Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 viewsGR 8 Chemistry (040820)
GR 8 Chemistry (040820)
Uploaded by
Keshia KatarinaRespiration is the process by which living things obtain energy from food. During respiration, glucose reacts with oxygen to release energy, which is used for life processes. Respiration is similar to burning in that it requires oxygen, produces carbon dioxide, and releases energy, but does not cause flames like burning fuel. Oxidation is the reaction of a substance with oxygen, such as the oxidation of carbon in glucose to carbon dioxide during respiration, or the oxidation of iron that causes rust.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Oxidation-Reduction Write UpDocument4 pagesOxidation-Reduction Write Upre5teNo ratings yet
- Subtopic: Oxidation Objectives: - Identify and Justify Oxidation As Exothermic ReactionDocument10 pagesSubtopic: Oxidation Objectives: - Identify and Justify Oxidation As Exothermic ReactionChalise SupremeNo ratings yet
- Subtopic: Oxidation Objectives: - Identify and Justify Oxidation As Exothermic ReactionDocument10 pagesSubtopic: Oxidation Objectives: - Identify and Justify Oxidation As Exothermic ReactionChalise SupremeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8Document14 pagesChapter 8wallacec1017No ratings yet
- 8E ChemistryDocument56 pages8E ChemistryNazNo ratings yet
- Name: Doaa Nassar Grade: 9B Teacher's Name: Ms. AfshariDocument35 pagesName: Doaa Nassar Grade: 9B Teacher's Name: Ms. AfshariDoaa NassarNo ratings yet
- Chem. - F8term 2 Chem 2019Document40 pagesChem. - F8term 2 Chem 2019Lobna ShabanNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions and Equations - Docx NotesDocument9 pagesChemical Reactions and Equations - Docx NotesRodel AzaresNo ratings yet
- Apuntes Sicence Tema 8Document4 pagesApuntes Sicence Tema 8larafernandezveloso10No ratings yet
- Notes - Types of Chemical ReactionsDocument3 pagesNotes - Types of Chemical ReactionsJayasutha RamanNo ratings yet
- Term - I I: Name: Grade: Viii (Igcse)Document23 pagesTerm - I I: Name: Grade: Viii (Igcse)AnonymusNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 File 1 PDFDocument7 pagesChapter 1 File 1 PDFAadi ProNo ratings yet
- Chemistry in Everyday LifeDocument18 pagesChemistry in Everyday LifeAjay A.RNo ratings yet
- G8 Chem Unit 8 NotesDocument7 pagesG8 Chem Unit 8 NotesHUDA FATHIMA 2031826No ratings yet
- Energy Changes-2Document12 pagesEnergy Changes-2Suresh ReddyNo ratings yet
- Unit - 8.1, 8.2Document27 pagesUnit - 8.1, 8.2trax.rahmanNo ratings yet
- The Similarities and Differences Between Oxidation and ThermalDocument4 pagesThe Similarities and Differences Between Oxidation and Thermaltamagucci3529No ratings yet
- Chemistry Thursday NotesDocument2 pagesChemistry Thursday Notesshaswatsathyamoorthy19No ratings yet
- Unit 4Document13 pagesUnit 4musa shahidNo ratings yet
- 5.1 Physical and Chemical ChangesDocument17 pages5.1 Physical and Chemical ChangesElly EllynaNo ratings yet
- Oxidation Grade7Document12 pagesOxidation Grade7saniaNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument4 pagesChemistryRahaf MohammedNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Rates of ReactionDocument3 pagesChemistry Rates of Reactionheyy0.0No ratings yet
- SHPS Respiratory System 6Document1 pageSHPS Respiratory System 6Nah Li ChuanNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Chemical Reactions NotesDocument12 pagesClass 10 Chemical Reactions NotesShreyash VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- (Short Revision Notes) : ChemistryDocument7 pages(Short Revision Notes) : ChemistryApoorv ChauhanNo ratings yet
