Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Notes For SCH Reading
Notes For SCH Reading
Uploaded by
PMG Bhuswal ProjectCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- VITO VIANO+Wiring+DiagramsDocument264 pagesVITO VIANO+Wiring+DiagramsIuliusKing65% (37)
- Impianto Elettrico M139 Inglese - AmendedDocument64 pagesImpianto Elettrico M139 Inglese - Amendedaiigee100% (3)
- Airtrek Wiring ManualDocument228 pagesAirtrek Wiring ManualRick Avlonitis92% (12)
- Use of Mercedes Wiring DiagramsDocument3 pagesUse of Mercedes Wiring DiagramsJarek Janicki50% (2)
- Electronics Manual CNCDocument219 pagesElectronics Manual CNCVojkan Milenovic100% (4)
- Microprocessor & Assembly Language Lab ManualDocument49 pagesMicroprocessor & Assembly Language Lab ManualMAHMOUD CERAY100% (1)
- 81aa03 Er1210Document9 pages81aa03 Er1210Mahesh KumbharNo ratings yet
- How To Read Wiring Diagram EW - ADocument12 pagesHow To Read Wiring Diagram EW - AEnrique Emmanuel100% (1)
- 4 - Reading RTG Electrical CircuitDocument57 pages4 - Reading RTG Electrical Circuitmliugong100% (4)
- Oracle Error MessagesDocument952 pagesOracle Error MessagesrohitkchaubeNo ratings yet
- Ds PalmSecure SDK Software Development Kit (FINAL)Document3 pagesDs PalmSecure SDK Software Development Kit (FINAL)Irwan AsminanNo ratings yet
- Lanatory Notes On The Schematic DiagramDocument225 pagesLanatory Notes On The Schematic Diagramsantoshkumar777100% (1)
- Explanatory Notes On The Schematic DiagramDocument11 pagesExplanatory Notes On The Schematic DiagramGovindappa RamappaNo ratings yet
- 170 ADO 350 00 24 VDC - 32 Pt. Discrete Output Module BaseDocument14 pages170 ADO 350 00 24 VDC - 32 Pt. Discrete Output Module BaseLoekman AkeemNo ratings yet
- EIA321CDocument10 pagesEIA321CawemetalNo ratings yet
- Elektrisch Schema (1-7) PDFDocument18 pagesElektrisch Schema (1-7) PDFjhw van nistelrooyNo ratings yet
- 32 PFL 340477Document67 pages32 PFL 340477Anonymous Gj5yPUC2JNo ratings yet
- 00-02-001, Systems OverviewDocument21 pages00-02-001, Systems OverviewВалентин СелищевNo ratings yet
- 170 Adi 350 00Document14 pages170 Adi 350 00Gabriel ZorattiNo ratings yet
- Edn 0715Document14 pagesEdn 0715Adnan BeganovicNo ratings yet
- General Specifications: Model LHS5100, LHM5100 Standard Builder FunctionDocument8 pagesGeneral Specifications: Model LHS5100, LHM5100 Standard Builder Functionsarfaraz055No ratings yet
- DR-309 Manual enDocument21 pagesDR-309 Manual enYOUSSEF ABDELSALAMNo ratings yet
- General Information: Section 0Document12 pagesGeneral Information: Section 0Jeremy WaldnerNo ratings yet
- M2 (Mechatronics)Document21 pagesM2 (Mechatronics)Sarah J SinfuegoNo ratings yet
- H Series Serial DriverDocument176 pagesH Series Serial DriversunhuynhNo ratings yet
- Mascott DCI 2003 EN PDFDocument262 pagesMascott DCI 2003 EN PDFArash Shams75% (8)
- GS33J05H20 01enDocument2 pagesGS33J05H20 01enkjh346gmail.comNo ratings yet
- Radio Link Calculations: Til-TekDocument10 pagesRadio Link Calculations: Til-TekmadumitroaeiNo ratings yet
- NET Topology SFB52 eDocument13 pagesNET Topology SFB52 ekubikNo ratings yet
- Uenr1735uenr1735-04 SisDocument38 pagesUenr1735uenr1735-04 SisLuis Montana Camacho100% (2)
- Plugin-DCS Write UpDocument16 pagesPlugin-DCS Write Upnainesh goteNo ratings yet
- ISeries Instruments Addendum 104633-00 16aug2012Document98 pagesISeries Instruments Addendum 104633-00 16aug2012Thanh Luan NguyenNo ratings yet
- Lab 3Document2 pagesLab 3drfaizalNo ratings yet
- 5 Pin Interface, Version 2.9, 01.02.2010Document10 pages5 Pin Interface, Version 2.9, 01.02.2010msalem73No ratings yet
- Multipurpose Programming CableDocument7 pagesMultipurpose Programming CableJozo ĆurčićNo ratings yet
- Application Data: Model 353 Controllers Extending I/O Capability With EthernetDocument9 pagesApplication Data: Model 353 Controllers Extending I/O Capability With EthernetÁgost VitaNo ratings yet
- RAM ROM and PldsDocument37 pagesRAM ROM and PldsRaj Kumar YadavNo ratings yet
- Sinumerik Basic FunctionsFB10306enDocument2,025 pagesSinumerik Basic FunctionsFB10306enkeizerpeterNo ratings yet
- Dn0127056 3 en Global PDF Online A4Document90 pagesDn0127056 3 en Global PDF Online A4Bhaskar KumarNo ratings yet
- Ser'S Manual: Programmable ControllersDocument24 pagesSer'S Manual: Programmable Controllersdiego sNo ratings yet
- Simatic S5 318-3UA11 Central Controller Interface Module: ManualDocument37 pagesSimatic S5 318-3UA11 Central Controller Interface Module: ManualAutomacao16No ratings yet
