Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Peloponnesian War, Collins Military Atlas, PP 16 To 17
The Peloponnesian War, Collins Military Atlas, PP 16 To 17
Uploaded by
Om SANTOSCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Playbook: Game Desig N byDocument48 pagesPlaybook: Game Desig N byMat K100% (2)
- U.S. Foreign Policy Goals-1Document5 pagesU.S. Foreign Policy Goals-1Jasmine Clemons-Mills [STUDENT]100% (1)
- Airforce FilesDocument23 pagesAirforce FilesDanica LopezNo ratings yet
- The Seven Habits of Highly Effective People PDFDocument2 pagesThe Seven Habits of Highly Effective People PDFvakilgaurangiNo ratings yet
- Ethics Case Studies RaDocument23 pagesEthics Case Studies RaRajaDurai RamakrishnanNo ratings yet
- Peloponnesian War Timeline PDFDocument19 pagesPeloponnesian War Timeline PDFcaracallax100% (1)
- Peloponnesian WarDocument10 pagesPeloponnesian Warapi-347934096No ratings yet
- The Battle of MidwayDocument17 pagesThe Battle of Midwayapi-305725418No ratings yet
- South China Sea Paper 30 June 11 FinalDocument36 pagesSouth China Sea Paper 30 June 11 Finalroselleyap20No ratings yet
- South China Sea IssueDocument5 pagesSouth China Sea IssueShweta SinghNo ratings yet
- Eto 001Document116 pagesEto 001MrTransistorNo ratings yet
- Research Paper - Sino-Australia DilemmaDocument15 pagesResearch Paper - Sino-Australia Dilemmaggitau67_492603746No ratings yet
- 2012 Defense White PaperDocument417 pages2012 Defense White PaperSasha ChhabraNo ratings yet
- Battle of TrafalgarDocument21 pagesBattle of TrafalgarBajar CosasNo ratings yet
- Conflict South China SeaDocument12 pagesConflict South China SeaThai NinhNo ratings yet
- Preventing Military InterventionsDocument40 pagesPreventing Military InterventionsArmand G PontejosNo ratings yet
- The Strategic Need For National SecurityDocument3 pagesThe Strategic Need For National SecurityPed SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Under Pressure: FALINTIL - Forcas de Defesa de Timor-Leste.Document75 pagesUnder Pressure: FALINTIL - Forcas de Defesa de Timor-Leste.erees123No ratings yet
- Chinas Strategy in The South China SeaDocument28 pagesChinas Strategy in The South China SeaarciblueNo ratings yet
- Powell PaperDocument13 pagesPowell PaperParkerNo ratings yet
- OCD-CAR Presentation On The OPLAN KAWAYAN - EQ Readiness PlanDocument11 pagesOCD-CAR Presentation On The OPLAN KAWAYAN - EQ Readiness PlanRJay JacabanNo ratings yet
- The Flag and Heraldic Code of The Philippines (Republic Act No. 8491)Document3 pagesThe Flag and Heraldic Code of The Philippines (Republic Act No. 8491)yellow heiressNo ratings yet
- Sea Power Centre - Australia: An Effects-Based Anti-Submarine Warfare StrategyDocument52 pagesSea Power Centre - Australia: An Effects-Based Anti-Submarine Warfare StrategyRex TyrannosaurNo ratings yet
- Philippine Pivot in South China SeaDocument3 pagesPhilippine Pivot in South China SealearningboxNo ratings yet
- A Study On The Factors Influencing The Seafarers' Stress PDFDocument8 pagesA Study On The Factors Influencing The Seafarers' Stress PDFvdevivNo ratings yet
- Cwts - 02 Sep 19: Roselie R. VillanuevaDocument2 pagesCwts - 02 Sep 19: Roselie R. VillanuevaCharles GuillermoNo ratings yet
- Concept Paper On Missile Capability Acquisition ForDocument14 pagesConcept Paper On Missile Capability Acquisition Forkenneth20april100% (1)
- Battle Review of PEFTOK in KoreaDocument3 pagesBattle Review of PEFTOK in KoreaJonathanAndroTan100% (1)
- Republic of The Philippines Polytechnic University of The Philippines Maragondon Annex Alfonso CampusDocument46 pagesRepublic of The Philippines Polytechnic University of The Philippines Maragondon Annex Alfonso CampusAllyson Charissa AnsayNo ratings yet