- RBSE Class 8 Science Notes Chapter 4 Chemical Reactions - RBSE GuideDocument3 pagesRBSE Class 8 Science Notes Chapter 4 Chemical Reactions - RBSE GuideAlpine AcademiaNo ratings yet
- Effects of Oxidation in Everyday LifeDocument8 pagesEffects of Oxidation in Everyday LifeNur Masyittah IrmiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations CBSE Notes For Class 10 Science Chemistry Download in PDFDocument9 pagesChapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations CBSE Notes For Class 10 Science Chemistry Download in PDFNaved ShaikhNo ratings yet
- 7.3 Chemical ReactionsDocument39 pages7.3 Chemical Reactionsevnhooi2625No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and EquationsDocument12 pagesChapter 1 Chemical Reactions and EquationsPrabhuPalanichamyNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Chemistry Oxygen Hydrogen and Carbon DioxideDocument15 pagesIGCSE Chemistry Oxygen Hydrogen and Carbon DioxideS M AkashNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions Mastery BookletDocument22 pagesChemical Reactions Mastery Bookletapi-422428700No ratings yet
- Combustion: Flames Fuel Exothermic Fuel Oxidant Heat Light Flames Radical Thermal RunawayDocument7 pagesCombustion: Flames Fuel Exothermic Fuel Oxidant Heat Light Flames Radical Thermal RunawayVel MuruganNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Energy and Chemical Changes Form 4Document29 pagesChapter 5 Energy and Chemical Changes Form 4mydqueNo ratings yet
- The Air, Oxygen, and Co2Document9 pagesThe Air, Oxygen, and Co2osmantayfunsel2008No ratings yet
- 2324 T2 Chemistry C4 Chemical ReactionsDocument66 pages2324 T2 Chemistry C4 Chemical ReactionswilsonconcepcionNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions Year 8Document7 pagesChemical Reactions Year 8christalNo ratings yet
- Krish (Notes) : Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and EquationsDocument20 pagesKrish (Notes) : Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and EquationsVivek saklaniNo ratings yet
- Fire Protection and Arson InvestigationDocument16 pagesFire Protection and Arson InvestigationBenhur malok MangindalatNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and EquationsDocument10 pagesChapter 1 Chemical Reactions and EquationsShabnam GolaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions 1Document28 pagesChemical Reactions 1clouieenriquez07No ratings yet
- Material Changes (Unit 9.1-9.3)Document17 pagesMaterial Changes (Unit 9.1-9.3)Arin RahmanNo ratings yet
- Materialchanges 1Document21 pagesMaterialchanges 1I Am Gone CrazyNo ratings yet
- Sci. 411 Chemical Reactions Edleen AquinoDocument26 pagesSci. 411 Chemical Reactions Edleen Aquinojoebane capapas jr.No ratings yet
- Changes in MatterDocument23 pagesChanges in MatterKaryll ColumnaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions and EquationsDocument5 pagesChemical Reactions and EquationsSupriya SanjeevaNo ratings yet
- Chemical ReactionsDocument30 pagesChemical ReactionsIftikhar Hussain RizviNo ratings yet
- Chemical ReactionDocument28 pagesChemical Reactionmariajessicaarce1212No ratings yet
- accurate note Chemical Reactions & EquationsDocument5 pagesaccurate note Chemical Reactions & EquationsCuzco CuckooNo ratings yet
- Mixtures and Solutions: Fizz Quiz 3-1 Chemical Reactions Vocabulary and ContentDocument7 pagesMixtures and Solutions: Fizz Quiz 3-1 Chemical Reactions Vocabulary and ContentMrsNguyen95014No ratings yet
- Prepared By: Lee Hock TiangDocument27 pagesPrepared By: Lee Hock TiangNick LeeNo ratings yet
- Class VIII Chemical Changes Day 2Document15 pagesClass VIII Chemical Changes Day 2Edu TainmentNo ratings yet
