Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bio Reviewer 4TH QTR
Bio Reviewer 4TH QTR
Uploaded by
KEANNA RUBIAOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Bio Reviewer 4TH QTR
Bio Reviewer 4TH QTR
Uploaded by
KEANNA RUBIACopyright:
Available Formats
FEEDBACK MECHANISM ○ Somatostatin - a cyclic
● Stimulus - external factors that peptide well known for its
cause change in the body. strong regulatory effects
● Homeostasis - the act of being throughout the body.
balanced ○ Not eating - Low sugar level
● Feedback Loops ■ Makes sugar level go
up.
● Thermoregulation
- Controlling the body temp
- Heating mechanisms are
activated (shivering)
- Cooling mechanisms are
activated (sweating)
➔ Stimulus produces change in the - Perspiration during a fever
body means that the body is doing
◆ May nalaglag na butiki normal response
➔ Change is detected by receptor
◆ Using the 5 senses (hear, Types of Thermoregulations
taste, feel, see & smell) 1. Ectotherm
➔ Information is sent along afferent - Outside
pathway to the brain - Also called cold-blooded /
◆ Response to the falling ipis conformers
(shock, disgust) - Adjust temp is based on the
➔ Info sent along afferent pathway to environment
effector - Hot-high body temp, Cold-Low
◆ Doing the response body temp
➔ Response of effector feedsback to - Mollusks, insects, aquatic,
the influence magnitude of stimulus & reptiles, crabs & dragonfly
returns variable to homeostasis
◆ Calming down 2. Endotherm
- Inside
NEGATIVE FEEDBACK - Have their own temp, doesn’t
base their temp on the
environment
- Also called warm-blooded /
regulator
- Birds & Humans
POSITIVE FEEDBACK
● Stimulus adds more stimulus
to the bod.
● Pregnancy
○ High oxytocin levels –
Adds more oxytocin
★ Negative feedback ● Cuts
○ Gain balance ○ Bleeding – bleeds
■ Eating sugar - more in order for the
increasing sugar level platelets to clot the
■ Makes sugar level go blood.
down
Nicole Andre Bautista
ANATOMICAL REGION - Skin repair (migrate,
proliferate, and differentiate to
restore the epidermal barrier
● Melanocytes
- in the layer of basal
cells at the deepest
part of the epidermis
- cell in the skin and
eyes that produces
and contains the
pigment called melanin
● Langerhans Cell (LCs)
- outermost guard of the
cutaneous immune
system
- play an important role
during the
inflammatory phase of
acute wound healing
● Merkel Cell
- special type of cell
found right below the
epidermis (top layer of
skin)
- receive the sensation
of touch and may be
involved in touch
DERMIS (Corium another term) -
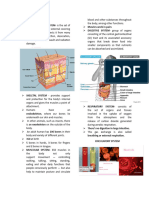
INTEGUMENTARY middle layer & inner layer of the two
SKIN - the largest organ of the body main layers of the skin
- support and protect the skin
Other integumentary and deeper layers, assist in
1. Hair thermoregulation, and aid in
2. Nails sensation
3. Sweat and oil glands Papillary dermis - thin upper layer
Reticular dermis - thick lower layer
EPIDERMIS - the outermost layer of skin
● Keratinocytes HYPODERMIS - bottom layer of skin
- most dominant cell type in your body
constituting the epidermis - subcutaneous tissue
(“beneath the skin,”)
Nicole Andre Bautista
Other term SKELETAL SYSTEM
● Corpuscle - Tactile, Lamellar & Locomotion
Follicle 1. Active Locomotion
● Insensible & Sensible - requirement of energy
● Vasoconstriction & Vasodilation - ability to move from one place to
another
SKIN COLORATION
● Cyanosis - a bluish color in the skin, 2. Passive Locomotion
lips, and nail beds caused by a - non requirement of energy
shortage of oxygen in the blood
(blue-purple tint) ➢ Aerial locomotion
● Jaundice - a yellow discoloration of ○ self-generated movements of
the body tissue resulting from the any animal through the air.
accumulation of excess bilirubin. ○ ginagamit ang air to move,
● Erythema - redness of the skin organisms of capable of flying
caused by injury or another (birds, eagle)
inflammation-causing condition
(RASH / SUNBURN) ➢ Terrestrial locomotion
○ any of several forms of animal
movement such as walking
and running, jumping
(saltation), and crawling.
➢ Aquatic locomotion
○ movement through water
either by swimming or by
progression in contact with the
substrate
Hydrostatic skeletons
GLANDS - use a cavity filled with water
- An organ that makes one or more - jellyfish and sea anemones
substances, such as hormones,
digestive juices, sweat, tears, saliva, Exoskeletal - meaning outside shell
or milk (mollusks & crabs)
● Eccrine sweat glands - occur over Endoskeletal - inside (human)
most of the body and open directly
onto the skin's surface. stabilizing Hematopoiesis - blood production
body temperature
● Apocrine glands - open into the hair
follicle, leading to the surface of the Functions of the Skeletal
skin (skin, breast, eyelid, and ear) 1. Movement: Skeletal system provides
points of attachment for muscles.
