Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Module-8-Some-Metabolic-Activities-of-Bacteria-INDIVIDUAL ZuRkv
Module-8-Some-Metabolic-Activities-of-Bacteria-INDIVIDUAL ZuRkv
Uploaded by
PrezyCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- 2023 Assessments FinalDocument12 pages2023 Assessments FinalTumuhimbise MosesNo ratings yet
- Exercise 13Document27 pagesExercise 13Jamie Paola SevillaNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate Metabolism of BacteriaDocument5 pagesCarbohydrate Metabolism of BacteriaMukund VatsNo ratings yet
- Advanced Pharmaceutical analysisFrom EverandAdvanced Pharmaceutical analysisRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Staphylococcus VS, StreptococcusDocument5 pagesStaphylococcus VS, StreptococcuschokasaNo ratings yet
- Characterisation 2Document13 pagesCharacterisation 2ckmdeckedlknedclswNo ratings yet
- A. Test To Differentiate Between Staphylococci and StreptococciDocument1 pageA. Test To Differentiate Between Staphylococci and StreptococciNor ShasalbilaNo ratings yet
- LabourDocument18 pagesLabourAyanayuNo ratings yet
- New Text DocumentDocument3 pagesNew Text Documenthari krishnaa athotaNo ratings yet
- Lab Report MicrobiologyDocument11 pagesLab Report Microbiologysalman ahmedNo ratings yet
- Uses of Carbohydrate Fermentation Test: EnterobacteriaceaeDocument12 pagesUses of Carbohydrate Fermentation Test: EnterobacteriaceaeChristyl JoNo ratings yet
- Informe6 MicrobiologiaDocument7 pagesInforme6 MicrobiologiaAlejandra HenaoNo ratings yet
- Catalase TestDocument2 pagesCatalase TestsekaralingamNo ratings yet
- What Is The Phenotype of Your Pure Culture: MCB 3020L Lab Experiment 4Document7 pagesWhat Is The Phenotype of Your Pure Culture: MCB 3020L Lab Experiment 4Darth ZenterNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Biochemical Activity, Session 2ADocument16 pagesChapter 9 Biochemical Activity, Session 2AJoshua ZeelanderNo ratings yet
- Full Lab Report 2Document14 pagesFull Lab Report 2api-526073261No ratings yet
- Microbial PhysiologyDocument2 pagesMicrobial Physiologyjoeljose07No ratings yet
- Biochemical Test of BacteriaDocument26 pagesBiochemical Test of BacteriaazizahNo ratings yet
- Microbiology Lab ReportDocument4 pagesMicrobiology Lab ReportNasran Na'imNo ratings yet
- Lec 3 BacteDocument7 pagesLec 3 BacteMitchee ZialcitaNo ratings yet
- IMViC 2Document5 pagesIMViC 2grecianeronica84No ratings yet
- Media & Biochemical Tests: Laboratory ObjectivesDocument36 pagesMedia & Biochemical Tests: Laboratory ObjectivesHiba Abu-jumahNo ratings yet
- BIOCHEMICAL TESTS - PPTX MLSDocument111 pagesBIOCHEMICAL TESTS - PPTX MLSyewollolijfikreNo ratings yet
- Catalase Test Protocol - LibraryDocument5 pagesCatalase Test Protocol - LibraryMartina IsnainiNo ratings yet
- Ute Kale Tal Biolog I A 2014Document6 pagesUte Kale Tal Biolog I A 2014leztlyNo ratings yet
- VID11A - Identification of Bacteria Using Biochemical TestsDocument11 pagesVID11A - Identification of Bacteria Using Biochemical TestsHazely TagasaNo ratings yet
- Pratical Two ReportDocument13 pagesPratical Two ReportMUBIRU SAMUEL EDWARDNo ratings yet
- Microbiolal TestingDocument8 pagesMicrobiolal Testingmalakst200No ratings yet
- Catalase TestDocument29 pagesCatalase TestmaleehaNo ratings yet
- Biochemical Activities of BacteriasDocument7 pagesBiochemical Activities of BacteriasEbruAkharmanNo ratings yet
