Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 viewsNOTES 1st Sem P F
NOTES 1st Sem P F
Uploaded by
Rea1) Progesterone is a key hormone that helps maintain pregnancy by relaxing the uterus and preventing premature contractions and abortion. It also thickens the uterine lining.
2) The placenta functions to supply oxygen and nutrients to the developing fetus while removing waste products. It produces hormones like human chorionic gonadotropin and human placental lactogen that help sustain the pregnancy.
3) Fertilization typically occurs around 8-10 days after implantation in the uterus. The fertilized egg then undergoes cell division and develops into an embryo over the next few weeks.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Obstetrics & Gynecologyc MnemonicsDocument12 pagesObstetrics & Gynecologyc MnemonicsMuhammad Luqman Nul HakimNo ratings yet
- Development Biology Multiple Choice QuestionDocument16 pagesDevelopment Biology Multiple Choice QuestionGuruKPO81% (16)
- Nurs 5002 - Case Study 3Document14 pagesNurs 5002 - Case Study 3api-308904543No ratings yet
- MCN Notes 2Document26 pagesMCN Notes 2Rogeimar Claire MangomayaoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 The Growing FetusDocument4 pagesChapter 9 The Growing FetusCarrie ANo ratings yet
- MCN LectureDocument8 pagesMCN LectureEmily BernatNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - Process of Conception and Stage of Fetal DevelopmentDocument25 pagesModule 2 - Process of Conception and Stage of Fetal DevelopmentKatie HolmesNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1physiology of PregnancyDocument42 pagesLecture 1physiology of PregnancyBlessie Zyren BasinangNo ratings yet
- Reporductive SystemDocument31 pagesReporductive SystemEmma Joel OtaiNo ratings yet
- Maternal and Child (Healthy Pregnancy)Document37 pagesMaternal and Child (Healthy Pregnancy)Lenny SucalditoNo ratings yet
- GA&E 13 - Fertilization & ImplantationDocument49 pagesGA&E 13 - Fertilization & ImplantationSu ZikaiNo ratings yet
- Female Cycles GAD 203Document20 pagesFemale Cycles GAD 203alhobabighnemNo ratings yet
- OB 1st SemDocument4 pagesOB 1st SemMai CarbonNo ratings yet
- 178 Anatomy Reproductive SystemDocument29 pages178 Anatomy Reproductive SystemJohn Mark JuarezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9: Nursing Care During Normal Pregnancy and Care of The Developing FetusDocument8 pagesChapter 9: Nursing Care During Normal Pregnancy and Care of The Developing FetusAlyssaGrandeMontimor100% (1)
- MCN Nursing 1Document107 pagesMCN Nursing 1Fau Fau DheoboNo ratings yet
- 178 Anatomy Reproductive SystemDocument25 pages178 Anatomy Reproductive SystemJUVY ANN PATOSANo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive Ogans Internal Organs of ReproductionDocument22 pagesFemale Reproductive Ogans Internal Organs of ReproductionAngela NeriNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive Ogans Internal Organs of ReproductionDocument22 pagesFemale Reproductive Ogans Internal Organs of ReproductionAecille VillarNo ratings yet
- Fertilization and ImplantationDocument3 pagesFertilization and ImplantationTandingco, Olivia Mari H.No ratings yet
- Maternal and Child Health NursingDocument22 pagesMaternal and Child Health NursingRam Van MunsterNo ratings yet
- NCM 107 Study GuideDocument3 pagesNCM 107 Study GuideJamilah BanglanNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Pregnancy & Functions of Placenta-1Document31 pagesPhysiology of Pregnancy & Functions of Placenta-1Ajit ShahNo ratings yet
- RevkeDocument11 pagesRevkeLowellyn Grezen VillaflorNo ratings yet
- Midterm PPT MaternalDocument13 pagesMidterm PPT Maternaladrianleet18No ratings yet
- Care of The Mother and Fetus During The Perinatal PeriodDocument37 pagesCare of The Mother and Fetus During The Perinatal PeriodSana ChanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 29 - Development and Inheritance: ST ND RD STDocument5 pagesChapter 29 - Development and Inheritance: ST ND RD STtomorrow.today.yesterday .yesterdayNo ratings yet
- NSVDDocument32 pagesNSVDChris Oliver Kevin Ledesma100% (3)
- Notes Maternal Health NursingdsdsDocument21 pagesNotes Maternal Health NursingdsdsL Rean Carmelle MAGALLONESNo ratings yet
- I. Anatomy & Physiology: Readiness For Child BearingDocument3 pagesI. Anatomy & Physiology: Readiness For Child BearingRalph Tama Mangacop BenitoNo ratings yet
- 1-4 Fertilization & Fetal DevelopmentDocument9 pages1-4 Fertilization & Fetal DevelopmentElla DionedaNo ratings yet
- Care of The Mother and Fetus During The Perinatal PeriodDocument37 pagesCare of The Mother and Fetus During The Perinatal PeriodSana ChanNo ratings yet
- h1 Reproductive Physiology Course Summary NotesDocument11 pagesh1 Reproductive Physiology Course Summary NotesHoney BaseriNo ratings yet
- MCHN 3RD LectDocument9 pagesMCHN 3RD LectZahNo ratings yet
