI. What Are The Different Components of The Skeletal System?Aria IsipNo ratings yet
- I. What Are The Different Components of The Skeletal System?Document6 pagesI. What Are The Different Components of The Skeletal System?Aria IsipNo ratings yet
- Dissector Answers - Deep Back & Spinal CordDocument9 pagesDissector Answers - Deep Back & Spinal CordUloko ChristopherNo ratings yet
- Movement and LocomotionDocument8 pagesMovement and LocomotionRonnith NandyNo ratings yet
- SkeletalsystemDocument43 pagesSkeletalsystemSamantha EllaineNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: The Skeletal System - Osteology: Reading: Moore, Dalley, & Agur ObjectivesDocument10 pagesChapter 2: The Skeletal System - Osteology: Reading: Moore, Dalley, & Agur ObjectivesVarsha SNo ratings yet
- داتا زتونة مديول الجينيرال أناتوميDocument69 pagesداتا زتونة مديول الجينيرال أناتوميAhmed MohamedNo ratings yet
- LabSci1 Lab Ex15Document10 pagesLabSci1 Lab Ex15Hannah MondillaNo ratings yet
- Myology ComposDocument117 pagesMyology ComposjehanNo ratings yet
- Vertebral JointDocument5 pagesVertebral Jointاحمد البزورNo ratings yet
- The Skeletal System Human Body (206) Axial Skeleton (80) Skull (28) A. Paired Bones (11x2 22)Document17 pagesThe Skeletal System Human Body (206) Axial Skeleton (80) Skull (28) A. Paired Bones (11x2 22)Leo Cordel Jr.No ratings yet
- Las Sses4 Q1 W5Document14 pagesLas Sses4 Q1 W5Joan AgranoNo ratings yet
- Exp-4, To Study The General Features of Axial and Appendicular Skeletal SystemDocument3 pagesExp-4, To Study The General Features of Axial and Appendicular Skeletal SystemKeshab KapoorNo ratings yet
- PDS01A - Lesson 1Document30 pagesPDS01A - Lesson 1aresfenrirNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The SpineDocument12 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The SpineKinahZildredBibitNo ratings yet
- Surgical Anatomy of Mandible DeptDocument92 pagesSurgical Anatomy of Mandible DeptGopinath Thilak100% (7)
- 2ND Grading Laboratory SheetsDocument16 pages2ND Grading Laboratory SheetsAllecia Leona Arceta SoNo ratings yet
- Presentation OrthoDocument51 pagesPresentation OrthoPrateek ShivamNo ratings yet
- Anatomy 1Document69 pagesAnatomy 1ravinder malwalNo ratings yet
- Compana 2Document4 pagesCompana 2Adrienne Chelsea GabayNo ratings yet
- ACT 5 - Skeletal - Lab Sheet 2 Copy KoDocument12 pagesACT 5 - Skeletal - Lab Sheet 2 Copy KoMariah Ray Rint100% (1)
- Temporo Mandibular JointDocument146 pagesTemporo Mandibular Jointdentistpro.orgNo ratings yet
- ST - Paulos Hospital Millennium Medical College: Gross Anatomy:Upper LimbDocument256 pagesST - Paulos Hospital Millennium Medical College: Gross Anatomy:Upper LimbetNo ratings yet
- Anatomy BonesDocument11 pagesAnatomy BonesDunkin DonutNo ratings yet
- Joints of The Lower Limb DiagramsDocument39 pagesJoints of The Lower Limb Diagramssanullah123khan.13No ratings yet
- Anatomy 2019 1Document6 pagesAnatomy 2019 1YMORNo ratings yet
- Osteology of The Upper Limb LectureDocument40 pagesOsteology of The Upper Limb LectureFavour OnyeaboNo ratings yet
- Veterinary OsteologyDocument279 pagesVeterinary OsteologyTatenda Mageja100% (2)
- Thorax Anatomy..Document21 pagesThorax Anatomy..Dungani AllanNo ratings yet
- Antome Bones (BONES)Document7 pagesAntome Bones (BONES)Sadon B AsyNo ratings yet
- Fractures Around The Elbow JointDocument31 pagesFractures Around The Elbow Jointalimran MahmudNo ratings yet
- SkullBonesPages1 4 PDFDocument122 pagesSkullBonesPages1 4 PDFJennifer FirestoneNo ratings yet
- Laboratory 3 SkeletalDocument9 pagesLaboratory 3 SkeletalKyla InoferioNo ratings yet
- The Vertebral Column: FunctionsDocument11 pagesThe Vertebral Column: FunctionsNoralina IshakNo ratings yet
- Movement and Locomotion-23-24Document3 pagesMovement and Locomotion-23-24Chintan ShahNo ratings yet
- Human Bones NotesDocument20 pagesHuman Bones NotesARATHY M NAIR 2147718No ratings yet
