Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Alexander The Great Conquest Map, Collins Military History
Alexander The Great Conquest Map, Collins Military History
Uploaded by
Om SANTOSOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Alexander The Great Conquest Map, Collins Military History
Alexander The Great Conquest Map, Collins Military History
Uploaded by
Om SANTOSCopyright:
Available Formats
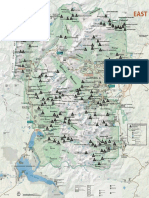
alexander the great and the successor wars
. 170 Bc
ae a cae Wars between the G re ek city-states continued after the Pelo DONNES ian Alexander's sudden death precipitated a series of wars that ended only 2 Antigonus ‘One Eye’ waskilled at the Battle of Ipsus in 301 8c, ending the most
Battle of a Chaeronea: Macedon : : th the Cae - the region.
.
{under Philip II) overpowers : = my) arrival of Roman powerin Alexander's' generals (the i
SeTOUS
fede eHeTOBE b f Alexander’s g generals to control the entire
he St RYof One 9 a ' Pe eeire.ey
:
B
Theban-led coalition Wa r until the.no rthern state of M d ced On OVE rwh elmed a Th eban-led Diadochoi, or Successors} fought to inherit, if not his throne, at least an eeeeeae eaeae
CS coalition at the Battle of Chaeronea IN) 338 pee ; | empire of their own. By the assassination of Seleucus, the last of the old Persian heartland and Macedoniaitself. Macedonian intrigues with the
Oo 336BC Alexander's officers, in 280 8c, three main successor states emerged: Carthaginians during the Second Punic War werenotforgotten in Rome which
: = oieee‘bas , Macedon, Egypt and the Seleucid Kingdom that stretched from the eastern declared waron Philip V in 200 Bc. The waeton were defeated in 197Bc and
Pop ee The victorious Macedonianking, Philip Il, was assassinated in 336 Bc. Two yearslater, his son AlexanderIII led the shores of the Mediterranean to Baghdad again in 1688c. Between the Macedonian wars, Romeintervenedin the eastern
}| © Macedonian nee
army into Asia, on a one-way journey that won him the reputation of the greatest field commanderof the
| ee mee YJ a a i Asia Mi g . ela eal : 3 Over a century after Alexander's death, the Egypt of the Ptolemys and the Aegean where smaller states allied with her against Antiochus Ill, ruler of the
Seleucid empire {map below). Antiochus was defeated at Magnesia in 190sc, the
| i 334 BC ncien wort = € shattered a coo ay ed by ee sal’aps 2 ne ma sid INOr, Personauy teauing : ea Soe Seleucids in the Middle East/Syria were at war over the ports and cities that success of cavalry under his own commandfailing to stop the legions
| Alexander invades Persia =» cavalry charge that nearly cost himhislife. Alexander’s communications with Macedon werevulnerable to the Persian were part of Coele-Syria, the modern-day Mediterranean Middle East. In demolishing his phalanx.
| | fleet, which was also capable of supporting revolts within Greece, so he led the army against the coastal cities of the 218 Bc, fresh from suppressing seriesof eastern rebellions
f 333 BC eastern Mediterranean. King DariusIII of Persia arrived in 333 Bc, but he was defeatedat Issus, and his army disinte-
Battle of Issus the Seleucid Kingdom’s young ruler, AntiochusIll, invaded
. grated. The Persian Empire began to fracture. Its provinces included a wide variety of races, subject peoples with no Coele-Syria and marched against Egypt. The ensuingBattle of :
5 i 331 Bc 7 particular allegiance to the ruling Achaemenid dynasty. Egypt's cities surrendered to Alexander. Alexander's general Raphia (217 gc)left Palestine in Egyptian hands while Antiochus’
| Battle of Gaugamela (or Arbela): Ptolemy wasto found the lastdynastyof pharaohs, which endedwith Cleopatra VII. In 331 Bc Alexander marchedinto 4
the devoted his considerable energy to further campaigns in
il | Alexander defeats Darius heartlandof Asia for a final confrontation with Darius, who had raised and equipped another army. Dariusfled the field at = Baccuba and ae | ie
i | ee Gaugamela, and was pursued for some monthsby Alexanderuntil assassinated by Bessus,the satrap of Bactria. far east as the Punjab. Cynoscephalge™.. “3
:i
| aese Alexander devoted the nextten years to conquering the farthest reaches of the Persian Empire. In 323 Bc, aged only 3 | a the hellenistic world, 19 ) i1€SIC.PERGAN
| 33, and having conquered mostofthecivilised world, he died of fever (or possibly poison). 188 Bc a) GRAECO-
280 Bc [99 independentGreek states
Three main successor states
igs hee ae ae :
< Panias | /b G
emerge: Macedon, Egypt and Bi ea B CG waz BC at 1541,
the Seleucid kingdom
ee “]
a + “ale
exandria
A
on 47 Co
217 Bc ene depen LIBYANS
aes © GEDROSIA
Sa Kingdom of Pergamum ARABIA
| Battle of Raphia between ~
Antiochus and Egypt Es Hellenised non-Greek kingdoms .
