Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Algebra s1
Algebra s1
Uploaded by
Freddy BravoCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Math Study Guide/Notes For Final Exam MCR3U Grade 11 FunctionsDocument31 pagesMath Study Guide/Notes For Final Exam MCR3U Grade 11 FunctionsNiki58% (12)
- 033 SurbhiGole A1Document18 pages033 SurbhiGole A1Surbhi GoleNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 ME502Document4 pagesAssignment 1 ME502Md Adil0% (1)
- Turunan TrigonoDocument2 pagesTurunan TrigonoJosNo ratings yet
- M1 +Review+of+Mathematical+FoundationsDocument4 pagesM1 +Review+of+Mathematical+FoundationsKpop HarteuNo ratings yet
- Potenciación IV: Leyes de Xponentes: Trabajando en ClaseDocument2 pagesPotenciación IV: Leyes de Xponentes: Trabajando en ClaseGaBy Meza FabianNo ratings yet
- Alevelsb p2 Ex11hDocument7 pagesAlevelsb p2 Ex11hmailshreyashsNo ratings yet
- LimitesDocument7 pagesLimitesBelennNo ratings yet
- Prueba ElectivoDocument7 pagesPrueba ElectivoBelennNo ratings yet
- April Dif1 2022Document1 pageApril Dif1 2022Tatjana ZecNo ratings yet
- 5.exploration With CAS-I.Lab5Document5 pages5.exploration With CAS-I.Lab5Yash KumarNo ratings yet
- Solution Class 11Document15 pagesSolution Class 11Abhi YTNo ratings yet
- Sesión 9 Nivelación 2024Document10 pagesSesión 9 Nivelación 2024J E T A XNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Simplifying RAEDocument8 pagesReviewer Simplifying RAEJashmine Mhae Mercado ArelladoNo ratings yet
- E Math NotesDocument10 pagesE Math NotesAnnette ChiangNo ratings yet
- Binomial Theorem+ P& C BOOKLET Final - 08.10.20 Without AnsDocument96 pagesBinomial Theorem+ P& C BOOKLET Final - 08.10.20 Without AnsShibhaditya DohareNo ratings yet
- Quantum Bouncing Ball PDFDocument2 pagesQuantum Bouncing Ball PDFbillytho1991No ratings yet
- 作業2Document4 pages作業28n6rhs8hygNo ratings yet
- Chapter Three Systems of Linear Algebraic Equations TDocument36 pagesChapter Three Systems of Linear Algebraic Equations TAbdulaziz H. Al-MutairiNo ratings yet
- Math 1 NotesDocument7 pagesMath 1 Notesanas_tiyamaulaniNo ratings yet
- Lecture NotesDocument90 pagesLecture NotesSharad RaykhereNo ratings yet
- Evej JMCADocument5 pagesEvej JMCACuevas Amador Josue ManuelNo ratings yet
- A A X X: The Laws and Properties of Exponents Operation Action Law/Property Example(s)Document10 pagesA A X X: The Laws and Properties of Exponents Operation Action Law/Property Example(s)sorin_a68No ratings yet
- 2017 Mid SolDocument13 pages2017 Mid SolvickyNo ratings yet
- Q3 - The Laws On Radicals Simplifying Radical Expressions STUDENTSDocument13 pagesQ3 - The Laws On Radicals Simplifying Radical Expressions STUDENTSMMALTEZ, RALPH CHRISTIAN, R.No ratings yet
- 2Document1 page2Jazel Heart EspañolaNo ratings yet
- Mensuration R: Pure MathematicsDocument3 pagesMensuration R: Pure Mathematicspatricia eileenNo ratings yet
- My First L TEX Document: 2 K 123 Ijk 2 I 123 Abc 3 2 3 2 3 2 2 2Document2 pagesMy First L TEX Document: 2 K 123 Ijk 2 I 123 Abc 3 2 3 2 3 2 2 2leluz__No ratings yet
