Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pa Tho Physiology
Pa Tho Physiology
Uploaded by
danevaqOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Pa Tho Physiology
Pa Tho Physiology
Uploaded by
danevaqCopyright:
Available Formats
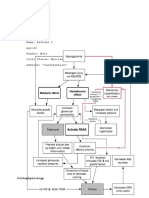
Predisposing factors: Age Race Obesity Diet Family History of DM Family History of HPN
Predisposing factors: Drinking alcohol Smoking Physical inactivity Pregnancy Stress
Insulin resistance or insufficient insulin secretion
Body compensates by further
insulin production
Insulin production
Hyperinsulinemia
Stimulation of beta-cells
Stimulation of alpha cells
Hyperglucagonemia
Inhibition of Insulin production
Production of Glucagon
Exhaustion of alpha and beta cells
Increased Blood glucose level
Protein utilization
Glucose utilization
Glucoheogenesis
CHON metabolism
Chronic elevation of blood glucose
Urea
Cellular starvation
Renal gluco threshold
e Muscle wasting Further in blood glucose Polyphagia Uric acid production Urea
Excretion of glucose in th urine
Weight loss Fatigue
Nausea & vomiting
Osmotic pressu
Reabsorption of wate electrolytes Sluggish blood flow Polyuria Hypoperfusion Fluid loss
Cellular dehydratio
Immune system
Eyes
Brain
Kidneys
Delayed wound healing
Affects retinal vein
Blurring of vision
Blockage in the minute capillaries
Damaged nephrons
Fibrosis Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy Blockage in the optic nerve Decreased LOC
Diabetic Neuropathy Opacity of the lens
Diabetic Nephropathy
Cataract
Diabetic Retinopathy
EXAMINATIONS
Laboratories: 1. CBC 2 CBG 3. Glycosylated hemoglobin A1c 4. Urinalysis 5. Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT)-
Diagnostic: 1. Ultrasound 2. Opthalmologic examination
Diagnosis: DIABETES MELLITUS
MANAGEMENT
Medical Management: 1. Medications Insulin Oral Hypoglycemic agents 2. IV fluids
Surgical Management: 1. Transplant pancreatic cells 2. Amputation of
Nursing Management:
Administer medication Monitor VS, I & O Careful monitoring of blood glucose level Individualized meal plan to meet nutritional needs, with 50%CHON, 30%Fats, 20%CHO Weight reduction by exercise or regular physical activity program Psychological assessment to determine the impact of the disorder on the patient and family Stress the importance of complying with the prescribed treatment program, necessary lifestyle modifications such as improving food selection, increasing physical activity and smoking cessation. Meticulous foot care. Urge the patient to have regular ophthalmologic examinations to detect diabetic retinopathy. Stress the importance of regular screenings: FBS, Kidney (BUN and Creatinine) Need for self-examination of the skin including injection site.
PROGNOSIS
IF TREATED: 1. Good compliance of meds. 2. Good financial support 3. Good family support
IF NOT TREATED: 1. Poor compliance of meds. 2. Poor financial support 3. Poor family support
IF NOT TREATED
Chronic and uncontrolled elevation of blood glucose level
Damaged glomerulus
Acute Renal Failure Hyperosmolar Hyperglycemic Non-Ketotic Coma
Chronic Renal Failure
DEATH
You might also like
- Acupuncture Study Guide FinalDocument50 pagesAcupuncture Study Guide Finalgraymagiker1092No ratings yet
- Weaknes S/ Fatigue Polyphag IaDocument5 pagesWeaknes S/ Fatigue Polyphag IaEwert Hesketh Nillama PaquinganNo ratings yet
- Diabetic Ketoacidosis Case StudyDocument6 pagesDiabetic Ketoacidosis Case StudyJohn AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- Addisons DiseaseDocument12 pagesAddisons DiseaseChinju CyrilNo ratings yet
- IMED - FAIMER International Medical Education Directory - School Friendly)Document1 pageIMED - FAIMER International Medical Education Directory - School Friendly)Mohamed SidekNo ratings yet