- 2 Introduction To Embryology and FetalDocument55 pages2 Introduction To Embryology and Fetaldemeke andebetNo ratings yet
- EMBRYOLOGYDocument30 pagesEMBRYOLOGYMSc. PreviousNo ratings yet
- DoReMi Ni Lalala EDITED PDFDocument156 pagesDoReMi Ni Lalala EDITED PDFEleonor Katreeya LimsiNo ratings yet
- Competency 1-The Family Before Birth: 1. Explain The Structure and Function of The Female Reproductive SystemDocument4 pagesCompetency 1-The Family Before Birth: 1. Explain The Structure and Function of The Female Reproductive SystemEnorl FerdinandNo ratings yet
- OR Write-Up CSDocument13 pagesOR Write-Up CSalex_tan1981No ratings yet
- Handout On ReproDocument4 pagesHandout On ReproJoe JosephNo ratings yet
- Fertilization and Implantation Copy To StudentsDocument40 pagesFertilization and Implantation Copy To StudentsRiya SinghNo ratings yet
- NCM 108 - Nursing Care During Normal Pregnancy and Care of The Developing FetusDocument5 pagesNCM 108 - Nursing Care During Normal Pregnancy and Care of The Developing FetusKristine BartsNo ratings yet
- Reproduction NotesDocument27 pagesReproduction NotesAyra AlbairaNo ratings yet
- Maternal and Child NursingDocument43 pagesMaternal and Child NursingSophia WongNo ratings yet
- Week 2 Sex and FertDocument17 pagesWeek 2 Sex and FertAbmil Ching TinggalongNo ratings yet
- MENSTRUATION: Monthly Discharge of Blood From The Uterus Occurring Form Puberty To MenopauseDocument18 pagesMENSTRUATION: Monthly Discharge of Blood From The Uterus Occurring Form Puberty To Menopauselyka resurreccionNo ratings yet
- Part, Function and Process of Reproduction SystemDocument31 pagesPart, Function and Process of Reproduction SystemSavia NaldiNo ratings yet
- Week 12-Female InfertilityDocument2 pagesWeek 12-Female InfertilityJaimie Charlotte Marie LangilleNo ratings yet
- Embryology Lecture Note 2Document19 pagesEmbryology Lecture Note 2jestreametefiaNo ratings yet
- MCN Lec Antepartal To Ob ClassificationDocument11 pagesMCN Lec Antepartal To Ob ClassificationJay EstrellaNo ratings yet
- OB CompiledDocument156 pagesOB CompiledMikeeeNo ratings yet
- MCN Midterm 1Document12 pagesMCN Midterm 1sherelyn legaspiNo ratings yet
- Menstruation FertilizationDocument2 pagesMenstruation FertilizationJamie Rose GarciaNo ratings yet
- 1.1c Implantation & Placental DevelopmentDocument5 pages1.1c Implantation & Placental DevelopmentBea Samonte100% (1)
- Module 2 HandsoutDocument10 pagesModule 2 HandsoutErin SaavedraNo ratings yet
- PEDIA-REVIEWER EditedDocument7 pagesPEDIA-REVIEWER EditedTO THE MOONNo ratings yet
- Parts of The SystemDocument14 pagesParts of The SystembookonscribdNo ratings yet
- MaternalDocument6 pagesMaternalBlessed Glaiza MarianoNo ratings yet
- Dasar2 Biomolekuler Repro WanitaDocument51 pagesDasar2 Biomolekuler Repro WanitaFitriaNo ratings yet
- The PlacentaDocument3 pagesThe PlacentaLiezelNo ratings yet
- Post Partum HemorrhageDocument9 pagesPost Partum HemorrhageghsNo ratings yet
- Ovum, Functions, Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandOvum, Functions, Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Office Word DocumentDocument11 pagesNew Microsoft Office Word DocumentMihaela AndreiNo ratings yet
- Ncert Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 3 Human ReproductionDocument14 pagesNcert Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 3 Human ReproductionDeepanjan DASNo ratings yet
- WHLP Science10 Q3 W1 2Document15 pagesWHLP Science10 Q3 W1 2Christian DecenaNo ratings yet
- Science 10Document51 pagesScience 10Michelle LapuzNo ratings yet
- Quiz 8 To 46Document7 pagesQuiz 8 To 46JhayneNo ratings yet
- Embryology Chapter 3Document23 pagesEmbryology Chapter 3Abdisamed AllaaleNo ratings yet
- A Study of Knowledge and Practices Among Adolescents Girls Regarding Menstruation in Government Schools of AmritsarDocument4 pagesA Study of Knowledge and Practices Among Adolescents Girls Regarding Menstruation in Government Schools of AmritsarInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Secrets To Happy MarriagesDocument30 pagesSecrets To Happy Marriagesrobert543100% (1)
- Grade 6 Human Reproduction New Vocabulary: English WordDocument9 pagesGrade 6 Human Reproduction New Vocabulary: English WordSalome TamaraNo ratings yet
- Biology For 12th Class CbseDocument245 pagesBiology For 12th Class Cbseramanadk100% (2)
- 1st Periodical Test I Science ReviewerDocument7 pages1st Periodical Test I Science Reviewercatherine tamayoNo ratings yet
- Handbook 16-1-23Document52 pagesHandbook 16-1-23Janani M GowdaNo ratings yet
- OB CompiledDocument156 pagesOB CompiledMikeeeNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument5 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyShem DelolaNo ratings yet
- Reproduction Test For Anatomy & Physiology IIDocument33 pagesReproduction Test For Anatomy & Physiology IIlhayes1234100% (5)
- Shatavari PDFDocument9 pagesShatavari PDFSurendra Kumar SwarnkarNo ratings yet
