Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lab4 Completed
Lab4 Completed
Uploaded by
Khalid MalikCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Gabriel Rincon-Mora-Analog IC Design With Low-Dropout Regulators (LDOs) (Electronic Engineering) (2009) PDFDocument373 pagesGabriel Rincon-Mora-Analog IC Design With Low-Dropout Regulators (LDOs) (Electronic Engineering) (2009) PDFNguyen HaNo ratings yet
- Smart Street Lighting System - Project ReportDocument8 pagesSmart Street Lighting System - Project Reportअनिमेष ठाकुर91% (33)
- Automated Broad and Narrow Band Impedance Matching for RF and Microwave CircuitsFrom EverandAutomated Broad and Narrow Band Impedance Matching for RF and Microwave CircuitsNo ratings yet
- Lab2 CompletedDocument14 pagesLab2 CompletedKhalid MalikNo ratings yet
- Lab5 CompletedDocument8 pagesLab5 CompletedKhalid MalikNo ratings yet
- Lab3 CompletedDocument16 pagesLab3 CompletedKhalid MalikNo ratings yet
- T F W R: O Design AND Simulate A ULL AVE Ectifier CircuitDocument4 pagesT F W R: O Design AND Simulate A ULL AVE Ectifier CircuitJunaid NazirNo ratings yet
- Ena Lab 2Document6 pagesEna Lab 2Halar MustafaNo ratings yet
- Ena Lab 4Document5 pagesEna Lab 4Halar MustafaNo ratings yet
- Lab 12 Basic ElectronicsDocument7 pagesLab 12 Basic ElectronicsMansoor AliNo ratings yet
- Design and Analysis of A Differential Di PDFDocument32 pagesDesign and Analysis of A Differential Di PDFbiboNo ratings yet
- Load Flow Analysis For A Given Network Using ETAPDocument4 pagesLoad Flow Analysis For A Given Network Using ETAPAkhter IqbalNo ratings yet
- Expt 7, Comparator (Updated)Document3 pagesExpt 7, Comparator (Updated)Danish MujibNo ratings yet
- Expt 7, Comparator (Updated)Document3 pagesExpt 7, Comparator (Updated)Danish MujibNo ratings yet
- Analog Electronics SampleDocument17 pagesAnalog Electronics SampleManoj1508AravindNo ratings yet
- Date: Page No.: Miracle Educational Society Group of InstitutionsDocument6 pagesDate: Page No.: Miracle Educational Society Group of Institutionsphani srinivasNo ratings yet
- Ena Lab 10Document4 pagesEna Lab 10Halar MustafaNo ratings yet
- Analog Electronics GATE IES PSU Study Materials PDFDocument17 pagesAnalog Electronics GATE IES PSU Study Materials PDFDharmveer SinghNo ratings yet
- MOSFET As An AMPLIFIERDocument16 pagesMOSFET As An AMPLIFIERJohnny Edward KingsleyNo ratings yet
- Industry Report Deee 5th Sem 2022-2023 Sachin New1Document31 pagesIndustry Report Deee 5th Sem 2022-2023 Sachin New1Rathod SachinNo ratings yet
- Time Current Characteristics of Over-Current Relay Suing ETAPDocument8 pagesTime Current Characteristics of Over-Current Relay Suing ETAPAkhter IqbalNo ratings yet
- Time Current Characteristics of Fuse Using ETAPDocument7 pagesTime Current Characteristics of Fuse Using ETAPAkhter IqbalNo ratings yet
- GR15 PDFDocument41 pagesGR15 PDFomkar maitreeNo ratings yet
- Short Circuit Analysis For A Given Network Using ETAPDocument4 pagesShort Circuit Analysis For A Given Network Using ETAPAkhter Iqbal100% (1)
- Lecture # 08 - Power Supply-Full Wave RectifierDocument14 pagesLecture # 08 - Power Supply-Full Wave Rectifiersaadkhanak9No ratings yet
- Open-Ended InverterDocument2 pagesOpen-Ended InverterAkhter IqbalNo ratings yet
- RC Phase Shift Oscillator 230510 - 195846Document32 pagesRC Phase Shift Oscillator 230510 - 195846Pranav msNo ratings yet
- College of Technology and Engineering: Training Report of "132kV Grid Sub-Station, Sukher"Document24 pagesCollege of Technology and Engineering: Training Report of "132kV Grid Sub-Station, Sukher"Harish MahlaNo ratings yet
- PDC Lab ManualDocument68 pagesPDC Lab Manualnama varapuNo ratings yet
- Einstein: College of EngineeringDocument80 pagesEinstein: College of EngineeringPoonkothaiMyilNo ratings yet
