Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Hes 029 Lab Sas 6
Hes 029 Lab Sas 6
Uploaded by
Crislyn Jilou Bugas AdlawanOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Hes 029 Lab Sas 6
Hes 029 Lab Sas 6
Uploaded by
Crislyn Jilou Bugas AdlawanCopyright:
Available Formats
Crislyn Jilou B.
Adlawan Anatomy & Physiology -Laboratory
SWU BSN1-A9 BS NURSING / FIRST YEAR Session # 6
LESSON PREVIEW/REVIEW
1. What are the similarities and differences of Plant, Animal, and Human Cell when it comes to their structure: What
does this cell have that this/these cells do not have?
>Plant, animal, and human cells share some basic parts like the skin (cell membrane), control center
(nucleus), jelly inside (cytoplasm), and power factories (mitochondria). But they're not exactly the same.
Plants have a strong wall, green factories (chloroplasts), and a big water storage (vacuole). Animals and
humans don't have these, but they have cleaners (lysosomes), division helpers (centrioles), and sometimes
tails or hairs (flagella or cilia). These changes help them do their special jobs in different ways, like plants
making food and animals moving around.
.
CHECK FOR UNDERSTANDING
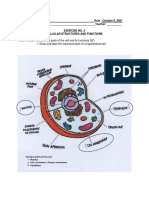
LABEL FUNCTION
1. CELL MEMBRANE The cell membrane controls what goes in and out of the cell, acting
like a gatekeeper to maintain the cell's internal environment and allow
communication with the outside world
2. GOLGI APPARATUS The Golgi apparatus modifies, sorts, and packages proteins and lipids
for transport to their specific destinations inside or outside the cell.
3. NUCLEAR The nuclear envelope separates the nucleus from the rest of the cell,
ENVELOPE regulating the movement of materials in and out of the nucleus and
protecting the genetic material inside.
4. CYTOPLASM The cytoplasm is a jelly-like substance that supports and suspends
the cell's organelles. It's where many cellular processes occur.
5. MITOCHONDRION Mitochondria are the powerhouses of the cell, producing energy (ATP)
through cellular respiration, which fuels various cellular activities
6. ROUGH The RER is involved in protein synthesis, with ribosomes on its surface
ENDOPLASMIC helping to make and modify proteins that are destined for various
RETICULUM cellular locations.
7. NUCLEOLUS The nucleolus is responsible for producing ribosomes, which are
essential for protein synthesis
8. LYSOSOME Lysosomes contain enzymes that break down waste materials and
cellular debris, playing a role in cellular digestion and recycling
9. RIBOSOME Ribosomes are the cellular machinery for protein synthesis,
translating genetic instructions from the nucleus into functional
proteins.
Instruction: Draw a human cell membrane and identify the hydrophobic and hydrophilic part of the membrane.
AL STRATEGY: SUCCESS CRITERIA
1. I can able to define a cell and discuss its essential functions
2. I can identify the significance of the cell membrane and clarify its responsibility in regulating the
movement of substances in and out of the cell.