- Maternal and Child Health Nursing TestDocument21 pagesMaternal and Child Health Nursing TestAt Day's Ward50% (2)
- Gender and Society: Lanie N. E. Avelino, LPT, Ma Eimee D. Potato, EddDocument13 pagesGender and Society: Lanie N. E. Avelino, LPT, Ma Eimee D. Potato, EddFranz Simeon ChengNo ratings yet
- Biochemical Investigation of Infertile Couple-My PresentationDocument91 pagesBiochemical Investigation of Infertile Couple-My PresentationOlukoyejo OluwaboriNo ratings yet
- MCQ Hap-II, Bp201tDocument39 pagesMCQ Hap-II, Bp201tANUJ DEVNo ratings yet
- QuestionDocument10 pagesQuestionserviceNo ratings yet
- Nuisance or Natural and Healthy Should Monthly Menstruation Be Optional For Women PDFDocument3 pagesNuisance or Natural and Healthy Should Monthly Menstruation Be Optional For Women PDFDieWeisseLeserinNo ratings yet
- Bahasa InggrisDocument10 pagesBahasa Inggriskarina lestariNo ratings yet
- Breasts A To ZDocument42 pagesBreasts A To Zalex1413No ratings yet
- Hormonal Cycle Lesson PlanDocument9 pagesHormonal Cycle Lesson PlanGunaNo ratings yet
- AUB QuizletDocument3 pagesAUB QuizletElizalde HusbandNo ratings yet
- Cmca - ReviewerDocument47 pagesCmca - ReviewerAdrianne BastasaNo ratings yet
NOTES 1st Sem P F
NOTES 1st Sem P F
Uploaded by
Rea0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views6 pages1) Progesterone is a key hormone that helps maintain pregnancy by relaxing the uterus and preventing premature contractions and abortion. It also thickens the uterine lining.
2) The placenta functions to supply oxygen and nutrients to the developing fetus while removing waste products. It produces hormones like human chorionic gonadotropin and human placental lactogen that help sustain the pregnancy.
3) Fertilization typically occurs around 8-10 days after implantation in the uterus. The fertilized egg then undergoes cell division and develops into an embryo over the next few weeks.
Original Description:
this is my notes. thank you
Original Title
NOTES-1st-sem-P-F
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1) Progesterone is a key hormone that helps maintain pregnancy by relaxing the uterus and preventing premature contractions and abortion. It also thickens the uterine lining.
2) The placenta functions to supply oxygen and nutrients to the developing fetus while removing waste products. It produces hormones like human chorionic gonadotropin and human placental lactogen that help sustain the pregnancy.
3) Fertilization typically occurs around 8-10 days after implantation in the uterus. The fertilized egg then undergoes cell division and develops into an embryo over the next few weeks.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views6 pagesNOTES 1st Sem P F
NOTES 1st Sem P F
Uploaded by
Rea1) Progesterone is a key hormone that helps maintain pregnancy by relaxing the uterus and preventing premature contractions and abortion. It also thickens the uterine lining.
2) The placenta functions to supply oxygen and nutrients to the developing fetus while removing waste products. It produces hormones like human chorionic gonadotropin and human placental lactogen that help sustain the pregnancy.
3) Fertilization typically occurs around 8-10 days after implantation in the uterus. The fertilized egg then undergoes cell division and develops into an embryo over the next few weeks.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 6
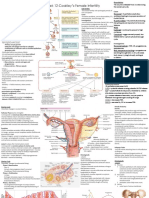
CHARACTERISTICS OF PROGESTERONE 16-2- weeks placenta became fully Hysterectomy - surgical removal of uterus.
HIGH LEVEL OF PROGESTERONE: functional HRT - Hormonal Replacement Therapy
1. Relaxes, quiet down the uterine Atherosclerosis - thickening of the wall which is used to minimize the effect of
2. Thickening of the uterus of the blood vessels in the heart menopause.
3. No cramping or spontaneous abortion. Arteriosclerosis - narrowing of the Perimenopausal - irregular changes in cycle
4. Lassitude (feeling of laziness during blood vessels happens the menstrual cycle stops
menstruation) Vaginismus - dryness of the vagina, 2 arteries and 1 vein in the umbilical cord of
5. Water retention tension in the muscle around the vagina the baby
6. Increase in body temperature Completion Curettage - incomplete
7. Thermogenic abortion before 20 weeks. HUMAN PLACENTAL LACTOGEN
8. Negative feedback to hypothalamus and Fractional Curettage / Diagnostic Insulin inhibitor / anti insulin
pituitary Curettage - removes tissue from the Normal amount of sugar can cause high
LOW LEVEL OF PROGESTERONE: inside of the uterus due to heavy level of glucose during pregnancy
1. Uterine cramping prior to menstruation or bleeding GDM (Gestation Diabetes Mellitus) if they
mittelschmerz (sci term for uterine Umbilical cord - 53cm (21in) - in term 2 previously have a history of Diabetes
cramping) cm (½ in) Mellitus or when the mother is overweight.
