Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lecture#4
Lecture#4
Uploaded by
ABDULLAH MAQBOOL0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views7 pagesThe document discusses energy conservation in power production through techniques like regeneration in gas turbine engines using a regenerator to preheat incoming gas with exhaust heat. It defines the effectiveness of regenerators and provides the equation for calculating the thermal efficiency of an ideal Brayton cycle with regeneration. Assignments related to analyzing the Brayton cycle are also listed.
Original Description:
Original Title
Lecture#4 (1)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses energy conservation in power production through techniques like regeneration in gas turbine engines using a regenerator to preheat incoming gas with exhaust heat. It defines the effectiveness of regenerators and provides the equation for calculating the thermal efficiency of an ideal Brayton cycle with regeneration. Assignments related to analyzing the Brayton cycle are also listed.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views7 pagesLecture#4
Lecture#4
Uploaded by
ABDULLAH MAQBOOLThe document discusses energy conservation in power production through techniques like regeneration in gas turbine engines using a regenerator to preheat incoming gas with exhaust heat. It defines the effectiveness of regenerators and provides the equation for calculating the thermal efficiency of an ideal Brayton cycle with regeneration. Assignments related to analyzing the Brayton cycle are also listed.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 7
Energy Conservation and Management
EE-315
Dr. Muhammad Sarfraz Akram
Assistant Professor
Institute of Energy & Environmental Engineering
University of the Punjab
Email: msakram.ieee@pu.edu.pk
Energy Conservation in Power Production
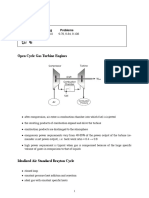
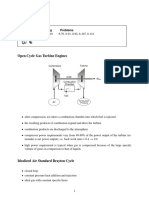
• In a Brayton cycle operating as gas turbine engine, the
temperature of the exhaust gas leaving the turbine T4 is often
higher than the temperature of the gas leaving the compressor
T2 as seen in Fig.
• Therefore, the gas leaving the compressor can be heated in a
regenerator by the hot exhaust gases.
• Regenerator is a counterflow heat exchanger, which is in
some cases also known as recuperator, and recovers waste
heat.
• The thermal efficiency of the Brayton cycle increases as a
result of regeneration because the portion of energy of the
exhaust gases is used to preheat the gas entering to the
combustion chamber.
• Thus, in turn, regeneration can reduce the fuel input required
for the same network output from the cycle. The addition of a
regenerator (operating without thermal losses) does not affect
the network output of the cycle.
• A regenerator with higher effectiveness will conserve more
fuel.
Energy Conservation in Power Production
The effectiveness ε of the regenerator operating under adiabatic
conditions is defined by
The regeneration is possible only when T4 ≫ T2.
The effectiveness of most regenerators used in practical engine
operations is below 0.85.
Under the cold-air standard temperature assumptions, thermal
efficiency of an ideal Brayton cycle with regeneration depends
on the ratio of minimum to maximum temperatures and the
pressure ratio, and estimated by
Energy Conservation in Power Production
Energy Conservation in Power Production
Assignments
Problem 9.1 – 9.8 (Brayton cycle)
Energy Production, Conversion, Storage, Conservation, and Coupling
Author: Yaşar Demirel
Energy Conservation and Recovery
• Energy conservation mainly refers to reducing energy consumption and increasing
efficiency in energy usage.
• Energy recovery also may be a part of energy conservation through captured and hence
reduced waste energy.
• Energy conservation is an important part of controlling climate change by reducing
greenhouse gas emissions.
• Energy conservation facilitates the replacement of nonrenewable resources with renewable
energy and is often the most economical solution to energy shortages.
• Energy conservation may lead to increased security, financial gain, and environmental
protection. For example, electric motors consume a considerable amount of electrical
energy and operate at efficiencies between 70 and 90 %. Therefore, using an electric motor
operating with higher efficiency will conserve energy throughout its useful life.
• Energy recovery leads to reducing the energy input by reducing the overall waste energy
from a system. For example, a waste energy, mainly in the form sensible or latent heat, from
a subsystem may be usable in another part of the same system. Therefore, energy recovery
may be a part of energy conservation.
Energy Conservation and Recovery
• There is a large potential for energy recovery in industries and utilities leading to reduced
use of fossil fuels and hence greenhouse gas emission.
• Hot water from processes such as power plants and steel mills may be used for heating of
homes and offices in the nearby area. Energy conservation through insulation or improved
buildings may also help. Low temperature heat recovery would be more effective for a short
distance from producer to consumer.
• Regenerative brake is used in electric cars and trains, where the part of kinetic energy is
recovered and stored as chemical energy in a battery.