- Apssecrs: Installation and Reference GuideDocument30 pagesApssecrs: Installation and Reference GuideErwin HernandezNo ratings yet
- Controlwave Efm (Electronic Flow Meter) : Instruction ManualDocument10 pagesControlwave Efm (Electronic Flow Meter) : Instruction ManualtabletdrummondenergyNo ratings yet
- Analogue Module AK 4014 en Description U - Erhardt+LeimerDocument6 pagesAnalogue Module AK 4014 en Description U - Erhardt+LeimerDs KuzmenkoNo ratings yet
- Interfacing With The ISA BusDocument12 pagesInterfacing With The ISA BusseyfiNo ratings yet
- Universal Digital Repeater DR-109: Technical DocumentationDocument16 pagesUniversal Digital Repeater DR-109: Technical DocumentationSergeyNo ratings yet
- General Specifications: Model VP6H4150 Output To External Recorder PackageDocument2 pagesGeneral Specifications: Model VP6H4150 Output To External Recorder PackageDhirender DagarNo ratings yet
- GCB Manual ADocument11 pagesGCB Manual AneslouNo ratings yet
- Ethernet Communication ModuleDocument11 pagesEthernet Communication Modulemuneeb.irfan9873No ratings yet
- GMR35 Software AdaptionDocument4 pagesGMR35 Software AdaptionMauricio Schmidt MunizNo ratings yet
- 07 KT 97Document54 pages07 KT 97max_ingNo ratings yet
- Tek Tr502 - SM Tracking GenDocument69 pagesTek Tr502 - SM Tracking GenayohaiNo ratings yet
- L4 EaDocument7 pagesL4 EaIoanaNicoletaNo ratings yet
- QL ServiceManualDocument98 pagesQL ServiceManualOscar Arthur KoepkeNo ratings yet
- A29040B Series: 512K X 8 Bit CMOS 5.0 Volt-Only, Preliminary Uniform Sector Flash MemoryDocument29 pagesA29040B Series: 512K X 8 Bit CMOS 5.0 Volt-Only, Preliminary Uniform Sector Flash MemoryMirta PurkNo ratings yet
- CompTIA A+ CertMike: Prepare. Practice. Pass the Test! Get Certified!: Core 1 Exam 220-1101From EverandCompTIA A+ CertMike: Prepare. Practice. Pass the Test! Get Certified!: Core 1 Exam 220-1101No ratings yet
- PLC: Programmable Logic Controller – Arktika.: EXPERIMENTAL PRODUCT BASED ON CPLD.From EverandPLC: Programmable Logic Controller – Arktika.: EXPERIMENTAL PRODUCT BASED ON CPLD.No ratings yet
- Radio Shack TRS-80 Expansion Interface: Operator's Manual Catalog Numbers: 26-1140, 26-1141, 26-1142From EverandRadio Shack TRS-80 Expansion Interface: Operator's Manual Catalog Numbers: 26-1140, 26-1141, 26-1142No ratings yet
- High-Performance D/A-Converters: Application to Digital TransceiversFrom EverandHigh-Performance D/A-Converters: Application to Digital TransceiversNo ratings yet
- TGE 3668 - Rev-01 - Write-Up of Generator Primary Water SystemDocument11 pagesTGE 3668 - Rev-01 - Write-Up of Generator Primary Water SystemPMG Bhuswal ProjectNo ratings yet
- National Smart Grid Mission OMDocument12 pagesNational Smart Grid Mission OMPMG Bhuswal ProjectNo ratings yet
- Bharati Krsna Tirthaji, V. S. Agrawala (Editor) - Vedic Mathematics - Sixteen Simple Mathematical Formulae From The Vedas-Motilal Books (1970)Document424 pagesBharati Krsna Tirthaji, V. S. Agrawala (Editor) - Vedic Mathematics - Sixteen Simple Mathematical Formulae From The Vedas-Motilal Books (1970)PMG Bhuswal ProjectNo ratings yet
- Commissioning of DAVRDocument70 pagesCommissioning of DAVRPMG Bhuswal Project100% (1)
- Smart Grid Kumud WadhwaDocument52 pagesSmart Grid Kumud WadhwaPMG Bhuswal ProjectNo ratings yet
- DocScanner Jul 14, 2023 4-53 PM-5Document1 pageDocScanner Jul 14, 2023 4-53 PM-5PMG Bhuswal ProjectNo ratings yet
- SyllabusDocument1 pageSyllabusPMG Bhuswal ProjectNo ratings yet
- Bhusawal 1X660 CO 106 R03 PDFDocument1 pageBhusawal 1X660 CO 106 R03 PDFPMG Bhuswal ProjectNo ratings yet
- RCD Presentation On MERC MYT Regulations, 2019Document18 pagesRCD Presentation On MERC MYT Regulations, 2019PMG Bhuswal ProjectNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument2 pagesUntitledPMG Bhuswal ProjectNo ratings yet
- Bhusawal HPH Rev02 PDFDocument26 pagesBhusawal HPH Rev02 PDFPMG Bhuswal ProjectNo ratings yet
- MCQ On Power Systems 5eea6a0f39140f30f369e734 PDFDocument20 pagesMCQ On Power Systems 5eea6a0f39140f30f369e734 PDFPMG Bhuswal ProjectNo ratings yet
- Pre CommisioningDocument7 pagesPre CommisioningPMG Bhuswal ProjectNo ratings yet
- Bhusawal 1X660 DMS 110 R01Document1 pageBhusawal 1X660 DMS 110 R01PMG Bhuswal ProjectNo ratings yet
- CRS - SLD-Turbine Valve MCC - 6KB-R02Document2 pagesCRS - SLD-Turbine Valve MCC - 6KB-R02PMG Bhuswal ProjectNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument8 pagesUntitledPMG Bhuswal ProjectNo ratings yet