- Ambisyon NatinDocument3 pagesAmbisyon NatinRoy VidalNo ratings yet
- ScriptDocument18 pagesScriptSanjay BabuNo ratings yet
- DND-OPA - Philippine Defense Newsletter - 008 - July 2012 IssueDocument12 pagesDND-OPA - Philippine Defense Newsletter - 008 - July 2012 IssueKagawaran Ng Tanggulang PambansaNo ratings yet
- Developing Organizations and Leaders Reading L101RC Defining Organizational Vision Dr. Kevin E. GentzlerDocument3 pagesDeveloping Organizations and Leaders Reading L101RC Defining Organizational Vision Dr. Kevin E. Gentzlerwinnie adaseNo ratings yet
- Introduction To National SecurityDocument3 pagesIntroduction To National SecurityEricson PaguiriganNo ratings yet
- Why Leadership Is So ImportantDocument1 pageWhy Leadership Is So Importantmorredenise2No ratings yet
- Policy Paper SampleDocument6 pagesPolicy Paper SampleLesnalef TerronesNo ratings yet
- The Spratly Islands DisputeDocument36 pagesThe Spratly Islands DisputeSuzaku Lee0% (1)
- Frequently Asked Questions (Faqs) : Flight Plan 2028Document5 pagesFrequently Asked Questions (Faqs) : Flight Plan 2028Trez Villaluz100% (1)
- Two Faculties of Man: Chapter 4 (Moral Decision)Document37 pagesTwo Faculties of Man: Chapter 4 (Moral Decision)kioraNo ratings yet
- Persons With DisabilityDocument3 pagesPersons With DisabilityMohamad Tomindug BauloNo ratings yet
- History Roles & Org of Naf - SC 34Document25 pagesHistory Roles & Org of Naf - SC 34tasiNo ratings yet
- Substantive Policy Issues. 02.23.2023Document9 pagesSubstantive Policy Issues. 02.23.2023Bernadette Ruth Masuli100% (1)
- Polytechnic College of Davao Del Sur, Inc. Mac Arthur Highway, Kiagot, Digos City Midterm Examination Nstp-Cwts NAME: - SCOREDocument5 pagesPolytechnic College of Davao Del Sur, Inc. Mac Arthur Highway, Kiagot, Digos City Midterm Examination Nstp-Cwts NAME: - SCOREFelix Ray DumaganNo ratings yet
- Rotc 1Document51 pagesRotc 1Ray Niel Liquisen ValenciaNo ratings yet
- South China Sea Study GuideDocument8 pagesSouth China Sea Study Guideapi-297586186No ratings yet
- Our Country Is in Grave DangerDocument75 pagesOur Country Is in Grave DangerVERA Files100% (2)
- Developing An Effective Command PhilosophyDocument7 pagesDeveloping An Effective Command PhilosophyBrandon CrowleyNo ratings yet
- Joyner, Spratly Islands Dispute ASEANDocument56 pagesJoyner, Spratly Islands Dispute ASEANLow Huai PinNo ratings yet
- Strategic Comparison of China and USA in The South China Sea by Yemeen HasanDocument10 pagesStrategic Comparison of China and USA in The South China Sea by Yemeen HasanJournal of Peace and DiplomacyNo ratings yet
- China ADIZDocument16 pagesChina ADIZ22309806773No ratings yet
- 3.1 Theory - The Evolution of HandwritingDocument33 pages3.1 Theory - The Evolution of HandwritingAidil the greatNo ratings yet
- Raymunda Moreno - The Leader's Role in Resolving Conflict and NegotiationDocument42 pagesRaymunda Moreno - The Leader's Role in Resolving Conflict and Negotiationdynamic_edge0% (1)
- Enhancing Jointness in The Arm ForcesDocument4 pagesEnhancing Jointness in The Arm ForcesElijah AramburoNo ratings yet
- World WarsDocument15 pagesWorld WarsJose VarghesNo ratings yet
- Final Paper MultiDocument17 pagesFinal Paper Multiapi-447150883100% (1)
- Valentines Day HistoryDocument5 pagesValentines Day HistorygouchshinaNo ratings yet
- Rotc LecturesDocument20 pagesRotc LecturesJhon Rey F. AmponinNo ratings yet
- Great Power Politics in Southeast Asia T PDFDocument22 pagesGreat Power Politics in Southeast Asia T PDFIrfan KhanNo ratings yet
- The Dispute in The West Philippine SeaDocument29 pagesThe Dispute in The West Philippine SeaNoreen AlbrandoNo ratings yet
- CorregidorDocument11 pagesCorregidorMadz RoñoNo ratings yet