- C. Henry Edwards, David E. Penney - Elementary Differential Equations (6th Edition) (2008, Pearson Education) (Elsolucionario - Org) (601-645)Document45 pagesC. Henry Edwards, David E. Penney - Elementary Differential Equations (6th Edition) (2008, Pearson Education) (Elsolucionario - Org) (601-645)Noriel J ANo ratings yet
- Ecuación de Onda HugoDocument4 pagesEcuación de Onda HugoIng. Arnulfo Guerra MadridNo ratings yet
- Lecture8 PDFDocument4 pagesLecture8 PDFRabia SalamNo ratings yet
- Lecture8 PDFDocument4 pagesLecture8 PDFJdkfkvNo ratings yet
- Cse-Iii-Engineering Mathematics - Iii (15mat31) - Solution PDFDocument68 pagesCse-Iii-Engineering Mathematics - Iii (15mat31) - Solution PDFM.A rajaNo ratings yet
- PrácticasDocument4 pagesPrácticasmariamira.marbella4No ratings yet
- P1 Week 9Document20 pagesP1 Week 9Kirsten DBeerNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mathematics Model Question Paper 2 With Detailed SolutionsDocument7 pagesEngineering Mathematics Model Question Paper 2 With Detailed SolutionsSumith SumithNo ratings yet
- Actividad 6Document2 pagesActividad 6gusvorop417No ratings yet
- LovemathsDocument2 pagesLovemathstsiemidanielNo ratings yet
- LovemathsDocument2 pagesLovemathstsiemidanielNo ratings yet
- Mensuration R: Pure MathematicsDocument8 pagesMensuration R: Pure Mathematicsquang hưngNo ratings yet
- Platinum Mathematics Grade - (Z-Library)Document380 pagesPlatinum Mathematics Grade - (Z-Library)Mawande WandarhNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 1Document4 pagesProblem Set 1Kyla MariñoNo ratings yet
- Sessional I Mth104 Cag Bte A Sp14Document5 pagesSessional I Mth104 Cag Bte A Sp14farjadtahirNo ratings yet
- Nested Derivatives: A Simple Method For Computing Series Expansions of Inverse FunctionsDocument18 pagesNested Derivatives: A Simple Method For Computing Series Expansions of Inverse FunctionsMochFakhrulNo ratings yet
- Logaritmes I Equacions ExponencialsDocument10 pagesLogaritmes I Equacions Exponencialsmv11376No ratings yet
- 0819 ExerciseDocument10 pages0819 ExerciseCathy LeungNo ratings yet
- XI - Maths - Chapter 13 - APPLICATION OF DERIVATIVES - (W.E) - 11.03.2015 (179-187)Document9 pagesXI - Maths - Chapter 13 - APPLICATION OF DERIVATIVES - (W.E) - 11.03.2015 (179-187)Aditya KumarNo ratings yet
- SeqSer GDocument8 pagesSeqSer GSamuel SmallmanNo ratings yet
- Review of Pre-Calculus - Calculus Volume 1 - OpenStaxDocument4 pagesReview of Pre-Calculus - Calculus Volume 1 - OpenStaxShane BuragaNo ratings yet
- Index LawsDocument1 pageIndex Lawsapi-360487416No ratings yet
- Mathematics 21 Sample Final ExamDocument2 pagesMathematics 21 Sample Final ExamEvernim OmpacanNo ratings yet
- F17XB2 2014-15 Class Test Mathematics For Engineers and Scientists 2 Attempt All Questions (B)Document2 pagesF17XB2 2014-15 Class Test Mathematics For Engineers and Scientists 2 Attempt All Questions (B)BuyuNo ratings yet
- M257 316 2012 Lecture 31Document3 pagesM257 316 2012 Lecture 31Feby CahyaniNo ratings yet
