Professional Documents
Culture Documents
MEM
MEM
Uploaded by
PRATHAMESH KAMALAKAR 0070 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views2 pagesThis document contains questions and answers related to measuring instruments:
1. It defines key characteristics of measuring instruments such as accuracy, precision, resolution, range, and hysteresis. It also differentiates between accuracy and precision.
2. It defines dead time as the time lag between an input signal passing through a system and the output signal, and defines a dead zone as a hypoxic area in oceans/lakes where few organisms can survive.
3. It provides examples of displacement measuring instruments like proximity sensors and accelerometers, and applications of LVDT sensors in various industries. Strain transducers are used to measure force. Common temperature units include Celsius, Fahrenheit and Kelvin.
Original Description:
kkp
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document contains questions and answers related to measuring instruments:
1. It defines key characteristics of measuring instruments such as accuracy, precision, resolution, range, and hysteresis. It also differentiates between accuracy and precision.
2. It defines dead time as the time lag between an input signal passing through a system and the output signal, and defines a dead zone as a hypoxic area in oceans/lakes where few organisms can survive.
3. It provides examples of displacement measuring instruments like proximity sensors and accelerometers, and applications of LVDT sensors in various industries. Strain transducers are used to measure force. Common temperature units include Celsius, Fahrenheit and Kelvin.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views2 pagesMEM
MEM
Uploaded by
PRATHAMESH KAMALAKAR 007This document contains questions and answers related to measuring instruments:
1. It defines key characteristics of measuring instruments such as accuracy, precision, resolution, range, and hysteresis. It also differentiates between accuracy and precision.
2. It defines dead time as the time lag between an input signal passing through a system and the output signal, and defines a dead zone as a hypoxic area in oceans/lakes where few organisms can survive.
3. It provides examples of displacement measuring instruments like proximity sensors and accelerometers, and applications of LVDT sensors in various industries. Strain transducers are used to measure force. Common temperature units include Celsius, Fahrenheit and Kelvin.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 2
Q.1 Attempt any Four.
a) Name different static characteristics of measuring instruments.
Accuracy. Sensitivity. Precision. Linearity. Resolution. Repeatability. Range.
Tolerance. Hysteresis
b) Differentiate between accuracy and precision.
Accuracy measures how close results are to the true or known value. Precision, on
the other hand, measures how close results are to one another.
c) Define i) Dead time ii) Dead Zone
1) Dead time the amount of time that lapses from the point at which the input
signal is specified and passes through the controlled system through to the output
signal being output.
2] Dead zones are low-oxygen, or hypoxic, areas in the world's oceans and lakes.
Because most organisms need oxygen to live, few organisms can survive in hypoxic
conditions
d) Define i) Range ii) Span
The difference between the lowest and highest values.
the distance from the end of the thumb to the end of the little finger of a spread
hand
e) Which transducers will you use for measurement of flow?
f) Name the different displacement measuring instrument.
Proximity sensors (to measure displacement) and accelerometers (to measure
acceleration) are the two most common types of measuring devices used in
machine protection systems for condition monitoring, fault detection, diagnostic,
and on-line (often real-time) control of large and complex machinery.
g) What are the applications of LVDT?
LVDT sensors are used by manufacturers across the industry spectrum, from
aerospace, automotive and construction to electronics, energy and environmental,
and are critical to the development of products of all sizes.
h) Which transducers will you use for measurement of force?
Strain transducers are used to measure deformations that have occurred due to
forces acting on an existing body
I) State different units for temperature measurement.
Celsius, Fahrenheit and Kelvin are the three common temperature scales.
Q.2 Attempt any Three.
a) Explain different sources of error in measurements and in measuring
instruments.
Variation of temperature, humidity, gravity, wind, refraction, magnetic declination
etc. are most common natural phenomena which may cause measurement errors.
If they are not properly observed while taking measurements, the results will be
incorrect. Example: Length error of tape or chain due to temperature change.
b) Describe the block diagram of generalized measurement system & various
elements.
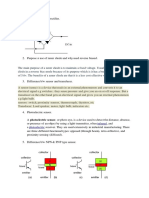
c) Explain construction and working of LVDT.
LVDT construction involves mounting a primary winding, P, and two secondary
windings, S1 and S2, on a cylindrical former. The secondary windings have the
same number of turns and are placed identically on either side of the primary
winding. Then, a movable soft iron core is placed inside the cylindrical former.
d) Differentiate between active and passive transducer.
The active transducer changes the energy without using the auxiliary power supply
whereas the passive transducer uses the exterior power supply for the conversion
of energy.
e) Explain Ionization Gauge.