- CH3 - Diode Rectifiers DesignDocument24 pagesCH3 - Diode Rectifiers DesignSaid Ahmed AliNo ratings yet
- Ic Applications Lab Manual: Iii Btech, Ece-Ist SemesterDocument59 pagesIc Applications Lab Manual: Iii Btech, Ece-Ist SemesterAkshay PabbathiNo ratings yet
- Design of RF To DC Rectifier at GSM Band For EnergyDocument9 pagesDesign of RF To DC Rectifier at GSM Band For EnergyAchmad ShodikinNo ratings yet
- Lecture # 07 - Power Supply-Half Wave RectifierDocument22 pagesLecture # 07 - Power Supply-Half Wave Rectifiersaadkhanak9No ratings yet
- Final ESD Lab ManualDocument28 pagesFinal ESD Lab ManualVincent Padi AshieNo ratings yet
- Ac To DC Converter Project Report PDFDocument75 pagesAc To DC Converter Project Report PDFVishal Bhadalda100% (1)
- Ac To DC Converter Project ReportDocument75 pagesAc To DC Converter Project ReportPranav Tripathi79% (14)
- Batch 1 Beemp.Document13 pagesBatch 1 Beemp.22h51a6608No ratings yet
- LIC Lab ManualDocument57 pagesLIC Lab ManualsfundsNo ratings yet
- EPC BEC303 List of ExpsDocument51 pagesEPC BEC303 List of Expskaranphutane2254No ratings yet
- b13 Forced Commutation Using ArduinoDocument62 pagesb13 Forced Commutation Using ArduinoAlexandru Stefan AndriesNo ratings yet
- AUPEC 2020 Shuvra FinalDocument7 pagesAUPEC 2020 Shuvra FinalAK KhanNo ratings yet
- MTPA and Field Weakening Control of Synchronous Reluctance MotorDocument5 pagesMTPA and Field Weakening Control of Synchronous Reluctance MotorIVAN FELIPE BERNAL GOMEZNo ratings yet
- Matlab-Dc Motor1Document21 pagesMatlab-Dc Motor1Krishna SaraswatNo ratings yet
- Research Paper Improvement of Power System Stability by Simultaneous AC-DC Power TransmissionDocument6 pagesResearch Paper Improvement of Power System Stability by Simultaneous AC-DC Power Transmissionmaazsiddiqui.ee7193No ratings yet
- Be8261 BeeieDocument82 pagesBe8261 BeeieMohammed OvaizNo ratings yet
- IC Lab MaualDocument59 pagesIC Lab MaualKumar Goud.K100% (2)
- Performance Analysis of A High Voltage DC (HVDC) Transmission System Under Steady State and Faulted ConditionsDocument8 pagesPerformance Analysis of A High Voltage DC (HVDC) Transmission System Under Steady State and Faulted ConditionsrichatNo ratings yet
- IJAPE Guideforauthors 2012Document5 pagesIJAPE Guideforauthors 2012Ashish PorwalNo ratings yet
- EC2403 RF and Microwave EngineeringDocument152 pagesEC2403 RF and Microwave EngineeringKushal MpvsNo ratings yet
- Design and Implementation of Cascaded H Bridge Multilevel Inverter Using Digital Control Schemes IJERTV6IS050317Document4 pagesDesign and Implementation of Cascaded H Bridge Multilevel Inverter Using Digital Control Schemes IJERTV6IS050317Sateesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Wave Shaping Square, Triangular and Saw ToothDocument16 pagesWave Shaping Square, Triangular and Saw ToothKiranpreet SinghNo ratings yet
- Lab 3 Rectifiers and FiltersDocument6 pagesLab 3 Rectifiers and FiltersAlisha AasNo ratings yet
- EE6311 LIC Lab - VidyarthiplusDocument66 pagesEE6311 LIC Lab - VidyarthiplusArun KumarNo ratings yet
- Ed ManualDocument66 pagesEd ManualshilpaNo ratings yet
- IC HDL Lab ManualDocument82 pagesIC HDL Lab ManualRakshitha AngelNo ratings yet
- Ps Exp 1 PDFDocument6 pagesPs Exp 1 PDFrv_andeNo ratings yet
- Electronic Circuits LatestDocument69 pagesElectronic Circuits LatestSai SadiqNo ratings yet
- LIC Lab ManualDocument79 pagesLIC Lab ManualSakthikumar Balasundaram67% (3)
- Network ProjectDocument12 pagesNetwork ProjectAyush SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- Lab 1Document7 pagesLab 1Khalid MalikNo ratings yet
- LAB TasksDocument2 pagesLAB TasksKhalid MalikNo ratings yet
- Lab 8Document5 pagesLab 8Khalid MalikNo ratings yet
