Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Quadratic Equation
Quadratic Equation
Uploaded by
Leeanna ElhizCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Math Reviewer 9Document8 pagesMath Reviewer 9Kurt Dela PenaNo ratings yet
- Quadratic Equation CalculatorDocument4 pagesQuadratic Equation Calculatorapi-150547803No ratings yet
- Quadratic EquationDocument13 pagesQuadratic EquationHaimen BuisanNo ratings yet
- Quadratic Equation CalculatorDocument4 pagesQuadratic Equation Calculatorapi-140032165No ratings yet
- Quadratic EquationsDocument13 pagesQuadratic EquationsRenDenverL.DequiñaIINo ratings yet
- Quadratic Equation CalculatorDocument4 pagesQuadratic Equation Calculatorapi-150547803No ratings yet
- Week 1 FinalDocument16 pagesWeek 1 FinalRizza Mae ReponteNo ratings yet
- Best Method For Solving Quadratic InequalitiesDocument7 pagesBest Method For Solving Quadratic InequalitiesGoodmobo 123No ratings yet
- Ecuación CuadráticaDocument2 pagesEcuación CuadráticaTatiana LoorNo ratings yet
- Ax BX +C 0 Ax BX +C 0: Grade 9 Summarized ModuleDocument2 pagesAx BX +C 0 Ax BX +C 0: Grade 9 Summarized ModuleIsrael MarquezNo ratings yet
- Presentation - Quadraticequations-111211090004-Phpapp02 - 1524500815 - 313961 (3) - 1-1Document17 pagesPresentation - Quadraticequations-111211090004-Phpapp02 - 1524500815 - 313961 (3) - 1-1Mayank YadavNo ratings yet
- Quadratic EquationDocument2 pagesQuadratic EquationDexanne BulanNo ratings yet
- G9 Math Q1 - Week 1 Intro of Quadratic EquationDocument18 pagesG9 Math Q1 - Week 1 Intro of Quadratic EquationMechael ManzanoNo ratings yet
- Solving Neq1Document6 pagesSolving Neq1SAYID MABRUR RABBANI AL BABNo ratings yet
- G9MATHQ1M2Document46 pagesG9MATHQ1M2SITTIE FARISHA MAGAPISANo ratings yet
- Ecuaciones de 2do GradoDocument17 pagesEcuaciones de 2do GradoCARLOS LEONEL BARRERA GAMBOANo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Math Q1 M1Document12 pagesGrade 9 Math Q1 M1Renny Romero Luzada100% (2)
- Chapter 8. Quadratic Equations and Functions: X A B C A XDocument21 pagesChapter 8. Quadratic Equations and Functions: X A B C A XJoy CloradoNo ratings yet
- L2-Equation & Inequalities Oct 21-After ClassDocument35 pagesL2-Equation & Inequalities Oct 21-After ClassVINAYAGADHARSINI RAJENDRANNo ratings yet
- Introduction To MathematicsDocument8 pagesIntroduction To Mathematicsnjihiawambui29No ratings yet
- Sat Oc4 May30Document3 pagesSat Oc4 May30Ayan KhanNo ratings yet
- Quadratic Equations: Use This Sheet To Help YouDocument4 pagesQuadratic Equations: Use This Sheet To Help Youtrevbuiter6961100% (1)
- Quadratic Equations ReportDocument1 pageQuadratic Equations ReportI Putu Eka Prana YogaNo ratings yet
- Solving Quadratics by Factorising (1.02f)Document47 pagesSolving Quadratics by Factorising (1.02f)aaaaaaaNo ratings yet
- Project in Math: Submitted By: John Joseph F. Valencia Submitted To: Ace ContrerasDocument6 pagesProject in Math: Submitted By: John Joseph F. Valencia Submitted To: Ace Contrerasanon_402943846No ratings yet
- CH1 Lecture 4Document41 pagesCH1 Lecture 4hussainy.sharafNo ratings yet
- Applications of Equalities and InequalitiesDocument14 pagesApplications of Equalities and Inequalities鄭仲抗No ratings yet
- Lesson 4: Quadratic Equation: Standard FormDocument5 pagesLesson 4: Quadratic Equation: Standard FormChanchan LebumfacilNo ratings yet