You might also like
- Boiler Operation Engineer Exam, Interview Q&A, Terminology, and Boiler OverviewFrom EverandBoiler Operation Engineer Exam, Interview Q&A, Terminology, and Boiler OverviewRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Air Cooled Heat Exchanger Handbook: Fundamentals, Calculations, Design and Q&AFrom EverandAir Cooled Heat Exchanger Handbook: Fundamentals, Calculations, Design and Q&ANo ratings yet
- Study of a reluctance magnetic gearbox for energy storage system applicationFrom EverandStudy of a reluctance magnetic gearbox for energy storage system applicationRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Cogeneration & Trigeneration: by Varun Pratap SinghDocument48 pagesCogeneration & Trigeneration: by Varun Pratap Singhdanny buiNo ratings yet
- Energy Conservation Technique in IndustriesDocument29 pagesEnergy Conservation Technique in IndustriesPrashant IngoleNo ratings yet
- EconomizerDocument7 pagesEconomizernsralmasiNo ratings yet
- Energy Conservation Techniques For Industries: Presentation byDocument29 pagesEnergy Conservation Techniques For Industries: Presentation byYashobhit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Jenbacher Gasm BHKW enDocument28 pagesJenbacher Gasm BHKW ensaniterm100% (1)
- Combined Cycle, Combined Cycle With Heat Recovery..Document4 pagesCombined Cycle, Combined Cycle With Heat Recovery..abdul100% (1)
- Furnaces Energy SavingDocument10 pagesFurnaces Energy SavingqaisarharisNo ratings yet
- Cogeneration & CHP: Benefits of Gas Engine CHPDocument2 pagesCogeneration & CHP: Benefits of Gas Engine CHPPablo MartínezNo ratings yet
- Prospect of Combined Cycle Power Plant Over Conventional Single Cycle Power Plants in Bangladesh - A Case StudyDocument5 pagesProspect of Combined Cycle Power Plant Over Conventional Single Cycle Power Plants in Bangladesh - A Case StudyTaskinJamalNo ratings yet
- The Brayton Cycle With RegenerationDocument14 pagesThe Brayton Cycle With RegenerationMuh Indrawan100% (1)
- Gas Engines, Combined Cycles and TrigenerationDocument9 pagesGas Engines, Combined Cycles and Trigenerationsimon107No ratings yet
- Cog en Era Ti OnDocument12 pagesCog en Era Ti OnMayank DubeyNo ratings yet
- Natural Gas EquipmentDocument26 pagesNatural Gas Equipmenthanisshi100% (1)
- A Review of Automobile Waste Heat Recovery System: Prof. Murtaza Dholkawala, Mr. Ahire Durgesh VijayDocument7 pagesA Review of Automobile Waste Heat Recovery System: Prof. Murtaza Dholkawala, Mr. Ahire Durgesh VijayJijo GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Training Report CCPPDocument38 pagesTraining Report CCPPTaresh MittalNo ratings yet
- Combined Gas and Steam Power PlantDocument8 pagesCombined Gas and Steam Power Planttushar1128100% (1)
- Lec - 8 PP - Combined Cycle PPDocument19 pagesLec - 8 PP - Combined Cycle PPLog XNo ratings yet
- Fuel & Energy AssignmentDocument6 pagesFuel & Energy AssignmentZarar SaleemNo ratings yet
- Cogeneration Heat Power CHPDocument10 pagesCogeneration Heat Power CHPMKOZERDEMNo ratings yet
- Cogeneration CycleDocument30 pagesCogeneration Cyclekaladher5311937No ratings yet
- Cogeneration - Combined Heat and Power (CHP)Document23 pagesCogeneration - Combined Heat and Power (CHP)Reyes SanchezNo ratings yet
- Combined Cycle Power PlantDocument29 pagesCombined Cycle Power Plantrajib0403050cuet100% (1)
- Combined Cycle Power PlantDocument7 pagesCombined Cycle Power Plantchella2705100% (1)
- Gas Turbine Performance EnhancementsDocument14 pagesGas Turbine Performance Enhancementsmahmouddiaa554No ratings yet
- Thermal Analysis of Open-Cycle Regenerator Gas-Turbine Power-PlantDocument6 pagesThermal Analysis of Open-Cycle Regenerator Gas-Turbine Power-Plantحسام جدوNo ratings yet
- Study On Thermal Storage From Exhaust of A Diesel EngineDocument38 pagesStudy On Thermal Storage From Exhaust of A Diesel EngineHimanshu SharmaNo ratings yet
- Steam Power Plant: Pros & Cons: What This Power Station Presents Advantages DisadvantagesDocument4 pagesSteam Power Plant: Pros & Cons: What This Power Station Presents Advantages Disadvantagesyanblade100% (2)