- University of The Philippines: Please PrintDocument3 pagesUniversity of The Philippines: Please PrintlabellejolieNo ratings yet
- Star Wars Insider 83 Medstar Intermezzo by Michael Reeves Steve PerryDocument14 pagesStar Wars Insider 83 Medstar Intermezzo by Michael Reeves Steve PerryjohnNo ratings yet
- Nur 105 Adult Health I: Diabetes MellitusDocument70 pagesNur 105 Adult Health I: Diabetes MellitusrikramNo ratings yet
- Hyperosmolar Hyperglycemic Syndrome (HHNS)Document19 pagesHyperosmolar Hyperglycemic Syndrome (HHNS)Camila BuadoNo ratings yet
- Case Study in Diabetes Mellitus: in Partial Fulfillment in The Requirements of NCM 311 Code 0570Document19 pagesCase Study in Diabetes Mellitus: in Partial Fulfillment in The Requirements of NCM 311 Code 0570Ralph Asura UchihaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine - DI, DM I & II 04/13/2016: Review of Endocrine Pancreas: Endocrine and Exocrine Gland Alpha CellsDocument6 pagesEndocrine - DI, DM I & II 04/13/2016: Review of Endocrine Pancreas: Endocrine and Exocrine Gland Alpha Cellsapi-314805004No ratings yet
- Diabetes MellitusDocument9 pagesDiabetes MellitusglamyposhNo ratings yet
- Eating DisordersDocument46 pagesEating Disordersedrinsne100% (1)
- Quiz 10 NotesDocument5 pagesQuiz 10 NotescwissenbNo ratings yet
- Grp.10 DiabetesDocument15 pagesGrp.10 DiabetesVanessa JanneNo ratings yet
- Chronic PancreatitisDocument4 pagesChronic PancreatitisRania Medhat SleemNo ratings yet
- © 2022 Lippincott Advisor - Diseases and Conditions - HypoglycemiaDocument9 pages© 2022 Lippincott Advisor - Diseases and Conditions - HypoglycemiaBaebee LouNo ratings yet
- Metabolic SyndromeDocument55 pagesMetabolic SyndromeAakash BalasubramanianNo ratings yet
- Quiz Blessings #6Document7 pagesQuiz Blessings #6Rachel LiuNo ratings yet
- Dental Management of Diabetic PatientsDocument30 pagesDental Management of Diabetic PatientsChitrang KolawaleNo ratings yet
- Lecture 34 - Hypoglycemia in ChildrenDocument32 pagesLecture 34 - Hypoglycemia in ChildrenjohnsonkkuriakoseNo ratings yet
- DIABETES CorrectedDocument16 pagesDIABETES CorrectedBlaise PascalNo ratings yet
- DR ZegeyeDocument1,254 pagesDR ZegeyesirawNo ratings yet
- Presented by Rudy Kaprisyah I11108011Document26 pagesPresented by Rudy Kaprisyah I11108011rudyxperiaNo ratings yet
- Diabetic Ketoacidosis Case StudyDocument6 pagesDiabetic Ketoacidosis Case StudyHomework Ping100% (2)
- Diabetes Mellitus: NZ Diploma in Enrolled NursingDocument38 pagesDiabetes Mellitus: NZ Diploma in Enrolled NursingRegina PunNo ratings yet
- Hyperemesis Gravidarum and Its Homoeopathic ManagementDocument8 pagesHyperemesis Gravidarum and Its Homoeopathic ManagementAmreen KausarNo ratings yet
- Diabetes MellitusDocument66 pagesDiabetes MellitusNatson ZmNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - Regular InsulinDocument8 pagesDrug Study - Regular InsulinRaijenne VersolaNo ratings yet
- Medical Abbreviation For Diabetes Mellitus With Endocrine System Abbreviation Medical Term Meaning / DefinitionDocument26 pagesMedical Abbreviation For Diabetes Mellitus With Endocrine System Abbreviation Medical Term Meaning / DefinitionCt AinnNo ratings yet
- Pheo Esrd and NeonateDocument45 pagesPheo Esrd and NeonateLea TanNo ratings yet
- Nutrition in CirrhosisDocument40 pagesNutrition in CirrhosisAuliangi TamayoNo ratings yet
- Assessment and Management of Patients With Diabetes MellitusDocument82 pagesAssessment and Management of Patients With Diabetes MellitusMuhidin AeNo ratings yet
- 6 Mary Lou Sole, Deborah Goldenberg Klein, Marthe J. Moseley - EndokrinDocument56 pages6 Mary Lou Sole, Deborah Goldenberg Klein, Marthe J. Moseley - EndokrinyaminmuhNo ratings yet