- PelWar Timeline MaxDocument2 pagesPelWar Timeline MaxRamón CardozoNo ratings yet
- Seminarska NalogaDocument11 pagesSeminarska NalogaŠtefan MinecraftNo ratings yet
- The History of Greece, VOL 4 - William Mitford (1830)Document344 pagesThe History of Greece, VOL 4 - William Mitford (1830)WaterwindNo ratings yet
- Pericles Playbook FinalDocument44 pagesPericles Playbook FinalOliverChrisLudwig100% (1)
- Peloponnesian War Timeline PDFDocument19 pagesPeloponnesian War Timeline PDFcaracallax100% (1)
- Peter Krentz - The Thirty at Athens-Cornell University Press (1982)Document82 pagesPeter Krentz - The Thirty at Athens-Cornell University Press (1982)Igor HaberNo ratings yet
- The Peloponnesian War, Collins Military Atlas, PP 16 To 17Document1 pageThe Peloponnesian War, Collins Military Atlas, PP 16 To 17Om SANTOSNo ratings yet
- Summary of The Peloponnesian WarDocument6 pagesSummary of The Peloponnesian WarDan RankinNo ratings yet
- The Melos - Athens Dialogue.Document5 pagesThe Melos - Athens Dialogue.CristinaBahnaruNo ratings yet
- EndnotesDocument7 pagesEndnotesapi-198054641No ratings yet
- 3.7 Thucydides - The Funeral Oration of PericlesDocument5 pages3.7 Thucydides - The Funeral Oration of PericlesRocket FireNo ratings yet
- Battle of Aegospotami: PreludeDocument5 pagesBattle of Aegospotami: Preludealbert DominguezNo ratings yet
- Faction ID Name Value W&P Mil. League Dip. Oracle Ostr. Games AnyDocument5 pagesFaction ID Name Value W&P Mil. League Dip. Oracle Ostr. Games AnyRogerNo ratings yet
- Peloponnesian WarDocument14 pagesPeloponnesian Waralbert DominguezNo ratings yet
- Battle of AegospotamiDocument3 pagesBattle of AegospotamibillNo ratings yet
- Terrell DG, Peace of Nicias (Scribd)Document11 pagesTerrell DG, Peace of Nicias (Scribd)David G TerrellNo ratings yet
- History of Peloponnesian WarDocument25 pagesHistory of Peloponnesian WarGleanne Rose OrtizNo ratings yet
The Peloponnesian War, Collins Military Atlas, PP 16 To 17
The Peloponnesian War, Collins Military Atlas, PP 16 To 17
Uploaded by
Om SANTOSOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
The Peloponnesian War, Collins Military Atlas, PP 16 To 17
The Peloponnesian War, Collins Military Atlas, PP 16 To 17
Uploaded by
Om SANTOSCopyright:
Available Formats
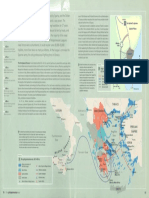
the peloponnesian war
431 Bc The war between the Peloponnesian League, led by Sparta, and the Delian
431 to 404 Bc
loss of 160 Athenian and 56 allied triremes in the confined waters
Peloponnesian War starts
of Syracuse harbour equalised the naval forces available to both — Labdalum
League, led by Athens, pitted a land power against a sea power. The
429 Bc sides for the first time in 50 years. at fort captured by Spartans
Athenian naval victory at asymmetric nature of the conflict helped prolong hostilities for 27 years. Sparta was now able to establish a series of fleets in western
Naupactus
Asia Minor that contested Athens’ sea lines of communication \ Fpipolae Plateau
Athens collected tribute from allies who were bound to her by treaty, and across the Aegean and the Hellespont. Although Athens had lost
425 Bc
Athens captures Sphacteria. their fleet of 300 triremes allowed them to win the majority of the naval naval superiority and had suffered a series of political upheavals at
Spartan peace overtures home, its superior tactical prowess still enabled its navy to win a
rebuffed battles, even when outnumbered. Although the Peloponnesian League's series of naval battles over an eight-year period. Yet these were
422 Bc naval forces were outnumbered, It could muster some 30,000-35,000 not enough; Athenian allies rebelled and ceased paying tribute,
further weakening the Athenian navy. In 405 Bc the Athenian fleet,
Spartan victory at Amphipolis.