- Intro Micro Lab 5Document11 pagesIntro Micro Lab 5Sadaph Ali ShahNo ratings yet
- Bio 331 Lab 5-2020Document39 pagesBio 331 Lab 5-2020ybnr7pgsbrNo ratings yet
- BIO6LabExam2StudyGuide LimDocument9 pagesBIO6LabExam2StudyGuide Limthu_vu_29No ratings yet
- Blood Agar Media:: Differentiates Between Alpha, Beta & Gamma Hemolytic StreptococciDocument18 pagesBlood Agar Media:: Differentiates Between Alpha, Beta & Gamma Hemolytic StreptococciHusssain100% (1)
- Test Bank For Diagnostic Microbiology 4th Edition Mahon Full DownloadDocument18 pagesTest Bank For Diagnostic Microbiology 4th Edition Mahon Full Downloadjameswalkertmdncfbxwe100% (39)
- Biochemical TestsDocument21 pagesBiochemical TestsContact AmsibNo ratings yet
- Media Biochemical TestsDocument36 pagesMedia Biochemical TestsIsmail Bazly ZarirNo ratings yet
- Group 2 - Bacte Lab. ExamDocument11 pagesGroup 2 - Bacte Lab. ExamANo ratings yet
- Report 800Document5 pagesReport 800Western Ang'ong'aNo ratings yet
- Biochemical TestsDocument41 pagesBiochemical TestsChinthikaNo ratings yet
- Modelling of The Alcohol Dehydrogenase Production in Baker's YeastDocument10 pagesModelling of The Alcohol Dehydrogenase Production in Baker's Yeast321No ratings yet
- Praktikum Mikrobiologi Gram NegatifDocument44 pagesPraktikum Mikrobiologi Gram Negatifrids_No ratings yet
- Biochemical - TestsDocument5 pagesBiochemical - TestsMohsen Haleem100% (1)
- Lab Report Pathogen Microbe 1Document11 pagesLab Report Pathogen Microbe 1Syazmin KhairuddinNo ratings yet
- Biochemical: ReactionsDocument62 pagesBiochemical: ReactionsIsaacJ22No ratings yet
- Biochemical Methods For Staphylococci IdentificationDocument12 pagesBiochemical Methods For Staphylococci IdentificationJuliannaViktoriiaNo ratings yet
- Microbiology Unknown ReportDocument25 pagesMicrobiology Unknown Reportacj56100% (1)
- Microbiology 8Document4 pagesMicrobiology 8Sandali PunsalaNo ratings yet
- Biochemical Tests For BacteriaDocument16 pagesBiochemical Tests For BacteriaNichols Amy Tarun100% (1)
- Lab Class 3 - Detection of Specified Organisms and Identification of BacteriaDocument3 pagesLab Class 3 - Detection of Specified Organisms and Identification of BacteriakomalramNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Activity No. 2 - Analysis of Carbohydrates - 1Document4 pagesLaboratory Activity No. 2 - Analysis of Carbohydrates - 1Juliane JaynNo ratings yet
- Practical 4: Bacteria Isolation and Biochemical Identification Techniques (Demonstration)Document3 pagesPractical 4: Bacteria Isolation and Biochemical Identification Techniques (Demonstration)Baby girlNo ratings yet
- Immobilised Yeast: NCBE, University of ReadingDocument5 pagesImmobilised Yeast: NCBE, University of ReadingVipin ChandranNo ratings yet
- Practical 8 BiochemDocument6 pagesPractical 8 BiochemKINISHAA A/P TAMIL SELVEN / UPMNo ratings yet
- Lab 8Document28 pagesLab 8Mustafa A. DawoodNo ratings yet
- Catalase TestDocument12 pagesCatalase Testshiva121294No ratings yet
- Differential and Selective MediaDocument8 pagesDifferential and Selective Mediaangelinarod33445No ratings yet
- Organic Reaction Mechanisms 2009: An annual survey covering the literature dated January to December 2009From EverandOrganic Reaction Mechanisms 2009: An annual survey covering the literature dated January to December 2009A. C. KnipeNo ratings yet