- Chapter - Chemical Reactions and Equations (PART - 3) : by - Tejashwini C KDocument8 pagesChapter - Chemical Reactions and Equations (PART - 3) : by - Tejashwini C KTejashwini CkNo ratings yet
- All About Exothermic ReactionDocument11 pagesAll About Exothermic ReactionAkshay IndoraNo ratings yet
- Final Research (Hady)Document6 pagesFinal Research (Hady)Hady SalehNo ratings yet
- Simple Chemical Reactions Class 7.Document19 pagesSimple Chemical Reactions Class 7.ZUNI100% (4)
- 99998324Document7 pages99998324Ashish Urff ĐãkšhNo ratings yet
- Combustion and Flame 8thDocument13 pagesCombustion and Flame 8thPratibha GuptaNo ratings yet
- Physical and Chemical Reactions : 6th Grade Chemistry Book | Children's Chemistry BooksFrom EverandPhysical and Chemical Reactions : 6th Grade Chemistry Book | Children's Chemistry BooksNo ratings yet
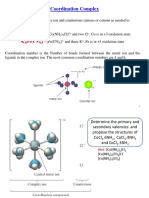
- Coordination Chem 1 PDFDocument10 pagesCoordination Chem 1 PDFSundar SinghNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 5 TREATMENT METHODS FOR RURAL WATER SUPPLYDocument9 pagesChapter - 5 TREATMENT METHODS FOR RURAL WATER SUPPLYdawana samuelNo ratings yet
- Mixing The Warm Cool Palette Anna WakitschDocument8 pagesMixing The Warm Cool Palette Anna WakitschAlison De Sando ManzoniNo ratings yet
- Catalytic Asymmetric Synthesis of Cannabinoids and Menthol From NeralDocument7 pagesCatalytic Asymmetric Synthesis of Cannabinoids and Menthol From NeralSamir SahaNo ratings yet
- Mineral Processing Introduction 1Document57 pagesMineral Processing Introduction 1tatek.anberbirNo ratings yet
- Solar-Riat, US Highway 190 West, Killeen, TX 76541, USADocument13 pagesSolar-Riat, US Highway 190 West, Killeen, TX 76541, USAShafira RiskinaNo ratings yet
- The Empty Palm Oil Fruit Bunch As The Potential SoDocument7 pagesThe Empty Palm Oil Fruit Bunch As The Potential SoTOMMY LEENo ratings yet
- Experiment To Study The Exothermic and Endothermic ReactionsDocument12 pagesExperiment To Study The Exothermic and Endothermic ReactionsAzneezal Ar-Rashid100% (2)
- Chemistry 14A AnswersDocument8 pagesChemistry 14A AnswersJong.Gun.KimNo ratings yet
- STS Detailed OutlineDocument11 pagesSTS Detailed OutlineCHARLES KEVIN MINANo ratings yet
- Extraction and Uses of Metals 1 QP PDFDocument12 pagesExtraction and Uses of Metals 1 QP PDFAngus AnizNo ratings yet
- Plastic Waste Management PDFDocument59 pagesPlastic Waste Management PDFAnonymous HOI7owj9ONo ratings yet
- Catalytic Hydrogenation by Using Raney NickelDocument5 pagesCatalytic Hydrogenation by Using Raney NickelSampotterNo ratings yet
- Electrical Characterization and Poole-Frenkel Effect in Sol-Gel Derived Zno:Al Thin FilmsDocument11 pagesElectrical Characterization and Poole-Frenkel Effect in Sol-Gel Derived Zno:Al Thin Filmsचन्द्रभाल सिंहNo ratings yet
- EDTA METHOD (Sulphate)Document2 pagesEDTA METHOD (Sulphate)Bhinitha Chandrasagaran100% (1)
- Salt Analysis (XIII)Document12 pagesSalt Analysis (XIII)Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- Amperometric Titration - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument2 pagesAmperometric Titration - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaQaisar NadeemNo ratings yet
- Explosives and Pyrotechnic Propellants For Use In: Long Term Deep Space MissionsDocument31 pagesExplosives and Pyrotechnic Propellants For Use In: Long Term Deep Space MissionsbisuNo ratings yet
- TRANSITION ELEMENTS (D-Block Elements)Document2 pagesTRANSITION ELEMENTS (D-Block Elements)Manoj YadavNo ratings yet
- Caffeine Determination by HPLCDocument3 pagesCaffeine Determination by HPLCnga_yan0% (1)