Brasidas and Cleon both killed hoplites, more than twice as many as Athens. At the league’s core was the maintaining its eastern sea lanes in the Hellespont, was destroyed
Spartan army, the only professional fighting force in Greece. while beached and Athens, faced with imminent starvation, sur-
421 Bc rendered a year later.
negotiation of Peace of Nicias
(new Athenian leader]
The first phase of the war, the Archidamian War (431-421 Bc], saw the Spartan army invade Attica each year, while
2 At their third attempt, the Syracusan army
the Corinthian navy attempted to break out of the Gulf of Corinth. The Athenian admiral, Phormio, operating from
418 Bc extended a defensive wall past the
2 siege of syracuse,
Battle of Mantinea: Sparta Naupactus, defeated a succession of Corinthian sorties and prevented Corinth from maintaining its economic links Athenian siege lines, preventing the total
defeats Argive-led army to colonies in Italy. Athens established a base at Pylos on the western coast of the Peloponnese. Sparta landed a blockade of the city [map right). The 415-413 Bc
Spartan general Gylippus then trapped the
small army on an adjacent island (Sphacteria), but Athenian naval forces isolated them. After a series of failed nego- (|= Syracusans
407 Bc tiations, Athenian naval forces were able in 425 Bc to land superior Athenian land forces on to the island, destroying
Athenian fleet within the great harbour
[= Athenians
Spartan fleet wins naval battle and the besiegers found themselves cut
the majority of the Spartan force and capturing the survivors. = Spartan advance
off Notium off. The surrender and enslavement of the
sae Athenian walls
Negotiations followed, culminating in the Peace of Nicias in 421 Bc, but it was no more than an armistice. Many of expeditionary force was a catastrophe for
Athens and its fleet never recovered its
«eee Syracusan walls
406 Bc Sparta’s allies became disaffected and formed a new league with Argos. At the Battle of Mantinea (418 Bc), Sparta won Plemmyrium
Athenians win victory at qualitative advantage.
the one and only large hoplite battle of the Peloponnesian War when it defeated an Argive-led army that included an
Arginusae, and again decline
offer of peace Athenian contingent. This victory, plus the Athenian invasion of
Sicily, prompted a renewal of hostilities.
405 Bc In 415 Bc, Athens launched a pre-emptive attack on
Athenian fleet destroyed while
beached at Hellespont
Syracuse, a potential Spartan ally. The fact that the Athenians THRACE
could launch the original expedition and subsequently reinforce
404 Bc
it without hindrance from the Peloponnesian League testifies ACG
Fi det tc bidamnus
Athens surrenders to their control over the western sea routes to Sicily. But the Seq
PERSIAN
4a The whole Greek world became involved in the prolonged war between EMPIRE
_ Athens and Sparta from 431 sc (map right). Sparta was stronger on ‘Arginusae Islands
land, but Athens kept firm control of the sea. After ten years an uneasy Tyrrhenian
peace was made (421 Bc], but when Athens lost almost its entire fleet Sea © Sardes
in Sicily, the Spartans pressed home their advantage. Even so, it was IONIA
only with considerable naval and financial support from the Persians
lotium 407 BC 4.