- Exe Sum Eng Tangedco 251121Document10 pagesExe Sum Eng Tangedco 251121PMG Bhuswal ProjectNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument1 pageUntitledPMG Bhuswal ProjectNo ratings yet
- Single Line Diagram of Generator Transformer Unit#4 Bay: 400KV Bus I 400KV Bus IIDocument7 pagesSingle Line Diagram of Generator Transformer Unit#4 Bay: 400KV Bus I 400KV Bus IIPMG Bhuswal ProjectNo ratings yet
- English Alphabets Reading Writing Worksheets PDFSevaDocument10 pagesEnglish Alphabets Reading Writing Worksheets PDFSevaPMG Bhuswal ProjectNo ratings yet
- Field and Stator Ground Fault Protection Modules: Grid SolutionsDocument64 pagesField and Stator Ground Fault Protection Modules: Grid SolutionsPMG Bhuswal ProjectNo ratings yet
- Prof. Ch. SAI BABU: TopicDocument79 pagesProf. Ch. SAI BABU: TopicPMG Bhuswal ProjectNo ratings yet
- INTCV385 - HV and MV Switchgear (CB, CT, CVT, DC and SA) Operaion, Maintenance - L2 - v1Document3 pagesINTCV385 - HV and MV Switchgear (CB, CT, CVT, DC and SA) Operaion, Maintenance - L2 - v1PMG Bhuswal ProjectNo ratings yet
- Data Base Management SystemDocument59 pagesData Base Management SystemAnurag GoelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - C Programming LanguageDocument26 pagesChapter 2 - C Programming LanguageJobet Reyes PalomaNo ratings yet
- BSC Ist Year Programming in CDocument219 pagesBSC Ist Year Programming in CSAIPRASAD VEMULANo ratings yet
- CC102 Week-4 Lesson-Introduction To Java ProgrammingDocument28 pagesCC102 Week-4 Lesson-Introduction To Java ProgrammingTred MoonNo ratings yet
- My System Analysis Lecture Notes-1Document13 pagesMy System Analysis Lecture Notes-1Zainab Baba mallamNo ratings yet
- Understanding Operating Systems Fifth EditionDocument70 pagesUnderstanding Operating Systems Fifth EditionWIPEOUT79No ratings yet
- Part A - Micro-Project Proposal: Assembly Language Program To Print StringDocument7 pagesPart A - Micro-Project Proposal: Assembly Language Program To Print StringRahul B. Fere0% (1)
- Unit 3 - Operating System - WWW - Rgpvnotes.in PDFDocument24 pagesUnit 3 - Operating System - WWW - Rgpvnotes.in PDFPrakrti MankarNo ratings yet
- Module Week 1 IctDocument10 pagesModule Week 1 IctCharleen RomeroNo ratings yet
- 3259 - Basics of CHN LabDocument67 pages3259 - Basics of CHN LabArun JyothiNo ratings yet
- History & Development of JavaDocument15 pagesHistory & Development of JavaShrey NagpalNo ratings yet
- B.tech - CSE - CPS - 2020 - 2021 - Curriculum and Syllabus Without SLODocument250 pagesB.tech - CSE - CPS - 2020 - 2021 - Curriculum and Syllabus Without SLOSai CharanNo ratings yet
- Lab VIEWDocument70 pagesLab VIEWMihaela EnacheNo ratings yet
- Cempra3 Process Control 2022Document30 pagesCempra3 Process Control 2022AndrewNo ratings yet
- Manual of Information Technology Audit: Office of The Comptroller & Auditor General of IndiaDocument28 pagesManual of Information Technology Audit: Office of The Comptroller & Auditor General of IndiaMohit TewariNo ratings yet
- COMPUTE!'s Beginner's Guide To Assembly Language On The TI-99/4ADocument272 pagesCOMPUTE!'s Beginner's Guide To Assembly Language On The TI-99/4Aremow100% (1)
- Principles of Information Systems, Tenth Edition: Software: Systems and Application SoftwareDocument59 pagesPrinciples of Information Systems, Tenth Edition: Software: Systems and Application Softwarerian takaNo ratings yet
- 3.4.2 Virtual Machine PDFDocument4 pages3.4.2 Virtual Machine PDFBlessed Endibye KanyembaNo ratings yet
- Can Bus. Receiving Data On Fuel Level From The Can Bus (281009 v3)Document9 pagesCan Bus. Receiving Data On Fuel Level From The Can Bus (281009 v3)Wilfredo A MolinaNo ratings yet
- PTU Lab PracticalsDocument67 pagesPTU Lab PracticalskartikavasthiNo ratings yet
- ITCT 2023 Study MaterialDocument54 pagesITCT 2023 Study MaterialchandanNo ratings yet
- Fis 533020e PDFDocument17 pagesFis 533020e PDFmarusea2009No ratings yet
- Computing BasicDocument55 pagesComputing BasicCandyNo ratings yet
- 144 BCA Honors MAJORDocument57 pages144 BCA Honors MAJORswamyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 0 - CS50's Introduction To Programming With PythonDocument8 pagesLecture 0 - CS50's Introduction To Programming With Pythonmonish anandNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced LevelDocument16 pagesCambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced LevelAl-Sami MashrafeeNo ratings yet
- Seisan DocumentDocument379 pagesSeisan DocumentpachernyangyuenNo ratings yet
Notes For SCH Reading
Notes For SCH Reading
Uploaded by
PMG Bhuswal ProjectOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Notes For SCH Reading