- Solving Quadratic Equation by Extracting Square Roots FactoringDocument7 pagesSolving Quadratic Equation by Extracting Square Roots FactoringBaems AmborNo ratings yet
- Homework Study 20Document2 pagesHomework Study 20Mastergamer 48No ratings yet
- The Quadratic Formula Explained - PurplemathDocument3 pagesThe Quadratic Formula Explained - PurplemathHappy SunshineNo ratings yet
- Quadratic EquationDocument4 pagesQuadratic EquationVinayak UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- Quadratic Equations Workbook By: Ben McgaheeDocument8 pagesQuadratic Equations Workbook By: Ben Mcgaheemaihuongmaihuong1905No ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Grade 9 Mathematics Week 2Document7 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Grade 9 Mathematics Week 2Paul John TasicNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6. Quadratic EquationsDocument14 pagesChapter 6. Quadratic Equationshoneygarg1986No ratings yet
- Quadratic Equations: Ax + BX + C 0Document1 pageQuadratic Equations: Ax + BX + C 0Ofelia SamoiuNo ratings yet
- Equations Tranformable To Quadratic EquationsDocument6 pagesEquations Tranformable To Quadratic EquationsLiomer Zabala-Mubo CredoNo ratings yet
- Module in Mathematics 9: Pasay - M9 - Q1-W1-02Document5 pagesModule in Mathematics 9: Pasay - M9 - Q1-W1-02Shein SheilaNo ratings yet
- Numerical Method Lecture Note Quick PDFDocument21 pagesNumerical Method Lecture Note Quick PDFsharunnizamNo ratings yet
- Jesryl Ortega - Assessment-Week-2Document8 pagesJesryl Ortega - Assessment-Week-2Kendel GaanNo ratings yet
- MEI AS Mathematics: Quadratic Functions: Section 2: The Quadratic FormulaDocument6 pagesMEI AS Mathematics: Quadratic Functions: Section 2: The Quadratic Formulabobjeffords687No ratings yet
- College Algebra - Equations, Inequalities and Mathematical ModelingDocument32 pagesCollege Algebra - Equations, Inequalities and Mathematical ModelingNIKITA NOVENONo ratings yet
- Quadratic EquationDocument15 pagesQuadratic EquationSAGAR POUDELNo ratings yet
- Supplementals For Grade 9 - MathematicsDocument5 pagesSupplementals For Grade 9 - MathematicsNEIJAN NEQUINNo ratings yet
- Math 10 U1 - U8 DefinitionsDocument17 pagesMath 10 U1 - U8 DefinitionsShoaib AbbasNo ratings yet
- Math Grade 9Document7 pagesMath Grade 9Pede CasingNo ratings yet
- Ch1 - Quadratic Equation and InequalitiesDocument12 pagesCh1 - Quadratic Equation and InequalitieslolileeNo ratings yet
- MAT Reasoning About Solutions Practice: Non CalculatorDocument5 pagesMAT Reasoning About Solutions Practice: Non CalculatorSanil KatulaNo ratings yet
- Miscellaneous Equations and InequalitiesDocument13 pagesMiscellaneous Equations and InequalitiesFons Roxas-ChuaNo ratings yet
- Handout Elementary AlgebraDocument219 pagesHandout Elementary Algebrairham bin tauhidNo ratings yet
- + BX + C 0 (X - H) K: Solving Quadratic Equations by Completing The SquareDocument16 pages+ BX + C 0 (X - H) K: Solving Quadratic Equations by Completing The SquareAserHelloNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Math W1 LASDocument12 pagesGrade 9 Math W1 LASJuliana Keren MonsaleNo ratings yet
- Proiect - de - Lectie - Ec - de - GR - II (3) ENGLISHMATH ERASMUSDocument4 pagesProiect - de - Lectie - Ec - de - GR - II (3) ENGLISHMATH ERASMUSSuler Antonia LacramioaraNo ratings yet