2. Releases FHS, and LH, positive feedback to Wharton’s jelly - gelatinous Insulin subcutaneous regulators injections
hypothalamus and pituitary gland mucopolysaccharide prevents pressure are used for pregnant mothers since they
on the veins and arteries. can’t take meds.
3 Placental Hormones: Amnion - have no nerve attached to it.
HCG - Human Chorionic Gonadotropin Graafian follicle / secondary oocyte -
HPL - Human Placental Lactogen or HCS holds mature cells which are rich in
(Human Chorionic Somatomammotropin) estrogen and progesterone.
Relaxin Prostaglandin - chemical prone to pain
receptors which will tear the graafian
Stages of Ovum and Follicle: follicle to release egg cell during
Primary Follicle ovulation. It is also released during
Graafian Follicle delivery.
Corpus Luteum Get the temperature during early
Mature Corpus Luteum morning because there’s no activity
Corpus Albicans yet.
-ectomy - suffix used to describe a
surgically removal of something
FERTILIZATION, IMPLANTATION, Day 2 - First cell division (zygote) 2 important hormones in pregnancy - estrogen
EMBRYONIC, AND FETAL DEVELOPMENT Day 3 - Morula (mulberry/aratilis and progesterone.
Fertilization - also known as conception, shaped), when it enters the uterus it’s
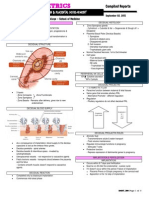
and impregnation. called blastocyst. PLACENTA
Implantation - 8-10 days after fertilization, Day 4 - Blastocyst - will enter into the Pancake in latin (400-600g. - 11lbs)
can also known as decidualization. uterus for implantation. Trophoblast Supplies the fetus oxygen and food and
On or after 42 weeks of gestation - with or with yolk sac and its villi will connect to transport waste products out of the fetal
without signs of labor, the baby needed to the endometrium. system.
be delivered / the mother should undergo Day 8-10 - Embryonic cells: ectoderm, Left lateral position - lifts the uterus away
labor. mesoderm, and endoderm. from the inferior vena cava which prevents
SHS (Supine Hypertensive Syndrome).
Terms used to denote fetal growth: Upper portion of the uterus is the ideal 30 separate segments or cotyledons
Ovum - ovulation to fertilization. place for decidualization. (“square” shaped)
Zygote - fertilization to implantation. Upper portion of the uterus (2/3) is Check the number of cotyledons that are in
Embryo - implantation to 5-8 weeks. contractile, while the lower portion the maternal side, if not then there’s still
Fetus - 5-8 weeks until term. (1/3) is relaxed. some fragment left in the mother’s womb.
Conceptus - pregnancy tissue (fetal parts Simultaneous contraction of the upper 2 sides of placenta: maternal side -
and placental parts). and lower portion can cause fetal (connected to the mother) dirty side or
distress. Duncan side, fetal side - (covered in
Outer third of fallopian tube - ampullar Human cell = 46 chromosomes, 22 pairs amnion) smooth and shiny side or the
portion (most wide) (XX - female, XY - male) Schultz side.
Hyaluronidase - (proteolytic enzyme) Aberration in the number of Chorion on Schultz's side is used for skin
released by the spermatozoa and dissolves chromosomes can result to abnormal grafting.
the layer of cells protecting the ovum. offspring or spontaneous abortion. Duncan’s side was used as a formulation to
Corona radiata - innermost layer of Vaginal spotting occurs during some beauty products.
follicular cells, adhering to the oocyte implantation due to ruptured Almost all drugs may be able to cross
before it leaves the ovarian follicle. capillaries. placental circulation, take precaution
Zona pellucida - supports communication Desidua basalis - part of endometrium before taking medication.
between oocytes and follicle cells during that lies under the embryo. Portion Teratogenic - may cause abortion or birth
oogenesis. where trophoblast cells establish defect. It can be drugs, radiation, viruses,
communication with maternal blood the environment, and many more.
Stages of fetal development: vessels.
Day 1 - Fertilization - union of ovum and
spermatozoon.
OHA (Oral Hypoglycemic Agent) - when 24th week SURFACTANT - “lubricant of
given to mother with GDM it may cross the lungs”, secreted by the alveoli.
placental circulation which can cause Alveoli will adhere together and
hypoglycemia to the fetus. collapse if there’s no surfactant.
Umbilical Cord - has 2 arteries, 1 vein: AVA 24th week - the ear is capable of
(artery, vein, artery), arteries carries responding to sound (perfect time to
deoxygenated blood, while veins carry play music to babies).
oxygenated blood, nutrients, hormones, Insulin does not cross the placenta
etc. from the mother to the fetus, that is
why they are prone to DM/GDM.
HORMONES
Human Chorionic Gonadotropin - first ADDITIONAL TERMS
placental hormone, 1-2 weeks after birth it Zygote - fertilized ovum.
is negative to the woman’s blood serum. Morula - cleavage undergo 3-4 days of
Progesterone - “hormone that maintains cell division.
pregnancy”, prevents premature labor by Blastocyst - morula entering the
decreasing the contractility of the uterus. uterus.
Estrogen - “hormone of women”, Decidua - endometrium after
stimulates uterine growth (thickening of implantation.
the uterus). Embryo - zygote implanted.