Notes For SCH Reading
Uploaded by
PMG Bhuswal ProjectCopyright:
Available Formats
Components other than modules such as switches, MCBs,relays, transformers,
etc., have designations and specification of their own. The brief specification
for ordering these components can be obtained from the list of components
from the schematic diagram. (/YL001..).
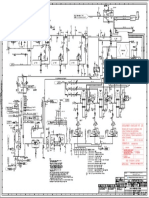
Explanatory Notes on the Schematic Diagram
The schematic diagram shows all essential functions of the hardware and
software and all electrical connections of the components, including the
interconnections for the given excitation system. For purposes of clarity and for
practical use, all internal module information has been deliberately omitted from
the schematic diagram. Such details, if needed, can be obtained from the data
sheets for the modules in question. Plant-specific hardware and software
settings can be obtained from the Test/ Commissioning report.
The schematic diagram comprises the following sections:
-- List of symbols used /YA006,/YA007
-- Cable list /YD003...
-- Views of the swing frame /YD101,../YD115
-- Lists of components /YL001...
-- Block diagrams for the system /YU101
hardware
-- Block diagrams for the system /YU105..
software
-- Lists of connections AU010,AU020, ..
-- Measurement circuits in general CE...
-- Hardware and software for the DE...
regulator channels
-- Hardware and software for the
alarm circuits/operator commands
and operation messages EG...
-- Hardware and software for
monitoring the electronics EW...
-- Hardware and software for
protection of the excitation EY...
-- Hardware and software, field circuit-
breaker and field flashing circuit GS...
EDN 99-655-162 Rev.00 Page 3 of 9
-- Hardware and software for power
supply in general GW...
-- Hardware and software for the
excitation monitoring and for
the converters, including converter
controls GX...
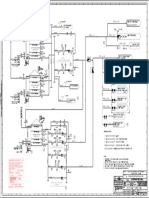
The view of the swing frame in schematic sheet No./YD101 shows not only
the names of the modules but also, usually, a cross-reference to the page of the
schematic diagram on which the pertinent connections for the module are to be
found. The UN 0662 modules for the (freely programmable) binary controls
(AB21 ... AB57) are an exception here. These are equipped but not specifically
assigned to given pages of the diagram. For that reason, no cross-reference is
made to the schematic diagram for these modules. Locations where no entry is
made for the type designation of module but where a cross-reference to the
schematic diagram appears are locations left open for standard optional
equipment.
The organization of the schematic diagram, the designations for signals, and
cross-references to the schematic diagram all conform to the Kraftwerks-
Kennzeichen-System (Power Plant Identification Code), KKS. As seen from the
examples below, every signal has a signal designation and a diagram cross-
reference. The signal designation gives the signal a specific and unambiguous
name made up of the name of the functional group (e.g., GS020) and the signal
code (e.g., XU12). The cross-reference to the diagram indicates the page in the
schematic diagram on which the associated signal source, or sink, can be
found. The signals are also described in plain text where that is helpful.
This plain text provides the user with information on the functional
characteristics of the signal in question (it is not an identification of the signal).
Different text can be used to designate the same signal at the output and the
input. There are often different texts at the signal branching points as well, to
explain their specific functions at the signal sinks.
EDN 99-655-162 Rev.00 Page 4 of 9
Signal output from the binary Controls
(1) Schematic diagram number
For identification, filing, and reordering the set of schematic diagrams
pertinent to this installation
(2) Name of the functional group
All the components and functioning parts shown on the given page of the
Schematic Diagram are functional components of this group. The listing
for a "functional group" can be comprised of one page or several pages.
(3) Page Number
The pages for a given functional group are numbered in ascending order,
starting with /YS.... Sheets showing functions of the binary controls start
with /YS5.. .
(4) Designation of Location
Designation of the physical location common to the components or
connections shown on the Schematic Diagram page. Example "AB":
Swing frame A, Tier B.