- What Is CogenerationDocument3 pagesWhat Is CogenerationmuthuNo ratings yet
- GPFDocument200 pagesGPFspvengiNo ratings yet
- Energy Conservation in Boiler by Variable Speed Drives (VSD)Document6 pagesEnergy Conservation in Boiler by Variable Speed Drives (VSD)Anonymous clm7qP5No ratings yet
- Gas Turbine: Olar LoungeDocument34 pagesGas Turbine: Olar Loungepkdevan68100% (1)
- Exploiting Waste Heat in Small and Medium-Sized Combined Heat and Power Plants Using Steam InjectionDocument11 pagesExploiting Waste Heat in Small and Medium-Sized Combined Heat and Power Plants Using Steam InjectionAnonymous VfmEOJ6wE1No ratings yet
- Topic: - Power Cogeneration Plant: Term Paper OF Project ManagementDocument13 pagesTopic: - Power Cogeneration Plant: Term Paper OF Project ManagementankuaaaNo ratings yet
- Gas TurbinesDocument22 pagesGas Turbineswayzodeneeraj100% (1)
- SPE-197965-MS Transforming Waste Heat To Electric Power in Oil and Gas Compression Systems Using Supercritical Carbon DioxideDocument7 pagesSPE-197965-MS Transforming Waste Heat To Electric Power in Oil and Gas Compression Systems Using Supercritical Carbon Dioxide叶芊No ratings yet
- CogenerationDocument5 pagesCogenerationnabeelNo ratings yet
- Estimation of Energy Saving Potential For A Gas Turbine Power Station Through Empirical and Computational Energy Audit ApproachesDocument17 pagesEstimation of Energy Saving Potential For A Gas Turbine Power Station Through Empirical and Computational Energy Audit ApproachesMubeenNo ratings yet
- Research For ReportingDocument4 pagesResearch For ReportingAnonymous cMvETWUNo ratings yet
- Improving of Refinery Furnaces Efficiency Using Mathematical ModelingDocument6 pagesImproving of Refinery Furnaces Efficiency Using Mathematical Modelingusman_hafeez86No ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Lecture 6Document32 pagesThermodynamics Lecture 6MarkJude Morla100% (1)
- Combined Gas and Steam: (COGAS) Plant. Multiple Stage Turbine or Steam Cycles Are AlsoDocument12 pagesCombined Gas and Steam: (COGAS) Plant. Multiple Stage Turbine or Steam Cycles Are AlsoRobinsyahNo ratings yet
- Options For Co-GenerationDocument12 pagesOptions For Co-GenerationAnonymous N3LpAXNo ratings yet
- Gas TurbineDocument23 pagesGas TurbineNur Achmad Busairi100% (1)
- Co Generation Unit 4Document52 pagesCo Generation Unit 4Johnson Johnson100% (2)
- Cogeneration PDFDocument19 pagesCogeneration PDFMandeep Singh100% (1)
- 10.1515 - Arh 2022 0128Document16 pages10.1515 - Arh 2022 0128ocaballero252No ratings yet
- Introduction To CCPP by BABDocument27 pagesIntroduction To CCPP by BABBilawal AhmedNo ratings yet
- تقرير مادة نظم القدرةDocument12 pagesتقرير مادة نظم القدرةHassan allaNo ratings yet
- ProgressDocument29 pagesProgressVictor BettNo ratings yet
- Clean Ironmaking and Steelmaking Processes: Efficient Technologies for Greenhouse Emissions AbatementFrom EverandClean Ironmaking and Steelmaking Processes: Efficient Technologies for Greenhouse Emissions AbatementNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamic analysis of geothermal heat pumps for civil air-conditioningFrom EverandThermodynamic analysis of geothermal heat pumps for civil air-conditioningRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Comparison of Diesel and Petrol EnginesFrom EverandComparison of Diesel and Petrol EnginesRating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Lecture#5Document7 pagesLecture#5ABDULLAH MAQBOOLNo ratings yet
- Lecture#2Document9 pagesLecture#2ABDULLAH MAQBOOLNo ratings yet
- BAY VIEW From by Abdullah Maqbool Roll No 14 Energy Engg Eve SectionDocument1 pageBAY VIEW From by Abdullah Maqbool Roll No 14 Energy Engg Eve SectionABDULLAH MAQBOOLNo ratings yet
- Design of A Dumping GrateDocument13 pagesDesign of A Dumping GrateABDULLAH MAQBOOL100% (1)
- Institute of Energy and Environmental Engineering Univerity of Punjab, Lahore Pakistan Sc. (Engg.) Energy Engineering (Evening-Program) Assignment OnDocument19 pagesInstitute of Energy and Environmental Engineering Univerity of Punjab, Lahore Pakistan Sc. (Engg.) Energy Engineering (Evening-Program) Assignment OnABDULLAH MAQBOOLNo ratings yet
