Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Natural Regions of The World
Natural Regions of The World
Uploaded by
shrey jain0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
214 views3 pages1. The document describes three main natural regions of the world: the equatorial region, tropical deserts, and tropical monsoon regions.
2. The equatorial region lies between 10 degrees north and south of the equator with dense, tropical rainforests and year-round high temperatures. Tropical deserts are hot, dry regions between 15-30 degrees north and south, featuring thorny plants and little rainfall.
3. Tropical monsoon regions lie between 10-25 degrees north and south, experiencing distinct wet and dry seasons due to shifting wind patterns, and supporting deciduous forests and important agricultural areas.
Original Description:
Original Title
Natural Regions of the World
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1. The document describes three main natural regions of the world: the equatorial region, tropical deserts, and tropical monsoon regions.
2. The equatorial region lies between 10 degrees north and south of the equator with dense, tropical rainforests and year-round high temperatures. Tropical deserts are hot, dry regions between 15-30 degrees north and south, featuring thorny plants and little rainfall.
3. Tropical monsoon regions lie between 10-25 degrees north and south, experiencing distinct wet and dry seasons due to shifting wind patterns, and supporting deciduous forests and important agricultural areas.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
214 views3 pagesNatural Regions of The World
Natural Regions of The World
Uploaded by
shrey jain1. The document describes three main natural regions of the world: the equatorial region, tropical deserts, and tropical monsoon regions.
2. The equatorial region lies between 10 degrees north and south of the equator with dense, tropical rainforests and year-round high temperatures. Tropical deserts are hot, dry regions between 15-30 degrees north and south, featuring thorny plants and little rainfall.
3. Tropical monsoon regions lie between 10-25 degrees north and south, experiencing distinct wet and dry seasons due to shifting wind patterns, and supporting deciduous forests and important agricultural areas.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
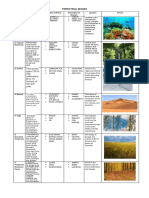
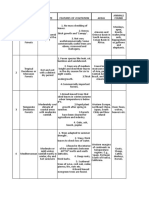
Natural Regions of the World
LOCATION AREA CLIMATE NATURAL VEGETATION HUMAN
ADAPTATION
1. EQUATORIAL REGION
Between 10 S. America: Amazon High Temperature and Heavy Rainfall Tropical/ Equatorial Rain Forests/Selvas in Oppressive
ﹾN and 10ﹾS Basin- Coastal Temperature: hot throughout the year Amazon Basin climate and
of the lowlands between due to vertical rays of the Sun Forests thick and luxuriant- trees, creepers, impenetrable
Equator the Guiana and throughout the year and 12 hours of bushes, shrubs, ferns and orchids vegetation
Brazilian Highlands daily sunshine Trees broad leaved, evergreen.