Human Placental Lactogen - promoting Cryptorchidism - undescended testes
production of milk, mammary gland to infants.
growth, regulates maternal glucose. Pseudohermaphroditism - intersex
Relaxin - ready to soften the bones, both mullerian and wolfian duct
causes waddling gait of the mother developed.
(walking like a duck). Fraternal or dizygotic - non identical
because there are 2 amnions, 2 chorion,
Amniotomy - artificial rupture of the 2 placenta.
amniotic membrane using a tongue Identical or monozygotic twins - 2
depressor or fingers. amnions, 1 chorion, 1 placenta.
Amniocentesis technique - determine the
L/S ratio (2:1 normal ratio), primary test of
fetal maturity. Administer steroids if the
needed ratio is not met.
4 STAGES OF LABOR Phases of Contraction: Immediate drying
1. ) 1st Stage of Labor (Dilatation Stage / Increment (crescendo) - increase Skin-to-skin contact
Cervical Stage) - onset of first contraction to intensity of contraction Proper cord clamping & cutting
full cervical dilation. Acme (apex) - peak height of Non separation of the baby to mother
RMLE - Right Mediolateral Episiotomy contraction and breast feeding initiation
(location of episiotomy) Decrement (decrescendo) - decreasing
Show - bloody discharge contraction Unang yakap, Yakap ng ina, Yakap ng
SHS - Supine Hypotensive Syndrome. buhay
Patient should be position in Left Lateral 3 Phases of first stage of Labor: Oil bathing
Position to avoid putting pressure to the Latent (0-7cm dilation), contraction: Eye care or crede prophylaxis
patient’s vena cava mild (20-40 sec) Initial temperature (rectum) : heat loss
LAMAZE - special breathing pattern Active (4-7 cm dilation), contraction: thru evaporation, convection,
(pant and blow) moderate (40-6- sec) conduction, and radiation
Caput succedanum - edema is formed in Transition (8-10 cm dilation), Cord care
the baby’s scalp because of early pushing contraction: strong (60-70 sec) Anthropometric measurement :
of the baby out of uterine area. weight, height/length, HC, CC, AC
Monitor BP q15 minutes but if the Dorsal recumbent - position of the Immunization
mother is having contractions, it is not mother in labor room Dressing and taking vital signs of the
adviced to get the BP and FHT. Lithotomy - position in delivery room baby (except BP)
1-2 minutes - call out the time of birth
How to determine cervix dilation: 2. ) 2nd Stage of Labor (Delivery Stage / Dry the baby (30 sec), stimulate
position the patient in dorsal recumbent Expulsion Stage) - from full cervical breathing
position dilation up to the delivery of the baby Place the baby on the mother’s
place a rubber protector under the buttocks Offer psychological support. Do not stomach (for skin-to-skin contact
put lubricant in your first 2 fingers and leave the mother alone. Place bonnet and linen
insert it in the vaginal orifice. Assist/couch: caution to bear down Administer vaccine:
10cm - fully dilated cervix, ready for labor. when needed Vitamin k - 0.1 ml, IM: vastus
When to transfer to delivery room? lateralis, and rectus femoris. To
Intensity of the contraction Primigravida - cervix is 10 cm prevent anemia and for blood
- determined using hand/palpation dilated w/ buldging clotting.
Mild - minimally tense, hard as the nose Multigravida - cervix is 8-9 cm Hepatitis B - 0.5ml, IM: right vastus
Moderate - feels firm, hard as the chin dilated lateralis. To prevent hepa b.
Strong - wooden board, hard as the Do EINC (Essential Intrapartum and BCG - 0.05ml, ID: Deltoid. To
forehead Newborn Care): prevent TB.
3. ) 3rd Stage of Labor (Placental Stage) - Preterm - labor before maturation of How to determine CPD:
from delivery of the baby up to the delivery of the fetus (20-30 weeks) Ultrasound
the placenta Posterm - 42 weeks (optimal) labor is Weight of the fetus
5-30 minutes - for primigravida delayed until fetus is delivered. Fundal height
5-10 minutes - for multigravida Ultrasound
Watchful waiting - watch and wait for Theories of Labor: Leopold’s Maneuver
the signs of placental separation 1. Uterine Myometrial Irritability / Uterine
especially if the uterus is relaxed as Stretch Theory Sugar in urine - +1 normal due to the
these actions should be caused uterine - uterine muscle stretches which presence of prolactin (anti insulin agent)
inversion. results to release of prostaglandin and Protein in urine - pre eclampsia can lead to
Inject oxytocin after placental delivery induces contraction and labor. hypertesion
