Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Poster QCP en
Poster QCP en
Uploaded by
Yaser MCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5822)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (898)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (403)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Mispa I180 BrochureDocument2 pagesMispa I180 BrochureYaser MNo ratings yet
- Reminders of Drug Effects On Laboratory Test ResulDocument7 pagesReminders of Drug Effects On Laboratory Test ResulYaser MNo ratings yet
- 2.OVJ 005 11 10S.AKhanetalDocument9 pages2.OVJ 005 11 10S.AKhanetalYaser MNo ratings yet
- Table E2-2 - Properties of Useful Diagnostic Tests ReproduceDocument1 pageTable E2-2 - Properties of Useful Diagnostic Tests ReproduceYaser MNo ratings yet
- Afias Igra-TbDocument6 pagesAfias Igra-TbYaser MNo ratings yet
- A Novel Point-Of-Care Device For Blood Potassium Detection of Patients On Dialysis: Comparison With A Reference MethodDocument2 pagesA Novel Point-Of-Care Device For Blood Potassium Detection of Patients On Dialysis: Comparison With A Reference MethodYaser MNo ratings yet
- Vidas&MinividasDocument4 pagesVidas&MinividasYaser MNo ratings yet
- Elisa The EssentialsDocument22 pagesElisa The EssentialsYaser MNo ratings yet
- التدريس الفعال - أكثر من 1000 طريقة للتدريس الناجح - 81410Document410 pagesالتدريس الفعال - أكثر من 1000 طريقة للتدريس الناجح - 81410Yaser MNo ratings yet
- 2 1642 Fan Shaped Quintet PGo 16 9Document3 pages2 1642 Fan Shaped Quintet PGo 16 9Yaser MNo ratings yet
- Diasorin Company Presentation Eng March 2022 1Document13 pagesDiasorin Company Presentation Eng March 2022 1Yaser MNo ratings yet
- 10.1515 - TJB 2018 0462Document5 pages10.1515 - TJB 2018 0462Yaser MNo ratings yet
- Company Presentation Agosto 2015Document27 pagesCompany Presentation Agosto 2015Yaser MNo ratings yet
- RBC Indices and Extended RBC Parameters: Learning GuideDocument39 pagesRBC Indices and Extended RBC Parameters: Learning GuideYaser MNo ratings yet
- Comparison of 3 Immunodiagnostic Tests For Latent Tuberculosis Infection Among Thai PrisonersDocument1 pageComparison of 3 Immunodiagnostic Tests For Latent Tuberculosis Infection Among Thai PrisonersYaser MNo ratings yet
- Page - 40Document14 pagesPage - 40Yaser MNo ratings yet
- انسجه نظريDocument7 pagesانسجه نظريYaser MNo ratings yet
- History of Microbiology Lecture PowerPoint VMCCTDocument31 pagesHistory of Microbiology Lecture PowerPoint VMCCTYaser MNo ratings yet
- Consent Information SheetDocument2 pagesConsent Information SheetYaser MNo ratings yet
- Maglumi Ft3 (Clia) : Intended UseDocument4 pagesMaglumi Ft3 (Clia) : Intended UseYaser MNo ratings yet
- 6th Charles Merieux Conference 2019 Pre Post Analytical Errors in HematologyDocument7 pages6th Charles Merieux Conference 2019 Pre Post Analytical Errors in HematologyYaser MNo ratings yet
- Resp Results Interpretation Guide 1.20.2020Document2 pagesResp Results Interpretation Guide 1.20.2020Yaser MNo ratings yet
- IndianJPatholOncol 7 4 625 630Document6 pagesIndianJPatholOncol 7 4 625 630Yaser MNo ratings yet
- Argene Covid-19 Solutions Ce Marked - 9321502 007-Gb-A 3 0Document2 pagesArgene Covid-19 Solutions Ce Marked - 9321502 007-Gb-A 3 0Yaser MNo ratings yet
- The Effect of High Temperature On The Hematological Parameters of Bakery WorkersDocument4 pagesThe Effect of High Temperature On The Hematological Parameters of Bakery WorkersYaser MNo ratings yet
- Vidas FebDocument6 pagesVidas FebYaser MNo ratings yet
- Vidas Sars Cov-2 BrochureDocument2 pagesVidas Sars Cov-2 BrochureYaser MNo ratings yet
- 393 FullDocument6 pages393 FullYaser MNo ratings yet
- 173 FullDocument13 pages173 FullYaser MNo ratings yet
- Emergency Panel Vidas ShowpadDocument4 pagesEmergency Panel Vidas ShowpadYaser MNo ratings yet
Poster QCP en
Poster QCP en
Uploaded by
Yaser MOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Poster QCP en
Poster QCP en
Uploaded by
Yaser MCopyright:
Available Formats
Externalization of Internal Quality Control in Hematology
Philippe Milian – Manuela Pastore HORIBA Medical, Montpellier, France
Introduction Material & Methods
The objectives of internal quality control are to detect immediate errors and monitor over time precision and The ABX Quality Control Program (QCP) is an online inter-laboratory comparison for all HORIBA Medical
accuracy of the method. However to lead an exhaustive self-evaluation, peer-related bias and relative impre- hematology customers that can be accessed at the website http://qcp.horiba-abx.com.