- Enantioselective Organocatalysis: Reactions and Experimental ProceduresFrom EverandEnantioselective Organocatalysis: Reactions and Experimental ProceduresPeter I. DalkoRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Metal Catalyzed Cross-Coupling Reactions and MoreFrom EverandMetal Catalyzed Cross-Coupling Reactions and MoreArmin de MeijereNo ratings yet
- Developmental Biology Notes 3Document26 pagesDevelopmental Biology Notes 3PrezyNo ratings yet
- Genetics CH 3-4Document19 pagesGenetics CH 3-4PrezyNo ratings yet
- Devbio 1Document10 pagesDevbio 1PrezyNo ratings yet
- MicrobioLec Q and A Notes ZMAzPDocument6 pagesMicrobioLec Q and A Notes ZMAzPPrezyNo ratings yet
- Exercise 9 DevbiolabDocument4 pagesExercise 9 DevbiolabPrezyNo ratings yet
- D-K For PlasmodiaDocument2 pagesD-K For PlasmodiaPrezyNo ratings yet
- SDG 4Document43 pagesSDG 4PrezyNo ratings yet
- D-K For Helminth EggsDocument2 pagesD-K For Helminth EggsPrezyNo ratings yet
- D-K For Amoebae and FlagellatesDocument2 pagesD-K For Amoebae and FlagellatesPrezyNo ratings yet
Module-8-Some-Metabolic-Activities-of-Bacteria-INDIVIDUAL ZuRkv
Module-8-Some-Metabolic-Activities-of-Bacteria-INDIVIDUAL ZuRkv
Uploaded by
PrezyOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Module-8-Some-Metabolic-Activities-of-Bacteria-INDIVIDUAL ZuRkv
Module-8-Some-Metabolic-Activities-of-Bacteria-INDIVIDUAL ZuRkv
Uploaded by
PrezyCopyright:
Available Formats
Name: Precy B.
Ramada Date: November 15, 2022
Module 8 – Individual Output
Some Metabolic Activities of Bacteria
Perform the activities in the following online simulations:
Catalase test: https://learn.chm.msu.edu/vibl/vibl/Catalase/catalase_HTML5Canvas.html
Oxidase Test: https://learn.chm.msu.edu/vibl/vibl/Oxidase/oxidase_HTML5Canvas.html
Place an image of your results and fill up the table of your online simulation here:
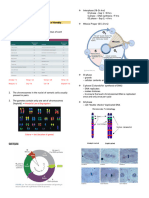
Catalase Test
Bacteria used Catalase Result Image
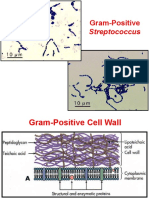
Streptococcus pyogenes negative
Staphylococcus aureus positive
Interpretation/Inference:
When mixed with H2O, the isolated colony of Streptococcus pyogenes showed no bubbling while
the Staphylococcus aureus showed an immediate strong bubbling. This simply means that Streptococcus
pyogenes is a catalase-negative bacteria. These bacteria may be anaerobes or may be facultative
anaerobes that only ferment and do not respire using oxygen as a terminal electron acceptor. On the other
hand, Staphylococcus aureus is an example of a catalase-positive bacteria which means having the ability
to respire using oxygen and uses the catalase enzyme to protect them from the toxic by-products of
oxygen metabolism.
Oxidase Test
Bacteria used Oxidase Result Image
Neisseria gonorrhoeae Positive
Salmonella enteritidis Negative
Enterobacter aerogenes Negative
Interpretation/Inference:
Upon rubbing the bacteria onto the DrySlide, Neisseria gonorrhoeae turned purple-black in color
while both Salmonella enteritidis and Enterobacter aerogenes were colorless or showed no changes in
color. This means that the enzyme, cytochrome c oxidase is present in Neisseria gonorrhoeae but absent
in Salmonella enteritidis and Enterobacter aerogenes. The oxidase-positive bacteria are aerobic and can
use oxygen as a terminal electron acceptor in respiration whereas the oxidase-negative bacteria just
simply do not contain the enzyme that oxidizes the test reagent but may respire using other oxidases in
electron transport.