EDN 99-655-162 Rev.00 Page 5 of 9
(5) Assignment of connection for the signal
Together with (4) above, identifies the plug-in location and connection
(pin) for the signal (inputs at the left, outputs at the right on the schematic
diagram). In the present example, "AB-X49:2b27" means:
Tier AB, location 49, 2nd half of plug (lower position), pin row ":b" (or "a"
or "c"), Pin No. 27.
NOTE:-For input or output signals generated or used internally (in the swing
frame) this entry is the full identification of the hardware employed.
Detailed information on these standard interfaces can be obtained from
Data Sheet. (UN 0662).
Generally, the entry for this hardware assignment is needed only for the
factory tests. Hardware connections from pin to pin within a tier are made
with WIRE-WRAP wires and identified with a "w". Connections between
the tiers (without the "w") are via 9- or 21-conductor system cables, some
of which are plugged onto the same pins (refer to the Cable List,
Schematic Diagram /YD003).
(6) Processing priority
with the 1st priority ("1") functions are processed at intervals of 20 ms.
Functions with the 2nd and 3rd priorities are Processed in the processor
at programmable multiples of this 20 ms interval.
(7) Internal address
The value of the signal (for binary signals: the status) is stored under this
address (RAM). This information is needed to program the function and
for functional analysis via the Micro-Terminal.
(8) Output address to UN 0665 (without an "Assignment of
Connection")
The appropriate LED on a UN 0665 signaling unit responds whenever
the signal output is set at logical "1". In the example "F74":
LED 16 (= HEX F) of the UN 0665 display unit with the "house address"
HEX 740. This information is needed to program the function.
(9) Output address, binary or analog (with an "Assignment of
Connection")
This information defines the software address for the output, which
depends on the "house address" selected with the pin number on the
input/output module ("Assignment of Connection"). In the example "35E":
Unit 3 (= Output 4, refer to Data Sheet of UN 0662) of the input/output
module with "house address" HEX 5E0. This information is needed to
program the function.
(10) KKS designation for the signal
This consists of the functional group name (e.g., GS020) and the signal
code (e.g., XU12). For output signals, the functional group name is
normally identical to the designation in the page heading (2). There is a
EDN 99-655-162 Rev.00 Page 6 of 9
different signal code for each signal within any given functional group.
Naturally, the outputs for signal branching (as in the present example)
have identical signal codes.
(11) Signal cross-reference
Designation of the sheet for the signal sink
(12) Plain text
Optional description of the function of the signal.
EDN 99-655-162 Rev.00 Page 7 of 9
Signal Input for the Binary Controls (Example):
(1) Plain text
Optional description of the origin and signal meanings.
(2) KKS signal designation.
Consists of the name of the functional group which the signal is coming
from and the signal name.
(3) Signal cross-reference
Designation of the sheet for the signal sources.
(4) Input address, binary or analog (with an "Assignment of
Connection")
This information defines the software address for the input, which
depends on the” house address" selected with the pin number on the
input/output module. In the example "02E": Unit 0 (= Input 1, refer to
Data Sheet of UN 0662) of the UN 0662 input/output module with
"house address" HEX 2E0. This information is needed to program the
function and for a functional analysis via the Micro-Terminal.
(5) Internal address
The same address number as the signal source. Used to program the
function and for a functional analysis via the Micro-Terminal.
EDN 99-655-162 Rev.00 Page 8 of 9
(6) Input address, binary or analog (without an "Assignment of
Connection")
This input (address) is already being used at another location (Page).
(The hardware assigned can be found there).
Direct hardware signals on modules (Example):
(1) Location of the module
Together with the designation of location in the page heading (in this
example, "AA"), this tells where the module is placed (In this example,
"AA-29" means swing frame A, Tier A, Location 29).
(2) WIRE-WRAP Connection
The connections marked with a "w" are WIRE-WRAP connections. All
connections in Tiers AA, AB without a "w" are connections made via
system cables (refer to the Cable List, Schematic Diagram /YD003).