- SAT - Passport To Advanced Math Module - 7: Topic-Polynomials and Algebraic FractionsDocument9 pagesSAT - Passport To Advanced Math Module - 7: Topic-Polynomials and Algebraic FractionsMadhav AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Lista DerivadasDocument11 pagesLista DerivadasJesús García AbreuNo ratings yet
- 4ACh01 (Quadratic Equations in One Unknown)Document32 pages4ACh01 (Quadratic Equations in One Unknown)api-3826695No ratings yet
- APL Tut 1Document10 pagesAPL Tut 1Suhani AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Factoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)From EverandFactoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)No ratings yet
- Kundalini Yoga - Pranayama (Breathing Techniques)Document7 pagesKundalini Yoga - Pranayama (Breathing Techniques)JohnNo ratings yet
- Queens Gambit Declined ExtractDocument15 pagesQueens Gambit Declined ExtractJuan Andres Auernheimer100% (1)
- 波尔加习题集5334 1200ppi 超清CB导出习题】Document1,592 pages波尔加习题集5334 1200ppi 超清CB导出习题】andyNo ratings yet
- Filipino Chess Master GamesDocument2 pagesFilipino Chess Master GamesJuan KakakaNo ratings yet
- Anders Tejler - Blackmar-Diemer Gambit - Euwe DefenceDocument63 pagesAnders Tejler - Blackmar-Diemer Gambit - Euwe DefenceJacques EychenneNo ratings yet
- MA - ENG - Chesscomp - User Manual DGT Pi - Ver1805Document27 pagesMA - ENG - Chesscomp - User Manual DGT Pi - Ver1805chambrezNo ratings yet
- MOFFATT W. Memorable Chess Games (1913) en 202Document202 pagesMOFFATT W. Memorable Chess Games (1913) en 202Jothaeff100% (1)
- SMD Molinow 2022Document8 pagesSMD Molinow 2022Hasty KorompotNo ratings yet
- A General Reinforcement Learning Algorithm That Masters Chess, Shogi, and Go Through Self-PlayDocument6 pagesA General Reinforcement Learning Algorithm That Masters Chess, Shogi, and Go Through Self-PlaySnowdenNo ratings yet
- Modern Methods For Training A Chess PlayerDocument7 pagesModern Methods For Training A Chess PlayerFe Tus100% (1)
- Levon Aronian Best Games 2015 SinquefieldDocument527 pagesLevon Aronian Best Games 2015 SinquefieldMichael Chukwuma Mkpadi67% (6)
- Color Name HEX Color Shades MixDocument4 pagesColor Name HEX Color Shades MixVinith VemanaNo ratings yet
- GrasshoppersDocument40 pagesGrasshoppersTate NgNo ratings yet
- First Octave - Basic Fingering Chart For Flute and Piccolo - The Woodwind Fingering GuideDocument2 pagesFirst Octave - Basic Fingering Chart For Flute and Piccolo - The Woodwind Fingering GuideJosé RõdrijzNo ratings yet
- Edith Cowan University: Mount LawleyDocument2 pagesEdith Cowan University: Mount LawleySaleh BalfasNo ratings yet
- LA-9104P VAW00 Inspiron 3521-5Document1 pageLA-9104P VAW00 Inspiron 3521-5samarxdasNo ratings yet
- LcZero ELO Estimate List Approximation (L.e.e.l PDFDocument42 pagesLcZero ELO Estimate List Approximation (L.e.e.l PDFGuiye SantosNo ratings yet
- Angra - Temple of Hate PDFDocument27 pagesAngra - Temple of Hate PDFIVAN VARGASNo ratings yet
- Ecm 8Document1 pageEcm 8Misa GamezNo ratings yet
- 738512Document1 page738512AlexandreNo ratings yet
- First Chess Adventures With The Sicilian DefenceDocument28 pagesFirst Chess Adventures With The Sicilian Defenceosbert snudgeNo ratings yet