and coastal Mean Annual: 27 degree Celsius Mainly Asian
Columbia- Brazil , Annual Range: small, 3 degree Celsius Structure of the Equatorial Forests: part is under
Equador and the Diurnal Range: small, 7 degree Four distinct Layers agriculture;
coast of French Celsius The emergent layer: tallest trees (over 50m), main crops:
Guinea such as, mahogany and kapok, widely spaced, Wheat, rice,
Africa: The Congo Convectional Type- very heavy, every seeds dispersed by wind tapioca,
Basin (Zaire) and the afternoon throughout the year The canopy: lower than the emergent layer, mangoes
Guinea Coast of Annual : 250cm formed by crowns of trees, several tiers, blocks
West Africa Max rainfall twice: around equinoxes sunlight and wind. Growing quickly towards Plantation
Southern Asia: Wettest months: March & September light, they have straight trunks with few farming
Malaysia, Indonesia High Humidity: About 80% branches. Seeds dispersed by animals common:
and Papua (New Sky Always Cloudy: prevents nights Sugarcane,
Guinea), southern from becoming cold The understory: under the canopy, with not rubber, coffee,
Philippines much light, air humid- trees large leaved to tea coconut,
maximise the light absorbed. tobacco
The forest floor: plants and leaves arranged in
rosettes to avoid upper leaves shading the lower Cocoa, oil
ones. Ferns have divided fronds to get palms, bananas,
maximum light yams in Africa
Uneconomical for commercial exploitation-
dense and occur in non-social strands (No one
species in an area)
Imp. Trees- Hardwood – Mahogany, ebony,
rosewood- good for furniture
2. TROPICAL DESERTS (HOT DRY DESERT)
LOCATION AREA CLIMATE NATURAL VEGETATION HUMAN
ADAPTATION
On the North Africa: Sahara Daily range of temperature Xerophytic vegetation With irrigation
western (largest) and greater than annual range Thorny and leathery leaves- to protect agriculture is
margins of Kalahari deserts Hot summers with very little from being eaten by animals and leaves possible
continenets Asia: The Thar and rain, cool winters reduced to thorns to reduce loss of
between 15ﹾ the Arabian Deserts Mean Temp: Hottest month- 30 water by transpiration
to N. America: Eg- to 35℃; Coldest month- 20℃ Long roots- go down deep in search of
30 ﹾNorth Californian, Mexican Lies in offshore region of trade water
and South of deserts winds, hence so arid. Main plants: cacti, scrubs, short grasses,
the Equator S. America: Atacama Annual Rainfall: less than prickly pear; date palms in oasis
(driest) 25cm; usually convectional
Australia: The Great with violent thunderstorms
Australian Desert
3. TROPICAL MONSOON REGION
LOCATION AREA CLIMATE NATURAL VEGETATION HUMAN
ADAPTATION
Lies Asia: India, Pakistan, Seasonal Climate due to Mostly deciduous, shed their leaves during Most densely
between 10ﹾ Bangladesh, Sri differential rate of heating of summers populated and
to Lanka, Myanmar, land and sea Forests less luxuriant than those of the rich agricultural
25 ﹾNorth Southern China, Hot summers, cold winters wit Equatorial region regions
and South of Cambodia, Laos, a distinct rainy season Trees: hard wood and broad leaved Coffee, oilseeds,
the Equator Vietnam, Taiwan South- West Monsoon winds Main trees: teak, sal, bamboo, sandalwood, rubber, coconut
and Philippines bring rains after summer acacia plantations
Central America: Rainfall – 25 to 250 cm Rice, jute,
West Indies depending on location sugarcane main
North eastern North-East Monsoon winds crops
Australia blow in winters which are Wheat,millets,