3. I can describe the concept of the fluid-mosaic model and understand how it explains the structure of the
cell membrane
You might also like
- SERVOPRO 4000 Series - Service ManualDocument190 pagesSERVOPRO 4000 Series - Service ManualGuillermo Zapata100% (1)
- Aws Lambda TutorialDocument393 pagesAws Lambda Tutorialswathi sree75% (4)
- Master Data Governance For Custom ObjectDocument188 pagesMaster Data Governance For Custom ObjectDuy NguyenNo ratings yet
- Saudi Aramco Engineering Standards-Electrical-CommissioningDocument61 pagesSaudi Aramco Engineering Standards-Electrical-Commissioningsyedsalmanali9193% (15)
- Raw Material Handling Plant: Download The Original AttachmentDocument36 pagesRaw Material Handling Plant: Download The Original AttachmentJaved AlamNo ratings yet
- Solutions Nss NC 11Document19 pagesSolutions Nss NC 11saadullahNo ratings yet
- Module For Anaphy CellDocument11 pagesModule For Anaphy CellBJ Bernardo IlNo ratings yet
- Cell The Basic Unit of Life 1Document22 pagesCell The Basic Unit of Life 1Matt Andrei AmorosoNo ratings yet
- Act 1. Physiology Lab. Group 5Document21 pagesAct 1. Physiology Lab. Group 5YEO, REGGIE ALBERT A.No ratings yet
- Cell Structure and FunctionsDocument23 pagesCell Structure and FunctionsAngel OrodioNo ratings yet
- XOXOXDocument7 pagesXOXOXVazima QtNo ratings yet
- LESSON 1 General BiologyDocument93 pagesLESSON 1 General Biologygelisan haruhiNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and FunctionDocument6 pagesCell Structure and FunctionYeshua Dan BigasaNo ratings yet
- Exercise 1 The CellDocument4 pagesExercise 1 The CellKATHLEEN MAE HERMONo ratings yet
- Act 3 Animal Cell.Document8 pagesAct 3 Animal Cell.SidNo ratings yet
- BIOCHEM (Exercise 1)Document4 pagesBIOCHEM (Exercise 1)KATHLEEN MAE HERMONo ratings yet
- Cell Wall: Plant Cells Have A Large Vacuole That Helps Maintain TheDocument6 pagesCell Wall: Plant Cells Have A Large Vacuole That Helps Maintain TheErnie RetesNo ratings yet
- Module 1-2Document21 pagesModule 1-2Edel Ruth Pal-Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Exercise 02 - The Animal CellDocument4 pagesExercise 02 - The Animal CellYsabel De LeonNo ratings yet
- BiochemistryDocument4 pagesBiochemistryAaliyah Ashley CerboNo ratings yet
- g11 Els OrganellesDocument3 pagesg11 Els OrganellesJarod PeñaflorNo ratings yet
- Notes Human AnatomyDocument4 pagesNotes Human AnatomyLeslie Ann MesolisNo ratings yet
- Enumerate The Different Eukaryotic Cell Organelles and Its FunctionDocument3 pagesEnumerate The Different Eukaryotic Cell Organelles and Its FunctionMarie ClaireNo ratings yet
- What Are CellsHS PDFDocument12 pagesWhat Are CellsHS PDFIbrahim SiddigNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology Chapter-Ii Introduction To The Detailed Structure of The BodyDocument31 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Chapter-Ii Introduction To The Detailed Structure of The BodyAzher MahmoodNo ratings yet
- Ch. 3 Cell ReviewDocument5 pagesCh. 3 Cell ReviewDivine GelasiusNo ratings yet
- Animal Cell Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesAnimal Cell Lesson PlanGilda Genive AriolaNo ratings yet
- Bio 221 Lecture NotesDocument10 pagesBio 221 Lecture NotesMuhammad LawalNo ratings yet
- Edible Plant CellDocument4 pagesEdible Plant CellgeorgiaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 - Cell OrganellesDocument3 pagesLesson 2 - Cell OrganellesAly FayeNo ratings yet
- General Biology Modules 1 3Document36 pagesGeneral Biology Modules 1 3Glen MillarNo ratings yet
- Cell Grade 7Document65 pagesCell Grade 7SUDARAT THONGPHAYONGNo ratings yet