Oe i er ; a - ie Pr ‘ ee | < o. poe oe Pes = it FR eae ae
Tak ~S
De a > wee : 7 aa S
200 Bc RN Lieu.Sl c n
3 iJ EZ qeGNicaes : es | 7 | v
Rome declares war on Philip V al att CA in es et pSSAG &p> C e
: of Macedon. ° : ears "
| ° AE aracand
197 and 168 Bc| fea see oe a? |
Macedonians defeated | autaca
Haens £ hesus® . U.
333 BC SZeugma
wa arshi) ©
a t SSN @Alexand-; y 2
a"7 =oey | Ber ea (Aleppg : She Zadracyhers = | (Mery) dy Perbent
The meteoric career of : \ Antec jt “ i ae 5 eds 9 2Usia
Alexander brought the y “‘Yalicartiassa aea
‘
2 e € ‘A “(Teaesh g AhAY : 7 Cc
Macedonian army to the limits 7 ; “Melos oo Rhode a
| e os D's : AZ Vhara é (Balkh) a
- aspian ates : *
ee ”ele?
woo Heap Aeron: | odicedy ag f1c
. 3 : :
led his mento victory over the C Rf r
Eups, C Rp A
PARTHIA
i* : a
A R41 ae
‘ @Artacoana .
itee ,
Persian army,the cities of Zic@t in Se y "les oO €,Ne ~ P/ cxandria Arion _«
|
Phoenicia, mountaintribes and
oe, z »
a pete és ae
.
ibeiieded 332 B J ‘
ce Ateinies 4; ite
<_.Gabae
Scythian horsemen. That his M & 8 gBYLONI ’
: | : | empire would notoutlive him sama KSPiladlphi serene
wasevidentbefore his death: ea, jerusalgmga, (Amma sk
false newsof his demise Cyrene a “ Alexandria ay oe “% 7 }
triggered several revolts prior ay An “i mea (Rhacotis 2. *elusium ‘} { FB
to his fatal sicknessat oe ok B “. araeton'u : AC 5 gee
| Baghdad.