S, America- Eastern offshore, hence, basically dry pulses, tobacco,
Brazil winds but bring some rainfall tea
Parts of east Africa to South- East Asia
You might also like
- Year 9 Geography Exam RevisionDocument7 pagesYear 9 Geography Exam RevisionJieshun Wang100% (2)
- Chapter 23 Terrestrial EcosystemsDocument10 pagesChapter 23 Terrestrial EcosystemsKarmina SantosNo ratings yet
- 01 IronDocument21 pages01 IronvhinzsanguinaryNo ratings yet
- Biome Characteristics Countries Temperature and Precipitation Species PresentDocument12 pagesBiome Characteristics Countries Temperature and Precipitation Species PresentBismarck John SalazarNo ratings yet
- eaaeb-ecosystemsDocument12 pageseaaeb-ecosystemsShadab MohammadNo ratings yet
- Climate Latitude Temperature Precipitation Vegetation Life Economy Mineral ResourcesDocument35 pagesClimate Latitude Temperature Precipitation Vegetation Life Economy Mineral Resourceskannan PNo ratings yet
- Natural Region 2Document2 pagesNatural Region 2Dithya VinodNo ratings yet
- EcosystemDocument7 pagesEcosystemMuhammad HabibNo ratings yet
- hhtDocument1 pagehhtvishnuchauhan1101No ratings yet
- Natural Regions of The WorldDocument5 pagesNatural Regions of The Worldaryan.mandlik12No ratings yet
- BIOMESDocument10 pagesBIOMESDev Pratap singhNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Biomes Part 1Document19 pagesChapter 4 Biomes Part 1mauryapcfilesNo ratings yet
- Geography Zones CompDocument2 pagesGeography Zones CompBinu Kumar SNo ratings yet
- Biomes ReviewerDocument4 pagesBiomes ReviewerKate Mae GeronimoNo ratings yet
- Sci 2Document6 pagesSci 2Jvyn GamingNo ratings yet
- Natural VegetationDocument4 pagesNatural VegetationliquoriceNo ratings yet
- Biomes TableDocument2 pagesBiomes Tabledeensraja3No ratings yet
- 12.terrestrial EcosystemDocument7 pages12.terrestrial Ecosystemsalihundamravikumar100No ratings yet
- BiomesDocument3 pagesBiomesJESMELYN RAMOSNo ratings yet
- Geography ProjectDocument18 pagesGeography ProjectIbrahim NawabNo ratings yet
- Natural Vegetation of IndiaDocument4 pagesNatural Vegetation of Indiadeekshaa685No ratings yet
- Climatic Regions.1.EquatorialDocument16 pagesClimatic Regions.1.EquatorialVikram Das100% (1)
- Unit 3 Biomes: Biomes Desription Type of Plants and Animals Tempature/ ClimateDocument3 pagesUnit 3 Biomes: Biomes Desription Type of Plants and Animals Tempature/ Climaterysii gamesNo ratings yet
- Pee - DesertsDocument1 pagePee - DesertsKASIA SyNo ratings yet
- BiomesDocument74 pagesBiomesHallares, Maxine Kate F.No ratings yet
- Assland EcosystemsDocument4 pagesAssland Ecosystemssalihundamravikumar100No ratings yet
- 2.1 Biomes Table - AnswersDocument3 pages2.1 Biomes Table - Answersberrached.samaNo ratings yet
- Biomes 3) - TaigaDocument2 pagesBiomes 3) - TaigaJOHAYNIENo ratings yet
- Topic 2 - Biomes and Biodiversity (AutoRecovered)Document12 pagesTopic 2 - Biomes and Biodiversity (AutoRecovered)Jomari TawatNo ratings yet
- Forest O Level Geography..Document3 pagesForest O Level Geography..Roshaan NaeemNo ratings yet
- Terrestrial EcosystemDocument6 pagesTerrestrial EcosystemJaykumar 003No ratings yet
- Equatorial Forest Mediterranean ForestDocument42 pagesEquatorial Forest Mediterranean ForestVinayak ChaturvediNo ratings yet
- Example of BiomesDocument5 pagesExample of BiomesJhozeph UyNo ratings yet
- World VegetationDocument11 pagesWorld VegetationAixha MallickNo ratings yet
- Lanscapes TeresaDocument2 pagesLanscapes TeresaMtgarcia PatonNo ratings yet