- Cell DelacruzDocument46 pagesCell DelacruzKylamae BautistaNo ratings yet
- Gen Zoology ReviewerDocument19 pagesGen Zoology ReviewerDarey ApostolNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and Cell OrganisationDocument16 pagesCell Structure and Cell OrganisationanippoNo ratings yet
- Marquez 3d CellDocument5 pagesMarquez 3d CellSatori TendōNo ratings yet
- 1st ClassDocument8 pages1st ClassSamson AdewaleNo ratings yet
- 9th Unit 1Document17 pages9th Unit 1[36] IX-B P.Vishnu Vardhan ReddyNo ratings yet
- PLB Plant Biology: Introduction To CellDocument9 pagesPLB Plant Biology: Introduction To CellElle AdetounNo ratings yet
- Biology Chapter 1 NotesDocument6 pagesBiology Chapter 1 Notesmohan.shenoy52No ratings yet
- Worksheet: Name: - Class: - DateDocument7 pagesWorksheet: Name: - Class: - DateKaung Myat SanNo ratings yet
- CellDocument11 pagesCellNicole ArangurenNo ratings yet
- Genbio1 Unit1 Chapter1 (Week2)Document48 pagesGenbio1 Unit1 Chapter1 (Week2)Sofia EgbalicNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2ALevels of Organization in Animal ComplexityDocument15 pagesLecture 2ALevels of Organization in Animal ComplexityElleNo ratings yet
- m2 DraftDocument4 pagesm2 DraftMae lea AndoloyNo ratings yet
- DR. WZCA SEC 1 SCIENCE Revision Notes For Chapter 6Document14 pagesDR. WZCA SEC 1 SCIENCE Revision Notes For Chapter 6Cole- Min Khant KyawNo ratings yet
- Acad Fall08 ThecellDocument13 pagesAcad Fall08 Thecellhassanmusahassan81No ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Parts and Functions of The CellDocument26 pagesLesson 2 Parts and Functions of The CellDavid BayaniNo ratings yet
- Isnain - Biochem Lec - Assignment 1Document4 pagesIsnain - Biochem Lec - Assignment 1Erich IsnainNo ratings yet
- Bi12 LG U02-KeyDocument6 pagesBi12 LG U02-KeyZahida SultanNo ratings yet
- Cell AnalogyDocument17 pagesCell AnalogyJianne CabildoNo ratings yet
- "Life Begins With Cells": Cell Biology IDocument23 pages"Life Begins With Cells": Cell Biology ITeacher Ella MorillaNo ratings yet
- Cell TissueDocument36 pagesCell TissueMary Grace NavarroNo ratings yet
- Biochem The Celleluar Basis of LifeDocument21 pagesBiochem The Celleluar Basis of Lifealmira garciaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Ans Physiology Cell Structures and Functions - LAB EXERCISEDocument3 pagesAnatomy Ans Physiology Cell Structures and Functions - LAB EXERCISEMARY KATE L. CEBALLOSNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles - Notes Cell Theory Cells Are The Basic Unit of Life. The Cell Theory States ThatDocument7 pagesCell Organelles - Notes Cell Theory Cells Are The Basic Unit of Life. The Cell Theory States ThatSpongie BobNo ratings yet
- LAS 4 - Plant and Animal CellsDocument7 pagesLAS 4 - Plant and Animal CellsJeanne RanielleNo ratings yet
- Cell Classix Session3 Made by Purnima Sharma 1Document7 pagesCell Classix Session3 Made by Purnima Sharma 1jeetjyoti787No ratings yet
- Animal CellDocument31 pagesAnimal CellAlyssa Sofia AlihNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Cell Structure and Function - NotesDocument8 pagesUnit 2 - Cell Structure and Function - Notesronel.jnmsNo ratings yet
- CellsDocument4 pagesCellscalustre2016No ratings yet
- W1 Bio 1Document4 pagesW1 Bio 1Joven J. AndohoyanNo ratings yet
- 3 - CellsDocument28 pages3 - CellsKat MicaelNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and Functions PDFDocument5 pagesCell Structure and Functions PDFViswasriNo ratings yet
- Parts of A Cell BIOLOGYDocument43 pagesParts of A Cell BIOLOGYSam Ferbyn LomotanNo ratings yet
- Nur Sas 21Document1 pageNur Sas 21Crislyn Jilou Bugas AdlawanNo ratings yet