- Quadratic Equations: Squared DegreeDocument8 pagesQuadratic Equations: Squared DegreeNilo ValeraNo ratings yet
- 1.4: Quadratic EquationsDocument3 pages1.4: Quadratic EquationsabdulrahmanNo ratings yet
- Solve Equation: EquationsDocument6 pagesSolve Equation: Equationsapi-126876773No ratings yet
- Solving Quadratic Equation by Using The Quadratic FormulaDocument29 pagesSolving Quadratic Equation by Using The Quadratic FormulaAngels Of RoseNo ratings yet
- Quadratics: - by Rishit DuttaDocument12 pagesQuadratics: - by Rishit DuttaRishit DuttaNo ratings yet
- Hidden Quadratic EquationsDocument8 pagesHidden Quadratic EquationsFLORENo ratings yet
- Famous ComposersDocument5 pagesFamous ComposersLeeanna ElhizNo ratings yet
- Musical Elements in The Classical PeriodDocument2 pagesMusical Elements in The Classical PeriodLeeanna ElhizNo ratings yet
- Quadratic InequalitiesDocument2 pagesQuadratic InequalitiesLeeanna ElhizNo ratings yet
- Direct VariationsDocument2 pagesDirect VariationsLeeanna ElhizNo ratings yet
- Indirect VariationDocument2 pagesIndirect VariationLeeanna ElhizNo ratings yet
Quadratic Equation
Quadratic Equation
Uploaded by
Leeanna ElhizOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Quadratic Equation
Quadratic Equation
Uploaded by
Leeanna ElhizCopyright:
Available Formats
Math
Grade 9
you'll often learn about quadratic equations, which are equations of the form:
ax^2 + bx + c = 0
where 'x' represents the unknown variable, and 'a', 'b', and 'c' are constants (with 'a' not equal to zero).
The quadratic equation can have two solutions, one solution, or no real solutions depending on the value of the
discriminant (the value inside the square root in the quadratic formula). The discriminant is given by:
Δ = b^2 - 4ac
Here are the possible cases based on the value of the discriminant:
1. If Δ > 0: Two distinct real solutions.
2. If Δ = 0: One real solution (also known as a repeated or double root).
3. If Δ < 0: No real solutions (the solutions are complex or involve imaginary numbers).
To find the solutions for 'x', you can use the quadratic formula:
x = (-b ± √Δ) / 2a
Where ± indicates that you'll have two solutions: one with a plus sign and the other with a minus sign.
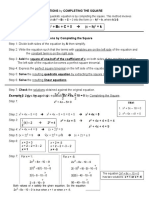
To solve a quadratic equation, follow these steps:
Step 1: Write down the quadratic equation in the standard form: ax^2 + bx + c = 0 Step 2: Calculate the discriminant
(Δ) using Δ = b^2 - 4ac Step 3: Determine the number of solutions based on the value of Δ (as mentioned above).
Step 4: If Δ > 0, find the two solutions using the quadratic formula. If Δ = 0, find the one solution. If Δ < 0, note that
there are no real solutions. Step 5: Simplify the solutions, and you're done!
Example: Let's solve the quadratic equation: 2x^2 - 5x + 2 = 0
Step 1: The coefficients are: a = 2, b = -5, and c = 2 Step 2: Calculate the discriminant: Δ = (-5)^2 - 4 * 2 * 2 = 25 - 16
= 9 Step 3: Since Δ > 0, there are two distinct real solutions. Step 4: Use the quadratic formula: x = [5 ± √(9)] / 2 * 2 x
= [5 ± 3] / 4
Step 5: Simplify the solutions: x1 = (5 + 3) / 4 = 8 / 4 = 2 x2 = (5 - 3) / 4 = 2 / 4 = 0.5
The solutions to the equation 2x^2 - 5x + 2 = 0 are x = 2 and x = 0.5.