References:
https://learn.chm.msu.edu/vibl/vibl/Catalase/catalase_HTML5Canvas.html
https://learn.chm.msu.edu/vibl/vibl/Oxidase/oxidase_HTML5Canvas.html
You might also like
- 2023 Assessments FinalDocument12 pages2023 Assessments FinalTumuhimbise MosesNo ratings yet
- Exercise 13Document27 pagesExercise 13Jamie Paola SevillaNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate Metabolism of BacteriaDocument5 pagesCarbohydrate Metabolism of BacteriaMukund VatsNo ratings yet
- Advanced Pharmaceutical analysisFrom EverandAdvanced Pharmaceutical analysisRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Staphylococcus VS, StreptococcusDocument5 pagesStaphylococcus VS, StreptococcuschokasaNo ratings yet
- Characterisation 2Document13 pagesCharacterisation 2ckmdeckedlknedclswNo ratings yet
- A. Test To Differentiate Between Staphylococci and StreptococciDocument1 pageA. Test To Differentiate Between Staphylococci and StreptococciNor ShasalbilaNo ratings yet
- LabourDocument18 pagesLabourAyanayuNo ratings yet
- New Text DocumentDocument3 pagesNew Text Documenthari krishnaa athotaNo ratings yet
- Lab Report MicrobiologyDocument11 pagesLab Report Microbiologysalman ahmedNo ratings yet
- Uses of Carbohydrate Fermentation Test: EnterobacteriaceaeDocument12 pagesUses of Carbohydrate Fermentation Test: EnterobacteriaceaeChristyl JoNo ratings yet
- Informe6 MicrobiologiaDocument7 pagesInforme6 MicrobiologiaAlejandra HenaoNo ratings yet
- Catalase TestDocument2 pagesCatalase TestsekaralingamNo ratings yet
- What Is The Phenotype of Your Pure Culture: MCB 3020L Lab Experiment 4Document7 pagesWhat Is The Phenotype of Your Pure Culture: MCB 3020L Lab Experiment 4Darth ZenterNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Biochemical Activity, Session 2ADocument16 pagesChapter 9 Biochemical Activity, Session 2AJoshua ZeelanderNo ratings yet
- Full Lab Report 2Document14 pagesFull Lab Report 2api-526073261No ratings yet
- Microbial PhysiologyDocument2 pagesMicrobial Physiologyjoeljose07No ratings yet
- Biochemical Test of BacteriaDocument26 pagesBiochemical Test of BacteriaazizahNo ratings yet
- Microbiology Lab ReportDocument4 pagesMicrobiology Lab ReportNasran Na'imNo ratings yet
- Lec 3 BacteDocument7 pagesLec 3 BacteMitchee ZialcitaNo ratings yet
- IMViC 2Document5 pagesIMViC 2grecianeronica84No ratings yet
- Media & Biochemical Tests: Laboratory ObjectivesDocument36 pagesMedia & Biochemical Tests: Laboratory ObjectivesHiba Abu-jumahNo ratings yet
- BIOCHEMICAL TESTS - PPTX MLSDocument111 pagesBIOCHEMICAL TESTS - PPTX MLSyewollolijfikreNo ratings yet
- Catalase Test Protocol - LibraryDocument5 pagesCatalase Test Protocol - LibraryMartina IsnainiNo ratings yet
- Ute Kale Tal Biolog I A 2014Document6 pagesUte Kale Tal Biolog I A 2014leztlyNo ratings yet
- VID11A - Identification of Bacteria Using Biochemical TestsDocument11 pagesVID11A - Identification of Bacteria Using Biochemical TestsHazely TagasaNo ratings yet
- Pratical Two ReportDocument13 pagesPratical Two ReportMUBIRU SAMUEL EDWARDNo ratings yet
- Microbiolal TestingDocument8 pagesMicrobiolal Testingmalakst200No ratings yet
- Catalase TestDocument29 pagesCatalase TestmaleehaNo ratings yet
- Biochemical Activities of BacteriasDocument7 pagesBiochemical Activities of BacteriasEbruAkharmanNo ratings yet
- Intro Micro Lab 5Document11 pagesIntro Micro Lab 5Sadaph Ali ShahNo ratings yet
- Bio 331 Lab 5-2020Document39 pagesBio 331 Lab 5-2020ybnr7pgsbrNo ratings yet
- BIO6LabExam2StudyGuide LimDocument9 pagesBIO6LabExam2StudyGuide Limthu_vu_29No ratings yet
- Blood Agar Media:: Differentiates Between Alpha, Beta & Gamma Hemolytic StreptococciDocument18 pagesBlood Agar Media:: Differentiates Between Alpha, Beta & Gamma Hemolytic StreptococciHusssain100% (1)