that they were able to overcome the Athenian navy. p >. 7
3
‘lonian Sea a | z CS oe
1 the peloponnesian war, 431-404 sc | | &
2
ee Athens and members of
the Delian League ® allies of Sparta in Magna Graecia
[| ally of Athens ===» Athenian campaigns
fee Sparta and allies =<» Spartan campaigns : faken by
\a Athens 416
|_| neutral states >< Athenian victory
3
@ _allies of Athens in Magna Graecia >< Spartan victory ae e A<Cythera |
(taken by Athens 424 BC)
16 the peloponnesian war
You might also like
- Playbook: Game Desig N byDocument48 pagesPlaybook: Game Desig N byMat K100% (2)
- U.S. Foreign Policy Goals-1Document5 pagesU.S. Foreign Policy Goals-1Jasmine Clemons-Mills [STUDENT]100% (1)
- Airforce FilesDocument23 pagesAirforce FilesDanica LopezNo ratings yet
- The Seven Habits of Highly Effective People PDFDocument2 pagesThe Seven Habits of Highly Effective People PDFvakilgaurangiNo ratings yet
- Ethics Case Studies RaDocument23 pagesEthics Case Studies RaRajaDurai RamakrishnanNo ratings yet
- Peloponnesian War Timeline PDFDocument19 pagesPeloponnesian War Timeline PDFcaracallax100% (1)
- Peloponnesian WarDocument10 pagesPeloponnesian Warapi-347934096No ratings yet
- The Battle of MidwayDocument17 pagesThe Battle of Midwayapi-305725418No ratings yet
- South China Sea Paper 30 June 11 FinalDocument36 pagesSouth China Sea Paper 30 June 11 Finalroselleyap20No ratings yet
- South China Sea IssueDocument5 pagesSouth China Sea IssueShweta SinghNo ratings yet
- Eto 001Document116 pagesEto 001MrTransistorNo ratings yet
- Research Paper - Sino-Australia DilemmaDocument15 pagesResearch Paper - Sino-Australia Dilemmaggitau67_492603746No ratings yet
- 2012 Defense White PaperDocument417 pages2012 Defense White PaperSasha ChhabraNo ratings yet
- Battle of TrafalgarDocument21 pagesBattle of TrafalgarBajar CosasNo ratings yet
- Conflict South China SeaDocument12 pagesConflict South China SeaThai NinhNo ratings yet
- Preventing Military InterventionsDocument40 pagesPreventing Military InterventionsArmand G PontejosNo ratings yet
- The Strategic Need For National SecurityDocument3 pagesThe Strategic Need For National SecurityPed SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Under Pressure: FALINTIL - Forcas de Defesa de Timor-Leste.Document75 pagesUnder Pressure: FALINTIL - Forcas de Defesa de Timor-Leste.erees123No ratings yet
- Chinas Strategy in The South China SeaDocument28 pagesChinas Strategy in The South China SeaarciblueNo ratings yet
- Powell PaperDocument13 pagesPowell PaperParkerNo ratings yet
- OCD-CAR Presentation On The OPLAN KAWAYAN - EQ Readiness PlanDocument11 pagesOCD-CAR Presentation On The OPLAN KAWAYAN - EQ Readiness PlanRJay JacabanNo ratings yet
- The Flag and Heraldic Code of The Philippines (Republic Act No. 8491)Document3 pagesThe Flag and Heraldic Code of The Philippines (Republic Act No. 8491)yellow heiressNo ratings yet
- Sea Power Centre - Australia: An Effects-Based Anti-Submarine Warfare StrategyDocument52 pagesSea Power Centre - Australia: An Effects-Based Anti-Submarine Warfare StrategyRex TyrannosaurNo ratings yet
- Philippine Pivot in South China SeaDocument3 pagesPhilippine Pivot in South China SealearningboxNo ratings yet