- 1 Chapter.2 Mole Concept: Practice Questions: WWW - Shenischool.inDocument3 pages1 Chapter.2 Mole Concept: Practice Questions: WWW - Shenischool.inGuru DeepNo ratings yet
- Matter WorksheetDocument4 pagesMatter WorksheetShikha AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Process Synthesis and Analysis of Green Plastic Monomer Production From CelluloseDocument8 pagesProcess Synthesis and Analysis of Green Plastic Monomer Production From CelluloseMaycon PaimNo ratings yet
- Report in Technical Analysis CEMENTDocument26 pagesReport in Technical Analysis CEMENTNatrium KirchhoffNo ratings yet
- StoichiometryDocument17 pagesStoichiometryGianna BaldoradoNo ratings yet
- Mackintosh Paper PDFDocument4 pagesMackintosh Paper PDFheheNo ratings yet
- Semana 02 O - Portland, Blended and Other Hydraulic Cement C - PCA Chapter 3 PDFDocument38 pagesSemana 02 O - Portland, Blended and Other Hydraulic Cement C - PCA Chapter 3 PDFBrandon PonteNo ratings yet
- The Complete Book On Emulsifiers With Uses Formulae and Processes - 2nd Revised EditionDocument46 pagesThe Complete Book On Emulsifiers With Uses Formulae and Processes - 2nd Revised EditionBILAL AMJADNo ratings yet
- Melamine Tehnical SheetDocument2 pagesMelamine Tehnical SheetlyesNo ratings yet
GR 8 Chemistry (040820)
GR 8 Chemistry (040820)
Uploaded by
Keshia Katarina0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views8 pagesRespiration is the process by which living things obtain energy from food. During respiration, glucose reacts with oxygen to release energy, which is used for life processes. Respiration is similar to burning in that it requires oxygen, produces carbon dioxide, and releases energy, but does not cause flames like burning fuel. Oxidation is the reaction of a substance with oxygen, such as the oxidation of carbon in glucose to carbon dioxide during respiration, or the oxidation of iron that causes rust.
Original Description:
Original Title
Gr 8 Chemistry (040820)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentRespiration is the process by which living things obtain energy from food. During respiration, glucose reacts with oxygen to release energy, which is used for life processes. Respiration is similar to burning in that it requires oxygen, produces carbon dioxide, and releases energy, but does not cause flames like burning fuel. Oxidation is the reaction of a substance with oxygen, such as the oxidation of carbon in glucose to carbon dioxide during respiration, or the oxidation of iron that causes rust.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views8 pagesGR 8 Chemistry (040820)
GR 8 Chemistry (040820)
Uploaded by
Keshia KatarinaRespiration is the process by which living things obtain energy from food. During respiration, glucose reacts with oxygen to release energy, which is used for life processes. Respiration is similar to burning in that it requires oxygen, produces carbon dioxide, and releases energy, but does not cause flames like burning fuel. Oxidation is the reaction of a substance with oxygen, such as the oxidation of carbon in glucose to carbon dioxide during respiration, or the oxidation of iron that causes rust.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 8
5.
2 More exothermic reactions
Respiration
• All life processes require energy.
Living things obtain their energy
from their food. The process in
which energy is released from food
is called respiration. In this process
a food substance called glucose
reacts with oxygen. The word
equation for this reaction is:
• The energy released in respiration
is used to make substances inside
the body and to make a body
move. Some of the energy is
released as heat.