cision should be taken into account. Standardization committees, such as the CLSI, suggest the integration Each laboratory has an online account where quality control results can be submitted daily or monthly
of inter-laboratory programs in order to determine the individual laboratory bias relative to a peer group. This (detail or summary report) to externalize the internal control data.
practice allows achieving two distinct but related aims. Inter-laboratory performances will delineate the opti- All results are centralized and processed in real time for a preliminary follow-up and monthly for a final
mum of the performances of the specific technology and define the state of art. Each laboratory can indeed and more detailed report. At any time and in real time the user can access the preliminary report of com-
evaluate and measure the individual results in comparison to the state of the art technology. In addition the parison with the peer group. The preliminary report is updated day by day.
inter-laboratory comparison consents the single laboratory to be aware of the relationship between the state The peer groups are constituted of customers using the same type of control on analogous instruments.
of the art and the medical needs. Therefore participation in an inter-laboratory program provides an effective The mean value obtained worldwide defines the TRUE VALUE of each parameter.
and real-time tool to complement external quality assessment programs (proficiency survey).
The QCP reports:
We present here the externalization of the internal quality control in HORIBA Medical hematology instruments.
. Results of the laboratory: average, CV and standard deviation of the Internal Quality Control (IQC)
and provides:
Results
. Inter-laboratory comparison: the precision index (PI) and accuracy index (SDI or Z-score)
Six hundred (600) users in 26 countries regularly
are compared to a world group of similar analyzers.
participate to QCP, providing more than 24,000
results that are processed every month. . Calculation of the uncertainty: the uncertainty defines an interval around the measurement result
The QCP provides a monthly report, comparing within which the value of the measure can be confidently expected to lie.
the lab results of the internal QC to the peers, . Evaluation of the performances through the Sigma values (Westgard, 2001): The “Sigma value”
and an annual report that allows to visualize the is the capacity of an analytical system calculated by the ratio between actual performances and required
trend over the time. Finally some case studies are performances or medical needs, (Ricos & al). This is then compared to the Sigma Objective that defines
presented to exemplify the role of QCP to help the
the state of the art capacity in agreement with the medical needs (Total error allowable (TEa) =6).
lab in quality assurance.
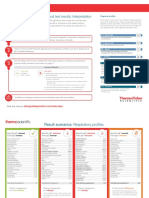
Monthly report
Inter-laboratory comparison. The graph (Fig.1) represents the level of precision (blue) and the accuracy
Each laboratory, having submitted its data, receives a monthly report including its results of the IQC, the (red) for all parameters of a lab compared to the peer mean indicated by the zero level. In this particular
comparison indexes (PI et SDI orZ-score), to the peer group performances, and QCP alert if the values example, precision is correct, however, MCV accuracy and of course HCT are inaccurate . These repre-
are outside the range, the uncertainty calculation and the sigma value. sentations, as shown below, allow to seize at a glance the global performance of the laboratory
and distinguish the defective parameters in order to promptly plan actions.