You might also like
- Math Reviewer 9Document8 pagesMath Reviewer 9Kurt Dela PenaNo ratings yet
- Quadratic Equation CalculatorDocument4 pagesQuadratic Equation Calculatorapi-150547803No ratings yet
- Quadratic EquationDocument13 pagesQuadratic EquationHaimen BuisanNo ratings yet
- Quadratic Equation CalculatorDocument4 pagesQuadratic Equation Calculatorapi-140032165No ratings yet
- Quadratic EquationsDocument13 pagesQuadratic EquationsRenDenverL.DequiñaIINo ratings yet
- Quadratic Equation CalculatorDocument4 pagesQuadratic Equation Calculatorapi-150547803No ratings yet
- Week 1 FinalDocument16 pagesWeek 1 FinalRizza Mae ReponteNo ratings yet
- Best Method For Solving Quadratic InequalitiesDocument7 pagesBest Method For Solving Quadratic InequalitiesGoodmobo 123No ratings yet
- Ecuación CuadráticaDocument2 pagesEcuación CuadráticaTatiana LoorNo ratings yet
- Ax BX +C 0 Ax BX +C 0: Grade 9 Summarized ModuleDocument2 pagesAx BX +C 0 Ax BX +C 0: Grade 9 Summarized ModuleIsrael MarquezNo ratings yet
- Presentation - Quadraticequations-111211090004-Phpapp02 - 1524500815 - 313961 (3) - 1-1Document17 pagesPresentation - Quadraticequations-111211090004-Phpapp02 - 1524500815 - 313961 (3) - 1-1Mayank YadavNo ratings yet
- Quadratic EquationDocument2 pagesQuadratic EquationDexanne BulanNo ratings yet
- G9 Math Q1 - Week 1 Intro of Quadratic EquationDocument18 pagesG9 Math Q1 - Week 1 Intro of Quadratic EquationMechael ManzanoNo ratings yet
- Solving Neq1Document6 pagesSolving Neq1SAYID MABRUR RABBANI AL BABNo ratings yet
- G9MATHQ1M2Document46 pagesG9MATHQ1M2SITTIE FARISHA MAGAPISANo ratings yet
- Ecuaciones de 2do GradoDocument17 pagesEcuaciones de 2do GradoCARLOS LEONEL BARRERA GAMBOANo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Math Q1 M1Document12 pagesGrade 9 Math Q1 M1Renny Romero Luzada100% (2)
- Chapter 8. Quadratic Equations and Functions: X A B C A XDocument21 pagesChapter 8. Quadratic Equations and Functions: X A B C A XJoy CloradoNo ratings yet
- L2-Equation & Inequalities Oct 21-After ClassDocument35 pagesL2-Equation & Inequalities Oct 21-After ClassVINAYAGADHARSINI RAJENDRANNo ratings yet
- Introduction To MathematicsDocument8 pagesIntroduction To Mathematicsnjihiawambui29No ratings yet
- Sat Oc4 May30Document3 pagesSat Oc4 May30Ayan KhanNo ratings yet
- Quadratic Equations: Use This Sheet To Help YouDocument4 pagesQuadratic Equations: Use This Sheet To Help Youtrevbuiter6961100% (1)
- Quadratic Equations ReportDocument1 pageQuadratic Equations ReportI Putu Eka Prana YogaNo ratings yet
- Solving Quadratics by Factorising (1.02f)Document47 pagesSolving Quadratics by Factorising (1.02f)aaaaaaaNo ratings yet
- Project in Math: Submitted By: John Joseph F. Valencia Submitted To: Ace ContrerasDocument6 pagesProject in Math: Submitted By: John Joseph F. Valencia Submitted To: Ace Contrerasanon_402943846No ratings yet
- CH1 Lecture 4Document41 pagesCH1 Lecture 4hussainy.sharafNo ratings yet
- Applications of Equalities and InequalitiesDocument14 pagesApplications of Equalities and Inequalities鄭仲抗No ratings yet
- Lesson 4: Quadratic Equation: Standard FormDocument5 pagesLesson 4: Quadratic Equation: Standard FormChanchan LebumfacilNo ratings yet
- Solving Quadratic Equation by Extracting Square Roots FactoringDocument7 pagesSolving Quadratic Equation by Extracting Square Roots FactoringBaems AmborNo ratings yet
- Homework Study 20Document2 pagesHomework Study 20Mastergamer 48No ratings yet
- The Quadratic Formula Explained - PurplemathDocument3 pagesThe Quadratic Formula Explained - PurplemathHappy SunshineNo ratings yet