3
22. Is food fuel? Explain your answer.
○ Yes – it contains energy which is released
in respiration for use in life processes.
4
23. Is respiration like burning?
Explain your answer.
○ In some ways – it requires oxygen,
produces carbon dioxide and release
energy. Both reactions produce some
heat from a fuel, but in respiration the fuel
does not burst into flames
Oxidation
• When a substance burns in air reacts with oxygen. This is called an
oxidation reaction. Oxygen combines with elements in the substance to
form a compound. In the examples in this chapter, incomplete combustion
causes carbon in a fuel to be oxidized to carbon monoxide. Complete
combustion results in carbon being oxidized to carbon dioxide. Oxidation
also occurs in respiration where the carbon in glucose is oxidized to carbon
dioxide.
• Rusting is another example of oxidation. When water vapour from the air
condenses on iron or steel it forms a film on the surface of the metal.
Oxygen dissolves in the water and reacts with the metal to form iron oxide.
This forms brown flakes of rust, which break off from the surface and
expose more metal to the oxygen dissolved in the water. The iron or steel
continues to produce rust until it has completely corroded. The word
equation for the reaction is:
Hand warmers and rusting
• Rusting is an exothermic reaction but as the reaction is slow the heat is
produced in small amounts and quickly spread into the air so that a rusting
object does not feel warm. Useful heat can be produced from rusting in the
design of some kinds of hand warmers. Iron powder is mixed with particles
of charcoal (carbon), salt water and an insulating substance such as
vermiculite. All these constituents of the hand warmer are enclosed in a
sealed airtight package. When the hand warmer is required the seal broken
and air mixes and the constituents, so that an oxidation reaction takes
place between the iron powder and oxygen. The salt water acts as catalyst
and speeds up the reaction so a large quantity of heat can be produced
quickly. The carbon particles take up the heat and spread it out through the
package, while the insulating material prevents it escaping too quickly so
that a smaller amount of heat is released steadily to warm the hands.
Reaction of metals with water
• Metal + water metal hydroxide + hydrogen
• Potassium + water potassium hydroxide + hydrogen
Reaction of metals with acid
• Metal + hydrochloric acid metal chloride + hydrogen
• Magnesium + hydrochloric acid magnesium chloride + hydrogen
• Metal + sulfuric acid metal sulfate + hydrogen
• Potassium + sulfuric acid potassium sulfate + hydrogen
• Metal + nitric acid metal nitrate + hydrogen
• Sodium + nitric acid sodium nitrate + hydrogen
You might also like
- Oxidation-Reduction Write UpDocument4 pagesOxidation-Reduction Write Upre5teNo ratings yet
- Subtopic: Oxidation Objectives: - Identify and Justify Oxidation As Exothermic ReactionDocument10 pagesSubtopic: Oxidation Objectives: - Identify and Justify Oxidation As Exothermic ReactionChalise SupremeNo ratings yet
- Subtopic: Oxidation Objectives: - Identify and Justify Oxidation As Exothermic ReactionDocument10 pagesSubtopic: Oxidation Objectives: - Identify and Justify Oxidation As Exothermic ReactionChalise SupremeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8Document14 pagesChapter 8wallacec1017No ratings yet
- 8E ChemistryDocument56 pages8E ChemistryNazNo ratings yet
- Name: Doaa Nassar Grade: 9B Teacher's Name: Ms. AfshariDocument35 pagesName: Doaa Nassar Grade: 9B Teacher's Name: Ms. AfshariDoaa NassarNo ratings yet
