Professional Documents
Culture Documents
NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Science Chapter 6 - Tissues - .
NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Science Chapter 6 - Tissues - .
Uploaded by
AshchatOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Science Chapter 6 - Tissues - .
NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Science Chapter 6 - Tissues - .
Uploaded by
AshchatCopyright:
Available Formats
NCERT Solutions for Class 9
Science
Chapter 6 – Tissues
Intext Questions:
1. What is a tissue?
Ans: Tissue is a collection of cells with comparable structures that are placed in
order to fulfil a given activity.
2. What is the utility of tissues in multicellular organisms?
Ans: Tissues in multicellular organisms are differentiated to perform a specific
function at a given location, a process known as division of labor. Nerve cells, for
example, make up the neurological tissue that aids in message transmission, whereas
muscular cells make up the muscle tissue and muscle tissue is a type of tissue that
aids in movement.
3. Name the types of simple permanent tissues
Ans: Parenchyma, Collenchymas, and Sclerenchyma are the three forms of simple
permanent tissues. Aerenchyma and chlorenchyma are two types of parenchyma
tissue.
4. Where is apical meristem found?
Ans: At the growing tips of stems and roots, the apical meristem is present.
5. Which tissue makes up the husk of coconut?
Class IX Science www.vedantu.com 1
Ans: Sclerenchyma tissue which is a form of simple permanent tissue makes up the
husk of the coconut.
6. What are the constituents of phloem?
Ans: The food-conducting tissue of plants is termed as phloem. Sieve tubes,
Companion cells, Phloem parenchyma, and Phloem fibers are the four components.
7. Name the tissue responsible for movement in our body.
Ans: Muscle Tissues are responsible for movement.
8. What does a neuron look like?
Ans: A neuron is made up of three parts: the cell body, the axon, and the dendrites.
Dendrites are a significant number of extensions that stretch outward from the cell
body and resemble branches. A nucleus and other cell organelles make up the cell
body. An axon is a tube-like structure that transports an electrical impulse from the
cell body to the neuron's opposite end structures.
9. Give three features of cardiac muscles.
Ans: Features of cardiac muscles:
● They are involuntary in nature.
● They are cylindrical, branched, and uninucleate in structure.
● Throughout their lives, they exhibit cyclic contraction and relaxation.
10. What are the functions of areolar tissue?
Ans: Areolar tissues are commonly seen in animals. They are connective tissues that
exist between the skin and the muscles. They can also be found in the bone marrow
Class IX Science www.vedantu.com 2
and around blood arteries and nerves. These tissues take up a lot of room inside the
organs. They protect the internal organs and aid in tissue restoration in the event of
harm.
EXERCISE
1. Define the term “tissue”.
Ans: A tissue is described as a group of cells with identical structures that
collaborate to execute a certain purpose.
2. How many types of elements together make up the xylem tissue? Name them.
Ans: The xylem tissue is made up of four main elements as mentioned:
● Vessels
● Tracheids
● Xylem fibres
● Xylem parenchyma
3. How are simple tissues different from complex tissues in plants?
Ans:
Simple Tissues Complex Tissues
Simple tissues consist of only one They are composed of various
type of cell. types of cells
The structures of all the cells are The roles and structures of
similar, and they perform similar different types of cells vary.
duties.
Class IX Science www.vedantu.com 3
Plants have three types of simple Xylem and phloem are two types of
tissues: parenchyma, collenchyma, complex permanent tissues found
and sclerenchyma. in plants.
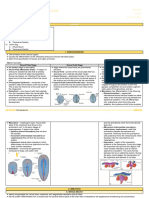
4. Differentiate between parenchyma, collenchyma and sclerenchyma, on the
basis of their cell wall.
Ans:
Parenchyma Collenchyma Sclerenchyma
Thin cell walls, The cell wall is There are no
cells are loosely thickened irregularly intercellular spaces
packed. at the corners, and because the cell
there is very little walls are evenly
space between the thickened.
cells.
Cell wall is made up Pectin and There is an extra
of cellulose. hemicellulose are layer of the cell
the two most wall that is mostly
important components made up of lignin.
of the cell wall.