- Lab - 7Document5 pagesLab - 7Khalid MalikNo ratings yet
- Lab - 9Document4 pagesLab - 9Khalid MalikNo ratings yet
- Lab - 4Document5 pagesLab - 4Khalid MalikNo ratings yet
- Lab - 5Document8 pagesLab - 5Khalid MalikNo ratings yet
- Lab - 2Document7 pagesLab - 2Khalid MalikNo ratings yet
- Lab - 3Document3 pagesLab - 3Khalid MalikNo ratings yet
- Lab - 6Document7 pagesLab - 6Khalid MalikNo ratings yet
- Lab 5Document19 pagesLab 5Khalid MalikNo ratings yet
- Kannur University B Tech s5 SyllubusDocument6 pagesKannur University B Tech s5 SyllubusappurajkvNo ratings yet
- Dcs Lab Manual 2018 191 PDFDocument37 pagesDcs Lab Manual 2018 191 PDFbala_athmaNo ratings yet
- 1000 Electronic Devices & Circuits MCQsDocument467 pages1000 Electronic Devices & Circuits MCQskibrom atsbha67% (3)
- Electrical and Electronic EngineeringDocument34 pagesElectrical and Electronic EngineeringANo ratings yet
- Excel Review Center - Manila Ece Review For October 2019 Board Exam Refresher Exam - ElecDocument4 pagesExcel Review Center - Manila Ece Review For October 2019 Board Exam Refresher Exam - ElecTintin DalatenNo ratings yet
- B 115 BDocument121 pagesB 115 BPetrica Dan DinuNo ratings yet
- 741b PDFDocument11 pages741b PDFrrr2013No ratings yet
- Aic Unit 3Document96 pagesAic Unit 3SYETC156HARSHAL RAHENWALNo ratings yet
- Design SolutionDocument5 pagesDesign SolutionsubbuNo ratings yet
- Sony Xm-255exDocument14 pagesSony Xm-255exsamuel ancesquiNo ratings yet
- Datasheet PDFDocument7 pagesDatasheet PDFVNo ratings yet
- Syllabus 1st YearDocument23 pagesSyllabus 1st YearS.m. ChandrashekarNo ratings yet
- 45 Watt ClassDocument5 pages45 Watt Classfirmansyah miraddanaNo ratings yet
- Listening BugDocument1 pageListening BugDiksha Tulsi67% (3)
- Op-Amp Based Static Over Current RelayDocument6 pagesOp-Amp Based Static Over Current RelayS Bharadwaj ReddyNo ratings yet
- X Building A Microcontroller Based PotentiostatDocument15 pagesX Building A Microcontroller Based PotentiostatJesús Munayco FloresNo ratings yet
- S5 SyllabusDocument75 pagesS5 SyllabusAnjali S KumarNo ratings yet
- Circuit Note: Fully Isolated Conductivity Measurement Data Acquisition SystemDocument10 pagesCircuit Note: Fully Isolated Conductivity Measurement Data Acquisition Systemnguyen thuanNo ratings yet
- 1.op Amp ParametersDocument4 pages1.op Amp ParametersPratik PasiyawalaNo ratings yet
- LicDocument26 pagesLicGopalakrishnan RenganathanNo ratings yet
- Development of A Basic Circuit of A Hot-Wire Anemometer: November 2004Document10 pagesDevelopment of A Basic Circuit of A Hot-Wire Anemometer: November 2004IkRretNopLeeDoNo ratings yet
- Circuit Analysis Study Guide - Cheat-SheetDocument11 pagesCircuit Analysis Study Guide - Cheat-SheetSimeonNo ratings yet
- National Amplifier LPF CalculatorDocument2 pagesNational Amplifier LPF CalculatorNieda NurNo ratings yet
- Ee and Ece Important MCQ PDF Op Amp Operational Amplifier 1www Allexamreview ComDocument6 pagesEe and Ece Important MCQ PDF Op Amp Operational Amplifier 1www Allexamreview ComFarmanNo ratings yet
- Introduction of CCD CircuitDocument37 pagesIntroduction of CCD CircuitAadityaNo ratings yet
- LdicDocument27 pagesLdicSri ChandanaNo ratings yet
- Logic UnitDocument43 pagesLogic UnitJuan Carvajal100% (1)
- Edc Lab Manuals Third SemesterDocument56 pagesEdc Lab Manuals Third SemesterSprout GigsNo ratings yet
Lab4 Completed
Lab4 Completed
Uploaded by
Khalid MalikOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lab4 Completed
Lab4 Completed
Uploaded by
Khalid MalikCopyright:
Available Formats
FACULTY OF ENGINEERING SCIENCES AND TECHNOLOGY
Hamdard Institute of Engineering & Technology
Hamdard University
Experiment No. 04
OBJECTIVE:
To design summing amplifier and differential amplifier using 741 Op-amp.
