Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Table of English Tenses
Table of English Tenses
Uploaded by
katerynavelOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Table of English Tenses
Table of English Tenses
Uploaded by
katerynavelCopyright:
Available Formats
Table of English Tenses
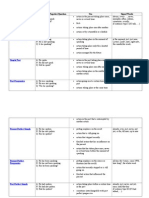
tense Affirmative/Negative/Questio n
Use action in the present taking place once, never or several times facts actions taking place one after another
Signal Words
Simple Present
A: He speaks. N: He does not speak. Q: Does he speak?
Present Progressive
A: He is speaking. N: He is not speaking. Q: Is he speaking?
always, every , never, normally, often, seldom, sometimes, usually if sentences action set by a type I (If I talk, ) timetable or schedule action taking place in the moment of at the speaking moment, just, action taking just now, place only for Listen!, a limited Look!, now, period of time right now action arranged for the future action in the past taking place once, yesterday, 2 never or minutes ago, several times in 1990, the actions taking other day, place one after last Friday another if sentence type II (If I action taking talked, ) place in the middle of another action action going on when, while, at a certain as long as
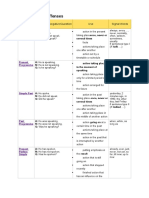
Simple Past
A: He spoke. N: He did not speak. Q: Did he speak?
Past Progressive A: He was speaking. N: He was not speaking.
time in the past actions taking place at the same time action in the past that is interrupted by another action putting emphasis on the result action that is still going on action that stopped recently finished action that has an influence on the present action that has taken place once, never or several times before the moment of speaking putting emphasis on the course or duration (not the result) action that recently stopped or is still going on finished action that influenced the present action taking place before a certain time in the past
Q: Was he speaking?
Present Perfect Simple
A: He has spoken. N: He has not spoken. Q: Has he spoken?
already, ever, just, never, not yet, so far, till now, up to now
Present Perfect Progressive
A: He has been speaking. N: He has not been speaking. Q: Has he been speaking?
all day, for 4 years, since 1993, how long?, the whole week
Past Perfect Simple
A: He had spoken. N: He had not spoken. Q: Had he spoken?
already, just, never, not yet, once, until that day
Past Perfect Progressive
A: He had been speaking. N: He had not been speaking. Q: Had he been speaking?
sometimes interchangeabl e with past perfect if sentence progressive type III (If I had talked, ) putting emphasis only on the fact (not the duration) action taking place before a certain time in the past sometimes interchangeabl for, since, the e with past whole day, perfect simple all day putting emphasis on the duration or course of an action in a year, next , tomorrow If-Satz Typ I (If you ask her, she will help you.) assumption: I assumption think, with regard to probably, the future perhaps decision made for the future in one year, next week, conclusion tomorrow with regard to the future action that is in one year, going on at a next week, certain time in tomorrow the future action in the future that cannot be influenced spontaneous decision
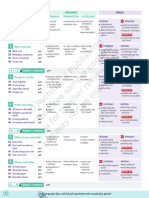
Future I Simple
A: He will speak. N: He will not speak. Q: Will he speak?
Future I Simple (going to) Future I Progressive
A: He is going to speak. N: He is not going to speak. Q: Is he going to speak? A: He will be speaking. N: He will not be speaking. Q: Will he be speaking?
A: He will have spoken. Future II Simple N: He will not have spoken. Q: Will he have spoken?
Future II Progressive
A: He will have been speaking. N: He will not have been speaking. Q: Will he have been speaking?
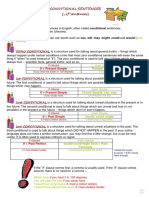
Conditional I Simple
A: He would speak. N: He would not speak. Q: Would he speak?
action that is sure to happen in the near future action that will be finished at a by Monday, certain time in in a week the future action taking place before a certain time in for , the the future last couple of hours, all day putting long emphasis on the course of an action if sentences action that type II might take (If I were place you, I would go home.) action that might take place putting emphasis on the course / duration of the action if sentences action that type III might have (If I had seen taken place in that, I would the past have helped.) action that might have taken place in the past puts emphasis on the course / duration of the action
Conditional I Progressive
A: He would be speaking. N: He would not be speaking. Q: Would he be speaking?
Conditional II Simple
A: He would have spoken. N: He would not have spoken. Q: Would he have spoken?
Conditional II Progressive
A: He would have been speaking. N: He would not have been speaking. Q: Would he have been speaking?