- Most Amazing Chess Moves-2Document41 pagesMost Amazing Chess Moves-2Said Alauddeen FaiszNo ratings yet
- Remembering Svetozar Gligoric I, Kiril PenusliskiDocument4 pagesRemembering Svetozar Gligoric I, Kiril Penusliskipp2_ow_105969576No ratings yet
- K6 Unit 5 ULANGAN HARIANDocument2 pagesK6 Unit 5 ULANGAN HARIANNur Sidik IndragunaNo ratings yet
- Giuoco Piano - WikipediaDocument22 pagesGiuoco Piano - WikipediaM.Ranjith kumarNo ratings yet
- Alekhine'S DefenceDocument8 pagesAlekhine'S Defencestef1234567890100% (1)
- Gibaud - Lazard (A45) : (,bryan)Document3 pagesGibaud - Lazard (A45) : (,bryan)radjachessNo ratings yet
- MCQ CSWIP Book Q & ADocument1 pageMCQ CSWIP Book Q & ASpCy RanaNo ratings yet
- 34 Tamil Nadu State Under - 11 Open and Girls Fide Rated Chess Championship - 2022 AICF Event Code: TNSCA Approval NoDocument7 pages34 Tamil Nadu State Under - 11 Open and Girls Fide Rated Chess Championship - 2022 AICF Event Code: TNSCA Approval NoS. Kanishka100% (1)
- Stewart, Ian - Mathematical Recreations - The Never-Ending Chess Game PDFDocument2 pagesStewart, Ian - Mathematical Recreations - The Never-Ending Chess Game PDFbiberli01No ratings yet
Algebra s1
Algebra s1
Uploaded by
Freddy BravoOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Algebra s1
Algebra s1
Uploaded by
Freddy BravoCopyright:
Available Formats
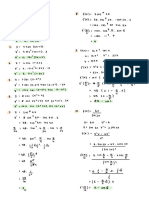
CICLO SAN MARCOS
TEOREMAS
LEYES DE EXPONENTES I I) BASES IGUALES
DEFINICIONES
1. Multiplicación
1. Exponente Natural am . an = am+n
xn x . x ................... x ; x R n Z+
–– –– Ejm.:
n veces
24 . 22 = 26
Ejm.:
xn+4 = xn . x4
b5 = b . b . b . b . b
4
1 2. División
2
am
2. Exponente Cero amn ; a 0
an
x0 = 1 ; xR–{0}
Ejm.:
Ejm.:
34
32
40 = 1 -20 = 32
(-3)0 = 1 (-2)0 =
x x
3. Exponente Negativo xx3
x3
1
xn ; x R – {0} n Z+ 55
xn
53
Ejm.: x2x-1 =
1 1 II) EXPONENTES IGUALES
32
32 9
3. Multiplicación
(-4)-3 = an . bn = (ab)n
4
1
Ejm.:
2
NUESTRO OBJETIVO ES TU INGRESO…
CICLO SAN MARCOS
x4y4z4 = (xyz)4
(2b)3 = 23 . b3 152 . 25 . 49
1. Reducir: M
m2n2p2 = 352 . 452
(3x)4 =
1
4. División a) b) 1 c)
1
3 2 9
an a
n
n
; b0 1
b b d) e) 5
5
Ejm.:
3 2n4 2n3
x3 x 2. Simplificar: N
2n4
y3 y
2
2 22 4 a) 2 b) 3 c) 1/3
2
3
3 9
d) 1/2 e) 1/5
x4
24 83
1
25
3 3. Calcular: F 32
3
a) 1 b) 2 c) 3
5
III) EXPONENTE DE EXPONENTE d) 4 e) 5
([a]m )n P amnp 4. Efectuar:
x4 . x6 . x8 . x10 ...............40
(32)3 = 36 = 729 M
x . x3 . x5 . x7 ............. 37
x2.2.5 = {(x2)2}5
a) x60 b) x54 c) x57 d) x63 e) x51
{(22)3}4 =
1. Simplificar:
x 2.3.5
=
NUESTRO OBJETIVO ES TU INGRESO…
CICLO SAN MARCOS 1
1 1 1
1 1 1 7. Si: x 3
1 1 1 x
N 2 3 4
2 3 4
Hallar el valor de:
a) 287 b) 281 c) 235 d) 123 e) 435 1 1 1
1
x x x
W x x
x x x
2. Halle el exponente final de “x”.
"b" veces
–– – – – –
(xa)bc . (xbc)a . xac . xac ...... xac a) 18 b) 21 c) 15 d) 20 e) 24
((x3a )b)c
E A E
8. Conociendo que: CD A ; CB ED
a) 0 b) 1 c) 2 d) 3 e) 4
E
CD
B
x Reducir: S A
3. Si: xx 2
xxx a) A b) B c) C d) D e) E
Calcular: P xx
4
a) 2 b) 1/2 c) 4 d) 2 e) 2
xmnmn x2m2n
a 1 9. Reducir: E
Si: b 5 ab
4.