- A Study On The Factors Influencing The Seafarers' Stress PDFDocument8 pagesA Study On The Factors Influencing The Seafarers' Stress PDFvdevivNo ratings yet
- Cwts - 02 Sep 19: Roselie R. VillanuevaDocument2 pagesCwts - 02 Sep 19: Roselie R. VillanuevaCharles GuillermoNo ratings yet
- Concept Paper On Missile Capability Acquisition ForDocument14 pagesConcept Paper On Missile Capability Acquisition Forkenneth20april100% (1)
- Battle Review of PEFTOK in KoreaDocument3 pagesBattle Review of PEFTOK in KoreaJonathanAndroTan100% (1)
- Republic of The Philippines Polytechnic University of The Philippines Maragondon Annex Alfonso CampusDocument46 pagesRepublic of The Philippines Polytechnic University of The Philippines Maragondon Annex Alfonso CampusAllyson Charissa AnsayNo ratings yet
- Ambisyon NatinDocument3 pagesAmbisyon NatinRoy VidalNo ratings yet
- ScriptDocument18 pagesScriptSanjay BabuNo ratings yet
- DND-OPA - Philippine Defense Newsletter - 008 - July 2012 IssueDocument12 pagesDND-OPA - Philippine Defense Newsletter - 008 - July 2012 IssueKagawaran Ng Tanggulang PambansaNo ratings yet
- Developing Organizations and Leaders Reading L101RC Defining Organizational Vision Dr. Kevin E. GentzlerDocument3 pagesDeveloping Organizations and Leaders Reading L101RC Defining Organizational Vision Dr. Kevin E. Gentzlerwinnie adaseNo ratings yet
- Introduction To National SecurityDocument3 pagesIntroduction To National SecurityEricson PaguiriganNo ratings yet
- Why Leadership Is So ImportantDocument1 pageWhy Leadership Is So Importantmorredenise2No ratings yet
- Policy Paper SampleDocument6 pagesPolicy Paper SampleLesnalef TerronesNo ratings yet
- The Spratly Islands DisputeDocument36 pagesThe Spratly Islands DisputeSuzaku Lee0% (1)
- Frequently Asked Questions (Faqs) : Flight Plan 2028Document5 pagesFrequently Asked Questions (Faqs) : Flight Plan 2028Trez Villaluz100% (1)
- Two Faculties of Man: Chapter 4 (Moral Decision)Document37 pagesTwo Faculties of Man: Chapter 4 (Moral Decision)kioraNo ratings yet
- Persons With DisabilityDocument3 pagesPersons With DisabilityMohamad Tomindug BauloNo ratings yet
- History Roles & Org of Naf - SC 34Document25 pagesHistory Roles & Org of Naf - SC 34tasiNo ratings yet
- Substantive Policy Issues. 02.23.2023Document9 pagesSubstantive Policy Issues. 02.23.2023Bernadette Ruth Masuli100% (1)
- Polytechnic College of Davao Del Sur, Inc. Mac Arthur Highway, Kiagot, Digos City Midterm Examination Nstp-Cwts NAME: - SCOREDocument5 pagesPolytechnic College of Davao Del Sur, Inc. Mac Arthur Highway, Kiagot, Digos City Midterm Examination Nstp-Cwts NAME: - SCOREFelix Ray DumaganNo ratings yet
- Rotc 1Document51 pagesRotc 1Ray Niel Liquisen ValenciaNo ratings yet
- South China Sea Study GuideDocument8 pagesSouth China Sea Study Guideapi-297586186No ratings yet
- Our Country Is in Grave DangerDocument75 pagesOur Country Is in Grave DangerVERA Files100% (2)
- Developing An Effective Command PhilosophyDocument7 pagesDeveloping An Effective Command PhilosophyBrandon CrowleyNo ratings yet
- Joyner, Spratly Islands Dispute ASEANDocument56 pagesJoyner, Spratly Islands Dispute ASEANLow Huai PinNo ratings yet