5. What are the functions of the stomata?
Ans: Stomata functions include the exchange of gases with the atmosphere. The
stomata are responsible for transpiration.
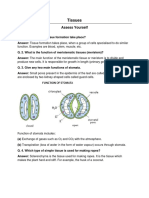
6. Diagrammatically show the difference between the three types of muscle
fibres.
Class IX Science www.vedantu.com 4
Ans: Striated muscles, smooth muscles (unstriated muscle fibre), and cardiac
muscles are the three types of muscular fibres.
Striated Muscle cells
Smooth muscle cells
Class IX Science www.vedantu.com 5
Cardiac muscle cells
7. What is the specific function of the cardiac muscle?
Ans: The cardiac muscle is responsible for controlling the heart's contraction and
relaxation.
8. Differentiate between striated, unstriated and cardiac muscles on the basis of
their structure and site/location in the body.
Ans:
Striated Muscles Unstriated Muscles Cardiac Muscles
On The Basis of Structure:
Cylindrical Long Cylindrical
Not branched Not branched Branched
Multinucleate Uninucleate Uninucleate
Its ends are blunt Its ends are Its ends are flat and
tapering wavy
Coloured alternate There are no bands Faint bands are
light and dark present present
bands
On The Basis of Location:
These muscles are The contraction These muscles
present in different and relaxation of control the heart's
body parts such as blood vessels, as contraction and
hands, legs, tongue, well as the relaxation.
etc. movement of food
Class IX Science www.vedantu.com 6
in the alimentary
canal, are all
controlled by these
muscles.
9. Draw a labeled diagram of a neuron.
Ans:
10. Name the following:
(a) Tissue that forms the inner lining of our mouth.
(b) Tissue that connects muscle to bone in humans.
(c) Tissue that transports food in plants.
(d) Tissue that stores fat in our body.
Class IX Science www.vedantu.com 7
(e) Connective tissue with a fluid matrix.
(f) Tissue present in the brain.
Ans:
(a) Epithelial tissue
(b) Dense regular connective tissue (tendons)
(c) Phloem
(d) Adipose tissue
(e) Blood
(f) Nervous tissue
11. Identify the type of tissue in the following: skin, the bark of a tree, bone,
lining of kidney tubule, vascular bundle.
Ans:
● Skin: Stratified squamous epithelial tissue
● The bark of a tree: Simple permanent tissue
● Bone: Connective tissue
● The lining of kidney tubule: Cuboidal epithelial tissue
● Vascular Bundle: Complex permanent tissue
12. Name the regions in which parenchyma tissue is present.
Ans: Leaves, fruits, and flowers.
13. What is the role of the epidermis in plants?
Class IX Science www.vedantu.com 8
Ans: Role of the epidermis:
● Protection of different parts of the plant.
● Epidermal cells present in roots, help in absorption of water.
● For protection against loss of water, mechanical injury, and parasitic fungus
by producing a waxy, water-resistant covering called cuticle, which is made
of cutin, on the outer surface of the plant.
14. How does the cork act as a protective tissue?
Ans: The cork, which is made up of dead cells, is the bark of a tree. It protects the
plant from mechanical damage and temperature extremes, as well as it prevents
water loss through evaporation.