HARDWARE REQUIREMENTS:
• Op-amp 741
• Power Supply
• Oscilloscope
• Bread board
• Resistors
THEORY:
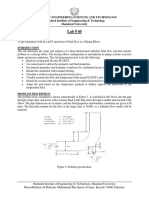
Summing Amplifier:
This is one of the linear applications of the Op-Amp. A circuit whose output is the sum of several
input signals is called a summer. In these circuits, the opposite end of the resistor is connected to
the inverting input is held at virtual ground by the feedback; therefore, adding new inputs does not
affect the response of the existing inputs. The equation for the given circuit can be written as:
Vo
Hamdard Institute of Engineering & Technology, Hamdard University
Shara e Madinat Al-Hikmah, Muhammad Bin Qasim Avenue, Karachi 74600, Pakistan.
FACULTY OF ENGINEERING SCIENCES AND TECHNOLOGY
Hamdard Institute of Engineering & Technology
Hamdard University
When Rf = R1 =R2, then
Vo = - (V1 + V2)
That is, the output is an inverted sum of the inputs.
An inverting amplifier can be modified to accommodate multiple input signals. Since the circuit is
linear, the output voltage can easily be found applying the superposition principle: The output
voltage is a weighted sum of the two input signals. The weighting factor is determined by applying
one of the input signals while the others are grounded, and analyzing the resulting circuit. Since
the circuit is linear, the analysis is repeated for all inputs and the final result is the addition of all
components. The advantage of this approach is that we can easily recognize the effect of each
signal on the circuit’s performance and the overall output can be obtained in most of the cases by
inspection. For the circuit shown below, the following equation results:
Vout = - (R3/R1 Vin1 + R3/R2 Vin2)
The summing amplifier can be extended to have any number of input signals. Consider that a two
bit digital signal is applied to the input in the above circuit. An analog voltage appears at the output
that is determined by the binary input. So a more general configuration based on this circuit can
be used to build digital-to-analog converters (DAC).
PROCEDURE:
1. Connect the relevant circuit for the summing configuration as shown in the circuit diagram.
2. Set the value of V1 and V2 to notice the output wave.
3. Note the reading of the output voltage Vo with respect to the input voltage.
4. Repeat the above steps by changing the values of two input voltages, and find the output voltage.
Hamdard Institute of Engineering & Technology, Hamdard University
Shara e Madinat Al-Hikmah, Muhammad Bin Qasim Avenue, Karachi 74600, Pakistan.
FACULTY OF ENGINEERING SCIENCES AND TECHNOLOGY
Hamdard Institute of Engineering & Technology
Hamdard University
S.No. Vin 1 Vin 2 Vout Theoretical Vout
1. 5 5.5 -11.118 105 v
2. 10 15 -11.118 250 v
3. 6 12 -11.118 180 v
1. Vout = Rf/R1 x v1 + Rf/R2 x v2
Vout = 30k/3k x 5 + 30k/3.3k x 5.5
Vout =105 v
2. Vout = Rf/R1 x v1 + Rf/R2 x v2
Vout = 30k/3k x 10 + 30k/3.3k x 15
Vout = 250 v
3. Vout = Rf/R1 x v1 + Rf/R2 x v2
Vout = 30k/3k x 6 + 30k/3.3k x 12
Vout = 180 v
Hamdard Institute of Engineering & Technology, Hamdard University
Shara e Madinat Al-Hikmah, Muhammad Bin Qasim Avenue, Karachi 74600, Pakistan.
FACULTY OF ENGINEERING SCIENCES AND TECHNOLOGY
Hamdard Institute of Engineering & Technology
Hamdard University
DIFFERENTIAL AMPLIFIER
The differential amplifiers amplify the difference between two voltages making this type of
operational amplifier circuit a Subtractor unlike a summing amplifier which adds or sums together
the input voltages. This type of operational amplifier circuit is commonly known as a Differential
Amplifier configuration. By connecting each input in turn to 0V ground we can use superposition
to solve for the output voltage Vout.
Hamdard Institute of Engineering & Technology, Hamdard University
Shara e Madinat Al-Hikmah, Muhammad Bin Qasim Avenue, Karachi 74600, Pakistan.
FACULTY OF ENGINEERING SCIENCES AND TECHNOLOGY
Hamdard Institute of Engineering & Technology
Hamdard University
When resistors, R1 = R2 and R3 = R4 the above transfer function for the differential amplifier can
be simplified to the following expression:
Vout = (R3/R2 xVin2 – ( R4/R1 xV1)
Vout (Vin2 – Vin1)
This expression shows that the amplifier amplifies the difference between the two input signals
Vin1 &Vin2 and rejects the common mode input signals; Vout = 0 if Vin1= Vin2. Therefore, the
differential amplifier is used in very noisy environment to reject common noise that appears at
both inputs. When the same signal is applied to both inputs, the voltage gain in this case is denoted
as common-mode gain ACM; for the case of the ideal differential amplifier ACM=0.