Commonly used drugs: methergine - 2. Oxytocin theory Amniocentesis - technique used to
methylegronovine maleate, ergotrate - pressure on the cervix by the
- ethylergonovine maleate (increases presenting part stimulates release of Medical terms:
uterine monitor activity by direct oxytocin in which cause uterine contraction. GDM - Gestation Diabetes Mellitus
stimulation target: uterine 3. Low progesterone theory CBC - Complete Blood Count
masculature) - low progesterone causing uterine OHA - Oral Hypoglycemic Agent
4. ) 4th Stage of Labor (Recovery Stage) - cramp. When progesterone decreases, TVUTz - Transvaginal Ultrasound
fundus is firm, it should be at/or just above estrogen increases during pregnancy in TAUTz - Transabdominal Ultrasound
umbilicus (1-2 finger breaths) and midline. which starts labor. BPD - Biparietal Diameter
If fundus is boggy (or relaxed), do 4. Theory of Aging Placenta BPP - Biophysical Profile
fundal massage but do not over - (40-42 weeks max), when BPS - Biophysical Scoring
massage as it can tire uterine muscle placenta matures it can result to more FHR - Fetal Heart Rate
LOCHIA - vaginal discharge: Red pressure in uterus in which diminished blood FHT - Fetal Heart Tone
(Rubra), Pink (Serosa), and White supply and will result to contraction. CPD -Cephalopelvid Disproportion
(Alba). 5. Estrogen Fetal Hormone & Prostaglandin CS - Cesarean Section
A full bladder displaces the uterus, a Theory NSD - Normal Spontaneous Delivery
factor of uterine atony. - hormones have stimulating effect AFD - Alpha-fetoprotein
NDT - Neural Tube Defect
LABOR 4 P’s of Labor CVS - Chorionic Villi Sampling
Labor - 30-42 weeks of pregnancy, when 1. Passage - woman’s pelvis PUBS - Percutaneous Umbilical Blood
fetus is sufficiently mature enough to 2. Passenger - the fetus Sampling
adopt extrauterine life yet not too large to 3. Power - uterine factors
cause mechanical difficulty during birth. 4. Psyche - woman’s psychological state
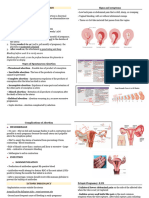
POSTPARTUM ASSESSMENT UTERUS EPISIOTOMY
Assess BUBBLE SHEB: REEDA - Redness, Edema, Ecchymosis Episiorrhaphy - surgical repair
Breast (bruise), Discharge, and Approximation Assess for REEDA & Hemorrhoids
Uterus of the skin. Cold or ice pack for vasoconstriction effect
Bowel Involution - uterus should go back to its reduce edema & relieve pain
Bladder pre pregnancy state Warm compress, 20 inches from perineum
Lochia Normal finding: firm to touch for 20 mins, 3x a day
Episiotomy Autolysis - reduction of weight of the Sitz bath, 2x a day or more, 38-42 c temp
Skin cells during involution
Homan’s Sign SKIN
Emotional Status BOWEL Diaphoresis - excessive sweating (1st 5
Bonding Auscultate 4 quadrants (LUQ, RUQ, days)
LLQ, and RLQ) - normal findings: there Chloasma (pigmentation in the face) & linea
Puerperium - from delivery of the placenta should be a sound in which indicates negra (mark across abdomen) fades
up to 6 weeks of birth. bowel movement Striae gravidarum - stretch marks, become
Breastfeed every 2 hours or every demand Inspect signs of distention silver streaks
A newborn can only hold an amount similar Mother is expected to defecate after
to a “squeeze of calamansi” 3-8 hours. HOMAN’S SIGN
Do not overfeed the baby or the baby will Pain in calf in dorsiflexion might indicate
vomit BLADDER thrombophlebitis or positive homan’s sign.
Void within 6-8 hours after delivery
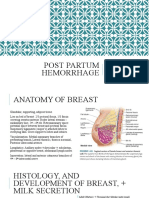
BREAST Assess: frequency, burning, or urgency EMOTIONAL STATUS
Palpate for engorgement for possible UTI Assess for postpartum blues (ask the ptx
Inspect the nipple Bladder can hamper in the way during “how are you feeling today?”)
Colostrum - first letdown of the breast delivery that is why it is important to Real cause: unknown
milk. Rich in antibodies that is why it is insert catheter Normal finding: the mother should be
yellowish in color happy about the baby.
Sucking stimulates the release of oxytocin LOCHIA
in which induces lactation (produces milk Vaginal flow delivery consisting of the BONDING
200-300 ml) blood (Rubra, Serosa, and Alba) “Claiming” - who looks or acts like the baby
Burp the baby after the baby in order to Inspect: type, quantity, amount, and “Identification” - giving name to the baby
prevent discomfort/stomachache odor Delay crede’s prophylaxis, allow eye-to-
Babies are nose breathers, it is important eye, touching, stroking, and cuddling.