- Nur Sas 23Document1 pageNur Sas 23Crislyn Jilou Bugas AdlawanNo ratings yet
- Hes 029 Lab Sas 19Document2 pagesHes 029 Lab Sas 19Crislyn Jilou Bugas AdlawanNo ratings yet
- Hes 029 Lab Sas 19Document2 pagesHes 029 Lab Sas 19Crislyn Jilou Bugas AdlawanNo ratings yet
- Nur Sas 13Document1 pageNur Sas 13Crislyn Jilou Bugas AdlawanNo ratings yet
- Hes 029 Lab Sas 1Document2 pagesHes 029 Lab Sas 1Crislyn Jilou Bugas AdlawanNo ratings yet
- Hes 029 Lec Sas 10Document1 pageHes 029 Lec Sas 10Crislyn Jilou Bugas AdlawanNo ratings yet
- Hes 029 Lec Sas 9Document1 pageHes 029 Lec Sas 9Crislyn Jilou Bugas AdlawanNo ratings yet
- Hes 029 Lab Sas 2Document2 pagesHes 029 Lab Sas 2Crislyn Jilou Bugas AdlawanNo ratings yet
- Session #3 SAS - AnaPhy (Lab)Document3 pagesSession #3 SAS - AnaPhy (Lab)Crislyn Jilou Bugas AdlawanNo ratings yet
- Hes 029 Lab Sas 5Document2 pagesHes 029 Lab Sas 5Crislyn Jilou Bugas AdlawanNo ratings yet
- E2847-14 Calibration and Accuracy Verification of Wideband Infrared ThermometersDocument17 pagesE2847-14 Calibration and Accuracy Verification of Wideband Infrared ThermometerslukiNo ratings yet
- CPE7012-B Coursework 2 Brief 2020-1Document6 pagesCPE7012-B Coursework 2 Brief 2020-1Prashant PrashantNo ratings yet
- Process CostingDocument49 pagesProcess CostingAccounting Files100% (2)
- Web Services For RPGersDocument68 pagesWeb Services For RPGersRizwan AhmedNo ratings yet
- Transportation and Transhipment ProblemsDocument4 pagesTransportation and Transhipment Problemstejashraj93No ratings yet
- Research Article: Skull Sex Estimation Based On Wavelet Transform and Fourier TransformDocument11 pagesResearch Article: Skull Sex Estimation Based On Wavelet Transform and Fourier Transformgloria smithNo ratings yet
- ACS758 DatasheetDocument22 pagesACS758 Datasheetmachadofelipe88No ratings yet
- Beirut Arab University: CVLE 210 StaticsDocument3 pagesBeirut Arab University: CVLE 210 StaticsbassamNo ratings yet
- Emet3006 2014Document3 pagesEmet3006 2014Scarl0sNo ratings yet
- 10 1002@14356007 A27049Document34 pages10 1002@14356007 A27049Adam Septiyono ArlanNo ratings yet
- Diplomado CCNPDocument172 pagesDiplomado CCNPalexis pedrozaNo ratings yet
- Codigos de FallaDocument5 pagesCodigos de FallaLuis Angel Condori MoralesNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4Document63 pagesLecture 4InfragNo ratings yet
- Design and Analysis of Steering System of Prototype Ship: Presented By: Guided byDocument28 pagesDesign and Analysis of Steering System of Prototype Ship: Presented By: Guided bysandeep kumar mandalNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Unit 2.10 OxfordDocument5 pagesChemistry Unit 2.10 OxfordMichelle LeeNo ratings yet
- Question BankDocument3 pagesQuestion BankKuldeepNo ratings yet
- Excel Short KeysDocument2 pagesExcel Short Keysdeepchandsharma100% (14)
- QFT1notes PDFDocument271 pagesQFT1notes PDFprivado088No ratings yet
- VNT Brochure NewDocument5 pagesVNT Brochure Newda vin ciNo ratings yet
- Highly Sensitive and Rugged GC/MS/MS Tool: For Pesticide Multiresidue Analysis in Food SamplesDocument8 pagesHighly Sensitive and Rugged GC/MS/MS Tool: For Pesticide Multiresidue Analysis in Food SamplesDesislav DonchevNo ratings yet
- Festo MPS Pa ControlDocument129 pagesFesto MPS Pa ControlKaan CanNo ratings yet
- 02 LRDocument11 pages02 LRDebashish DekaNo ratings yet
- Plugin Erect BaziDocument15 pagesPlugin Erect BazirendaoNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 4 Quarter 4 Week 6: NAME: - GR & SEC: - CompetencyDocument9 pagesMathematics 4 Quarter 4 Week 6: NAME: - GR & SEC: - CompetencyRea Mae CorreNo ratings yet