- BiomesDocument14 pagesBiomesJerico MarcosNo ratings yet
- Mendova ECOLOGYDocument1 pageMendova ECOLOGYAngelo MendovaNo ratings yet
- Activity Worksheet 1 Biome and Its ComponentsDocument4 pagesActivity Worksheet 1 Biome and Its ComponentsWinnie ToribioNo ratings yet
- Natural Vegetation Tabular FormDocument3 pagesNatural Vegetation Tabular Formvedantsaraf.21No ratings yet
- The Tundra Is T-WPS OfficeDocument2 pagesThe Tundra Is T-WPS OfficerechangservanezNo ratings yet
- Biome Information PacketDocument57 pagesBiome Information PacketJudy Ann MolinaNo ratings yet
- Major Biomes of The WorldDocument4 pagesMajor Biomes of The WorldNaga Chary100% (1)
- Patel-DivyaWeek 7 Assignment FinalDocument5 pagesPatel-DivyaWeek 7 Assignment FinalDivya PatelNo ratings yet
- The Tundra Is T-WPS OfficeDocument2 pagesThe Tundra Is T-WPS OfficerechangservanezNo ratings yet
- Terrestrial Biome: Biomes Geographical Location and Climatic Conditions Specific Plant Species Specific Animal SpeciesDocument20 pagesTerrestrial Biome: Biomes Geographical Location and Climatic Conditions Specific Plant Species Specific Animal SpeciesDayana ChelebievaNo ratings yet
- BiomesDocument9 pagesBiomesapi-26570979100% (1)
- AT A GLANCE - The Living WorldDocument3 pagesAT A GLANCE - The Living WorldHadad LwazeNo ratings yet
- 6 Biomes, Nutrient Cycles, Ecological SuccessionDocument54 pages6 Biomes, Nutrient Cycles, Ecological SuccessionFrances Joei O. PEREZNo ratings yet
- The Amazon Rainforest ComprehesionDocument2 pagesThe Amazon Rainforest ComprehesionTemiloluwa AkinwaleNo ratings yet
- Natural Vegetation - 3102Document13 pagesNatural Vegetation - 3102Khandoker mariatul IslamNo ratings yet
- Acacia Mangium: Willd. - A Fast Growing Tree For Tropical PlantationDocument14 pagesAcacia Mangium: Willd. - A Fast Growing Tree For Tropical PlantationTimothy LoeNo ratings yet
- Evidencia 2 de Ingles IntermedioDocument6 pagesEvidencia 2 de Ingles IntermedioLynn PedrazaNo ratings yet
- Class7 - Natural Vegetation and WildlifeDocument3 pagesClass7 - Natural Vegetation and WildlifekkkNo ratings yet
- Manuj Jindal IAS GC Leong World Climate TypesDocument19 pagesManuj Jindal IAS GC Leong World Climate Typesayan mitra100% (2)
- Climate (Chapter 6)Document12 pagesClimate (Chapter 6)Shivendu Vats Shivendu VatsNo ratings yet
- in Envi. Science - T. E. (Balderama, Zyra)Document7 pagesin Envi. Science - T. E. (Balderama, Zyra)Zyra BalderamaNo ratings yet
- Major Types of VegetationDocument9 pagesMajor Types of VegetationJoy TanNo ratings yet
- Section 3-4 Anna MoralesDocument2 pagesSection 3-4 Anna Morales2psn7xxgjfNo ratings yet
- Persebaran FloraDocument4 pagesPersebaran FloraDewi SadyaNo ratings yet
- The Complete U.S. Army Survival Guide to Tropical, Desert, Cold Weather, Mountain Terrain, Sea, and NBC EnvironmentsFrom EverandThe Complete U.S. Army Survival Guide to Tropical, Desert, Cold Weather, Mountain Terrain, Sea, and NBC EnvironmentsNo ratings yet
- Environmental Chemistry and AnalysisDocument12 pagesEnvironmental Chemistry and Analysissubhajit29in100% (1)
- Module 16 - BREAKING OF ROCKSDocument9 pagesModule 16 - BREAKING OF ROCKSLeah Camille Santos DetruzNo ratings yet
- Climate Change: by Kimberly .N. ChishiriDocument10 pagesClimate Change: by Kimberly .N. ChishirikevitynoeNo ratings yet
- A Comparison of Interpolation Methods On The Basis of Data ObtainedDocument14 pagesA Comparison of Interpolation Methods On The Basis of Data ObtainedArseni MaximNo ratings yet