- Chem. - F8term 2 Chem 2019Document40 pagesChem. - F8term 2 Chem 2019Lobna ShabanNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions and Equations - Docx NotesDocument9 pagesChemical Reactions and Equations - Docx NotesRodel AzaresNo ratings yet
- Apuntes Sicence Tema 8Document4 pagesApuntes Sicence Tema 8larafernandezveloso10No ratings yet
- Notes - Types of Chemical ReactionsDocument3 pagesNotes - Types of Chemical ReactionsJayasutha RamanNo ratings yet
- Term - I I: Name: Grade: Viii (Igcse)Document23 pagesTerm - I I: Name: Grade: Viii (Igcse)AnonymusNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 File 1 PDFDocument7 pagesChapter 1 File 1 PDFAadi ProNo ratings yet
- Chemistry in Everyday LifeDocument18 pagesChemistry in Everyday LifeAjay A.RNo ratings yet
- G8 Chem Unit 8 NotesDocument7 pagesG8 Chem Unit 8 NotesHUDA FATHIMA 2031826No ratings yet
- Energy Changes-2Document12 pagesEnergy Changes-2Suresh ReddyNo ratings yet
- Unit - 8.1, 8.2Document27 pagesUnit - 8.1, 8.2trax.rahmanNo ratings yet
- The Similarities and Differences Between Oxidation and ThermalDocument4 pagesThe Similarities and Differences Between Oxidation and Thermaltamagucci3529No ratings yet
- Chemistry Thursday NotesDocument2 pagesChemistry Thursday Notesshaswatsathyamoorthy19No ratings yet
- Unit 4Document13 pagesUnit 4musa shahidNo ratings yet
- 5.1 Physical and Chemical ChangesDocument17 pages5.1 Physical and Chemical ChangesElly EllynaNo ratings yet
- Oxidation Grade7Document12 pagesOxidation Grade7saniaNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument4 pagesChemistryRahaf MohammedNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Rates of ReactionDocument3 pagesChemistry Rates of Reactionheyy0.0No ratings yet
- SHPS Respiratory System 6Document1 pageSHPS Respiratory System 6Nah Li ChuanNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Chemical Reactions NotesDocument12 pagesClass 10 Chemical Reactions NotesShreyash VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- (Short Revision Notes) : ChemistryDocument7 pages(Short Revision Notes) : ChemistryApoorv ChauhanNo ratings yet
- RBSE Class 8 Science Notes Chapter 4 Chemical Reactions - RBSE GuideDocument3 pagesRBSE Class 8 Science Notes Chapter 4 Chemical Reactions - RBSE GuideAlpine AcademiaNo ratings yet
- Effects of Oxidation in Everyday LifeDocument8 pagesEffects of Oxidation in Everyday LifeNur Masyittah IrmiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations CBSE Notes For Class 10 Science Chemistry Download in PDFDocument9 pagesChapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations CBSE Notes For Class 10 Science Chemistry Download in PDFNaved ShaikhNo ratings yet
- 7.3 Chemical ReactionsDocument39 pages7.3 Chemical Reactionsevnhooi2625No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and EquationsDocument12 pagesChapter 1 Chemical Reactions and EquationsPrabhuPalanichamyNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Chemistry Oxygen Hydrogen and Carbon DioxideDocument15 pagesIGCSE Chemistry Oxygen Hydrogen and Carbon DioxideS M AkashNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions Mastery BookletDocument22 pagesChemical Reactions Mastery Bookletapi-422428700No ratings yet
- Combustion: Flames Fuel Exothermic Fuel Oxidant Heat Light Flames Radical Thermal RunawayDocument7 pagesCombustion: Flames Fuel Exothermic Fuel Oxidant Heat Light Flames Radical Thermal RunawayVel MuruganNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Energy and Chemical Changes Form 4Document29 pagesChapter 5 Energy and Chemical Changes Form 4mydqueNo ratings yet