- Strategic Comparison of China and USA in The South China Sea by Yemeen HasanDocument10 pagesStrategic Comparison of China and USA in The South China Sea by Yemeen HasanJournal of Peace and DiplomacyNo ratings yet
- China ADIZDocument16 pagesChina ADIZ22309806773No ratings yet
- 3.1 Theory - The Evolution of HandwritingDocument33 pages3.1 Theory - The Evolution of HandwritingAidil the greatNo ratings yet
- Raymunda Moreno - The Leader's Role in Resolving Conflict and NegotiationDocument42 pagesRaymunda Moreno - The Leader's Role in Resolving Conflict and Negotiationdynamic_edge0% (1)
- Enhancing Jointness in The Arm ForcesDocument4 pagesEnhancing Jointness in The Arm ForcesElijah AramburoNo ratings yet
- World WarsDocument15 pagesWorld WarsJose VarghesNo ratings yet
- Final Paper MultiDocument17 pagesFinal Paper Multiapi-447150883100% (1)
- Valentines Day HistoryDocument5 pagesValentines Day HistorygouchshinaNo ratings yet
- Rotc LecturesDocument20 pagesRotc LecturesJhon Rey F. AmponinNo ratings yet
- Great Power Politics in Southeast Asia T PDFDocument22 pagesGreat Power Politics in Southeast Asia T PDFIrfan KhanNo ratings yet
- The Dispute in The West Philippine SeaDocument29 pagesThe Dispute in The West Philippine SeaNoreen AlbrandoNo ratings yet
- CorregidorDocument11 pagesCorregidorMadz RoñoNo ratings yet
- PelWar Timeline MaxDocument2 pagesPelWar Timeline MaxRamón CardozoNo ratings yet
- Seminarska NalogaDocument11 pagesSeminarska NalogaŠtefan MinecraftNo ratings yet
- The History of Greece, VOL 4 - William Mitford (1830)Document344 pagesThe History of Greece, VOL 4 - William Mitford (1830)WaterwindNo ratings yet
- Pericles Playbook FinalDocument44 pagesPericles Playbook FinalOliverChrisLudwig100% (1)
- Peloponnesian War Timeline PDFDocument19 pagesPeloponnesian War Timeline PDFcaracallax100% (1)
- Peter Krentz - The Thirty at Athens-Cornell University Press (1982)Document82 pagesPeter Krentz - The Thirty at Athens-Cornell University Press (1982)Igor HaberNo ratings yet
- The Peloponnesian War, Collins Military Atlas, PP 16 To 17Document1 pageThe Peloponnesian War, Collins Military Atlas, PP 16 To 17Om SANTOSNo ratings yet
- Summary of The Peloponnesian WarDocument6 pagesSummary of The Peloponnesian WarDan RankinNo ratings yet
- The Melos - Athens Dialogue.Document5 pagesThe Melos - Athens Dialogue.CristinaBahnaruNo ratings yet
- EndnotesDocument7 pagesEndnotesapi-198054641No ratings yet
- 3.7 Thucydides - The Funeral Oration of PericlesDocument5 pages3.7 Thucydides - The Funeral Oration of PericlesRocket FireNo ratings yet
- Battle of Aegospotami: PreludeDocument5 pagesBattle of Aegospotami: Preludealbert DominguezNo ratings yet
- Faction ID Name Value W&P Mil. League Dip. Oracle Ostr. Games AnyDocument5 pagesFaction ID Name Value W&P Mil. League Dip. Oracle Ostr. Games AnyRogerNo ratings yet
- Peloponnesian WarDocument14 pagesPeloponnesian Waralbert DominguezNo ratings yet
- Battle of AegospotamiDocument3 pagesBattle of AegospotamibillNo ratings yet
- Terrell DG, Peace of Nicias (Scribd)Document11 pagesTerrell DG, Peace of Nicias (Scribd)David G TerrellNo ratings yet
- History of Peloponnesian WarDocument25 pagesHistory of Peloponnesian WarGleanne Rose OrtizNo ratings yet