If all the resistors are all of the same ohmic value, that is: R1 = R2 = R3 = R4 then the circuit will
become a Unity Gain Differential Amplifier and the voltage gain of the amplifier will be exactly
one or unity. Then the output expression would simply be Vout = V2 - V1. Also note that if input
V1 is higher than input V2 the output voltage sum will be negative, and if V2 is higher than V1,
the output voltage sum will be positive.
The Differential Amplifier circuit is a very useful op-amp circuit and by adding more resistors in
parallel with the input resistors R1 and R3, the resultant circuit can be made to either “Add” or
“Subtract” the voltages applied to their respective inputs. One of the most common ways of doing
this is to connect a “Resistive Bridge” commonly called a Wheatstone bridge.
PROCEDURE:
1. Make the circuit for Differential amplifier as given.
2. Set the value of V1 and V2 to notice the output wave.
3. Note the reading of the output voltage Vo with respect to the input voltage.
4. Repeat the above steps by changing the values of two input voltages, and find the output voltage.
S.No. Vin 1 Vin 2 Vout Theoretical Vout
1. 12 16 8.003 v 8v
Hamdard Institute of Engineering & Technology, Hamdard University
Shara e Madinat Al-Hikmah, Muhammad Bin Qasim Avenue, Karachi 74600, Pakistan.
FACULTY OF ENGINEERING SCIENCES AND TECHNOLOGY
Hamdard Institute of Engineering & Technology
Hamdard University
2. 4 5 2.03 v 2v
3. 10 10 3.03 mv 0v
1. Vout = Rf/Ri(v2-v1)
Vout = 30K/15k(16-12)
Vout = 2(4)
Vout = 8 v
2. Vout = Rf/Ri(v2-v1)
Vout = 30K/15k(5-4)
Vout = 2(1)
Vout = 2 v
3. Vout = Rf/Ri(v2-v1)
Vout = 30K/15k(10-10)
Vout = 2(0)
Vout = 0 v
Hamdard Institute of Engineering & Technology, Hamdard University
Shara e Madinat Al-Hikmah, Muhammad Bin Qasim Avenue, Karachi 74600, Pakistan.
FACULTY OF ENGINEERING SCIENCES AND TECHNOLOGY
Hamdard Institute of Engineering & Technology
Hamdard University
Hamdard Institute of Engineering & Technology, Hamdard University
Shara e Madinat Al-Hikmah, Muhammad Bin Qasim Avenue, Karachi 74600, Pakistan.
FACULTY OF ENGINEERING SCIENCES AND TECHNOLOGY
Hamdard Institute of Engineering & Technology
Hamdard University
Hamdard Institute of Engineering & Technology, Hamdard University
Shara e Madinat Al-Hikmah, Muhammad Bin Qasim Avenue, Karachi 74600, Pakistan.
FACULTY OF ENGINEERING SCIENCES AND TECHNOLOGY
Hamdard Institute of Engineering & Technology
Hamdard University
Hamdard Institute of Engineering & Technology, Hamdard University
Shara e Madinat Al-Hikmah, Muhammad Bin Qasim Avenue, Karachi 74600, Pakistan.
FACULTY OF ENGINEERING SCIENCES AND TECHNOLOGY
Hamdard Institute of Engineering & Technology
Hamdard University
EXERCISE:
1. For the summing amplifier given below apply power supplies ±7V, choose R2 to have
Vout = − (Vin1 + 2Vin2) if R1 = R3 =10K.
For R2,
A2= 2 , R3=10K
A2 = R3/R2
2 = 10k/R2
R2 = 10k/2
R2 = 5k
Hamdard Institute of Engineering & Technology, Hamdard University
Shara e Madinat Al-Hikmah, Muhammad Bin Qasim Avenue, Karachi 74600, Pakistan.
FACULTY OF ENGINEERING SCIENCES AND TECHNOLOGY
Hamdard Institute of Engineering & Technology
Hamdard University
2. For the differential amplifier, with power supplies ±7V, choose R1 to have Vout = Vin2 −Vin1
if R2 = R3 = R4 = 10K.
Hamdard Institute of Engineering & Technology, Hamdard University
Shara e Madinat Al-Hikmah, Muhammad Bin Qasim Avenue, Karachi 74600, Pakistan.
FACULTY OF ENGINEERING SCIENCES AND TECHNOLOGY
Hamdard Institute of Engineering & Technology
Hamdard University
R1 = R2 = R3 = R4 = 10K.
Vout = Vin2 –Vin1
Vout = 10 – 5
Vout = 5 v
Hamdard Institute of Engineering & Technology, Hamdard University
Shara e Madinat Al-Hikmah, Muhammad Bin Qasim Avenue, Karachi 74600, Pakistan.