Table 1
IQC Results. Table 1 sum-
marizes for each parameter
and for three levels (low,
normal, high) the laboratory
performance compared to
peers.
Fig.1
Precision Index interpretation CV Lab
CVI = PI =
CV peer group
PI should be < 1 with optimal value at 0.5
If PI>1, a red alert triangle is triggered. If PI>2, in
addition, a QCP alert is generated and informs the Uncertainty calculation Table 2 Sigma calculation
HORIBA Medical Technical Service in order to plan (TEa %)
intervention and actions. u (C) IQC =
√ (bias
√3
) + (SD)2 Sigma obj =
0,5 x CV %
Z-score Index interpretation (X Lab -X peer group) The uncertainty, required by
(TEa % - bias %)
SDI = Z-score = ISO 15189, is automatically Sigma =
If -1.5< Z-score <1.5 results are acceptable with SD peer group cv %
ideal value at 0. If the value falls between -1.5 and provided (Table 2).
-2 or 1.5 and 2, a red alert triangle is triggered. If The Sigma Lab allows positioning the lab performances to the me-
the value is <-2 or >2, in addtion, a QCP alert is ge- dical requirement where the Sigma Obj refers to the technological li-
nerated and informs the Horiba Medical Technical mits (Table 2).
Service in order to plan intervention and actions.
Annual report
The annual report contains the same analysis as the monthly re- The Fig 2 shows the On Fig. 3, the Sigma
port but in addition permits to follow the progression of perfor- monthly trend of the monthly trends are
mances over the time; it also provides the uncertainty calculation WBC parameter displaid compared to
taking into account the bias variability in that lapse of time. over a year. the medical require-
ments (6 as green
WBC Level N line) and the state of
the art (8.6 as blue
Fig.3
line).
Fig.2
The uncertainty on the analytical results is recalculated taking Table 4
into account the mean, the SD and bias over the year (Table 3).
Table 4 shows statistical description of external quality asses-
ment bias of normal level of WBC.
Table 3
Annual report
EXAMPLE 1 EXAMPLE 2
In the graph, the MCV of the IQC is not in agreement with For other parameters such as WBC (H) of the IQC
the defined needs. the performances of the instrument are better than
This may be due to the aknowledged fact that the control the medical needs.
RBC are stabilized cells whose volume increases over the
time. The state of the art is lower than the medical needs.
EXAMPLE 3
We show here that for the PLT (level N), the state
The SDI/PI graph shows that pre-
of the art and the medical needs are similar.
cision can be improved and that
However the performance of the instrument can
accuracy has been degrading over
be improved since the capability has been de-
the last 6 months. The bias on the
creasing over the last year.
high level confirms this derivation.
Conclusions Bibliography
The QCP is a powerful tool conceived to collect the laboratory results world-wide, make statistical elaboration based on the recognized Ricos C, Alvarez V, Cava F, Garcia-Lario JV, Hernandez A, Jimenez
recommendations and finally send a dedicated analysis back to each customers in real time and over a period of one year to visualize CV, Minchinela J, Perich C, Simon M. "Current databases on bio-
ISLH 2012
the progress of performances. Through these indexes, each lab precisely knows in which period and for which parameter actions logic variation: pros, cons and progress." Scand J Clin Lab Invest
must be realized and therefore it can define the adequate strategy. 1999;59:491-500. Updated in 2012.
Finally the QCP helps to improve the lab performance and contributes to meet the requirements of regulation and accreditation orga- Westgard QC: http://www.westgard.com/biodatabase1.htm
nizations by making statistical analysis .