- Complab Exercise 2 SharkDocument9 pagesComplab Exercise 2 SharkstephaniealmendralNo ratings yet
- Human SkelebonDocument74 pagesHuman Skelebonmuskaan.kukrejaNo ratings yet
- AnatomyDocument123 pagesAnatomyberdaderagaNo ratings yet
- Assignment As 3 Skeletal System: A. Give Your Responses To The FollowingDocument11 pagesAssignment As 3 Skeletal System: A. Give Your Responses To The FollowingNINA NORELLE GALVEZNo ratings yet
- SkeletonDocument40 pagesSkeletonRovin KamalNo ratings yet
- Advanced farriery knowledge: A study guide and AWCF theory course companionFrom EverandAdvanced farriery knowledge: A study guide and AWCF theory course companionNo ratings yet
- Informative Speech-"Deforestation": Senior High School DepartmentDocument2 pagesInformative Speech-"Deforestation": Senior High School DepartmentLemuel VillagenNo ratings yet
- Vicarious Liability JustificationDocument8 pagesVicarious Liability JustificationAryanNo ratings yet
- Pengaruh Merger Dan Akuisisi Terhadap Kinerja Keuangan PerusahaanDocument27 pagesPengaruh Merger Dan Akuisisi Terhadap Kinerja Keuangan PerusahaanApa 512No ratings yet
- Lightlink Adapter Plates: SpecificationsDocument7 pagesLightlink Adapter Plates: SpecificationsКирилл ЛысенкоNo ratings yet
- InnovationDocument20 pagesInnovationSayed EltaweelNo ratings yet
- Students Timetable Odd Sem 2023-24 - VAC1Document1 pageStudents Timetable Odd Sem 2023-24 - VAC1Saksham RustagiNo ratings yet
- La Guerra Ruso Japonesa Vista Por Shiba Ry6Tar6 : El Gran Novelista Hist6Rico J Apon6SDocument14 pagesLa Guerra Ruso Japonesa Vista Por Shiba Ry6Tar6 : El Gran Novelista Hist6Rico J Apon6SroxanamaldonadoNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument43 pagesUntitledThaddeus TungNo ratings yet
- p21 k-12 Global Ed IndicatorsDocument55 pagesp21 k-12 Global Ed Indicatorsapi-328107029100% (1)
- English 8 Summative Test 1Document9 pagesEnglish 8 Summative Test 1May Anne MagallanesNo ratings yet
- Primark PresentationDocument5 pagesPrimark PresentationFernando ChávarriNo ratings yet
- Peck D, 1998Document9 pagesPeck D, 1998Rafael LeeNo ratings yet
- Mapeh 6 Week 1 Lesson 2 Art - 074009Document4 pagesMapeh 6 Week 1 Lesson 2 Art - 074009Michelle AcdalNo ratings yet
- 20 Minute Manager - Managing Time - Clorox Services CompanyDocument6 pages20 Minute Manager - Managing Time - Clorox Services Companymaria pia otarolaNo ratings yet
- Excellence in Action EFQMDocument20 pagesExcellence in Action EFQMfrancoislcNo ratings yet
- Interactions of Matter: TimelineDocument32 pagesInteractions of Matter: TimelineLUKE HAMMONSNo ratings yet
- Pipework Pretest Checklist (Empty)Document1 pagePipework Pretest Checklist (Empty)Jorge Garcia100% (1)
- LO2 LP 1-7Document15 pagesLO2 LP 1-7Lily Cathylene Balongis EstoriaNo ratings yet
- 2017 CalendarDocument1 page2017 Calendarchamalds100% (1)
- ABAP Report WizardDocument20 pagesABAP Report Wizardbskris8727No ratings yet
- Game TheoryDocument36 pagesGame TheoryAmit ShuklaNo ratings yet
- ResearchDocument3 pagesResearchraika100% (1)
- Girl Scouting 101Document58 pagesGirl Scouting 101Maureen April Salazar AnitNo ratings yet
- Better Left BuriedDocument2 pagesBetter Left BuriedTestingNo ratings yet
- Legal Metrology Packaged Commodities Rules (India)Document44 pagesLegal Metrology Packaged Commodities Rules (India)Manoj DoliaNo ratings yet
- Apple Spray Schedule 2024 SKUAST KashmirDocument20 pagesApple Spray Schedule 2024 SKUAST Kashmirshakoor.ab.phd.cseNo ratings yet
- (Oxford Library of Psychology) Paul Verhaeghen, Christopher Hertzog - The Oxford Handbook of Emotion, Social Cognition, and Problem Solving in Adulthood-Oxford University Press (2014) PDFDocument353 pages(Oxford Library of Psychology) Paul Verhaeghen, Christopher Hertzog - The Oxford Handbook of Emotion, Social Cognition, and Problem Solving in Adulthood-Oxford University Press (2014) PDFMilos100% (6)
- 30 Items Assessment Exam in English 8Document3 pages30 Items Assessment Exam in English 8Kyros's MomNo ratings yet