- The Air, Oxygen, and Co2Document9 pagesThe Air, Oxygen, and Co2osmantayfunsel2008No ratings yet
- 2324 T2 Chemistry C4 Chemical ReactionsDocument66 pages2324 T2 Chemistry C4 Chemical ReactionswilsonconcepcionNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions Year 8Document7 pagesChemical Reactions Year 8christalNo ratings yet
- Krish (Notes) : Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and EquationsDocument20 pagesKrish (Notes) : Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and EquationsVivek saklaniNo ratings yet
- Fire Protection and Arson InvestigationDocument16 pagesFire Protection and Arson InvestigationBenhur malok MangindalatNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and EquationsDocument10 pagesChapter 1 Chemical Reactions and EquationsShabnam GolaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions 1Document28 pagesChemical Reactions 1clouieenriquez07No ratings yet
- Material Changes (Unit 9.1-9.3)Document17 pagesMaterial Changes (Unit 9.1-9.3)Arin RahmanNo ratings yet
- Materialchanges 1Document21 pagesMaterialchanges 1I Am Gone CrazyNo ratings yet
- Sci. 411 Chemical Reactions Edleen AquinoDocument26 pagesSci. 411 Chemical Reactions Edleen Aquinojoebane capapas jr.No ratings yet
- Changes in MatterDocument23 pagesChanges in MatterKaryll ColumnaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions and EquationsDocument5 pagesChemical Reactions and EquationsSupriya SanjeevaNo ratings yet
- Chemical ReactionsDocument30 pagesChemical ReactionsIftikhar Hussain RizviNo ratings yet
- Chemical ReactionDocument28 pagesChemical Reactionmariajessicaarce1212No ratings yet
- accurate note Chemical Reactions & EquationsDocument5 pagesaccurate note Chemical Reactions & EquationsCuzco CuckooNo ratings yet
- Mixtures and Solutions: Fizz Quiz 3-1 Chemical Reactions Vocabulary and ContentDocument7 pagesMixtures and Solutions: Fizz Quiz 3-1 Chemical Reactions Vocabulary and ContentMrsNguyen95014No ratings yet
- Prepared By: Lee Hock TiangDocument27 pagesPrepared By: Lee Hock TiangNick LeeNo ratings yet
- Class VIII Chemical Changes Day 2Document15 pagesClass VIII Chemical Changes Day 2Edu TainmentNo ratings yet
- Chapter - Chemical Reactions and Equations (PART - 3) : by - Tejashwini C KDocument8 pagesChapter - Chemical Reactions and Equations (PART - 3) : by - Tejashwini C KTejashwini CkNo ratings yet
- All About Exothermic ReactionDocument11 pagesAll About Exothermic ReactionAkshay IndoraNo ratings yet
- Final Research (Hady)Document6 pagesFinal Research (Hady)Hady SalehNo ratings yet
- Simple Chemical Reactions Class 7.Document19 pagesSimple Chemical Reactions Class 7.ZUNI100% (4)
- 99998324Document7 pages99998324Ashish Urff ĐãkšhNo ratings yet
- Combustion and Flame 8thDocument13 pagesCombustion and Flame 8thPratibha GuptaNo ratings yet
- Physical and Chemical Reactions : 6th Grade Chemistry Book | Children's Chemistry BooksFrom EverandPhysical and Chemical Reactions : 6th Grade Chemistry Book | Children's Chemistry BooksNo ratings yet
- Coordination Chem 1 PDFDocument10 pagesCoordination Chem 1 PDFSundar SinghNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 5 TREATMENT METHODS FOR RURAL WATER SUPPLYDocument9 pagesChapter - 5 TREATMENT METHODS FOR RURAL WATER SUPPLYdawana samuelNo ratings yet
- Mixing The Warm Cool Palette Anna WakitschDocument8 pagesMixing The Warm Cool Palette Anna WakitschAlison De Sando ManzoniNo ratings yet