to free the nose when breast feeding
You might also like
- Obstetrics & Gynecologyc MnemonicsDocument12 pagesObstetrics & Gynecologyc MnemonicsMuhammad Luqman Nul HakimNo ratings yet
- Development Biology Multiple Choice QuestionDocument16 pagesDevelopment Biology Multiple Choice QuestionGuruKPO81% (16)
- Nurs 5002 - Case Study 3Document14 pagesNurs 5002 - Case Study 3api-308904543No ratings yet
- MCN Notes 2Document26 pagesMCN Notes 2Rogeimar Claire MangomayaoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 The Growing FetusDocument4 pagesChapter 9 The Growing FetusCarrie ANo ratings yet
- MCN LectureDocument8 pagesMCN LectureEmily BernatNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - Process of Conception and Stage of Fetal DevelopmentDocument25 pagesModule 2 - Process of Conception and Stage of Fetal DevelopmentKatie HolmesNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1physiology of PregnancyDocument42 pagesLecture 1physiology of PregnancyBlessie Zyren BasinangNo ratings yet
- Reporductive SystemDocument31 pagesReporductive SystemEmma Joel OtaiNo ratings yet
- Maternal and Child (Healthy Pregnancy)Document37 pagesMaternal and Child (Healthy Pregnancy)Lenny SucalditoNo ratings yet
- GA&E 13 - Fertilization & ImplantationDocument49 pagesGA&E 13 - Fertilization & ImplantationSu ZikaiNo ratings yet
- Female Cycles GAD 203Document20 pagesFemale Cycles GAD 203alhobabighnemNo ratings yet
- OB 1st SemDocument4 pagesOB 1st SemMai CarbonNo ratings yet
- 178 Anatomy Reproductive SystemDocument29 pages178 Anatomy Reproductive SystemJohn Mark JuarezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9: Nursing Care During Normal Pregnancy and Care of The Developing FetusDocument8 pagesChapter 9: Nursing Care During Normal Pregnancy and Care of The Developing FetusAlyssaGrandeMontimor100% (1)
- MCN Nursing 1Document107 pagesMCN Nursing 1Fau Fau DheoboNo ratings yet
- 178 Anatomy Reproductive SystemDocument25 pages178 Anatomy Reproductive SystemJUVY ANN PATOSANo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive Ogans Internal Organs of ReproductionDocument22 pagesFemale Reproductive Ogans Internal Organs of ReproductionAngela NeriNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive Ogans Internal Organs of ReproductionDocument22 pagesFemale Reproductive Ogans Internal Organs of ReproductionAecille VillarNo ratings yet
- Fertilization and ImplantationDocument3 pagesFertilization and ImplantationTandingco, Olivia Mari H.No ratings yet
- Maternal and Child Health NursingDocument22 pagesMaternal and Child Health NursingRam Van MunsterNo ratings yet
- NCM 107 Study GuideDocument3 pagesNCM 107 Study GuideJamilah BanglanNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Pregnancy & Functions of Placenta-1Document31 pagesPhysiology of Pregnancy & Functions of Placenta-1Ajit ShahNo ratings yet
- RevkeDocument11 pagesRevkeLowellyn Grezen VillaflorNo ratings yet
- Midterm PPT MaternalDocument13 pagesMidterm PPT Maternaladrianleet18No ratings yet
- Care of The Mother and Fetus During The Perinatal PeriodDocument37 pagesCare of The Mother and Fetus During The Perinatal PeriodSana ChanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 29 - Development and Inheritance: ST ND RD STDocument5 pagesChapter 29 - Development and Inheritance: ST ND RD STtomorrow.today.yesterday .yesterdayNo ratings yet
- NSVDDocument32 pagesNSVDChris Oliver Kevin Ledesma100% (3)
- Notes Maternal Health NursingdsdsDocument21 pagesNotes Maternal Health NursingdsdsL Rean Carmelle MAGALLONESNo ratings yet
- I. Anatomy & Physiology: Readiness For Child BearingDocument3 pagesI. Anatomy & Physiology: Readiness For Child BearingRalph Tama Mangacop BenitoNo ratings yet
- 1-4 Fertilization & Fetal DevelopmentDocument9 pages1-4 Fertilization & Fetal DevelopmentElla DionedaNo ratings yet
- Care of The Mother and Fetus During The Perinatal PeriodDocument37 pagesCare of The Mother and Fetus During The Perinatal PeriodSana ChanNo ratings yet
- h1 Reproductive Physiology Course Summary NotesDocument11 pagesh1 Reproductive Physiology Course Summary NotesHoney BaseriNo ratings yet
- MCHN 3RD LectDocument9 pagesMCHN 3RD LectZahNo ratings yet
- 2 Introduction To Embryology and FetalDocument55 pages2 Introduction To Embryology and Fetaldemeke andebetNo ratings yet
- EMBRYOLOGYDocument30 pagesEMBRYOLOGYMSc. PreviousNo ratings yet
- DoReMi Ni Lalala EDITED PDFDocument156 pagesDoReMi Ni Lalala EDITED PDFEleonor Katreeya LimsiNo ratings yet
- Competency 1-The Family Before Birth: 1. Explain The Structure and Function of The Female Reproductive SystemDocument4 pagesCompetency 1-The Family Before Birth: 1. Explain The Structure and Function of The Female Reproductive SystemEnorl FerdinandNo ratings yet
- OR Write-Up CSDocument13 pagesOR Write-Up CSalex_tan1981No ratings yet
- Handout On ReproDocument4 pagesHandout On ReproJoe JosephNo ratings yet
- Fertilization and Implantation Copy To StudentsDocument40 pagesFertilization and Implantation Copy To StudentsRiya SinghNo ratings yet
- NCM 108 - Nursing Care During Normal Pregnancy and Care of The Developing FetusDocument5 pagesNCM 108 - Nursing Care During Normal Pregnancy and Care of The Developing FetusKristine BartsNo ratings yet