- Prevention Control of Chronic Non-Communicable DiseasesDocument43 pagesPrevention Control of Chronic Non-Communicable DiseasesDesrene DentonNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Diabetes InformationDocument15 pagesDiabetes Diabetes InformationbalatnplNo ratings yet
- Hepatobiliary System Functions of The Liver IncludeDocument19 pagesHepatobiliary System Functions of The Liver IncludeRacha MougharbelNo ratings yet
- EndocrinologyDocument50 pagesEndocrinologyCut TirayaNo ratings yet
- Diabetic KetoacidosisDocument12 pagesDiabetic Ketoacidosispolaris_027No ratings yet
- 109 Pregestational Nov2019Document68 pages109 Pregestational Nov2019Sean kevinNo ratings yet
- Module 8 Assessment and Management of Patients With DiabetesDocument44 pagesModule 8 Assessment and Management of Patients With DiabetesBlessed GarcianoNo ratings yet
- 340 Final StudyDocument21 pages340 Final StudyLeah ElizabethNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Action Indication Contra-Indication Side Effects Nursing ConsiderationsDocument11 pagesName of Drug Action Indication Contra-Indication Side Effects Nursing ConsiderationsMalou SanNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Mellitus 1230837681076571 2 160105033950Document26 pagesDiabetes Mellitus 1230837681076571 2 160105033950Gerome ManantanNo ratings yet
- Update On Childhood Diabetes MellitusDocument51 pagesUpdate On Childhood Diabetes MellitusJulie Carnetion DNo ratings yet
- DocumentDocument7 pagesDocumentabdo mo . M7.No ratings yet
- Nutritional Considerations For Older Adults: PhysiologyDocument9 pagesNutritional Considerations For Older Adults: PhysiologySavera NarejoNo ratings yet
- Acute Vs Chronic Renal Failure.Document3 pagesAcute Vs Chronic Renal Failure.Stephanie HurewitzNo ratings yet
- Aging and Endocrine DisordersDocument23 pagesAging and Endocrine DisordersadystiNo ratings yet
- Case Study 2020 Multiple Myeloma With BMT Leak Resulting in Septic ShockDocument56 pagesCase Study 2020 Multiple Myeloma With BMT Leak Resulting in Septic Shockapi-519485865No ratings yet
- C C C CDocument51 pagesC C C CpixiemedicNo ratings yet
- 1 - Endocrine DisordersDocument55 pages1 - Endocrine Disorderscephas chinkoliNo ratings yet
- Medical-Surgical Nursing: An Integrated Approach, 2E: Nursing Care of The Client: Endocrine SystemDocument29 pagesMedical-Surgical Nursing: An Integrated Approach, 2E: Nursing Care of The Client: Endocrine SystemWilbert Antonino CabanbanNo ratings yet
- CKD Case StudyDocument8 pagesCKD Case StudyEspiridionNo ratings yet
- 12 Nursing Managment of Childern With Endocarine Disorders 2nd SemesterDocument27 pages12 Nursing Managment of Childern With Endocarine Disorders 2nd SemesterFaisal M.AlruwailiNo ratings yet
- Diabetes MellitusDocument10 pagesDiabetes Mellitusjoeln_9No ratings yet
- Aquifer InternalMedicine11 - 45Document8 pagesAquifer InternalMedicine11 - 45JulieNo ratings yet
- BONISHADocument40 pagesBONISHAsj computersNo ratings yet
- Week 1 PHAR401F16-CKD-1-Intro (160822) - BBDocument34 pagesWeek 1 PHAR401F16-CKD-1-Intro (160822) - BBoxyc0n999No ratings yet
- Diabetes Mellitus Diabetes Mellitus DR Prakash H M DR Prakash H MDocument85 pagesDiabetes Mellitus Diabetes Mellitus DR Prakash H M DR Prakash H MrogeriotascaNo ratings yet
- Smoothies for Diabetics: Reverse Diabetes and Lower Blood Sugar with 36 Quick & Easy Delicious Diabetic Smoothie RecipesFrom EverandSmoothies for Diabetics: Reverse Diabetes and Lower Blood Sugar with 36 Quick & Easy Delicious Diabetic Smoothie RecipesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Diabetic Cooking for One and TwoFrom EverandDiabetic Cooking for One and TwoRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Type 2 Diabetes: How to Eat Better, Lower Blood Sugar, and Manage DiabetesFrom EverandType 2 Diabetes: How to Eat Better, Lower Blood Sugar, and Manage DiabetesNo ratings yet