2 xmnmn x2mn
a1
Calcular: R ab
a) 1 b) x c) x2(m+n-mn)
a) 30 b) 32 c) 34 d) 35 e) 33
d) xm+n-mn e) No se puede
5 n
2
2 50 760
n
10. Si: n = 1/9. Hallar: En
5. Calcular: E 7 . 7 . 49 42 7
a) 243 b) 81 c) 1/81 d) 1 e) 729
7
a) 650 b) 754 c) 755 d) 741 e) 1 2a2 . 4a2b
11. Calcular: P
8a2 . 16b2
6. Si: 2n = 3m; reducir:
52 . 2n 2n1 32 . 2n a) 1 b) 2 c) 4 d) 1/2 e) 1/4
L
3m3 22 . 3m1
a) 3/4 b) 4/3 c) 6/5 d) 2/9 e) 7/5
NUESTRO OBJETIVO ES TU INGRESO…
CICLO SAN MARCOS
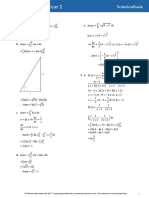
TEOREMAS
LEYES DE EXPONENTES II
I) RAÍZ DE UNA MULTIPLICACIÓN INDICADA
DEFINICIONES
n n n
xy x. y
n Ejm.:
x y yn x ;nN n2
3 3 3
2. 3 2. 3
(x R, además, cuando n es par, x 0)
3 3
5 . 25
Ejm.:
4 4
8 . 32
2 2
25 5 5 25
II) RAÍZ DE UNA DIVISIÓN
3 n
8 2 n x x ; y0
y n
y
4
16 2
1
Ejm.:
n 3
(x) n x ; n 0 81 3 81 3
27 3
3 3
3
Ejm.:
III) RAÍZ DE RAÍZ
2
41 /2 4 2 mn p m.n.p
x x
4.
m 45 6 120
n n
(x) n ( x)m xm ; n0 2 2
3
Ejm.: 3
3 5 4
(27)2/3 ( 27)2 (3)2 9 1 024
25-3/2 =
NUESTRO OBJETIVO ES TU INGRESO…
CICLO SAN MARCOS
2. Reducir:
24 72
3 4 24 24 3 73 73
CASOS ESPECIALES M 7 22 . 73 72
8
7
m n p m.n.p
xr . ys . zt xr.n.p . ys.p . zt a) 0 b) 1 c) 2 d) 4 e) N.A.
Ejm.: 1 2a
3. Reducir: R a
1 2a
S a b c
a) 1 b) 2 c) 3 d) 4 e) 5
m n p m.n.p
xa xb xc x(anb)pc ab
72a 21
ab
72b
4. Calcular: S ab
7 ab
Ejm.:
a) 1 b) 10 c) 3,5 d) 7 e) 2
1
1 3
3 3 3
x2 x2 x2 3
5. Calcular: T 64 3 (32) 5
xx x
a) 0 b) 1 c) 2 d) 3 e) 4
m n p mnp
xa xb xc x(anb)pc
3 4 3 5
6. Calcular: I 22 23 27 240
Ejm.: 3 3 3 3
a) 2 b) 8 c) 4 d) 2 2 e) 1
3 5 6 45factores
x2 x4 x7 3
–– – – – ––
3
x . x ............... x x3
7. Efectuar: A
x . x ..............x x1
–––– ––––
44 factores
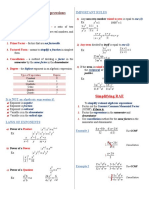
EJERCICIOS 6
3 2 4 3 a) x b) x c) x9 d) x-4 e) x-7
1. Reducir: N
a . a . a5
12 12 8. Calcular: S n 7n 3n
a) a47 b) a46/12 c) a3 a11 7n 3n
a) 7 b) 3 c) 21 d) 1/7 e) 1/3
d) a11 e) a47
NUESTRO OBJETIVO ES TU INGRESO…
CICLO SAN MARCOS
n2 n2
n2 10 6
9. Simplificar: T
n2 n2
25 15
a) 0,2 b) 0,4 c) 0,6 d) 0,8 e) 1,4
6 56
6 56
10. Reducir: R 56
5
6
5
a) 1 b) 2 c) 3 d) 6 e) 6
11. Si: aa = a + 1
aa
Calcular el valor de: E a (a 1)(a1)