: g coe‘ E G P
Memphis plicit y one 4ee
bo. . [ probable > i
| ae seas < — ify) es
psouscarnr ancienti
‘ anctuary ma ~ coasiine
x the ote of alexander =ghAmmone———
empire of Alexander, 323 BC
=== States federated to the empire
=== independentstates
routeof Alexander the Great
route of Nearchus's naval expedition, 325 BC
return route of Alexander's veterans and K \ndian
Dé
elephants under Craterus, 325 BC Z iia GY of the Brahmans nee B)
a\ Alexander's majorbattles
@” new cities founded, 336-100 Bc ie Pro,
Course
ble an
of hat
@ Cities partly replanned orrebuilt, 336-100 BC cu 19
You might also like
- Isizulu Fal (2023) Grade 9 June Controlled Test (Nhlangulana)Document10 pagesIsizulu Fal (2023) Grade 9 June Controlled Test (Nhlangulana)Kirsten Sampson100% (7)
- Paciencia y Fe From in The Heights The MusicalDocument17 pagesPaciencia y Fe From in The Heights The MusicalRoyalty100% (2)
- The Lion King - Drum KitDocument89 pagesThe Lion King - Drum Kitblackmouthdrums1123No ratings yet
- The Lion King - CelloDocument94 pagesThe Lion King - CelloJustin HernandezNo ratings yet
- I Saw Water Flowing - VaticanDocument3 pagesI Saw Water Flowing - VaticanChu Gia KhôiNo ratings yet
- Michel TournierDocument3 pagesMichel TournierLaura RuxandraNo ratings yet
- Personalul MedicalDocument19 pagesPersonalul Medicalm1tza88No ratings yet
- Columbia, The Gem of The Ocean: Thomas A'becket (1808-1890)Document2 pagesColumbia, The Gem of The Ocean: Thomas A'becket (1808-1890)Timothy Michael WynneNo ratings yet
- Current 1 FDTNDocument1 pageCurrent 1 FDTNAugustine yigaNo ratings yet
- Our Town May 13, 1922Document4 pagesOur Town May 13, 1922narberthcivicNo ratings yet
- Field of Glory - ArmiesDocument1 pageField of Glory - ArmiesTakedaVasiljevicIgorNo ratings yet
- Sax Alto Eb: Letra: Jonas de M Orais Correia Filho Música: Valmirina Ramos CorreiaDocument1 pageSax Alto Eb: Letra: Jonas de M Orais Correia Filho Música: Valmirina Ramos CorreiaJoao RamosNo ratings yet
- The Lion King - ViolinsDocument105 pagesThe Lion King - ViolinsJustin HernandezNo ratings yet
- Site Development Plan Auxiliary: General Notes: Legends & SymbolsDocument16 pagesSite Development Plan Auxiliary: General Notes: Legends & SymbolsIan de GaliciaNo ratings yet
- Violinoi LetDocument3 pagesViolinoi LetsmbiosisNo ratings yet
- Queen Aria para ImprimirDocument3 pagesQueen Aria para ImprimirViktoria AmorosNo ratings yet
- 8 B Ifc 00 Me SW00 00Document1 page8 B Ifc 00 Me SW00 00RehAn KhAlilNo ratings yet
- M - F - Gervais Kingdom of Denmark FullXL TreeDocument1 pageM - F - Gervais Kingdom of Denmark FullXL TreebruhNo ratings yet
- Phasing PlanDocument1 pagePhasing PlanNEWS CENTER MaineNo ratings yet
- Campsite Map Small-2016Document1 pageCampsite Map Small-2016api-529188810No ratings yet
- BoysanzacDocument22 pagesBoysanzacobed mulalaNo ratings yet
- Typical Apartment Type 1A - Power and Comms Layout Typical Apartment Type 2F - Power and Comms LayoutDocument1 pageTypical Apartment Type 1A - Power and Comms Layout Typical Apartment Type 2F - Power and Comms Layoutbatopotcholo03No ratings yet
- Binghatti Phoenix Presentation 02.02.024Document9 pagesBinghatti Phoenix Presentation 02.02.024prashant.tiwariNo ratings yet
- KJ 17 Tuhan Allah HadirDocument1 pageKJ 17 Tuhan Allah Hadir8vzgdxcynnNo ratings yet
- Ahad-Chilled Water SchematicDocument7 pagesAhad-Chilled Water SchematicVaisakh C&TNo ratings yet
- Chat GPoe TryDocument15 pagesChat GPoe TryPhilipp BoettcherNo ratings yet