You might also like
- English TensesDocument4 pagesEnglish TensesAgung ArdyantoNo ratings yet
- CELTA Assignment 2 GrammarDocument3 pagesCELTA Assignment 2 GrammarOlga ShiliaevaNo ratings yet
- 28 Present Continuous Tense - Turkish Language LessonsDocument4 pages28 Present Continuous Tense - Turkish Language LessonsAlongMXNo ratings yet
- Quranic Beginner Arabic GrammarDocument74 pagesQuranic Beginner Arabic GrammarAl Huda100% (2)
- Timpuri LeDocument3 pagesTimpuri LemadybyaNo ratings yet
- Tenses Chart With Examples, Use and Signal WordsDocument2 pagesTenses Chart With Examples, Use and Signal Wordssfiedlerc100% (1)
- Table of English TensesDocument3 pagesTable of English Tensesiuliana13No ratings yet
- English Tenses SummaryDocument2 pagesEnglish Tenses SummaryRedi BylekNo ratings yet
- English TensesDocument2 pagesEnglish TensesGustavo SteffenNo ratings yet
- Timpurile in EnglezaDocument3 pagesTimpurile in Englezavladis05No ratings yet
- TenseDocument3 pagesTenseKiki MulqiahNo ratings yet
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Questio N Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDocument5 pagesTense Affirmative/Negative/Questio N Use Signal Words: Simple PresentFitrie RnaNo ratings yet
- Table of English TensesDocument4 pagesTable of English TensesKashif WakeelNo ratings yet
- Table of English TensesDocument3 pagesTable of English TensesGonzalo AstorgaNo ratings yet
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDocument4 pagesTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDenis SăndicăNo ratings yet
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDocument3 pagesTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentSorin Mihai VassNo ratings yet
- Simple Present: I Talk, )Document3 pagesSimple Present: I Talk, )Krupesh PatelNo ratings yet
- Table of English TensesDocument2 pagesTable of English TensesMariana Crăciun100% (1)
- TenseDocument3 pagesTenseMădălina RădulescuNo ratings yet
- Verb TenseDocument1 pageVerb TenseDre GrossingNo ratings yet
- Table of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDocument3 pagesTable of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsAndrea Paredes GuerreroNo ratings yet
- Table TensesDocument4 pagesTable TensesmariminniNo ratings yet
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDocument3 pagesTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentLyana LorenzaNo ratings yet
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDocument3 pagesTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentAdaNo ratings yet
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDocument3 pagesTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentVeronica BurdujaNo ratings yet
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Questi On Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDocument3 pagesTense Affirmative/Negative/Questi On Use Signal Words: Simple PresentRuxanda RusuNo ratings yet
- Tabla TimpurilorDocument5 pagesTabla TimpurilorAndreea BirladeanuNo ratings yet
- Table of English TensesDocument3 pagesTable of English TensesCristina-Raluca RuşeţNo ratings yet
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDocument3 pagesTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentHazel-mae LabradaNo ratings yet
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDocument4 pagesTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentXorianopoulou SofiaNo ratings yet
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDocument3 pagesTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentJavier J SalazarNo ratings yet
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDocument3 pagesTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentPavlina HaralampievaNo ratings yet
- Table of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDocument3 pagesTable of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsAbdulaziz2012No ratings yet
- Table of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDocument3 pagesTable of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsTaris TallasaNo ratings yet
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Questi On Use Signal Words: Present SimpleDocument4 pagesTense Affirmative/Negative/Questi On Use Signal Words: Present SimpleRobertaNo ratings yet
- TensesDocument4 pagesTensesZandaNo ratings yet
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: PresentDocument3 pagesTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: PresentRaj KumarNo ratings yet
- Table of English Tenses: Tense Use Signal WordsDocument4 pagesTable of English Tenses: Tense Use Signal WordsAdriana MuresanNo ratings yet
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDocument3 pagesTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple Presentgulzar72No ratings yet
- Table of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDocument6 pagesTable of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsRatmi 'Bundanya Rena'No ratings yet
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDocument3 pagesTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentMariana PasatNo ratings yet
- Table of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDocument4 pagesTable of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Wordsanon1000No ratings yet
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: PresentDocument3 pagesTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Presentdddiana21No ratings yet