The ionization gauge is a special type of instrument used for measuring very low
pressures in the range 10−10 to 1 mbar.
f) Explain construction and working of Bourdon tube pressure gauge.
The Bourdon gauge consists of a tube bent into a coil or an arc. As the pressure in
the tube increases, the coil unwinds. A pointer connected to the end of the tube
can be attached to a lever and a pointer calibrated to indicate pressure. A typical
50 mm diameter tube has a displacement of up to 4 mm.
g) Explain Liquid in glass thermometer
Liquid-in-glass thermometers measure the thermal expansion of a liquid, which is
placed in a solid container, on a length scale. The mercury thermometer is one
example of liquid thermometers. Alcohol is also used with this type of instrument.
The temperature range is −80 to +330 °C depending on the liquid.
You might also like
- Maintenance Manual Aritco7000 - 7000300en01 - LDocument36 pagesMaintenance Manual Aritco7000 - 7000300en01 - LSami Vehmas50% (2)
- Drive Error List - YaskawaDocument18 pagesDrive Error List - YaskawaKrittaphak Hacheyram79% (14)
- Earthing Transformer (ZNyn11) ZigZag Transformer Report SampleDocument3 pagesEarthing Transformer (ZNyn11) ZigZag Transformer Report SampleKanhiya Prasad0% (1)
- 3 Hours / 70 Marks: Mechanical Engineering Measurement (MEM) Course Title: Course Code:22443Document36 pages3 Hours / 70 Marks: Mechanical Engineering Measurement (MEM) Course Title: Course Code:22443ketanpawar322No ratings yet
- Ei 1301 Industrial Instrumentation-1Document11 pagesEi 1301 Industrial Instrumentation-1mounitads300% (1)
- Geotechnical Instruments in Structural Monitoring: Xiaoli DingDocument12 pagesGeotechnical Instruments in Structural Monitoring: Xiaoli DingJuan Carlos Gonzalez LNo ratings yet
- Instrumentation and Control AssignmentDocument11 pagesInstrumentation and Control AssignmentRuairi Mc AloranNo ratings yet
- 2MARKSDocument21 pages2MARKSmuthupecmec4908No ratings yet
- Unit 5Document29 pagesUnit 5rajamanickam sNo ratings yet
- All AssignmentDocument12 pagesAll AssignmentChala GetaNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Sensors and ActuatorsDocument115 pagesPresentation On Sensors and ActuatorschibuikeNo ratings yet
- Manual 2Document11 pagesManual 2Tambu GoodnessNo ratings yet
- TransducersDocument40 pagesTransducersFemi Prince100% (1)
- Tta Question PaperDocument7 pagesTta Question PaperDESI BRAHMNNo ratings yet
- Instrumentation LabDocument26 pagesInstrumentation LabVivek SivaramanNo ratings yet
- Pidc Questions BankDocument33 pagesPidc Questions Bank3004 Divya Dharshini. MNo ratings yet
- 2550 TemperaturaDocument2 pages2550 Temperaturapollux23No ratings yet
- Q@ 9 TransducersDocument39 pagesQ@ 9 TransducersKhayyam HusnainNo ratings yet
- Dimension Measurement-Displacement MeasurementDocument12 pagesDimension Measurement-Displacement MeasurementBakaali HuzaifaNo ratings yet
- Determination of Coefficient of Linear Expansion of A Metal RodDocument3 pagesDetermination of Coefficient of Linear Expansion of A Metal RodKhadeejaNo ratings yet
- TransducerDocument87 pagesTransducerBobeth TubigNo ratings yet
- Assignment Transducers - PaulDocument5 pagesAssignment Transducers - PaulPaul Niño LagareNo ratings yet
- SA QB Solved Unit 1-2Document26 pagesSA QB Solved Unit 1-2Kundan PednekarNo ratings yet
- Unit1-Measuremrnts and Transducers-1Document77 pagesUnit1-Measuremrnts and Transducers-1Pavan PataneNo ratings yet
- ABCQ Metrology HandbookDocument15 pagesABCQ Metrology HandbookAntonio Melgaço da SilvaNo ratings yet
- CFM PDFDocument4 pagesCFM PDFDilip PatelNo ratings yet
- Notes, Oct.26, 2023Document5 pagesNotes, Oct.26, 2023سيمو بشيريNo ratings yet