---------------- * * * ---------------
EDN 99-655-162 Rev.00 Page 9 of 9
You might also like
- VITO VIANO+Wiring+DiagramsDocument264 pagesVITO VIANO+Wiring+DiagramsIuliusKing65% (37)
- Impianto Elettrico M139 Inglese - AmendedDocument64 pagesImpianto Elettrico M139 Inglese - Amendedaiigee100% (3)
- Airtrek Wiring ManualDocument228 pagesAirtrek Wiring ManualRick Avlonitis92% (12)
- Use of Mercedes Wiring DiagramsDocument3 pagesUse of Mercedes Wiring DiagramsJarek Janicki50% (2)
- Electronics Manual CNCDocument219 pagesElectronics Manual CNCVojkan Milenovic100% (4)
- Microprocessor & Assembly Language Lab ManualDocument49 pagesMicroprocessor & Assembly Language Lab ManualMAHMOUD CERAY100% (1)
- 81aa03 Er1210Document9 pages81aa03 Er1210Mahesh KumbharNo ratings yet
- How To Read Wiring Diagram EW - ADocument12 pagesHow To Read Wiring Diagram EW - AEnrique Emmanuel100% (1)
- 4 - Reading RTG Electrical CircuitDocument57 pages4 - Reading RTG Electrical Circuitmliugong100% (4)
- Oracle Error MessagesDocument952 pagesOracle Error MessagesrohitkchaubeNo ratings yet
- Ds PalmSecure SDK Software Development Kit (FINAL)Document3 pagesDs PalmSecure SDK Software Development Kit (FINAL)Irwan AsminanNo ratings yet
- Lanatory Notes On The Schematic DiagramDocument225 pagesLanatory Notes On The Schematic Diagramsantoshkumar777100% (1)
- Explanatory Notes On The Schematic DiagramDocument11 pagesExplanatory Notes On The Schematic DiagramGovindappa RamappaNo ratings yet
- 170 ADO 350 00 24 VDC - 32 Pt. Discrete Output Module BaseDocument14 pages170 ADO 350 00 24 VDC - 32 Pt. Discrete Output Module BaseLoekman AkeemNo ratings yet
- EIA321CDocument10 pagesEIA321CawemetalNo ratings yet
- Elektrisch Schema (1-7) PDFDocument18 pagesElektrisch Schema (1-7) PDFjhw van nistelrooyNo ratings yet
- 32 PFL 340477Document67 pages32 PFL 340477Anonymous Gj5yPUC2JNo ratings yet
- 00-02-001, Systems OverviewDocument21 pages00-02-001, Systems OverviewВалентин СелищевNo ratings yet
- 170 Adi 350 00Document14 pages170 Adi 350 00Gabriel ZorattiNo ratings yet
- Edn 0715Document14 pagesEdn 0715Adnan BeganovicNo ratings yet
- General Specifications: Model LHS5100, LHM5100 Standard Builder FunctionDocument8 pagesGeneral Specifications: Model LHS5100, LHM5100 Standard Builder Functionsarfaraz055No ratings yet
- DR-309 Manual enDocument21 pagesDR-309 Manual enYOUSSEF ABDELSALAMNo ratings yet
- General Information: Section 0Document12 pagesGeneral Information: Section 0Jeremy WaldnerNo ratings yet
- M2 (Mechatronics)Document21 pagesM2 (Mechatronics)Sarah J SinfuegoNo ratings yet
- H Series Serial DriverDocument176 pagesH Series Serial DriversunhuynhNo ratings yet
- Mascott DCI 2003 EN PDFDocument262 pagesMascott DCI 2003 EN PDFArash Shams75% (8)
- GS33J05H20 01enDocument2 pagesGS33J05H20 01enkjh346gmail.comNo ratings yet
- Radio Link Calculations: Til-TekDocument10 pagesRadio Link Calculations: Til-TekmadumitroaeiNo ratings yet
- NET Topology SFB52 eDocument13 pagesNET Topology SFB52 ekubikNo ratings yet
- Uenr1735uenr1735-04 SisDocument38 pagesUenr1735uenr1735-04 SisLuis Montana Camacho100% (2)
- Plugin-DCS Write UpDocument16 pagesPlugin-DCS Write Upnainesh goteNo ratings yet
- ISeries Instruments Addendum 104633-00 16aug2012Document98 pagesISeries Instruments Addendum 104633-00 16aug2012Thanh Luan NguyenNo ratings yet
- Lab 3Document2 pagesLab 3drfaizalNo ratings yet
- 5 Pin Interface, Version 2.9, 01.02.2010Document10 pages5 Pin Interface, Version 2.9, 01.02.2010msalem73No ratings yet
- Multipurpose Programming CableDocument7 pagesMultipurpose Programming CableJozo ĆurčićNo ratings yet
- Application Data: Model 353 Controllers Extending I/O Capability With EthernetDocument9 pagesApplication Data: Model 353 Controllers Extending I/O Capability With EthernetÁgost VitaNo ratings yet
- RAM ROM and PldsDocument37 pagesRAM ROM and PldsRaj Kumar YadavNo ratings yet
- Sinumerik Basic FunctionsFB10306enDocument2,025 pagesSinumerik Basic FunctionsFB10306enkeizerpeterNo ratings yet
- Dn0127056 3 en Global PDF Online A4Document90 pagesDn0127056 3 en Global PDF Online A4Bhaskar KumarNo ratings yet
- Ser'S Manual: Programmable ControllersDocument24 pagesSer'S Manual: Programmable Controllersdiego sNo ratings yet
- Simatic S5 318-3UA11 Central Controller Interface Module: ManualDocument37 pagesSimatic S5 318-3UA11 Central Controller Interface Module: ManualAutomacao16No ratings yet