- Plano Actual 1° Etapa Vista Hermosa 03-12-2022Document1 pagePlano Actual 1° Etapa Vista Hermosa 03-12-2022Juan Daniel GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Ranchez Approved Scheme 4Document1 pageRanchez Approved Scheme 4franciscoNo ratings yet
- 33 KV OUTDOOR SWITCH YARD For Earthing Layout 1 RABI - (Sheet-1of2)Document1 page33 KV OUTDOOR SWITCH YARD For Earthing Layout 1 RABI - (Sheet-1of2)SUSOVAN BISWASNo ratings yet
- BPD Questions On MacbethDocument9 pagesBPD Questions On MacbethJolly KushNo ratings yet
- Ea 0010Document1 pageEa 0010fereetNo ratings yet
- The Lion King - Trombone 1Document83 pagesThe Lion King - Trombone 1Justin HernandezNo ratings yet
- Voce Vai VerDocument1 pageVoce Vai Veraristeu 007No ratings yet
- 1SV90904 904D11 Sie C7 GF DWG ST 10301Document1 page1SV90904 904D11 Sie C7 GF DWG ST 10301Mahmoud ElshamyNo ratings yet
- Saint Saens Carnaval 08 Persons PDFDocument1 pageSaint Saens Carnaval 08 Persons PDFDoris GosoNo ratings yet
- Daniels 70th Week (20.07.24)Document1 pageDaniels 70th Week (20.07.24)Mike MurphyNo ratings yet
- STD-00-00000-EA-2384-96503-0001-05 Protection and Metering SLD For Transformer With 415V Secondary - Latest Revision RequiredDocument1 pageSTD-00-00000-EA-2384-96503-0001-05 Protection and Metering SLD For Transformer With 415V Secondary - Latest Revision RequiredSALAM JAIGADKARNo ratings yet
- 18-Alignment Plan &profile KM 90-100Document1 page18-Alignment Plan &profile KM 90-100Tamrayehu KuremaNo ratings yet
- Ídolos Del Rock FullscoreDocument25 pagesÍdolos Del Rock FullscoreCristopher GustavoNo ratings yet
- Planos de Casa Bungalow Americano 2 HabitacionesDocument1 pagePlanos de Casa Bungalow Americano 2 HabitacionesGabriel CostaNo ratings yet
- Ar 6BV2 1 102 00Document1 pageAr 6BV2 1 102 00dexter.plc005No ratings yet
- 2300019-DRAWING - Mannarah DetailsDocument1 page2300019-DRAWING - Mannarah DetailsMohammed MohiuddinNo ratings yet
- J1a - CD-100 DrawingsDocument27 pagesJ1a - CD-100 DrawingssanketNo ratings yet
- Parcial 2 PDFDocument1 pageParcial 2 PDFjorge etayoNo ratings yet
- Pop 44860 106 - Rev1Document2 pagesPop 44860 106 - Rev1Muhammad NURMANNo ratings yet
- Revisions: Research in MotionDocument2 pagesRevisions: Research in Motionzulkafli othmanNo ratings yet
- Sa Utc A+ SD Ew l1 085Document1 pageSa Utc A+ SD Ew l1 085satish daranalaNo ratings yet
- Mount Rainier MapDocument1 pageMount Rainier MapBilbao72No ratings yet
- 02 GloriaDocument17 pages02 Gloriaalessandro.russo.mandogmail.comNo ratings yet
- Behold! God The Lord Passed By!Document10 pagesBehold! God The Lord Passed By!Israel AfoakwahNo ratings yet
- Oil InterceptorDocument3 pagesOil InterceptorOkudetum RaphealNo ratings yet
- A.104-Basement Floor PDFDocument1 pageA.104-Basement Floor PDFdothi aiuyenNo ratings yet
- Cnph001 262 03 DR MG 000005 Gases Medicinales Sector 01d Tercer NivelDocument1 pageCnph001 262 03 DR MG 000005 Gases Medicinales Sector 01d Tercer NivelTony Jimenez ChNo ratings yet
- Deepak Filling Point-ModelDocument1 pageDeepak Filling Point-ModelPRUTHWIRAJ DAS [पृथ्वीराज दास]No ratings yet
- Level 3 General Arrangement Plan: A B C D E F G Suspended Slab NotesDocument1 pageLevel 3 General Arrangement Plan: A B C D E F G Suspended Slab NotesSubhekshya ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Mahiyangana D.S.qur ModelDocument1 pageMahiyangana D.S.qur ModelMuhammadWazimAkramNo ratings yet
- Reference 200 EastDocument1 pageReference 200 EastSimran KaurNo ratings yet