- Industrial Instrumentation - II Unit 1: 2 Marks & Question-AnswersDocument10 pagesIndustrial Instrumentation - II Unit 1: 2 Marks & Question-Answerslakshg11No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Applications of TransducersDocument24 pagesChapter 2 Applications of TransducersDevaki V Devi100% (1)
- SI 4 UnitDocument292 pagesSI 4 UnitRaagul SNo ratings yet
- Scribd Upload A Document Search Documents Explore Sign Up Log inDocument23 pagesScribd Upload A Document Search Documents Explore Sign Up Log inNayan ThakurNo ratings yet
- Sensor Technologies: Syed Khawar Hussain ShahDocument26 pagesSensor Technologies: Syed Khawar Hussain ShahM. RazaNo ratings yet
- The Thermistor Whose Resistance Increase by Increasing TemperatureDocument6 pagesThe Thermistor Whose Resistance Increase by Increasing Temperaturesai shiva100% (1)
- Shreyash Bhimanwar 111907050 Entc Experiment No. 1 Characterization of RTDDocument49 pagesShreyash Bhimanwar 111907050 Entc Experiment No. 1 Characterization of RTDshreyash100% (1)
- Conductivity Effect On The Capacitance Measurement of A Parallel-Plate Capacitive Sensor SystemDocument8 pagesConductivity Effect On The Capacitance Measurement of A Parallel-Plate Capacitive Sensor SystemKrisna SinghNo ratings yet
- TransducersDocument24 pagesTransducersSania NowshinNo ratings yet
- Saket Udar 18BEC0760: Definition: Measuring Devices Temperature, Displacement, Vibration EtcDocument6 pagesSaket Udar 18BEC0760: Definition: Measuring Devices Temperature, Displacement, Vibration EtcAlexzander PatelNo ratings yet
- TRANSDUCERDocument11 pagesTRANSDUCERLucks GonzalesNo ratings yet
- SENSOR and Signal Processing UnitDocument57 pagesSENSOR and Signal Processing UnitRohit Ghulanavar100% (1)
- MotorDocument10 pagesMotorbhasker pandeyNo ratings yet
- Sensors MCQs UNIT 1 To 5 For StudentsDocument29 pagesSensors MCQs UNIT 1 To 5 For StudentsMohit Singh100% (1)
- Physics of Sensors 23-24 - StudentsDocument63 pagesPhysics of Sensors 23-24 - Studentsommayekar19No ratings yet
- Characterization of An Electrochemical Pilot Plant Filterpress Reactor by Hydrodynamic and Mass Transport StudiesDocument12 pagesCharacterization of An Electrochemical Pilot Plant Filterpress Reactor by Hydrodynamic and Mass Transport StudiesSantiago Arias GalloNo ratings yet
- Emt 4103 Sensors and Transducers On 3rd June Lesson 3Document37 pagesEmt 4103 Sensors and Transducers On 3rd June Lesson 3SEAN WALLACENo ratings yet
- Chem101 Ho1Document12 pagesChem101 Ho1Jordan DingayanNo ratings yet
- Lab ManualDocument11 pagesLab ManualSujith SurapaneniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Flow & Temperture Sensors-1Document30 pagesChapter 3 Flow & Temperture Sensors-1alqahtaniabdullah271No ratings yet
- Title Page: Various Electrical TransducersDocument13 pagesTitle Page: Various Electrical TransducersKushal AvaiyaNo ratings yet
- BME MODULE-4 Mechanical MeasurementsDocument29 pagesBME MODULE-4 Mechanical Measurementsknowledge updatesNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1: Strain MeasurementDocument9 pagesExperiment 1: Strain MeasurementHoa LeNo ratings yet
- QB - Set 2 - Pe-Me 803aDocument8 pagesQB - Set 2 - Pe-Me 803abdrakshit420No ratings yet
- Ultrasonic Pulse VelocityDocument16 pagesUltrasonic Pulse VelocityShivamBose100% (1)
- Flow Measurement by Orifice Meter and by Ventury Meter BOMBAYDocument7 pagesFlow Measurement by Orifice Meter and by Ventury Meter BOMBAYCedric GallusNo ratings yet
- Sensor & Iot - Unit 2Document29 pagesSensor & Iot - Unit 2Biswa RocksNo ratings yet
- EEF264 Tutorial 2023Document3 pagesEEF264 Tutorial 2023nfornepNo ratings yet
- TRANSDUCERDocument14 pagesTRANSDUCERmicah micahNo ratings yet
- Unit - 2: Sensors and TransducersDocument66 pagesUnit - 2: Sensors and TransducersAkhil VarmaNo ratings yet
- PIDC - Unit IDocument46 pagesPIDC - Unit Ikumardhilip242No ratings yet