- Roll No 28Document14 pagesRoll No 28ABDULLAH MAQBOOLNo ratings yet
- Institute of Energy and Environmental Engineering University of The Punjab, Lahore Bsc. Energy Engineering (Evening Program) Assignment OnDocument8 pagesInstitute of Energy and Environmental Engineering University of The Punjab, Lahore Bsc. Energy Engineering (Evening Program) Assignment OnABDULLAH MAQBOOLNo ratings yet
- Solved Problems Ref SystemDocument5 pagesSolved Problems Ref SystemArchie Gil DelamidaNo ratings yet
- Utran GT26Document46 pagesUtran GT26ravinder_kapriNo ratings yet
- ICE Handout 2 PDFDocument14 pagesICE Handout 2 PDFFaizan AhmedNo ratings yet
- Class Test Sets NewDocument7 pagesClass Test Sets NewNSS GBPECNo ratings yet
- ME 6701 Power Plant Engineering EEE 5 Sem A & BDocument16 pagesME 6701 Power Plant Engineering EEE 5 Sem A & BprabuparthibanNo ratings yet
- Lec - 25 - Ideal Jet Propulsion CycleDocument17 pagesLec - 25 - Ideal Jet Propulsion CycleJunaid KhanNo ratings yet
- External Combustion Engines PDFDocument43 pagesExternal Combustion Engines PDFMariaEzzaSyUyNo ratings yet
- Brayton Cycle PDFDocument43 pagesBrayton Cycle PDFAdly_arkim100% (2)
- After Passing Through A Convergent-Divergent Nozzle, The Temperature of Air Will: A. Increase B. Decrease C. Remains The Same D. None of TheseDocument100 pagesAfter Passing Through A Convergent-Divergent Nozzle, The Temperature of Air Will: A. Increase B. Decrease C. Remains The Same D. None of TheseVJ JhanruxNo ratings yet
- PHD Thesis On Refrigeration and Air ConditioningDocument6 pagesPHD Thesis On Refrigeration and Air Conditioningafcmunxna100% (2)
- Pipe Terms PDFDocument109 pagesPipe Terms PDFLourdes Marie Rosalejos OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Applied ThermodynamicsDocument3 pagesApplied ThermodynamicsPRATAP SINGHNo ratings yet
- Gas Turbines Part 2.1Document49 pagesGas Turbines Part 2.1Maznan Jaafar100% (1)
- Analysis of Inlet Air Temperature Effect On Gas Turbine Compressor PerfornanceDocument9 pagesAnalysis of Inlet Air Temperature Effect On Gas Turbine Compressor PerfornanceRafraf Ezdine100% (3)
- Improved Design For Supercritical Co2 Brayton Cycle Powered Coal-Fired Power PlantDocument51 pagesImproved Design For Supercritical Co2 Brayton Cycle Powered Coal-Fired Power PlantIrshad AhmadNo ratings yet
- Seminar ReportDocument31 pagesSeminar ReportShivam Sharma100% (2)
- Report On Gas TurbineDocument33 pagesReport On Gas TurbineKanika Kumar100% (1)
- Nasa R.U5 Pwas4M: N76-933 COWSUNPTION Final R Eport (Pratt Ani WhitneyDocument142 pagesNasa R.U5 Pwas4M: N76-933 COWSUNPTION Final R Eport (Pratt Ani WhitneyMark Evan SalutinNo ratings yet
- MET303 - Ktu QbankDocument16 pagesMET303 - Ktu QbankANAND V VNo ratings yet
- Power Plant Questions and AnswersDocument379 pagesPower Plant Questions and AnswersAshok Govindharasu100% (4)
- Brayton CycleDocument9 pagesBrayton CyclevqxknpnkNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2 Brayton CycleDocument2 pagesTutorial 2 Brayton CycleShahran IezzatNo ratings yet
- 11 Lecture (Brayton Cycle)Document61 pages11 Lecture (Brayton Cycle)Asees Aamir100% (1)
- Gas Turbines For Aircraft Propulsion Chapter 9.9-10Document25 pagesGas Turbines For Aircraft Propulsion Chapter 9.9-10vipinNo ratings yet
- Analysis and Comparison of The Simple and Recompression Supercritical Co2 Cycles PDFDocument8 pagesAnalysis and Comparison of The Simple and Recompression Supercritical Co2 Cycles PDFagneyan dileepNo ratings yet
- Practice Problems For Thermal Engineering: September 2019Document24 pagesPractice Problems For Thermal Engineering: September 2019Roderick VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Combustion Brayton Cycle ReviewerDocument3 pagesCombustion Brayton Cycle ReviewerOwel CabugawanNo ratings yet
- Bryton Cycle PDFDocument9 pagesBryton Cycle PDFEddyNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Marine Gas Turbines, Rev.1978Document91 pagesIntroduction To Marine Gas Turbines, Rev.1978gnd100No ratings yet
- Report EISDocument35 pagesReport EISSyafiq SulaimanNo ratings yet