- Catalytic Asymmetric Synthesis of Cannabinoids and Menthol From NeralDocument7 pagesCatalytic Asymmetric Synthesis of Cannabinoids and Menthol From NeralSamir SahaNo ratings yet
- Mineral Processing Introduction 1Document57 pagesMineral Processing Introduction 1tatek.anberbirNo ratings yet
- Solar-Riat, US Highway 190 West, Killeen, TX 76541, USADocument13 pagesSolar-Riat, US Highway 190 West, Killeen, TX 76541, USAShafira RiskinaNo ratings yet
- The Empty Palm Oil Fruit Bunch As The Potential SoDocument7 pagesThe Empty Palm Oil Fruit Bunch As The Potential SoTOMMY LEENo ratings yet
- Experiment To Study The Exothermic and Endothermic ReactionsDocument12 pagesExperiment To Study The Exothermic and Endothermic ReactionsAzneezal Ar-Rashid100% (2)
- Chemistry 14A AnswersDocument8 pagesChemistry 14A AnswersJong.Gun.KimNo ratings yet
- STS Detailed OutlineDocument11 pagesSTS Detailed OutlineCHARLES KEVIN MINANo ratings yet
- Extraction and Uses of Metals 1 QP PDFDocument12 pagesExtraction and Uses of Metals 1 QP PDFAngus AnizNo ratings yet
- Plastic Waste Management PDFDocument59 pagesPlastic Waste Management PDFAnonymous HOI7owj9ONo ratings yet
- Catalytic Hydrogenation by Using Raney NickelDocument5 pagesCatalytic Hydrogenation by Using Raney NickelSampotterNo ratings yet
- Electrical Characterization and Poole-Frenkel Effect in Sol-Gel Derived Zno:Al Thin FilmsDocument11 pagesElectrical Characterization and Poole-Frenkel Effect in Sol-Gel Derived Zno:Al Thin Filmsचन्द्रभाल सिंहNo ratings yet
- EDTA METHOD (Sulphate)Document2 pagesEDTA METHOD (Sulphate)Bhinitha Chandrasagaran100% (1)
- Salt Analysis (XIII)Document12 pagesSalt Analysis (XIII)Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- Amperometric Titration - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument2 pagesAmperometric Titration - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaQaisar NadeemNo ratings yet
- Explosives and Pyrotechnic Propellants For Use In: Long Term Deep Space MissionsDocument31 pagesExplosives and Pyrotechnic Propellants For Use In: Long Term Deep Space MissionsbisuNo ratings yet
- TRANSITION ELEMENTS (D-Block Elements)Document2 pagesTRANSITION ELEMENTS (D-Block Elements)Manoj YadavNo ratings yet
- Caffeine Determination by HPLCDocument3 pagesCaffeine Determination by HPLCnga_yan0% (1)
- 1 Chapter.2 Mole Concept: Practice Questions: WWW - Shenischool.inDocument3 pages1 Chapter.2 Mole Concept: Practice Questions: WWW - Shenischool.inGuru DeepNo ratings yet
- Matter WorksheetDocument4 pagesMatter WorksheetShikha AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Process Synthesis and Analysis of Green Plastic Monomer Production From CelluloseDocument8 pagesProcess Synthesis and Analysis of Green Plastic Monomer Production From CelluloseMaycon PaimNo ratings yet
- Report in Technical Analysis CEMENTDocument26 pagesReport in Technical Analysis CEMENTNatrium KirchhoffNo ratings yet
- StoichiometryDocument17 pagesStoichiometryGianna BaldoradoNo ratings yet
- Mackintosh Paper PDFDocument4 pagesMackintosh Paper PDFheheNo ratings yet
- Semana 02 O - Portland, Blended and Other Hydraulic Cement C - PCA Chapter 3 PDFDocument38 pagesSemana 02 O - Portland, Blended and Other Hydraulic Cement C - PCA Chapter 3 PDFBrandon PonteNo ratings yet
- The Complete Book On Emulsifiers With Uses Formulae and Processes - 2nd Revised EditionDocument46 pagesThe Complete Book On Emulsifiers With Uses Formulae and Processes - 2nd Revised EditionBILAL AMJADNo ratings yet
- Melamine Tehnical SheetDocument2 pagesMelamine Tehnical SheetlyesNo ratings yet