- Modern Sensors HandbookFrom EverandModern Sensors HandbookPavel RipkaRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Radio Control for Model Ships, Boats and AircraftFrom EverandRadio Control for Model Ships, Boats and AircraftRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Handbook of Mechanical and Materials EngineeringFrom EverandHandbook of Mechanical and Materials EngineeringRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- Iriset: इरिसेट आउट डोि ससगनसलिंग प्रयोगशाला इरिसेट / ओ डी एस - 43 Experiment No.: Ods - 43Document7 pagesIriset: इरिसेट आउट डोि ससगनसलिंग प्रयोगशाला इरिसेट / ओ डी एस - 43 Experiment No.: Ods - 43Anonymous 9kzuGaYNo ratings yet
- Torque Acting On Current Loops. Magnetic Dipole MomentDocument13 pagesTorque Acting On Current Loops. Magnetic Dipole MomentKrishna BansalNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual-Michelson Interferometer V.aug.2023Document24 pagesLab Manual-Michelson Interferometer V.aug.2023Sanjieth R.VNo ratings yet
- 1KHW002461 FOX615 Installation pc2Document100 pages1KHW002461 FOX615 Installation pc2LinarteHjsaavedraNo ratings yet
- Design and Development of A Fluxgate MagnetometerDocument5 pagesDesign and Development of A Fluxgate MagnetometerMilorad RadenovicNo ratings yet
- EM Wave TheoryDocument4 pagesEM Wave TheoryBlair RenceNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5-Capacitance and InductanceDocument24 pagesChapter 5-Capacitance and InductancePoni HenryNo ratings yet
- Bulletin 194E, 16 100 ADocument23 pagesBulletin 194E, 16 100 AissacnochebuenaNo ratings yet
- A Semi-Detailed Lesson Plan For General SciencesDocument2 pagesA Semi-Detailed Lesson Plan For General Sciencesmela.kanlapan100% (4)
- OlutionDocument2 pagesOlutionfaldin 1No ratings yet
- Mullard ThyratronsForIndustrialControl 1954Document62 pagesMullard ThyratronsForIndustrialControl 1954feriferiNo ratings yet
- Basic Components of A Power SystemDocument11 pagesBasic Components of A Power SystemKrishna KumarNo ratings yet
- Yakout2020 Article SpintronicsFutureTechnologyForDocument24 pagesYakout2020 Article SpintronicsFutureTechnologyForneha patelNo ratings yet
- Ryerson University: State Your Assumptions in Answering The QuestionDocument16 pagesRyerson University: State Your Assumptions in Answering The QuestionMuhammad hashimNo ratings yet
- Sound IXDocument35 pagesSound IXarpankrishna739No ratings yet
- Assignment No #1 (Transformer)Document2 pagesAssignment No #1 (Transformer)Muhammad ShahzaibNo ratings yet
- AAiT Introduction To Electro-PneumaticsDocument71 pagesAAiT Introduction To Electro-PneumaticsSamuel WozabNo ratings yet
- PT. Kwarta Pratama Teknik - Company Profile - Update Juni 2024Document31 pagesPT. Kwarta Pratama Teknik - Company Profile - Update Juni 2024zakianurwachidah100% (1)
- Power System By: Roel B. Calano: Problem 1Document10 pagesPower System By: Roel B. Calano: Problem 1John Lloyd SantosNo ratings yet
- Telemecanique LC1D09M7 DatasheetDocument3 pagesTelemecanique LC1D09M7 DatasheetFelix Bocanegra RuizNo ratings yet
- Pre-Labs: (EE-455) Electrical Power System ProtectionDocument4 pagesPre-Labs: (EE-455) Electrical Power System ProtectionJurair SaqibNo ratings yet
- ACSS HS285 - Data-Diameter - EqualDocument2 pagesACSS HS285 - Data-Diameter - Equalpoci11No ratings yet
- Worksheet Ray OpticsDocument4 pagesWorksheet Ray OpticsYug GandhiNo ratings yet
- Models Acdc Spiral Inductor Using ComsolDocument8 pagesModels Acdc Spiral Inductor Using Comsolbkmmizan100% (1)
- Physics Magnetic BottlesDocument6 pagesPhysics Magnetic BottlesAin ZahraNo ratings yet
- Lab Activity - Collect The Information On Components of Transmission LineDocument5 pagesLab Activity - Collect The Information On Components of Transmission LineTuhin SahaNo ratings yet
- Week 1: Introduction: NM NM Ev Ev E DT T P EDocument9 pagesWeek 1: Introduction: NM NM Ev Ev E DT T P EInstituto Centro de Desenvolvimento da GestãoNo ratings yet