- Ground-Penetrating Radar (GPR) For Imaging Stratigraphic Features and Groundwater in Sand DunesDocument10 pagesGround-Penetrating Radar (GPR) For Imaging Stratigraphic Features and Groundwater in Sand DunesJAKA WIBISANANo ratings yet
- VCSDocument3 pagesVCSkarthika gopiNo ratings yet
- Doc-20230908-Wa0012 231117 212025Document12 pagesDoc-20230908-Wa0012 231117 212025m4522919No ratings yet
- Climate Change: By: Gabrielle Barrett, Tivonia Daley, Kayla Lawson and Dominque ValentineDocument18 pagesClimate Change: By: Gabrielle Barrett, Tivonia Daley, Kayla Lawson and Dominque ValentineTonique GordonNo ratings yet
- QUIZ - Coping With Coastal Erosion, Submersion, and Saltwater IntrusionDocument1 pageQUIZ - Coping With Coastal Erosion, Submersion, and Saltwater IntrusionCristina Maquinto67% (3)
- C. Venue: at The Seashore E. MechanicsDocument3 pagesC. Venue: at The Seashore E. Mechanicsjeph benitezNo ratings yet
- 07 Torsvik & Cocks 2011 - The Palaeozoic Palaeogeography of Central GondwanaDocument31 pages07 Torsvik & Cocks 2011 - The Palaeozoic Palaeogeography of Central GondwanaAnanda LimaNo ratings yet
- LP - Factors-Affecting-Climate COT1Document3 pagesLP - Factors-Affecting-Climate COT1Janet PagulayanNo ratings yet
- Limestone CavesDocument3 pagesLimestone CavesNIHARIKA SHAHNo ratings yet
- Title Lorem IpsumDocument24 pagesTitle Lorem IpsumredfortNo ratings yet
- 12 S.Y.B.a. GeographyDocument26 pages12 S.Y.B.a. GeographyMahadeo JadhavNo ratings yet
- The Evidence For Rapid Climate ChangeDocument5 pagesThe Evidence For Rapid Climate ChangeLovely RoseNo ratings yet
- Lesson-1, - 2 Enviro Chem 1Document38 pagesLesson-1, - 2 Enviro Chem 1JoudNo ratings yet
- Initial Fertilizer Product Registration Form Fillable PDFDocument2 pagesInitial Fertilizer Product Registration Form Fillable PDFapi-609761039No ratings yet
- Case Study No. 1-Groundwater Supply of Cavite ProvinceDocument25 pagesCase Study No. 1-Groundwater Supply of Cavite ProvincepicefeatiNo ratings yet
- 21 Geosynthetics Applications in Coastal Protection MACCAFERRIDocument58 pages21 Geosynthetics Applications in Coastal Protection MACCAFERRIGautam RaiNo ratings yet
- The Philippines National TerritoryDocument1 pageThe Philippines National TerritoryAshdadaNo ratings yet
- Mcqs - India Size and LocationDocument6 pagesMcqs - India Size and LocationAbc DefNo ratings yet
- Weathering. Form 1-4 Notes Compiled by MR K. Romo 0772858765Document16 pagesWeathering. Form 1-4 Notes Compiled by MR K. Romo 0772858765Sharon MasikiNo ratings yet
- Borehole DrillingDocument155 pagesBorehole DrillingMichael NcubeNo ratings yet
- Clasification of Structural DiscontinuitiesDocument25 pagesClasification of Structural DiscontinuitiesVinny NiniNo ratings yet
- Shrinkage and Atterberg Limits in Relation To Other Properties of Principal Soil Types in IsraelDocument19 pagesShrinkage and Atterberg Limits in Relation To Other Properties of Principal Soil Types in Israelbkollarou9632No ratings yet
- Road ActivitiesDocument6 pagesRoad Activitiesprasanna sNo ratings yet
- (15200477 - Bulletin of The American Meteorological Society) High-Resolution Operational Ocean Forecast and Reanalysis System For The Indian OceanDocument17 pages(15200477 - Bulletin of The American Meteorological Society) High-Resolution Operational Ocean Forecast and Reanalysis System For The Indian OceanBISWARUP DASNo ratings yet
- Final Exam - GEM 4102 Petroleum Geology - 2018-9Document12 pagesFinal Exam - GEM 4102 Petroleum Geology - 2018-9swf svNo ratings yet