FACULTY OF ENGINEERING SCIENCES AND TECHNOLOGY
Hamdard Institute of Engineering & Technology
Hamdard University
3. State few biomedical applications of differential amplifiers.
Answer: The differential amplifier is used in a number of biomedical engineering applications,
specifically to amplify signals from biotransducers and bio amplifier that produce a differential
output.
Hamdard Institute of Engineering & Technology, Hamdard University
Shara e Madinat Al-Hikmah, Muhammad Bin Qasim Avenue, Karachi 74600, Pakistan.
You might also like
- Gabriel Rincon-Mora-Analog IC Design With Low-Dropout Regulators (LDOs) (Electronic Engineering) (2009) PDFDocument373 pagesGabriel Rincon-Mora-Analog IC Design With Low-Dropout Regulators (LDOs) (Electronic Engineering) (2009) PDFNguyen HaNo ratings yet
- Smart Street Lighting System - Project ReportDocument8 pagesSmart Street Lighting System - Project Reportअनिमेष ठाकुर91% (33)
- Automated Broad and Narrow Band Impedance Matching for RF and Microwave CircuitsFrom EverandAutomated Broad and Narrow Band Impedance Matching for RF and Microwave CircuitsNo ratings yet
- Lab2 CompletedDocument14 pagesLab2 CompletedKhalid MalikNo ratings yet
- Lab5 CompletedDocument8 pagesLab5 CompletedKhalid MalikNo ratings yet
- Lab3 CompletedDocument16 pagesLab3 CompletedKhalid MalikNo ratings yet
- T F W R: O Design AND Simulate A ULL AVE Ectifier CircuitDocument4 pagesT F W R: O Design AND Simulate A ULL AVE Ectifier CircuitJunaid NazirNo ratings yet
- Ena Lab 2Document6 pagesEna Lab 2Halar MustafaNo ratings yet
- Ena Lab 4Document5 pagesEna Lab 4Halar MustafaNo ratings yet
- Lab 12 Basic ElectronicsDocument7 pagesLab 12 Basic ElectronicsMansoor AliNo ratings yet
- Design and Analysis of A Differential Di PDFDocument32 pagesDesign and Analysis of A Differential Di PDFbiboNo ratings yet
- Load Flow Analysis For A Given Network Using ETAPDocument4 pagesLoad Flow Analysis For A Given Network Using ETAPAkhter IqbalNo ratings yet
- Expt 7, Comparator (Updated)Document3 pagesExpt 7, Comparator (Updated)Danish MujibNo ratings yet
- Expt 7, Comparator (Updated)Document3 pagesExpt 7, Comparator (Updated)Danish MujibNo ratings yet
- Analog Electronics SampleDocument17 pagesAnalog Electronics SampleManoj1508AravindNo ratings yet
- Date: Page No.: Miracle Educational Society Group of InstitutionsDocument6 pagesDate: Page No.: Miracle Educational Society Group of Institutionsphani srinivasNo ratings yet
- Ena Lab 10Document4 pagesEna Lab 10Halar MustafaNo ratings yet
- Analog Electronics GATE IES PSU Study Materials PDFDocument17 pagesAnalog Electronics GATE IES PSU Study Materials PDFDharmveer SinghNo ratings yet
- MOSFET As An AMPLIFIERDocument16 pagesMOSFET As An AMPLIFIERJohnny Edward KingsleyNo ratings yet
- Industry Report Deee 5th Sem 2022-2023 Sachin New1Document31 pagesIndustry Report Deee 5th Sem 2022-2023 Sachin New1Rathod SachinNo ratings yet
- Time Current Characteristics of Over-Current Relay Suing ETAPDocument8 pagesTime Current Characteristics of Over-Current Relay Suing ETAPAkhter IqbalNo ratings yet
- Time Current Characteristics of Fuse Using ETAPDocument7 pagesTime Current Characteristics of Fuse Using ETAPAkhter IqbalNo ratings yet
- GR15 PDFDocument41 pagesGR15 PDFomkar maitreeNo ratings yet
- Short Circuit Analysis For A Given Network Using ETAPDocument4 pagesShort Circuit Analysis For A Given Network Using ETAPAkhter Iqbal100% (1)
- Lecture # 08 - Power Supply-Full Wave RectifierDocument14 pagesLecture # 08 - Power Supply-Full Wave Rectifiersaadkhanak9No ratings yet
- Open-Ended InverterDocument2 pagesOpen-Ended InverterAkhter IqbalNo ratings yet
- RC Phase Shift Oscillator 230510 - 195846Document32 pagesRC Phase Shift Oscillator 230510 - 195846Pranav msNo ratings yet