15. Complete the table:
Ans:
Class IX Science www.vedantu.com 9
You might also like
- Tissue Solutions Textual Questions and Answers: Is Called A TissueDocument11 pagesTissue Solutions Textual Questions and Answers: Is Called A TissueMr Pan GamingNo ratings yet
- TissuesDocument7 pagesTissuesRohitNo ratings yet
- What Is A Tissue? Ans:: Class: 9 (Science) Tissues Chapter - 2Document21 pagesWhat Is A Tissue? Ans:: Class: 9 (Science) Tissues Chapter - 2The Silent RepentantNo ratings yet
- TissuesDocument11 pagesTissuesManveethNo ratings yet
- Aakash Institute: NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Science Chapter 6 TissuesDocument13 pagesAakash Institute: NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Science Chapter 6 TissuesNischay MahamanaNo ratings yet
- CHAPTERDocument5 pagesCHAPTERmustafasamim518No ratings yet
- Chapter 7th TissueDocument6 pagesChapter 7th Tissuenakulvyan708No ratings yet
- Exercise-6.1: NCERT Solution For Class 9 Science - Chapter 6 TissuesDocument9 pagesExercise-6.1: NCERT Solution For Class 9 Science - Chapter 6 TissuesShah RukhNo ratings yet
- Tissue ClassworkDocument5 pagesTissue ClassworkRajesh Kanna A亗No ratings yet
- Chapter 6 BiologyDocument8 pagesChapter 6 BiologyMohammed mahfuzNo ratings yet
- Important Questions For CBSE Class 9 Science Chapter 6Document16 pagesImportant Questions For CBSE Class 9 Science Chapter 6VI A 19 Aaryan JadhavNo ratings yet
- Tissues Solved Examples Solved Example ICSE 0213445d 59d1 4ef6 9586 3cf7638047b9Document5 pagesTissues Solved Examples Solved Example ICSE 0213445d 59d1 4ef6 9586 3cf7638047b9akanksha0102guptaNo ratings yet
- PD 4 WJ SBJ UE7 XAASH4 U KZDocument11 pagesPD 4 WJ SBJ UE7 XAASH4 U KZPrincy GuptaNo ratings yet
- ST - John'S School, Greater Noida West Class IX ScienceDocument4 pagesST - John'S School, Greater Noida West Class IX ScienceIndia Tech with AstitvaNo ratings yet
- Animal TissuesDocument14 pagesAnimal Tissuesjitendragandhi250No ratings yet
- Tissues - NotesDocument14 pagesTissues - Notesphysicsbooks.storeNo ratings yet
- 9th Bio MTG Tissue QuesDocument13 pages9th Bio MTG Tissue QuesData ShareNo ratings yet
- 9 Science Imp ch6 3Document8 pages9 Science Imp ch6 3deepakNo ratings yet
- 642020112334AM-Class 9 Biology Notes-Chapter-6 Plant TissueDocument11 pages642020112334AM-Class 9 Biology Notes-Chapter-6 Plant TissueL Sri Madhi100% (1)
- Tissues Class 9Document13 pagesTissues Class 9Richa Nawani KaushikNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER-TISSUES (Class-9) Self Instructional Material S. P Model Higher Secondary School, M.A Road, Srinagar (Teacher: Burhana Rashid)Document4 pagesCHAPTER-TISSUES (Class-9) Self Instructional Material S. P Model Higher Secondary School, M.A Road, Srinagar (Teacher: Burhana Rashid)MuzafarNo ratings yet
- 2021 Chapter 6 Tissue Most IMP QuestionsDocument11 pages2021 Chapter 6 Tissue Most IMP QuestionsGauravNo ratings yet
- TissuesDocument23 pagesTissuesAadarsh RameshNo ratings yet
- Tissue Mat PDFDocument13 pagesTissue Mat PDFAyushman TripathyNo ratings yet
- Class 9TH Biology TissueDocument4 pagesClass 9TH Biology TissueChirag KashyapNo ratings yet
- Tissue Notes 9Document7 pagesTissue Notes 9Priyad MundadaNo ratings yet
- Chapter Science-9 CombinedDocument20 pagesChapter Science-9 CombinedAnushkaNo ratings yet
- BSRKV, Sainikpuri. Biology Notes Class 9 Ls 6 Tissues Plant TissuesDocument4 pagesBSRKV, Sainikpuri. Biology Notes Class 9 Ls 6 Tissues Plant TissuesSai Uday Shankar BommakantiNo ratings yet