- Quadratic EquationDocument4 pagesQuadratic EquationVinayak UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- Quadratic Equations Workbook By: Ben McgaheeDocument8 pagesQuadratic Equations Workbook By: Ben Mcgaheemaihuongmaihuong1905No ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Grade 9 Mathematics Week 2Document7 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Grade 9 Mathematics Week 2Paul John TasicNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6. Quadratic EquationsDocument14 pagesChapter 6. Quadratic Equationshoneygarg1986No ratings yet
- Quadratic Equations: Ax + BX + C 0Document1 pageQuadratic Equations: Ax + BX + C 0Ofelia SamoiuNo ratings yet
- Equations Tranformable To Quadratic EquationsDocument6 pagesEquations Tranformable To Quadratic EquationsLiomer Zabala-Mubo CredoNo ratings yet
- Module in Mathematics 9: Pasay - M9 - Q1-W1-02Document5 pagesModule in Mathematics 9: Pasay - M9 - Q1-W1-02Shein SheilaNo ratings yet
- Numerical Method Lecture Note Quick PDFDocument21 pagesNumerical Method Lecture Note Quick PDFsharunnizamNo ratings yet
- Jesryl Ortega - Assessment-Week-2Document8 pagesJesryl Ortega - Assessment-Week-2Kendel GaanNo ratings yet
- MEI AS Mathematics: Quadratic Functions: Section 2: The Quadratic FormulaDocument6 pagesMEI AS Mathematics: Quadratic Functions: Section 2: The Quadratic Formulabobjeffords687No ratings yet
- College Algebra - Equations, Inequalities and Mathematical ModelingDocument32 pagesCollege Algebra - Equations, Inequalities and Mathematical ModelingNIKITA NOVENONo ratings yet
- Quadratic EquationDocument15 pagesQuadratic EquationSAGAR POUDELNo ratings yet
- Supplementals For Grade 9 - MathematicsDocument5 pagesSupplementals For Grade 9 - MathematicsNEIJAN NEQUINNo ratings yet
- Math 10 U1 - U8 DefinitionsDocument17 pagesMath 10 U1 - U8 DefinitionsShoaib AbbasNo ratings yet
- Math Grade 9Document7 pagesMath Grade 9Pede CasingNo ratings yet
- Ch1 - Quadratic Equation and InequalitiesDocument12 pagesCh1 - Quadratic Equation and InequalitieslolileeNo ratings yet
- MAT Reasoning About Solutions Practice: Non CalculatorDocument5 pagesMAT Reasoning About Solutions Practice: Non CalculatorSanil KatulaNo ratings yet
- Miscellaneous Equations and InequalitiesDocument13 pagesMiscellaneous Equations and InequalitiesFons Roxas-ChuaNo ratings yet
- Handout Elementary AlgebraDocument219 pagesHandout Elementary Algebrairham bin tauhidNo ratings yet
- + BX + C 0 (X - H) K: Solving Quadratic Equations by Completing The SquareDocument16 pages+ BX + C 0 (X - H) K: Solving Quadratic Equations by Completing The SquareAserHelloNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Math W1 LASDocument12 pagesGrade 9 Math W1 LASJuliana Keren MonsaleNo ratings yet
- Proiect - de - Lectie - Ec - de - GR - II (3) ENGLISHMATH ERASMUSDocument4 pagesProiect - de - Lectie - Ec - de - GR - II (3) ENGLISHMATH ERASMUSSuler Antonia LacramioaraNo ratings yet
- Quadratic Equations: Squared DegreeDocument8 pagesQuadratic Equations: Squared DegreeNilo ValeraNo ratings yet
- 1.4: Quadratic EquationsDocument3 pages1.4: Quadratic EquationsabdulrahmanNo ratings yet
- Solve Equation: EquationsDocument6 pagesSolve Equation: Equationsapi-126876773No ratings yet
- Solving Quadratic Equation by Using The Quadratic FormulaDocument29 pagesSolving Quadratic Equation by Using The Quadratic FormulaAngels Of RoseNo ratings yet
- Quadratics: - by Rishit DuttaDocument12 pagesQuadratics: - by Rishit DuttaRishit DuttaNo ratings yet
- Hidden Quadratic EquationsDocument8 pagesHidden Quadratic EquationsFLORENo ratings yet
- Famous ComposersDocument5 pagesFamous ComposersLeeanna ElhizNo ratings yet
- Musical Elements in The Classical PeriodDocument2 pagesMusical Elements in The Classical PeriodLeeanna ElhizNo ratings yet
- Quadratic InequalitiesDocument2 pagesQuadratic InequalitiesLeeanna ElhizNo ratings yet
- Direct VariationsDocument2 pagesDirect VariationsLeeanna ElhizNo ratings yet
- Indirect VariationDocument2 pagesIndirect VariationLeeanna ElhizNo ratings yet