- College of Technology and Engineering: Training Report of "132kV Grid Sub-Station, Sukher"Document24 pagesCollege of Technology and Engineering: Training Report of "132kV Grid Sub-Station, Sukher"Harish MahlaNo ratings yet
- PDC Lab ManualDocument68 pagesPDC Lab Manualnama varapuNo ratings yet
- Einstein: College of EngineeringDocument80 pagesEinstein: College of EngineeringPoonkothaiMyilNo ratings yet
- CH3 - Diode Rectifiers DesignDocument24 pagesCH3 - Diode Rectifiers DesignSaid Ahmed AliNo ratings yet
- Ic Applications Lab Manual: Iii Btech, Ece-Ist SemesterDocument59 pagesIc Applications Lab Manual: Iii Btech, Ece-Ist SemesterAkshay PabbathiNo ratings yet
- Design of RF To DC Rectifier at GSM Band For EnergyDocument9 pagesDesign of RF To DC Rectifier at GSM Band For EnergyAchmad ShodikinNo ratings yet
- Lecture # 07 - Power Supply-Half Wave RectifierDocument22 pagesLecture # 07 - Power Supply-Half Wave Rectifiersaadkhanak9No ratings yet
- Final ESD Lab ManualDocument28 pagesFinal ESD Lab ManualVincent Padi AshieNo ratings yet
- Ac To DC Converter Project Report PDFDocument75 pagesAc To DC Converter Project Report PDFVishal Bhadalda100% (1)
- Ac To DC Converter Project ReportDocument75 pagesAc To DC Converter Project ReportPranav Tripathi79% (14)
- Batch 1 Beemp.Document13 pagesBatch 1 Beemp.22h51a6608No ratings yet
- LIC Lab ManualDocument57 pagesLIC Lab ManualsfundsNo ratings yet
- EPC BEC303 List of ExpsDocument51 pagesEPC BEC303 List of Expskaranphutane2254No ratings yet
- b13 Forced Commutation Using ArduinoDocument62 pagesb13 Forced Commutation Using ArduinoAlexandru Stefan AndriesNo ratings yet
- AUPEC 2020 Shuvra FinalDocument7 pagesAUPEC 2020 Shuvra FinalAK KhanNo ratings yet
- MTPA and Field Weakening Control of Synchronous Reluctance MotorDocument5 pagesMTPA and Field Weakening Control of Synchronous Reluctance MotorIVAN FELIPE BERNAL GOMEZNo ratings yet
- Matlab-Dc Motor1Document21 pagesMatlab-Dc Motor1Krishna SaraswatNo ratings yet
- Research Paper Improvement of Power System Stability by Simultaneous AC-DC Power TransmissionDocument6 pagesResearch Paper Improvement of Power System Stability by Simultaneous AC-DC Power Transmissionmaazsiddiqui.ee7193No ratings yet
- Be8261 BeeieDocument82 pagesBe8261 BeeieMohammed OvaizNo ratings yet
- IC Lab MaualDocument59 pagesIC Lab MaualKumar Goud.K100% (2)
- Performance Analysis of A High Voltage DC (HVDC) Transmission System Under Steady State and Faulted ConditionsDocument8 pagesPerformance Analysis of A High Voltage DC (HVDC) Transmission System Under Steady State and Faulted ConditionsrichatNo ratings yet
- IJAPE Guideforauthors 2012Document5 pagesIJAPE Guideforauthors 2012Ashish PorwalNo ratings yet
- EC2403 RF and Microwave EngineeringDocument152 pagesEC2403 RF and Microwave EngineeringKushal MpvsNo ratings yet
- Design and Implementation of Cascaded H Bridge Multilevel Inverter Using Digital Control Schemes IJERTV6IS050317Document4 pagesDesign and Implementation of Cascaded H Bridge Multilevel Inverter Using Digital Control Schemes IJERTV6IS050317Sateesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Wave Shaping Square, Triangular and Saw ToothDocument16 pagesWave Shaping Square, Triangular and Saw ToothKiranpreet SinghNo ratings yet
- Lab 3 Rectifiers and FiltersDocument6 pagesLab 3 Rectifiers and FiltersAlisha AasNo ratings yet
- EE6311 LIC Lab - VidyarthiplusDocument66 pagesEE6311 LIC Lab - VidyarthiplusArun KumarNo ratings yet
- Ed ManualDocument66 pagesEd ManualshilpaNo ratings yet
- IC HDL Lab ManualDocument82 pagesIC HDL Lab ManualRakshitha AngelNo ratings yet
- Ps Exp 1 PDFDocument6 pagesPs Exp 1 PDFrv_andeNo ratings yet
- Electronic Circuits LatestDocument69 pagesElectronic Circuits LatestSai SadiqNo ratings yet