- Work Sheet 4 Classification of Tissues A28 Group1Document6 pagesWork Sheet 4 Classification of Tissues A28 Group1Japet Floyd Alipio100% (1)
- Class 9 - CH6 TissuesDocument9 pagesClass 9 - CH6 Tissuesv.nikolikjNo ratings yet
- Tissues Class 9Document5 pagesTissues Class 9Arnav PatangeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6: "Tissues"Document5 pagesChapter 6: "Tissues"Anil TripathiNo ratings yet
- Tissues Notes Class IxDocument7 pagesTissues Notes Class Ixishaan singhNo ratings yet
- Science Chapter-6-TissueDocument11 pagesScience Chapter-6-TissueJEETNo ratings yet
- Worksheet On TissuesDocument5 pagesWorksheet On TissuesBryan AmoresNo ratings yet
- 09 Science Notes ch06 Tissues-UnlockedDocument5 pages09 Science Notes ch06 Tissues-UnlockedShekhar UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- JihijiojhiDocument5 pagesJihijiojhiGaurav Kumar GoyalNo ratings yet
- TissuesDocument5 pagesTissuesDarshilNo ratings yet
- Selina Concise Biology Solutions Class 7 Chapter 1 Plant and Animal TissuesDocument12 pagesSelina Concise Biology Solutions Class 7 Chapter 1 Plant and Animal TissuesAKSHAJ AGGARWALNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper of TissuesDocument9 pagesSample Paper of TissuesPritamprakash JhaNo ratings yet
- 11 Biology Notes Ch07 Structural Organisation in AnimalsDocument6 pages11 Biology Notes Ch07 Structural Organisation in AnimalsSham PhadtareNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Type: AnswerDocument15 pagesMultiple Choice Type: Answeranisur198287No ratings yet
- TissueDocument6 pagesTissuers6xhffn49No ratings yet
- Tissues: Assess YourselfDocument16 pagesTissues: Assess YourselfGamer JiNo ratings yet
- Tissues: 1. Ncert Intext QuestionsDocument10 pagesTissues: 1. Ncert Intext QuestionsKumar AbhishantNo ratings yet
- Plant and Animal TissuesDocument10 pagesPlant and Animal TissuesSanjay AdakNo ratings yet
- Animal Tissues: TissueDocument4 pagesAnimal Tissues: TissuePrasad SwaminathanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 TissuesDocument7 pagesChapter 6 Tissuesh8631259No ratings yet
- Tissues: One Mark QuestionsDocument12 pagesTissues: One Mark QuestionsSrividhya ManikandanNo ratings yet
- PDF 20221214 190246 0000Document11 pagesPDF 20221214 190246 0000Hiba ZiziNo ratings yet
- NCERT Chapter 6: Tissues (Plant Tissue and Animal Tissue)Document4 pagesNCERT Chapter 6: Tissues (Plant Tissue and Animal Tissue)Chetan Gautam100% (1)
- 642020112334AM-Class 9 Biology Notes-Chapter-6 Plant TissueDocument14 pages642020112334AM-Class 9 Biology Notes-Chapter-6 Plant Tissuekmdmohideen2297100% (1)
- Tissues NotesDocument7 pagesTissues NotesHarshitNo ratings yet
- Class IX Biology: Chapter 6: TissueDocument5 pagesClass IX Biology: Chapter 6: Tissuesidd230100% (2)
- Ix Plant Tissues 1Document7 pagesIx Plant Tissues 1ayushiguptab0406No ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Tissues Revision NotesDocument4 pagesChapter 6 - Tissues Revision NotesAbhishek100% (1)
- TissuesDocument74 pagesTissuesMonica Sree100% (1)
- Answer - Bio - Class 7 Chap 1Document6 pagesAnswer - Bio - Class 7 Chap 1Laiq Ur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Tissue, Glands, and Membranes Epithelial TissueDocument5 pagesTissue, Glands, and Membranes Epithelial TissueMoises MontalboNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Comprehensive Perinatal and Pediatric Respiratory Care 4th Edition by Whitaker Isbn 10 1439059438 Isbn 13 9781439059432Document7 pagesTest Bank For Comprehensive Perinatal and Pediatric Respiratory Care 4th Edition by Whitaker Isbn 10 1439059438 Isbn 13 9781439059432trangdatif0No ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument19 pagesRespiratory SystemSri Ganesh ComputersNo ratings yet