- Summary Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDocument1 pageSummary Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsCTMundialNo ratings yet
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDocument3 pagesTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Wordshpeter195798No ratings yet
- English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDocument3 pagesEnglish Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsAndreaNo ratings yet
- Table of English TensesDocument4 pagesTable of English Tensesdieba105No ratings yet
- Verb Tense Overview With ExamplesDocument5 pagesVerb Tense Overview With ExamplesSaulo ZunigaNo ratings yet
- TensesDocument5 pagesTensesGanesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Table of English TensesDocument5 pagesTable of English TensesMaria CristianNo ratings yet
- Simple Present: TalkedDocument4 pagesSimple Present: TalkedDangVanTamNo ratings yet
- Chart of English TensesDocument2 pagesChart of English TensesNorafiqah Rifhan RamlanNo ratings yet
- Table of English TensesDocument3 pagesTable of English TensesShoba DevarajanNo ratings yet
- Table of English TensesDocument3 pagesTable of English Tensesart.delormasNo ratings yet
- Table of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDocument4 pagesTable of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsthirtysecondsmarsNo ratings yet
- Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDocument3 pagesTenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Wordsyingying1102No ratings yet
- Chart of Verb TensesDocument4 pagesChart of Verb TensesRichard Niilo BettsNo ratings yet
- Tense Positive/negative/question Usage Signal WordsDocument4 pagesTense Positive/negative/question Usage Signal WordsMyriam GGoNo ratings yet
- Tenses: Use and Meaning: by Carlos Ojeda, 2010Document19 pagesTenses: Use and Meaning: by Carlos Ojeda, 2010Un Tal CarlosNo ratings yet
- Simple Present: I Talk, )Document2 pagesSimple Present: I Talk, )romina5_13No ratings yet
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDocument1 pageTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentVlasta LoncaricNo ratings yet
- Building A Large Annotated Corpus of English: The Penn TreebankDocument19 pagesBuilding A Large Annotated Corpus of English: The Penn TreebankMareike KläneNo ratings yet
- Gerund and To + Infi NitiveDocument1 pageGerund and To + Infi NitiveFelipe Lipe SteinerNo ratings yet
- Temario Examen InglesDocument1 pageTemario Examen InglesROSA ALEJANDRA ROMERO VERANo ratings yet
- I From II Form III Form of VerbDocument4 pagesI From II Form III Form of VerbDeepak GulwaniNo ratings yet
- Conventions 12.4.2022Document2 pagesConventions 12.4.2022Ameer AljamriNo ratings yet
- Cumulative Unit 2 Exam - v2 PDFDocument4 pagesCumulative Unit 2 Exam - v2 PDFHorotad JacksonNo ratings yet
- 14 Grammar Myths Your English Teacher Lied To You AboutDocument11 pages14 Grammar Myths Your English Teacher Lied To You AboutPaola PanniuraNo ratings yet
- A1 Writing Assessment 2 My Au Pair ExperienceDocument4 pagesA1 Writing Assessment 2 My Au Pair Experienceraulortiz11No ratings yet
- Morphological AnalysisDocument3 pagesMorphological AnalysisFalakNo ratings yet
- Unit 4: Extra Practice 2Document2 pagesUnit 4: Extra Practice 2MaamCRNo ratings yet
- 103 - The Difference Between Report and Explanation Text - KhansaDocument2 pages103 - The Difference Between Report and Explanation Text - KhansaKhansa Sweet7No ratings yet
- Personal Best A2 Students Book US Edition SSDocument2 pagesPersonal Best A2 Students Book US Edition SSVivian Díaz LópezNo ratings yet
- The Literal or Primary Meaning of A Word, in Contrast To The Feelings or Ideas That The Word SuggestsDocument3 pagesThe Literal or Primary Meaning of A Word, in Contrast To The Feelings or Ideas That The Word SuggestsMiguel Angelo UmayamNo ratings yet
- Adjectives Adverbs PrepositionDocument12 pagesAdjectives Adverbs PrepositionAbdul Aziz RNo ratings yet
- Change The Following Active Sentences Into Passive. Change The Following Active Sentences Into PassiveDocument1 pageChange The Following Active Sentences Into Passive. Change The Following Active Sentences Into PassivekracelNo ratings yet
- Descriptive LinguisticsDocument19 pagesDescriptive LinguisticsAlviano Prastio100% (6)
- Business English: UNIT 1: You and Your CompanyDocument7 pagesBusiness English: UNIT 1: You and Your CompanyHenoc MagalhaesNo ratings yet
- Doc2EJERCICIOS REPASO ARQUITECTURA INFORMATICADocument14 pagesDoc2EJERCICIOS REPASO ARQUITECTURA INFORMATICAvictorNo ratings yet
- Top Notch Fundamentals-2Document2 pagesTop Notch Fundamentals-2Derix SánchezNo ratings yet
- Material DemonstrativeDocument3 pagesMaterial Demonstrativejorge manuel pantoja llanosNo ratings yet
- Tiempos Verbales en InglesDocument4 pagesTiempos Verbales en InglesGabriela CastilloNo ratings yet
- Ficha Reported SpeechDocument2 pagesFicha Reported Speechelsamax100% (1)
- Learn 40 Common Irregular Verbs in English PDFDocument1 pageLearn 40 Common Irregular Verbs in English PDFLuis Carlos Romero ReyesNo ratings yet
- Conditional-Easy ExplanationDocument1 pageConditional-Easy ExplanationFernanda Shine SantosNo ratings yet
- Unit 7Document17 pagesUnit 7api-263631162No ratings yet
- Summer Vacation Homework Grade 4Document11 pagesSummer Vacation Homework Grade 4Pauline YuNo ratings yet
- Gótico 101Document84 pagesGótico 101Agustín SartorNo ratings yet