- Reproduction NotesDocument27 pagesReproduction NotesAyra AlbairaNo ratings yet
- Maternal and Child NursingDocument43 pagesMaternal and Child NursingSophia WongNo ratings yet
- Week 2 Sex and FertDocument17 pagesWeek 2 Sex and FertAbmil Ching TinggalongNo ratings yet
- MENSTRUATION: Monthly Discharge of Blood From The Uterus Occurring Form Puberty To MenopauseDocument18 pagesMENSTRUATION: Monthly Discharge of Blood From The Uterus Occurring Form Puberty To Menopauselyka resurreccionNo ratings yet
- Part, Function and Process of Reproduction SystemDocument31 pagesPart, Function and Process of Reproduction SystemSavia NaldiNo ratings yet
- Week 12-Female InfertilityDocument2 pagesWeek 12-Female InfertilityJaimie Charlotte Marie LangilleNo ratings yet
- Embryology Lecture Note 2Document19 pagesEmbryology Lecture Note 2jestreametefiaNo ratings yet
- MCN Lec Antepartal To Ob ClassificationDocument11 pagesMCN Lec Antepartal To Ob ClassificationJay EstrellaNo ratings yet
- OB CompiledDocument156 pagesOB CompiledMikeeeNo ratings yet
- MCN Midterm 1Document12 pagesMCN Midterm 1sherelyn legaspiNo ratings yet
- Menstruation FertilizationDocument2 pagesMenstruation FertilizationJamie Rose GarciaNo ratings yet
- 1.1c Implantation & Placental DevelopmentDocument5 pages1.1c Implantation & Placental DevelopmentBea Samonte100% (1)
- Module 2 HandsoutDocument10 pagesModule 2 HandsoutErin SaavedraNo ratings yet
- PEDIA-REVIEWER EditedDocument7 pagesPEDIA-REVIEWER EditedTO THE MOONNo ratings yet
- Parts of The SystemDocument14 pagesParts of The SystembookonscribdNo ratings yet
- MaternalDocument6 pagesMaternalBlessed Glaiza MarianoNo ratings yet
- Dasar2 Biomolekuler Repro WanitaDocument51 pagesDasar2 Biomolekuler Repro WanitaFitriaNo ratings yet
- The PlacentaDocument3 pagesThe PlacentaLiezelNo ratings yet
- Post Partum HemorrhageDocument9 pagesPost Partum HemorrhageghsNo ratings yet
- Ovum, Functions, Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandOvum, Functions, Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Office Word DocumentDocument11 pagesNew Microsoft Office Word DocumentMihaela AndreiNo ratings yet
- Ncert Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 3 Human ReproductionDocument14 pagesNcert Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 3 Human ReproductionDeepanjan DASNo ratings yet
- WHLP Science10 Q3 W1 2Document15 pagesWHLP Science10 Q3 W1 2Christian DecenaNo ratings yet
- Science 10Document51 pagesScience 10Michelle LapuzNo ratings yet
- Quiz 8 To 46Document7 pagesQuiz 8 To 46JhayneNo ratings yet
- Embryology Chapter 3Document23 pagesEmbryology Chapter 3Abdisamed AllaaleNo ratings yet
- A Study of Knowledge and Practices Among Adolescents Girls Regarding Menstruation in Government Schools of AmritsarDocument4 pagesA Study of Knowledge and Practices Among Adolescents Girls Regarding Menstruation in Government Schools of AmritsarInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Secrets To Happy MarriagesDocument30 pagesSecrets To Happy Marriagesrobert543100% (1)
- Grade 6 Human Reproduction New Vocabulary: English WordDocument9 pagesGrade 6 Human Reproduction New Vocabulary: English WordSalome TamaraNo ratings yet
- Biology For 12th Class CbseDocument245 pagesBiology For 12th Class Cbseramanadk100% (2)
- 1st Periodical Test I Science ReviewerDocument7 pages1st Periodical Test I Science Reviewercatherine tamayoNo ratings yet
- Handbook 16-1-23Document52 pagesHandbook 16-1-23Janani M GowdaNo ratings yet
- OB CompiledDocument156 pagesOB CompiledMikeeeNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument5 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyShem DelolaNo ratings yet
- Reproduction Test For Anatomy & Physiology IIDocument33 pagesReproduction Test For Anatomy & Physiology IIlhayes1234100% (5)
- Shatavari PDFDocument9 pagesShatavari PDFSurendra Kumar SwarnkarNo ratings yet
- Maternal and Child Health Nursing TestDocument21 pagesMaternal and Child Health Nursing TestAt Day's Ward50% (2)
- Gender and Society: Lanie N. E. Avelino, LPT, Ma Eimee D. Potato, EddDocument13 pagesGender and Society: Lanie N. E. Avelino, LPT, Ma Eimee D. Potato, EddFranz Simeon ChengNo ratings yet
- Biochemical Investigation of Infertile Couple-My PresentationDocument91 pagesBiochemical Investigation of Infertile Couple-My PresentationOlukoyejo OluwaboriNo ratings yet
- MCQ Hap-II, Bp201tDocument39 pagesMCQ Hap-II, Bp201tANUJ DEVNo ratings yet
- QuestionDocument10 pagesQuestionserviceNo ratings yet
- Nuisance or Natural and Healthy Should Monthly Menstruation Be Optional For Women PDFDocument3 pagesNuisance or Natural and Healthy Should Monthly Menstruation Be Optional For Women PDFDieWeisseLeserinNo ratings yet
- Bahasa InggrisDocument10 pagesBahasa Inggriskarina lestariNo ratings yet
- Breasts A To ZDocument42 pagesBreasts A To Zalex1413No ratings yet
- Hormonal Cycle Lesson PlanDocument9 pagesHormonal Cycle Lesson PlanGunaNo ratings yet
- AUB QuizletDocument3 pagesAUB QuizletElizalde HusbandNo ratings yet
- Cmca - ReviewerDocument47 pagesCmca - ReviewerAdrianne BastasaNo ratings yet