Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Article 1162 Key Notes
Article 1162 Key Notes
Uploaded by
Eliza Jayne Princess VizcondeOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Article 1162 Key Notes
Article 1162 Key Notes
Uploaded by
Eliza Jayne Princess VizcondeCopyright:
Available Formats
Article 1162 Key Notes
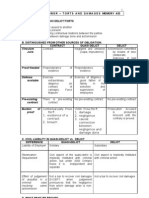
*Article 1162. Obligations derived from quasi-delicts shall be governed by the provisions of
Chapter 2, Title XVII of this Book, and by special laws.
Article 1162
- Obligations arising from quasi-delicts or torts
- act or omission which causes damage to another…there being fault or negligence
- no pre-existing contractual relation between parties
Quasi-Delict
- an act na nagawa from negligence or kapabayaan
- Another terms: (1) Torts, (2) Culpa
- a person who commits a tort (civil wrong), either intentionally or through negligence
Tortfeasor
- nakagawa ng kapabayaan
(1) There must be an act or omission
(2) There must be fault or negligence
(3) There must be damage caused
Requisites of Quasi-Delict
(4) There must be a direct relation or connection of cause and effect between the act or omission
and the damage
(5) There is no pre-existing contractual relation between the parties
(A) While playing softball with his friends, X broke the window glass of Y, his neighbor. The
accident would not have happened had they played a little farther from the house of Y.
- In this case, X is under obligation to pay the damage caused to Y by his act although there is no
pre-existing contractual relation between them because he is guilty of mere fault or negligence
without any criminal intent.
Example: Obligations arising (B) The father and, in case of his death or incapacity, the mother, are responsible for the
from Quasi-Delict damages caused by the minor children who live in their company.
- Minor Children: Nagcause/Source ng negligence pero hindi sila yung may obligation or liable to that
certain action
(C) The owners and manages or an establishment or enterprise are likewise responsible for
damages caused by their employees in the service of the branches in which the latter are
employed or on the occasion of their functions.
Crime Quasi-Delict
Criminal or malicious intent or criminal
Only negligence
negligence
Punishment Indemnification of the offended party
Affects public interest Concerns private interest
Two Liabilities: (1) Criminal Liability, (2) Civil
Only Civil Liability
Crimes vs. Quasi-Delicts Liability
Criminal Liability cannot be compromised or The liability for quasi-delict can be
settled by the parties themselves compromised as any other civil liability
The fault or negligence of the defendant need
The guilt of the accused must be proved
only be proved by preponderance (i.e.,
beyond reasonable doubt
superior or greater weight) of evidence.
You might also like
- Tenancy AgreementDocument11 pagesTenancy AgreementKhairudi96% (28)
- Sample Production AgreementDocument2 pagesSample Production AgreementCassandra Cooper100% (2)
- Western Express PDFDocument13 pagesWestern Express PDFAlicia RobertsNo ratings yet
- Mayor Vs TiuDocument1 pageMayor Vs TiuLara Cacal50% (4)
- Trust Act-IndianDocument40 pagesTrust Act-IndianArunaMLNo ratings yet
- 4 Sale of Condominium UnitDocument2 pages4 Sale of Condominium UnitAnonymous 3imVF9eR0% (1)
- 1161-1162 Obli Reviewer and NotesDocument3 pages1161-1162 Obli Reviewer and NoteselliNo ratings yet
- OBLIGATIONDocument2 pagesOBLIGATIONSophia VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- An Action or Omission That Constitutes An Offense That May Be Prosecuted by The State and Is Punishable by LawDocument5 pagesAn Action or Omission That Constitutes An Offense That May Be Prosecuted by The State and Is Punishable by LawAmer Lucman IIINo ratings yet
- Torts and DamagesDocument32 pagesTorts and DamagesTess Legaspi100% (3)
- Torts and Damages: San Beda College of LawDocument29 pagesTorts and Damages: San Beda College of LawRégine NaldoNo ratings yet
- Obl Icon Reviewer EditedDocument35 pagesObl Icon Reviewer EditedSage LingatongNo ratings yet
- Obli ConDocument6 pagesObli Conirenedumayaca18No ratings yet
- GDocument28 pagesGGeds DNo ratings yet
- RFBT - Law On ObligationsDocument11 pagesRFBT - Law On ObligationsVianca MaquilanNo ratings yet
- Exception: Contract of Carriage (In Here, The Basis of TheDocument20 pagesException: Contract of Carriage (In Here, The Basis of TheCelestino Law100% (1)