- Test Bank For Diagnostic Microbiology 4th Edition Mahon Full DownloadDocument18 pagesTest Bank For Diagnostic Microbiology 4th Edition Mahon Full Downloadjameswalkertmdncfbxwe100% (39)
- Biochemical TestsDocument21 pagesBiochemical TestsContact AmsibNo ratings yet
- Media Biochemical TestsDocument36 pagesMedia Biochemical TestsIsmail Bazly ZarirNo ratings yet
- Group 2 - Bacte Lab. ExamDocument11 pagesGroup 2 - Bacte Lab. ExamANo ratings yet
- Report 800Document5 pagesReport 800Western Ang'ong'aNo ratings yet
- Biochemical TestsDocument41 pagesBiochemical TestsChinthikaNo ratings yet
- Modelling of The Alcohol Dehydrogenase Production in Baker's YeastDocument10 pagesModelling of The Alcohol Dehydrogenase Production in Baker's Yeast321No ratings yet
- Praktikum Mikrobiologi Gram NegatifDocument44 pagesPraktikum Mikrobiologi Gram Negatifrids_No ratings yet
- Biochemical - TestsDocument5 pagesBiochemical - TestsMohsen Haleem100% (1)
- Lab Report Pathogen Microbe 1Document11 pagesLab Report Pathogen Microbe 1Syazmin KhairuddinNo ratings yet
- Biochemical: ReactionsDocument62 pagesBiochemical: ReactionsIsaacJ22No ratings yet
- Biochemical Methods For Staphylococci IdentificationDocument12 pagesBiochemical Methods For Staphylococci IdentificationJuliannaViktoriiaNo ratings yet
- Microbiology Unknown ReportDocument25 pagesMicrobiology Unknown Reportacj56100% (1)
- Microbiology 8Document4 pagesMicrobiology 8Sandali PunsalaNo ratings yet
- Biochemical Tests For BacteriaDocument16 pagesBiochemical Tests For BacteriaNichols Amy Tarun100% (1)
- Lab Class 3 - Detection of Specified Organisms and Identification of BacteriaDocument3 pagesLab Class 3 - Detection of Specified Organisms and Identification of BacteriakomalramNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Activity No. 2 - Analysis of Carbohydrates - 1Document4 pagesLaboratory Activity No. 2 - Analysis of Carbohydrates - 1Juliane JaynNo ratings yet
- Practical 4: Bacteria Isolation and Biochemical Identification Techniques (Demonstration)Document3 pagesPractical 4: Bacteria Isolation and Biochemical Identification Techniques (Demonstration)Baby girlNo ratings yet
- Immobilised Yeast: NCBE, University of ReadingDocument5 pagesImmobilised Yeast: NCBE, University of ReadingVipin ChandranNo ratings yet
- Practical 8 BiochemDocument6 pagesPractical 8 BiochemKINISHAA A/P TAMIL SELVEN / UPMNo ratings yet
- Lab 8Document28 pagesLab 8Mustafa A. DawoodNo ratings yet
- Catalase TestDocument12 pagesCatalase Testshiva121294No ratings yet
- Differential and Selective MediaDocument8 pagesDifferential and Selective Mediaangelinarod33445No ratings yet
- Organic Reaction Mechanisms 2009: An annual survey covering the literature dated January to December 2009From EverandOrganic Reaction Mechanisms 2009: An annual survey covering the literature dated January to December 2009A. C. KnipeNo ratings yet
- Enantioselective Organocatalysis: Reactions and Experimental ProceduresFrom EverandEnantioselective Organocatalysis: Reactions and Experimental ProceduresPeter I. DalkoRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Metal Catalyzed Cross-Coupling Reactions and MoreFrom EverandMetal Catalyzed Cross-Coupling Reactions and MoreArmin de MeijereNo ratings yet
- Developmental Biology Notes 3Document26 pagesDevelopmental Biology Notes 3PrezyNo ratings yet
- Genetics CH 3-4Document19 pagesGenetics CH 3-4PrezyNo ratings yet
- Devbio 1Document10 pagesDevbio 1PrezyNo ratings yet
- MicrobioLec Q and A Notes ZMAzPDocument6 pagesMicrobioLec Q and A Notes ZMAzPPrezyNo ratings yet
- Exercise 9 DevbiolabDocument4 pagesExercise 9 DevbiolabPrezyNo ratings yet
- D-K For PlasmodiaDocument2 pagesD-K For PlasmodiaPrezyNo ratings yet
- SDG 4Document43 pagesSDG 4PrezyNo ratings yet
- D-K For Helminth EggsDocument2 pagesD-K For Helminth EggsPrezyNo ratings yet
- D-K For Amoebae and FlagellatesDocument2 pagesD-K For Amoebae and FlagellatesPrezyNo ratings yet