a) aa b) a c) aa-1 d) aa+1 e) a-a
12. Sabiendo que: 1 1 1
a b ab
b a
ab ab
x x
Reducir: N a
b
x x
a) x b) 2x c) x/2 d) –x e) x/4
6 12 20
13. Reducir: W x . x. x. x .......... ...
a) 1/x b) 0 c) 2/x d) x e) x
ab bc ac
14. Simplificar: P xab . xbc . xca
a) 1 b) x c) 2x d) 3x e) 0
15. Indique el exponente final de “x” al reducir:
n n n n
E xn1 xn2 x2n3....... x19n20
NUESTRO OBJETIVO ES TU INGRESO…
You might also like
- Math Study Guide/Notes For Final Exam MCR3U Grade 11 FunctionsDocument31 pagesMath Study Guide/Notes For Final Exam MCR3U Grade 11 FunctionsNiki58% (12)
- 033 SurbhiGole A1Document18 pages033 SurbhiGole A1Surbhi GoleNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 ME502Document4 pagesAssignment 1 ME502Md Adil0% (1)
- Turunan TrigonoDocument2 pagesTurunan TrigonoJosNo ratings yet
- M1 +Review+of+Mathematical+FoundationsDocument4 pagesM1 +Review+of+Mathematical+FoundationsKpop HarteuNo ratings yet
- Potenciación IV: Leyes de Xponentes: Trabajando en ClaseDocument2 pagesPotenciación IV: Leyes de Xponentes: Trabajando en ClaseGaBy Meza FabianNo ratings yet
- Alevelsb p2 Ex11hDocument7 pagesAlevelsb p2 Ex11hmailshreyashsNo ratings yet
- LimitesDocument7 pagesLimitesBelennNo ratings yet
- Prueba ElectivoDocument7 pagesPrueba ElectivoBelennNo ratings yet
- April Dif1 2022Document1 pageApril Dif1 2022Tatjana ZecNo ratings yet
- 5.exploration With CAS-I.Lab5Document5 pages5.exploration With CAS-I.Lab5Yash KumarNo ratings yet
- Solution Class 11Document15 pagesSolution Class 11Abhi YTNo ratings yet
- Sesión 9 Nivelación 2024Document10 pagesSesión 9 Nivelación 2024J E T A XNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Simplifying RAEDocument8 pagesReviewer Simplifying RAEJashmine Mhae Mercado ArelladoNo ratings yet
- E Math NotesDocument10 pagesE Math NotesAnnette ChiangNo ratings yet
- Binomial Theorem+ P& C BOOKLET Final - 08.10.20 Without AnsDocument96 pagesBinomial Theorem+ P& C BOOKLET Final - 08.10.20 Without AnsShibhaditya DohareNo ratings yet
- Quantum Bouncing Ball PDFDocument2 pagesQuantum Bouncing Ball PDFbillytho1991No ratings yet
- 作業2Document4 pages作業28n6rhs8hygNo ratings yet
- Chapter Three Systems of Linear Algebraic Equations TDocument36 pagesChapter Three Systems of Linear Algebraic Equations TAbdulaziz H. Al-MutairiNo ratings yet
- Math 1 NotesDocument7 pagesMath 1 Notesanas_tiyamaulaniNo ratings yet
- Lecture NotesDocument90 pagesLecture NotesSharad RaykhereNo ratings yet
- Evej JMCADocument5 pagesEvej JMCACuevas Amador Josue ManuelNo ratings yet
- A A X X: The Laws and Properties of Exponents Operation Action Law/Property Example(s)Document10 pagesA A X X: The Laws and Properties of Exponents Operation Action Law/Property Example(s)sorin_a68No ratings yet
- 2017 Mid SolDocument13 pages2017 Mid SolvickyNo ratings yet
- Q3 - The Laws On Radicals Simplifying Radical Expressions STUDENTSDocument13 pagesQ3 - The Laws On Radicals Simplifying Radical Expressions STUDENTSMMALTEZ, RALPH CHRISTIAN, R.No ratings yet
- 2Document1 page2Jazel Heart EspañolaNo ratings yet
- Mensuration R: Pure MathematicsDocument3 pagesMensuration R: Pure Mathematicspatricia eileenNo ratings yet
- My First L TEX Document: 2 K 123 Ijk 2 I 123 Abc 3 2 3 2 3 2 2 2Document2 pagesMy First L TEX Document: 2 K 123 Ijk 2 I 123 Abc 3 2 3 2 3 2 2 2leluz__No ratings yet
- C. Henry Edwards, David E. Penney - Elementary Differential Equations (6th Edition) (2008, Pearson Education) (Elsolucionario - Org) (601-645)Document45 pagesC. Henry Edwards, David E. Penney - Elementary Differential Equations (6th Edition) (2008, Pearson Education) (Elsolucionario - Org) (601-645)Noriel J ANo ratings yet