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5822)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (898)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (403)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Mispa I180 BrochureDocument2 pagesMispa I180 BrochureYaser MNo ratings yet
- Reminders of Drug Effects On Laboratory Test ResulDocument7 pagesReminders of Drug Effects On Laboratory Test ResulYaser MNo ratings yet
- 2.OVJ 005 11 10S.AKhanetalDocument9 pages2.OVJ 005 11 10S.AKhanetalYaser MNo ratings yet
- Table E2-2 - Properties of Useful Diagnostic Tests ReproduceDocument1 pageTable E2-2 - Properties of Useful Diagnostic Tests ReproduceYaser MNo ratings yet
- Afias Igra-TbDocument6 pagesAfias Igra-TbYaser MNo ratings yet
- A Novel Point-Of-Care Device For Blood Potassium Detection of Patients On Dialysis: Comparison With A Reference MethodDocument2 pagesA Novel Point-Of-Care Device For Blood Potassium Detection of Patients On Dialysis: Comparison With A Reference MethodYaser MNo ratings yet
- Vidas&MinividasDocument4 pagesVidas&MinividasYaser MNo ratings yet
- Elisa The EssentialsDocument22 pagesElisa The EssentialsYaser MNo ratings yet
- التدريس الفعال - أكثر من 1000 طريقة للتدريس الناجح - 81410Document410 pagesالتدريس الفعال - أكثر من 1000 طريقة للتدريس الناجح - 81410Yaser MNo ratings yet
- 2 1642 Fan Shaped Quintet PGo 16 9Document3 pages2 1642 Fan Shaped Quintet PGo 16 9Yaser MNo ratings yet
- Diasorin Company Presentation Eng March 2022 1Document13 pagesDiasorin Company Presentation Eng March 2022 1Yaser MNo ratings yet
- 10.1515 - TJB 2018 0462Document5 pages10.1515 - TJB 2018 0462Yaser MNo ratings yet
- Company Presentation Agosto 2015Document27 pagesCompany Presentation Agosto 2015Yaser MNo ratings yet
- RBC Indices and Extended RBC Parameters: Learning GuideDocument39 pagesRBC Indices and Extended RBC Parameters: Learning GuideYaser MNo ratings yet
- Comparison of 3 Immunodiagnostic Tests For Latent Tuberculosis Infection Among Thai PrisonersDocument1 pageComparison of 3 Immunodiagnostic Tests For Latent Tuberculosis Infection Among Thai PrisonersYaser MNo ratings yet
- Page - 40Document14 pagesPage - 40Yaser MNo ratings yet
- انسجه نظريDocument7 pagesانسجه نظريYaser MNo ratings yet
- History of Microbiology Lecture PowerPoint VMCCTDocument31 pagesHistory of Microbiology Lecture PowerPoint VMCCTYaser MNo ratings yet
- Consent Information SheetDocument2 pagesConsent Information SheetYaser MNo ratings yet
- Maglumi Ft3 (Clia) : Intended UseDocument4 pagesMaglumi Ft3 (Clia) : Intended UseYaser MNo ratings yet
- 6th Charles Merieux Conference 2019 Pre Post Analytical Errors in HematologyDocument7 pages6th Charles Merieux Conference 2019 Pre Post Analytical Errors in HematologyYaser MNo ratings yet
- Resp Results Interpretation Guide 1.20.2020Document2 pagesResp Results Interpretation Guide 1.20.2020Yaser MNo ratings yet
- IndianJPatholOncol 7 4 625 630Document6 pagesIndianJPatholOncol 7 4 625 630Yaser MNo ratings yet
- Argene Covid-19 Solutions Ce Marked - 9321502 007-Gb-A 3 0Document2 pagesArgene Covid-19 Solutions Ce Marked - 9321502 007-Gb-A 3 0Yaser MNo ratings yet
- The Effect of High Temperature On The Hematological Parameters of Bakery WorkersDocument4 pagesThe Effect of High Temperature On The Hematological Parameters of Bakery WorkersYaser MNo ratings yet
- Vidas FebDocument6 pagesVidas FebYaser MNo ratings yet
- Vidas Sars Cov-2 BrochureDocument2 pagesVidas Sars Cov-2 BrochureYaser MNo ratings yet
- 393 FullDocument6 pages393 FullYaser MNo ratings yet
- 173 FullDocument13 pages173 FullYaser MNo ratings yet
- Emergency Panel Vidas ShowpadDocument4 pagesEmergency Panel Vidas ShowpadYaser MNo ratings yet