- 7-TORTS AND DAMAGES (San Beda) EditedDocument24 pages7-TORTS AND DAMAGES (San Beda) EditedLeayza Sta Maria CarreonNo ratings yet
- Torts and Damages 2011Document42 pagesTorts and Damages 2011emmaniago0829No ratings yet
- Law ReviewerDocument10 pagesLaw ReviewerDcimasaNo ratings yet
- Law ReviewerDocument10 pagesLaw ReviewerGrachelle SerranoNo ratings yet
- OBLICON REVIEWER Article 1162Document1 pageOBLICON REVIEWER Article 1162Oh SeluringNo ratings yet
- Torts DamagesDocument30 pagesTorts Damagessophie meNo ratings yet
- Torts Midterm Exam ReviewerDocument16 pagesTorts Midterm Exam ReviewerMary Ann LeuterioNo ratings yet
- Torts MidtermDocument51 pagesTorts MidtermJenely Joy Areola-TelanNo ratings yet
- RFBT NotesDocument8 pagesRFBT NotesMay Grethel Joy PeranteNo ratings yet
- ARTICLE 1156: 1. Negotiorum GestioDocument11 pagesARTICLE 1156: 1. Negotiorum GestioDell OleahNo ratings yet
- Torts Damages LectureDocument29 pagesTorts Damages LectureCharlemagne Perez PapioNo ratings yet
- San Beda Red Book 2018, Personal Notes,,, by Lee Anne Yabut 1Document32 pagesSan Beda Red Book 2018, Personal Notes,,, by Lee Anne Yabut 1jon jonNo ratings yet
- Torts and Damages: San Beda College of LawDocument31 pagesTorts and Damages: San Beda College of LawMaryjoy MelchorNo ratings yet
- Torts and DamagesDocument31 pagesTorts and DamagesMoncherie ColcolNo ratings yet
- Torts and Damages NotesDocument32 pagesTorts and Damages NotesNikki TanNo ratings yet
- Obligations and Contracts: San Beda College of LawDocument29 pagesObligations and Contracts: San Beda College of LawCarmela Lopez100% (1)
- OBLIGATIONS and CONTRACTSDocument34 pagesOBLIGATIONS and CONTRACTSKristine Ritchel TorresNo ratings yet
- Crim MidtermsDocument30 pagesCrim MidtermsMia UnabiaNo ratings yet
- Obligation and ContractsDocument28 pagesObligation and ContractsBryan Vince LeeNo ratings yet
- Notes and Reviewer - Obligation 1160Document3 pagesNotes and Reviewer - Obligation 1160elliNo ratings yet
- Requisites of Quasi-DelictDocument3 pagesRequisites of Quasi-DelictGiah MesionaNo ratings yet
- Quasi-Delict (January 6, 20180Document156 pagesQuasi-Delict (January 6, 20180Kim Boyles FuentesNo ratings yet
- Torts PDFDocument31 pagesTorts PDFSime SuanNo ratings yet
- Juridical Necessity Means That The Court May BeDocument9 pagesJuridical Necessity Means That The Court May BeAngel CastroNo ratings yet
- Notes On Tolentino - JheiDocument14 pagesNotes On Tolentino - JheiAngel DizonNo ratings yet
- Civillaw (Torts) Memoryaid A B O 2002Document14 pagesCivillaw (Torts) Memoryaid A B O 2002Maricar Corina CanayaNo ratings yet
- Obligations and ContractsDocument28 pagesObligations and ContractsEdsel Ian S. FuentesNo ratings yet
- Torts Memory Aid AteneoDocument11 pagesTorts Memory Aid AteneoStGabrielleNo ratings yet
- OBLICON Chapter IDocument3 pagesOBLICON Chapter IJayel Yasmin Albie SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Civil Code - Article 1156-162Document2 pagesCivil Code - Article 1156-162chubaboo67% (12)
- Mod12Wk14 TortsDamagesDocument36 pagesMod12Wk14 TortsDamagesJanine ChloeNo ratings yet
- Torts Quasi DelictsDocument10 pagesTorts Quasi DelictsAlex GraciaNo ratings yet
- Obligations and Contracts: San Beda College of LawDocument32 pagesObligations and Contracts: San Beda College of LawsaintNo ratings yet
- 1 TortsDocument18 pages1 TortsCelestino LawNo ratings yet
- ObliDocument10 pagesObliAndrea BannisterNo ratings yet
- ObliconDocument31 pagesObliconPler WiezNo ratings yet
- TORTS and DAMAGES - Exam Notes.Document16 pagesTORTS and DAMAGES - Exam Notes.Marianne Hope VillasNo ratings yet
- Q&a in Torts and DamagesDocument7 pagesQ&a in Torts and DamagesAxel FontanillaNo ratings yet
- RFBT (Pinnacle Notes)Document1 pageRFBT (Pinnacle Notes)Justz LimNo ratings yet
- Memo Aid ObliconDocument28 pagesMemo Aid ObliconJurish Ann JimenezNo ratings yet
- ARTICLE 1156 Blaw ReviewerDocument9 pagesARTICLE 1156 Blaw Reviewers.macalolot.marymaeNo ratings yet
- COMLAW - Midterm ReviewerDocument10 pagesCOMLAW - Midterm Reviewermerry grace tuanNo ratings yet
- Revised Penal Code Reyes NotesDocument5 pagesRevised Penal Code Reyes NotesMac ValdezNo ratings yet
- Galido, Darlyn J. - Civil Code Ateneo de Davao University College of LawDocument3 pagesGalido, Darlyn J. - Civil Code Ateneo de Davao University College of Lawnae sarangtaeNo ratings yet
- The Bible Against Slavery: An inquiry into the Patriarchal and Mosaic systems on the subject of Human RightsFrom EverandThe Bible Against Slavery: An inquiry into the Patriarchal and Mosaic systems on the subject of Human RightsNo ratings yet