- Apssecrs: Installation and Reference GuideDocument30 pagesApssecrs: Installation and Reference GuideErwin HernandezNo ratings yet
- Controlwave Efm (Electronic Flow Meter) : Instruction ManualDocument10 pagesControlwave Efm (Electronic Flow Meter) : Instruction ManualtabletdrummondenergyNo ratings yet
- Analogue Module AK 4014 en Description U - Erhardt+LeimerDocument6 pagesAnalogue Module AK 4014 en Description U - Erhardt+LeimerDs KuzmenkoNo ratings yet
- Interfacing With The ISA BusDocument12 pagesInterfacing With The ISA BusseyfiNo ratings yet
- Universal Digital Repeater DR-109: Technical DocumentationDocument16 pagesUniversal Digital Repeater DR-109: Technical DocumentationSergeyNo ratings yet
- General Specifications: Model VP6H4150 Output To External Recorder PackageDocument2 pagesGeneral Specifications: Model VP6H4150 Output To External Recorder PackageDhirender DagarNo ratings yet
- GCB Manual ADocument11 pagesGCB Manual AneslouNo ratings yet
- Ethernet Communication ModuleDocument11 pagesEthernet Communication Modulemuneeb.irfan9873No ratings yet
- GMR35 Software AdaptionDocument4 pagesGMR35 Software AdaptionMauricio Schmidt MunizNo ratings yet
- 07 KT 97Document54 pages07 KT 97max_ingNo ratings yet
- Tek Tr502 - SM Tracking GenDocument69 pagesTek Tr502 - SM Tracking GenayohaiNo ratings yet
- L4 EaDocument7 pagesL4 EaIoanaNicoletaNo ratings yet
- QL ServiceManualDocument98 pagesQL ServiceManualOscar Arthur KoepkeNo ratings yet
- A29040B Series: 512K X 8 Bit CMOS 5.0 Volt-Only, Preliminary Uniform Sector Flash MemoryDocument29 pagesA29040B Series: 512K X 8 Bit CMOS 5.0 Volt-Only, Preliminary Uniform Sector Flash MemoryMirta PurkNo ratings yet
- CompTIA A+ CertMike: Prepare. Practice. Pass the Test! Get Certified!: Core 1 Exam 220-1101From EverandCompTIA A+ CertMike: Prepare. Practice. Pass the Test! Get Certified!: Core 1 Exam 220-1101No ratings yet
- PLC: Programmable Logic Controller – Arktika.: EXPERIMENTAL PRODUCT BASED ON CPLD.From EverandPLC: Programmable Logic Controller – Arktika.: EXPERIMENTAL PRODUCT BASED ON CPLD.No ratings yet
- Radio Shack TRS-80 Expansion Interface: Operator's Manual Catalog Numbers: 26-1140, 26-1141, 26-1142From EverandRadio Shack TRS-80 Expansion Interface: Operator's Manual Catalog Numbers: 26-1140, 26-1141, 26-1142No ratings yet
- High-Performance D/A-Converters: Application to Digital TransceiversFrom EverandHigh-Performance D/A-Converters: Application to Digital TransceiversNo ratings yet
- TGE 3668 - Rev-01 - Write-Up of Generator Primary Water SystemDocument11 pagesTGE 3668 - Rev-01 - Write-Up of Generator Primary Water SystemPMG Bhuswal ProjectNo ratings yet
- National Smart Grid Mission OMDocument12 pagesNational Smart Grid Mission OMPMG Bhuswal ProjectNo ratings yet
- Bharati Krsna Tirthaji, V. S. Agrawala (Editor) - Vedic Mathematics - Sixteen Simple Mathematical Formulae From The Vedas-Motilal Books (1970)Document424 pagesBharati Krsna Tirthaji, V. S. Agrawala (Editor) - Vedic Mathematics - Sixteen Simple Mathematical Formulae From The Vedas-Motilal Books (1970)PMG Bhuswal ProjectNo ratings yet
- Commissioning of DAVRDocument70 pagesCommissioning of DAVRPMG Bhuswal Project100% (1)
- Smart Grid Kumud WadhwaDocument52 pagesSmart Grid Kumud WadhwaPMG Bhuswal ProjectNo ratings yet
- DocScanner Jul 14, 2023 4-53 PM-5Document1 pageDocScanner Jul 14, 2023 4-53 PM-5PMG Bhuswal ProjectNo ratings yet
- SyllabusDocument1 pageSyllabusPMG Bhuswal ProjectNo ratings yet
- Bhusawal 1X660 CO 106 R03 PDFDocument1 pageBhusawal 1X660 CO 106 R03 PDFPMG Bhuswal ProjectNo ratings yet
- RCD Presentation On MERC MYT Regulations, 2019Document18 pagesRCD Presentation On MERC MYT Regulations, 2019PMG Bhuswal ProjectNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument2 pagesUntitledPMG Bhuswal ProjectNo ratings yet
- Bhusawal HPH Rev02 PDFDocument26 pagesBhusawal HPH Rev02 PDFPMG Bhuswal ProjectNo ratings yet
- MCQ On Power Systems 5eea6a0f39140f30f369e734 PDFDocument20 pagesMCQ On Power Systems 5eea6a0f39140f30f369e734 PDFPMG Bhuswal ProjectNo ratings yet
- Pre CommisioningDocument7 pagesPre CommisioningPMG Bhuswal ProjectNo ratings yet
- Bhusawal 1X660 DMS 110 R01Document1 pageBhusawal 1X660 DMS 110 R01PMG Bhuswal ProjectNo ratings yet
- CRS - SLD-Turbine Valve MCC - 6KB-R02Document2 pagesCRS - SLD-Turbine Valve MCC - 6KB-R02PMG Bhuswal ProjectNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument8 pagesUntitledPMG Bhuswal ProjectNo ratings yet