- Ecuación de Onda HugoDocument4 pagesEcuación de Onda HugoIng. Arnulfo Guerra MadridNo ratings yet
- Lecture8 PDFDocument4 pagesLecture8 PDFRabia SalamNo ratings yet
- Lecture8 PDFDocument4 pagesLecture8 PDFJdkfkvNo ratings yet
- Cse-Iii-Engineering Mathematics - Iii (15mat31) - Solution PDFDocument68 pagesCse-Iii-Engineering Mathematics - Iii (15mat31) - Solution PDFM.A rajaNo ratings yet
- PrácticasDocument4 pagesPrácticasmariamira.marbella4No ratings yet
- P1 Week 9Document20 pagesP1 Week 9Kirsten DBeerNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mathematics Model Question Paper 2 With Detailed SolutionsDocument7 pagesEngineering Mathematics Model Question Paper 2 With Detailed SolutionsSumith SumithNo ratings yet
- Actividad 6Document2 pagesActividad 6gusvorop417No ratings yet
- LovemathsDocument2 pagesLovemathstsiemidanielNo ratings yet
- LovemathsDocument2 pagesLovemathstsiemidanielNo ratings yet
- Mensuration R: Pure MathematicsDocument8 pagesMensuration R: Pure Mathematicsquang hưngNo ratings yet
- Platinum Mathematics Grade - (Z-Library)Document380 pagesPlatinum Mathematics Grade - (Z-Library)Mawande WandarhNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 1Document4 pagesProblem Set 1Kyla MariñoNo ratings yet
- Sessional I Mth104 Cag Bte A Sp14Document5 pagesSessional I Mth104 Cag Bte A Sp14farjadtahirNo ratings yet
- Nested Derivatives: A Simple Method For Computing Series Expansions of Inverse FunctionsDocument18 pagesNested Derivatives: A Simple Method For Computing Series Expansions of Inverse FunctionsMochFakhrulNo ratings yet
- Logaritmes I Equacions ExponencialsDocument10 pagesLogaritmes I Equacions Exponencialsmv11376No ratings yet
- 0819 ExerciseDocument10 pages0819 ExerciseCathy LeungNo ratings yet
- XI - Maths - Chapter 13 - APPLICATION OF DERIVATIVES - (W.E) - 11.03.2015 (179-187)Document9 pagesXI - Maths - Chapter 13 - APPLICATION OF DERIVATIVES - (W.E) - 11.03.2015 (179-187)Aditya KumarNo ratings yet
- SeqSer GDocument8 pagesSeqSer GSamuel SmallmanNo ratings yet
- Review of Pre-Calculus - Calculus Volume 1 - OpenStaxDocument4 pagesReview of Pre-Calculus - Calculus Volume 1 - OpenStaxShane BuragaNo ratings yet
- Index LawsDocument1 pageIndex Lawsapi-360487416No ratings yet
- Mathematics 21 Sample Final ExamDocument2 pagesMathematics 21 Sample Final ExamEvernim OmpacanNo ratings yet
- F17XB2 2014-15 Class Test Mathematics For Engineers and Scientists 2 Attempt All Questions (B)Document2 pagesF17XB2 2014-15 Class Test Mathematics For Engineers and Scientists 2 Attempt All Questions (B)BuyuNo ratings yet
- M257 316 2012 Lecture 31Document3 pagesM257 316 2012 Lecture 31Feby CahyaniNo ratings yet
- SAT - Passport To Advanced Math Module - 7: Topic-Polynomials and Algebraic FractionsDocument9 pagesSAT - Passport To Advanced Math Module - 7: Topic-Polynomials and Algebraic FractionsMadhav AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Lista DerivadasDocument11 pagesLista DerivadasJesús García AbreuNo ratings yet
- 4ACh01 (Quadratic Equations in One Unknown)Document32 pages4ACh01 (Quadratic Equations in One Unknown)api-3826695No ratings yet
- APL Tut 1Document10 pagesAPL Tut 1Suhani AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Factoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)From EverandFactoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)No ratings yet
- Kundalini Yoga - Pranayama (Breathing Techniques)Document7 pagesKundalini Yoga - Pranayama (Breathing Techniques)JohnNo ratings yet