- Laporan Kasus Ulkus Kornea Jamur Dengan Hipopion .Eva RiantiDocument21 pagesLaporan Kasus Ulkus Kornea Jamur Dengan Hipopion .Eva RiantiBenk Setsuna F. SeieiNo ratings yet
- ENDOCRINE PRACTICE Rapid Electronic Article in Press: AACE/ACE Consensus StatementDocument66 pagesENDOCRINE PRACTICE Rapid Electronic Article in Press: AACE/ACE Consensus StatementMUHAMMAD09No ratings yet
- AD - Daftar Produk - 27 Mei 2021Document11 pagesAD - Daftar Produk - 27 Mei 2021adhimaswicaksono1991No ratings yet
- Aula Enem 4Document1 pageAula Enem 4Adriano JoseNo ratings yet
- THE SOCIAL TERRORIST, The Day AIDS Became A Global Threat! A Novel by Joseph P. ChaddockDocument112 pagesTHE SOCIAL TERRORIST, The Day AIDS Became A Global Threat! A Novel by Joseph P. ChaddockJoseph Caratti100% (1)
- MJH Life Sciences Not For Distribution: Why Pharmacopoeia Compliance Is DifficultDocument9 pagesMJH Life Sciences Not For Distribution: Why Pharmacopoeia Compliance Is DifficultLinh NguyenNo ratings yet
- Dissection of A Pig: What We Did and FeltDocument6 pagesDissection of A Pig: What We Did and FeltNouman KhanNo ratings yet
- Pharmacological Management of Congestive Heart FailureDocument28 pagesPharmacological Management of Congestive Heart FailureIndar WatiNo ratings yet
- CRISTIAN COLCERIU - PERSONALITATI CLUJENE Prof - Dr.ing - POMPILIU MANEADocument21 pagesCRISTIAN COLCERIU - PERSONALITATI CLUJENE Prof - Dr.ing - POMPILIU MANEAcristian colceriu100% (2)
- PD 7896 Infant CPR For New ParentsDocument4 pagesPD 7896 Infant CPR For New ParentsBrandie WilberNo ratings yet
- Hardware Architecture For Nanorobot Application in Cancer TherapyDocument7 pagesHardware Architecture For Nanorobot Application in Cancer TherapyCynthia CarolineNo ratings yet
- List of Product For CE ExcelDocument92 pagesList of Product For CE Excelsaledepartment.adqNo ratings yet
- Zoo 3102 Course OutlineDocument8 pagesZoo 3102 Course OutlineKent Lary TediosNo ratings yet
- 1 Acidity CleanseDocument11 pages1 Acidity CleanseSeetha Chimakurthi67% (3)
- The 10 Deadly Health Myths of The 21st CenturyDocument36 pagesThe 10 Deadly Health Myths of The 21st CenturyPrashanth Mohan100% (1)
- Chapter 23 Acquired Neuropathies PDFDocument106 pagesChapter 23 Acquired Neuropathies PDFzloncar3No ratings yet
- Artaud, Antonin - The Theater and Its DoubleDocument41 pagesArtaud, Antonin - The Theater and Its DoubleSeeWindNo ratings yet
- The Dynamic Rotation of Langer's Lines On Facial ExpressionDocument7 pagesThe Dynamic Rotation of Langer's Lines On Facial Expressionaulia rachmanNo ratings yet
- Horizontal Gene Transfer Among Bacteria and Its Role in Biological EvolutionDocument8 pagesHorizontal Gene Transfer Among Bacteria and Its Role in Biological EvolutionHarold Earl Cabungcal VenalNo ratings yet
- Traditional Approaches For The Management of Bala Roga: An Ayurveda PerspectiveDocument3 pagesTraditional Approaches For The Management of Bala Roga: An Ayurveda PerspectiveAditya BhatNo ratings yet
- Pakistan ArticleDocument5 pagesPakistan ArticleSaifuddinNo ratings yet
- PheoDocument4 pagesPheoantonijevicuNo ratings yet
- What Is Tummy Time: Is It Necessary For Newborns?: by Joyce Miller, BSC, DC, PHD, and Sharon Vallone, DC, FiccpDocument3 pagesWhat Is Tummy Time: Is It Necessary For Newborns?: by Joyce Miller, BSC, DC, PHD, and Sharon Vallone, DC, FiccpzikmonNo ratings yet
- Aloe VeraDocument39 pagesAloe VeraAyush TiwariNo ratings yet
- Petition To Save St. Lawrence Psych CenterDocument256 pagesPetition To Save St. Lawrence Psych Centerpritchie10No ratings yet
- ZF I Competitive ExamsDocument3 pagesZF I Competitive ExamsÂvï JâísNo ratings yet