- The Bible Against Slavery: Human Rights Laws Written in the Holy ScriptureFrom EverandThe Bible Against Slavery: Human Rights Laws Written in the Holy ScriptureRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Capacity Planning (Sample Problems)Document2 pagesCapacity Planning (Sample Problems)Eliza Jayne Princess VizcondeNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - Productivity, Competitiveness, and StrategyDocument1 pageModule 1 - Productivity, Competitiveness, and StrategyEliza Jayne Princess VizcondeNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - Productivity, Competitiveness, and Strategy (Illustrations)Document5 pagesModule 1 - Productivity, Competitiveness, and Strategy (Illustrations)Eliza Jayne Princess VizcondeNo ratings yet
- Approaches To Forecasting - Terms and FormulasDocument2 pagesApproaches To Forecasting - Terms and FormulasEliza Jayne Princess VizcondeNo ratings yet
- Approaches To ForecastingDocument3 pagesApproaches To ForecastingEliza Jayne Princess VizcondeNo ratings yet
- Art 1177 Anchor Savings Bank (Formerly Anchor Finance and Investment Corporation) vs. Henry H. Furigay, ET AL.Document2 pagesArt 1177 Anchor Savings Bank (Formerly Anchor Finance and Investment Corporation) vs. Henry H. Furigay, ET AL.chrisNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2. Nature and Effect of ObligationsDocument90 pagesChapter 2. Nature and Effect of ObligationsRhyllin RamosNo ratings yet
- Third Party Liability Insurance PDFDocument15 pagesThird Party Liability Insurance PDFAnonymous fk1QdO0% (1)
- What Are The Basic Components of Most Management Contract Fee Structures? Which Types of Fees Do Owners and Operators Prefer?Document2 pagesWhat Are The Basic Components of Most Management Contract Fee Structures? Which Types of Fees Do Owners and Operators Prefer?ZaraNo ratings yet
- Property LawDocument10 pagesProperty LawGurjeev SinghNo ratings yet
- Draft. SPK Pembiayaan - Id.enDocument5 pagesDraft. SPK Pembiayaan - Id.enpanji_wijay4No ratings yet
- 01 Section T1 - Invitation To Tender VFDocument12 pages01 Section T1 - Invitation To Tender VFSatish ShindeNo ratings yet
- Key Differences Between Sole Proprietorship and Joint Hindu Family Firm - A Comparison ChartDocument6 pagesKey Differences Between Sole Proprietorship and Joint Hindu Family Firm - A Comparison ChartVarun KocharNo ratings yet
- National Abaca Vs Pore DigestDocument3 pagesNational Abaca Vs Pore DigestcrapshoxNo ratings yet
- Lecture On Consummation StageDocument1 pageLecture On Consummation StageRalph Ronald CatipayNo ratings yet
- 1.business Laws - Unit I - Indian Contract Act, 1872 - Introduction - 1Document24 pages1.business Laws - Unit I - Indian Contract Act, 1872 - Introduction - 1Dr. Bhavana Raj KNo ratings yet
- Important Question by Shantanu & Tanya Academy: Company LAW Important Questions FOR December 2021Document7 pagesImportant Question by Shantanu & Tanya Academy: Company LAW Important Questions FOR December 2021punugauriNo ratings yet
- Project Mobilisation Phase: ARE 4122 Construction ManagementDocument28 pagesProject Mobilisation Phase: ARE 4122 Construction Managementtesfalem kirosNo ratings yet
- Bill of Export For Duty Free Goods Ex-BondDocument6 pagesBill of Export For Duty Free Goods Ex-BondPrashant TetaliNo ratings yet
- NokiaDocument6 pagesNokiaKaramoko MamadouNo ratings yet
- Financial Management PPT FinalDocument16 pagesFinancial Management PPT FinalGalinNo ratings yet
- MCM2C06Document106 pagesMCM2C06Rameeza RameeNo ratings yet
- LETTER OF INTENT TO PURCHASE REAL ESTATE v2Document2 pagesLETTER OF INTENT TO PURCHASE REAL ESTATE v2Donna Hilario100% (1)
- (Nov 2020) Latest Safecustody ListingDocument923 pages(Nov 2020) Latest Safecustody Listingcinta amaniNo ratings yet
- Ted Lowery Paper-Construction Law Update SeminarDocument11 pagesTed Lowery Paper-Construction Law Update SeminarCity AspireNo ratings yet
- Contract IndemnityDocument3 pagesContract Indemnitysudhir.kochhar3530No ratings yet
- Metropolitan Bank Vs Junnel S MarketingDocument2 pagesMetropolitan Bank Vs Junnel S MarketingMary Angelica SangalangNo ratings yet
- Utf-8 - 5 Rosales V AlfonsoDocument1 pageUtf-8 - 5 Rosales V Alfonsocmv mendozaNo ratings yet
- PDF Template Subcontractor Agreement TemplateDocument5 pagesPDF Template Subcontractor Agreement TemplateJesús Abel Ercila SanchezNo ratings yet