- Queens Gambit Declined ExtractDocument15 pagesQueens Gambit Declined ExtractJuan Andres Auernheimer100% (1)
- 波尔加习题集5334 1200ppi 超清CB导出习题】Document1,592 pages波尔加习题集5334 1200ppi 超清CB导出习题】andyNo ratings yet
- Filipino Chess Master GamesDocument2 pagesFilipino Chess Master GamesJuan KakakaNo ratings yet
- Anders Tejler - Blackmar-Diemer Gambit - Euwe DefenceDocument63 pagesAnders Tejler - Blackmar-Diemer Gambit - Euwe DefenceJacques EychenneNo ratings yet
- MA - ENG - Chesscomp - User Manual DGT Pi - Ver1805Document27 pagesMA - ENG - Chesscomp - User Manual DGT Pi - Ver1805chambrezNo ratings yet
- MOFFATT W. Memorable Chess Games (1913) en 202Document202 pagesMOFFATT W. Memorable Chess Games (1913) en 202Jothaeff100% (1)
- SMD Molinow 2022Document8 pagesSMD Molinow 2022Hasty KorompotNo ratings yet
- A General Reinforcement Learning Algorithm That Masters Chess, Shogi, and Go Through Self-PlayDocument6 pagesA General Reinforcement Learning Algorithm That Masters Chess, Shogi, and Go Through Self-PlaySnowdenNo ratings yet
- Modern Methods For Training A Chess PlayerDocument7 pagesModern Methods For Training A Chess PlayerFe Tus100% (1)
- Levon Aronian Best Games 2015 SinquefieldDocument527 pagesLevon Aronian Best Games 2015 SinquefieldMichael Chukwuma Mkpadi67% (6)
- Color Name HEX Color Shades MixDocument4 pagesColor Name HEX Color Shades MixVinith VemanaNo ratings yet
- GrasshoppersDocument40 pagesGrasshoppersTate NgNo ratings yet
- First Octave - Basic Fingering Chart For Flute and Piccolo - The Woodwind Fingering GuideDocument2 pagesFirst Octave - Basic Fingering Chart For Flute and Piccolo - The Woodwind Fingering GuideJosé RõdrijzNo ratings yet
- Edith Cowan University: Mount LawleyDocument2 pagesEdith Cowan University: Mount LawleySaleh BalfasNo ratings yet
- LA-9104P VAW00 Inspiron 3521-5Document1 pageLA-9104P VAW00 Inspiron 3521-5samarxdasNo ratings yet
- LcZero ELO Estimate List Approximation (L.e.e.l PDFDocument42 pagesLcZero ELO Estimate List Approximation (L.e.e.l PDFGuiye SantosNo ratings yet
- Angra - Temple of Hate PDFDocument27 pagesAngra - Temple of Hate PDFIVAN VARGASNo ratings yet
- Ecm 8Document1 pageEcm 8Misa GamezNo ratings yet
- 738512Document1 page738512AlexandreNo ratings yet
- First Chess Adventures With The Sicilian DefenceDocument28 pagesFirst Chess Adventures With The Sicilian Defenceosbert snudgeNo ratings yet
- Most Amazing Chess Moves-2Document41 pagesMost Amazing Chess Moves-2Said Alauddeen FaiszNo ratings yet
- Remembering Svetozar Gligoric I, Kiril PenusliskiDocument4 pagesRemembering Svetozar Gligoric I, Kiril Penusliskipp2_ow_105969576No ratings yet
- K6 Unit 5 ULANGAN HARIANDocument2 pagesK6 Unit 5 ULANGAN HARIANNur Sidik IndragunaNo ratings yet
- Giuoco Piano - WikipediaDocument22 pagesGiuoco Piano - WikipediaM.Ranjith kumarNo ratings yet
- Alekhine'S DefenceDocument8 pagesAlekhine'S Defencestef1234567890100% (1)
- Gibaud - Lazard (A45) : (,bryan)Document3 pagesGibaud - Lazard (A45) : (,bryan)radjachessNo ratings yet
- MCQ CSWIP Book Q & ADocument1 pageMCQ CSWIP Book Q & ASpCy RanaNo ratings yet
- 34 Tamil Nadu State Under - 11 Open and Girls Fide Rated Chess Championship - 2022 AICF Event Code: TNSCA Approval NoDocument7 pages34 Tamil Nadu State Under - 11 Open and Girls Fide Rated Chess Championship - 2022 AICF Event Code: TNSCA Approval NoS. Kanishka100% (1)
- Stewart, Ian - Mathematical Recreations - The Never-Ending Chess Game PDFDocument2 pagesStewart, Ian - Mathematical Recreations - The Never-Ending Chess Game PDFbiberli01No ratings yet