- Exe Sum Eng Tangedco 251121Document10 pagesExe Sum Eng Tangedco 251121PMG Bhuswal ProjectNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument1 pageUntitledPMG Bhuswal ProjectNo ratings yet
- Single Line Diagram of Generator Transformer Unit#4 Bay: 400KV Bus I 400KV Bus IIDocument7 pagesSingle Line Diagram of Generator Transformer Unit#4 Bay: 400KV Bus I 400KV Bus IIPMG Bhuswal ProjectNo ratings yet
- English Alphabets Reading Writing Worksheets PDFSevaDocument10 pagesEnglish Alphabets Reading Writing Worksheets PDFSevaPMG Bhuswal ProjectNo ratings yet
- Field and Stator Ground Fault Protection Modules: Grid SolutionsDocument64 pagesField and Stator Ground Fault Protection Modules: Grid SolutionsPMG Bhuswal ProjectNo ratings yet
- Prof. Ch. SAI BABU: TopicDocument79 pagesProf. Ch. SAI BABU: TopicPMG Bhuswal ProjectNo ratings yet
- INTCV385 - HV and MV Switchgear (CB, CT, CVT, DC and SA) Operaion, Maintenance - L2 - v1Document3 pagesINTCV385 - HV and MV Switchgear (CB, CT, CVT, DC and SA) Operaion, Maintenance - L2 - v1PMG Bhuswal ProjectNo ratings yet
- Data Base Management SystemDocument59 pagesData Base Management SystemAnurag GoelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - C Programming LanguageDocument26 pagesChapter 2 - C Programming LanguageJobet Reyes PalomaNo ratings yet
- BSC Ist Year Programming in CDocument219 pagesBSC Ist Year Programming in CSAIPRASAD VEMULANo ratings yet
- CC102 Week-4 Lesson-Introduction To Java ProgrammingDocument28 pagesCC102 Week-4 Lesson-Introduction To Java ProgrammingTred MoonNo ratings yet
- My System Analysis Lecture Notes-1Document13 pagesMy System Analysis Lecture Notes-1Zainab Baba mallamNo ratings yet
- Understanding Operating Systems Fifth EditionDocument70 pagesUnderstanding Operating Systems Fifth EditionWIPEOUT79No ratings yet
- Part A - Micro-Project Proposal: Assembly Language Program To Print StringDocument7 pagesPart A - Micro-Project Proposal: Assembly Language Program To Print StringRahul B. Fere0% (1)
- Unit 3 - Operating System - WWW - Rgpvnotes.in PDFDocument24 pagesUnit 3 - Operating System - WWW - Rgpvnotes.in PDFPrakrti MankarNo ratings yet
- Module Week 1 IctDocument10 pagesModule Week 1 IctCharleen RomeroNo ratings yet
- 3259 - Basics of CHN LabDocument67 pages3259 - Basics of CHN LabArun JyothiNo ratings yet
- History & Development of JavaDocument15 pagesHistory & Development of JavaShrey NagpalNo ratings yet
- B.tech - CSE - CPS - 2020 - 2021 - Curriculum and Syllabus Without SLODocument250 pagesB.tech - CSE - CPS - 2020 - 2021 - Curriculum and Syllabus Without SLOSai CharanNo ratings yet
- Lab VIEWDocument70 pagesLab VIEWMihaela EnacheNo ratings yet
- Cempra3 Process Control 2022Document30 pagesCempra3 Process Control 2022AndrewNo ratings yet
- Manual of Information Technology Audit: Office of The Comptroller & Auditor General of IndiaDocument28 pagesManual of Information Technology Audit: Office of The Comptroller & Auditor General of IndiaMohit TewariNo ratings yet
- COMPUTE!'s Beginner's Guide To Assembly Language On The TI-99/4ADocument272 pagesCOMPUTE!'s Beginner's Guide To Assembly Language On The TI-99/4Aremow100% (1)
- Principles of Information Systems, Tenth Edition: Software: Systems and Application SoftwareDocument59 pagesPrinciples of Information Systems, Tenth Edition: Software: Systems and Application Softwarerian takaNo ratings yet
- 3.4.2 Virtual Machine PDFDocument4 pages3.4.2 Virtual Machine PDFBlessed Endibye KanyembaNo ratings yet
- Can Bus. Receiving Data On Fuel Level From The Can Bus (281009 v3)Document9 pagesCan Bus. Receiving Data On Fuel Level From The Can Bus (281009 v3)Wilfredo A MolinaNo ratings yet
- PTU Lab PracticalsDocument67 pagesPTU Lab PracticalskartikavasthiNo ratings yet
- ITCT 2023 Study MaterialDocument54 pagesITCT 2023 Study MaterialchandanNo ratings yet
- Fis 533020e PDFDocument17 pagesFis 533020e PDFmarusea2009No ratings yet
- Computing BasicDocument55 pagesComputing BasicCandyNo ratings yet
- 144 BCA Honors MAJORDocument57 pages144 BCA Honors MAJORswamyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 0 - CS50's Introduction To Programming With PythonDocument8 pagesLecture 0 - CS50's Introduction To Programming With Pythonmonish anandNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced LevelDocument16 pagesCambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced LevelAl-Sami MashrafeeNo ratings yet
- Seisan DocumentDocument379 pagesSeisan DocumentpachernyangyuenNo ratings yet