- Unit 5Document8 pagesUnit 5CLAUDIU---ALIN BOARTANo ratings yet
- Slides To Draw and StudyDocument21 pagesSlides To Draw and StudyAndrea Galang CruzNo ratings yet
- Session No 1.1. A Tour of The CellDocument40 pagesSession No 1.1. A Tour of The CellShekaina Faith Cuizon LozadaNo ratings yet
- Colorful Pastel Cute Creative Kids Zone PresentationDocument7 pagesColorful Pastel Cute Creative Kids Zone PresentationMaulidatul HusnaNo ratings yet
- General Biology 2Document22 pagesGeneral Biology 2Lala ChanNo ratings yet
- Secondary and Anomalous Growth of Bougainvillea PDFDocument9 pagesSecondary and Anomalous Growth of Bougainvillea PDFIza SalvadorNo ratings yet
- BIO LE2 ReviewerDocument16 pagesBIO LE2 ReviewerMark JimenezNo ratings yet
- Session 1 Development of The Head and NeckDocument5 pagesSession 1 Development of The Head and NeckTobio KageyamaNo ratings yet
- ATLAS ThinPrep TPPTMorphologyLectureDocument116 pagesATLAS ThinPrep TPPTMorphologyLectureCristina CostaNo ratings yet
- The Digestive System Summative Test - Q3 - M1Document2 pagesThe Digestive System Summative Test - Q3 - M1Metchel100% (1)
- Week 1-2 - Veterinary Embryology IntroductionDocument8 pagesWeek 1-2 - Veterinary Embryology IntroductionAleia GoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of RetinaDocument18 pagesAnatomy of RetinaNuman QayyumNo ratings yet
- Trans 5 - Frog OrganogenesisDocument32 pagesTrans 5 - Frog Organogenesisangelica sherinnNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Human Anatomy Laboratory Manual With Cat Dissections 7 e 7th EditionDocument9 pagesSolution Manual For Human Anatomy Laboratory Manual With Cat Dissections 7 e 7th EditionCristianRodriguezpawry100% (88)
- DLL Science-6 Q2 W1Document8 pagesDLL Science-6 Q2 W1MELISSA PANAGANo ratings yet
- DPP XI Chapter - 6 Anatomy of Flowering Plants 15Document15 pagesDPP XI Chapter - 6 Anatomy of Flowering Plants 15Riya Mondal100% (1)
- T2L2 Embryonic and Fetal PeriodDocument29 pagesT2L2 Embryonic and Fetal PeriodStanley OdiraNo ratings yet
- KS3 Human Organ SystemDocument2 pagesKS3 Human Organ Systemejljn1No ratings yet
- Human Body (Eyewitness Workbooks) (Claire Watts)Document115 pagesHuman Body (Eyewitness Workbooks) (Claire Watts)Despoina AjlaNo ratings yet
- PlasmodesmataDocument11 pagesPlasmodesmataGyandip DekaNo ratings yet
- 01 Introductory PgyDocument76 pages01 Introductory Pgygbsreg gbsregNo ratings yet
- Ebook Developing Human Clinically Oriented Embryology 10Th Edition Moore Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument30 pagesEbook Developing Human Clinically Oriented Embryology 10Th Edition Moore Test Bank Full Chapter PDFStacieSharpnocje100% (11)
- Physical Science Report (Glenn Trono)Document17 pagesPhysical Science Report (Glenn Trono)Glenn TronoNo ratings yet
- Cell Parts and FunctionsDocument4 pagesCell Parts and FunctionsPrecious YeshakNo ratings yet
- Gross Anatomy LiverDocument51 pagesGross Anatomy LiverDeny ShajiniNo ratings yet
- Module 4-Anaphy - Fernandez, Rr12Document5 pagesModule 4-Anaphy - Fernandez, Rr12Veronica ShaneNo ratings yet
- CytoskeletonDocument4 pagesCytoskeletonharshika tembhurneNo ratings yet
- Tip 8 1 39Document3 pagesTip 8 1 39Juan Gavilanes EspinarNo ratings yet