- 132 KV HANSI-ModelDocument1 page132 KV HANSI-ModelShariq KhanNo ratings yet
- NEOSPARK 23-05-2024pdfDocument1 pageNEOSPARK 23-05-2024pdfbatthulavishal7842No ratings yet
- Menuet VIII HaydnDocument1 pageMenuet VIII HaydnLaurent LellouchNo ratings yet
- Marcha Principe Dinamarca Violin y PianoDocument3 pagesMarcha Principe Dinamarca Violin y PianoGala ViolinNo ratings yet
- Line Route Drawing Kpean To OpoboDocument15 pagesLine Route Drawing Kpean To OpoboEric PeekateNo ratings yet
- John AshberyDocument3 pagesJohn Ashberyapi-23461844100% (1)
- Rachayithala DirectoryaddressDocument159 pagesRachayithala DirectoryaddressCG DwarakanathNo ratings yet
- Topic: The African Slave Trade Part Tw0 (1519-1860) : DIRECTIONS: Using Document 4, Answer The Following QuestionsDocument3 pagesTopic: The African Slave Trade Part Tw0 (1519-1860) : DIRECTIONS: Using Document 4, Answer The Following QuestionsTrap ShaNo ratings yet
- Li'l Darlin' - 06 - Trumpet in BB 1Document1 pageLi'l Darlin' - 06 - Trumpet in BB 1radivojevicivan91No ratings yet
- 10 - OE Lexicon - BorrowingDocument42 pages10 - OE Lexicon - BorrowingFrancesc Oromí SoldevilaNo ratings yet
- Music ListDocument87 pagesMusic ListJady Liu0% (1)
- Gardel - Tango - PianoDocument3 pagesGardel - Tango - PianoAndrea Villalba100% (1)
- Trashegimtar 14.09.2022Document4,102 pagesTrashegimtar 14.09.2022Mikel FeratiNo ratings yet
- The of Leone Leoni's House in Milan, The Casa Degli Omenoni: The Artist and The PublicDocument17 pagesThe of Leone Leoni's House in Milan, The Casa Degli Omenoni: The Artist and The PublicEmilehoudinNo ratings yet
- B.arch Dissertation - Praduman BajajDocument58 pagesB.arch Dissertation - Praduman BajajRiya BansalNo ratings yet
- Notas Mat 1101 D Auxiliatura II 2023Document2 pagesNotas Mat 1101 D Auxiliatura II 2023Luis Fernando Canaviri OczachoqueNo ratings yet
- MURLIPURADocument10 pagesMURLIPURAAkNo ratings yet
- Esther Miracle Morales - Copy of InstaDocument1 pageEsther Miracle Morales - Copy of Instaapi-459384088No ratings yet
- Colegio de Montalban: Physical Education Department P. E. 2 (Rhythmic Activities)Document11 pagesColegio de Montalban: Physical Education Department P. E. 2 (Rhythmic Activities)Lourence PaduitNo ratings yet
- FrozenDocument4 pagesFrozenDaniel PirirNo ratings yet
- Anderson Communities CH 10Document23 pagesAnderson Communities CH 10sophielindy23No ratings yet
- Piura D PDFDocument35 pagesPiura D PDFmtrc743707No ratings yet
- Konfirmasi Guru Penerima Insentif 2020Document58 pagesKonfirmasi Guru Penerima Insentif 2020MusliminIminNo ratings yet
- Moe Sea Students Female PDFDocument219 pagesMoe Sea Students Female PDFVictoria Kairoo0% (1)
- What Are IgorotsDocument42 pagesWhat Are IgorotsJan Jericho MentoyNo ratings yet
- AttendanceDocument16 pagesAttendanceapi-298063936No ratings yet
- Moondog - Elf DanceDocument2 pagesMoondog - Elf DancefleivNo ratings yet
- Bien Chapter17Document2 pagesBien Chapter17Bien EstrellaNo ratings yet
- ESIC Stenographer Result 2019Document19 pagesESIC Stenographer Result 2019Nishant RoyNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Ilmiah Administrasi Publik (JIAP)Document8 pagesJurnal Ilmiah Administrasi Publik (JIAP)Sy4h4d4t JogjaNo ratings yet
- Pine Pinus SP Materia Medica HerbsDocument11 pagesPine Pinus SP Materia Medica HerbsAlejandra Guerrero100% (4)
- November 2015 NLE Performance of SchoolsDocument17 pagesNovember 2015 NLE Performance of SchoolsPRC Board100% (1)