- LIC Lab ManualDocument79 pagesLIC Lab ManualSakthikumar Balasundaram67% (3)
- Network ProjectDocument12 pagesNetwork ProjectAyush SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- Lab 1Document7 pagesLab 1Khalid MalikNo ratings yet
- LAB TasksDocument2 pagesLAB TasksKhalid MalikNo ratings yet
- Lab 8Document5 pagesLab 8Khalid MalikNo ratings yet
- Lab - 7Document5 pagesLab - 7Khalid MalikNo ratings yet
- Lab - 9Document4 pagesLab - 9Khalid MalikNo ratings yet
- Lab - 4Document5 pagesLab - 4Khalid MalikNo ratings yet
- Lab - 5Document8 pagesLab - 5Khalid MalikNo ratings yet
- Lab - 2Document7 pagesLab - 2Khalid MalikNo ratings yet
- Lab - 3Document3 pagesLab - 3Khalid MalikNo ratings yet
- Lab - 6Document7 pagesLab - 6Khalid MalikNo ratings yet
- Lab 5Document19 pagesLab 5Khalid MalikNo ratings yet
- Kannur University B Tech s5 SyllubusDocument6 pagesKannur University B Tech s5 SyllubusappurajkvNo ratings yet
- Dcs Lab Manual 2018 191 PDFDocument37 pagesDcs Lab Manual 2018 191 PDFbala_athmaNo ratings yet
- 1000 Electronic Devices & Circuits MCQsDocument467 pages1000 Electronic Devices & Circuits MCQskibrom atsbha67% (3)
- Electrical and Electronic EngineeringDocument34 pagesElectrical and Electronic EngineeringANo ratings yet
- Excel Review Center - Manila Ece Review For October 2019 Board Exam Refresher Exam - ElecDocument4 pagesExcel Review Center - Manila Ece Review For October 2019 Board Exam Refresher Exam - ElecTintin DalatenNo ratings yet
- B 115 BDocument121 pagesB 115 BPetrica Dan DinuNo ratings yet
- 741b PDFDocument11 pages741b PDFrrr2013No ratings yet
- Aic Unit 3Document96 pagesAic Unit 3SYETC156HARSHAL RAHENWALNo ratings yet
- Design SolutionDocument5 pagesDesign SolutionsubbuNo ratings yet
- Sony Xm-255exDocument14 pagesSony Xm-255exsamuel ancesquiNo ratings yet
- Datasheet PDFDocument7 pagesDatasheet PDFVNo ratings yet
- Syllabus 1st YearDocument23 pagesSyllabus 1st YearS.m. ChandrashekarNo ratings yet
- 45 Watt ClassDocument5 pages45 Watt Classfirmansyah miraddanaNo ratings yet
- Listening BugDocument1 pageListening BugDiksha Tulsi67% (3)
- Op-Amp Based Static Over Current RelayDocument6 pagesOp-Amp Based Static Over Current RelayS Bharadwaj ReddyNo ratings yet
- X Building A Microcontroller Based PotentiostatDocument15 pagesX Building A Microcontroller Based PotentiostatJesús Munayco FloresNo ratings yet
- S5 SyllabusDocument75 pagesS5 SyllabusAnjali S KumarNo ratings yet
- Circuit Note: Fully Isolated Conductivity Measurement Data Acquisition SystemDocument10 pagesCircuit Note: Fully Isolated Conductivity Measurement Data Acquisition Systemnguyen thuanNo ratings yet
- 1.op Amp ParametersDocument4 pages1.op Amp ParametersPratik PasiyawalaNo ratings yet
- LicDocument26 pagesLicGopalakrishnan RenganathanNo ratings yet
- Development of A Basic Circuit of A Hot-Wire Anemometer: November 2004Document10 pagesDevelopment of A Basic Circuit of A Hot-Wire Anemometer: November 2004IkRretNopLeeDoNo ratings yet
- Circuit Analysis Study Guide - Cheat-SheetDocument11 pagesCircuit Analysis Study Guide - Cheat-SheetSimeonNo ratings yet
- National Amplifier LPF CalculatorDocument2 pagesNational Amplifier LPF CalculatorNieda NurNo ratings yet
- Ee and Ece Important MCQ PDF Op Amp Operational Amplifier 1www Allexamreview ComDocument6 pagesEe and Ece Important MCQ PDF Op Amp Operational Amplifier 1www Allexamreview ComFarmanNo ratings yet
- Introduction of CCD CircuitDocument37 pagesIntroduction of CCD CircuitAadityaNo ratings yet
- LdicDocument27 pagesLdicSri ChandanaNo ratings yet
- Logic UnitDocument43 pagesLogic UnitJuan Carvajal100% (1)
- Edc Lab Manuals Third SemesterDocument56 pagesEdc Lab Manuals Third SemesterSprout GigsNo ratings yet