CERUMINOUS Your legs and arms move when the
- modified apocrine glands, which, muscles pull on the bones.
together with sebaceous glands, 2. Support: The backbone is the main
produce the cerumen, the ear wax support center for the upper body. It
holds your head up and protects your
MAMMARY spinal cord.
- Glandular organ located on the chest 3. Protection: The bones of your skull
- primary function is to secrete milk protect yourbrain. Your ribs
- Mammals get their name from the protectyour lungs and heart
Latin word mamma, "breast" frominjury.
4. Makes Blood: Red andwhite blood
SEBACEOUS cells areformed by tissue
- microscopic glands found in your hair calledmarrow, which is in thecenter of
follicles that secrete sebum (oily the bone.
substance that protects your skin)
Nicole Andre Bautista
5. Storage: Bones How do bones develop?
storeminerals, such ascalcium ● As an infant, most of your skeleton is
and phosphorus,for use by the cartilage
body ● Cartilage is a strong flexible tissue.
● Over time the cartilage is replaced by
Major Skeletal System Parts solid bone,usually complete by the
1. Axial Skeleton: The axial time you stop growing.
skeleton includesthe skull,
spine, ribsand sternum. (gitna 206 - adult
ng katawan naten) 300 - bata
2. Appendicular Skeleton: The
appendicular skeletonincludes CLAVICLE / COLLARBONE
the appendages of the body, - holds theshoulder joint away from the
which are theshoulders, arms, rest of the upper body and is only as
hips,and legs. thick as your little finger.
4 Basic bone shapes SCAPULA
1. Long - arms, legs & fingers - Located on the back side of the
2. Short - wrist & ankles ribcage and helps provide part of the
3. Flat - skull & sternum shoulder joint and movement for the
4. Irregular - spine arms.
4 Structure of bones VERTIBRAL COLUMN / SPINAL CORD
1. Periosteum - Covers Bones 1. Cervical region (neck bones)
2. Compact Bone - Lies 2. Thoracic region (ribs attach to)
beneath the periosteum – 3. Lumbar region (lower part of the
solid (pinaka matibay na part back)
ng buto)
3. Spongy Bone - Lies beneath COCCYX & SACRUM
the compact bone – butas - terminal segment of the spine &
butas provide weight-bearing support
4. Bone Marrow - Fills the gaps - shield-shaped bony structure that is
between the spongy bone located at the base of the lumbar
vertebrae and that is connected to
● Inside the compact bone is a the pelvis
layer of spongy bone.
● It has many small spaces, is HUMERUS (Upper Arm Bone)
light weight, but strong. - the largest bone of the upper
● Spongy bone is also found at extremity
the ends of bones. In the
spaces of many bones there RADIUS & ULNA
is a soft connective tissue - Radius on top
called marrow. - Ulna on Bot
Two types of Marrow: CARPALS (WRIST BONES)
- Red Marrow (produces most of the - bones of the wrist
body’s blood cells)
- Yellow Marrow (stores fat that can METACARPALS (TOP OF HANDS)
serve as an energy reserve.) - a group of five bones of the hand
between the phalanges and the
The structure of bones make it both strong carpus
and light weight.
▪ 20 % of an adults body weight is bone. PHALANGES (LITTLE FINGERS)
▪ Bone is made up of 2 minerals: - The 14 bones that are found in the
► Calcium fingers of each hand and also in the
► Phosphorus toes of each foot.
● Osteogenesis - creation of bone
Nicole Andre Bautista
JOINTS
- is a place where two bones come
together. allow thebones to move
indifferent ways.
Two types of joints:
• Immovable - allows little / no movement
• Movable
- Allow the body to move in a wide
range of movements Bones. movable
joints are held together by strong
connective tissue called ligaments.
RIB CAGE Four types of movable joints:
- protect the organs inside the chest. • Hinge
These organs include the heart and • Ball-and-socket
lungs. • Pivot
• Gliding
STERNUM (BREASTBONE)
- he long flat bone that forms the Ball-and-Socket
center front of the chest wall. - Round end of bone fitting snuggly
within another bone
PELVIS Ex. Shoulder & Hip
- area of the body below the abdomen
that is located between the hip bones Allows the greatest range of motion.
and contains the bladder and rectum - The ball-and-socket joint allows you
to swing your arms freely in a circle.
FEMUR
- the longest and strongest bone in Hinge Joint
your body - Movement in one direction like a
door.
TIBIA & FIBULA Ex. Knee and Elbow
- shinbone, the larger of the two - Allows forward or backward motion.
bones in the lower leg.
- a long bone in the lower extremity Pivot Joint
& smaller and thinner - Bone resting atop another bone
permitting free movement.
TARSALS Ex. Neck, Wrist & Ankles
- consist of seven short bones - Allows one bone to rotate
located at the proximal region of the around another.
foot ▪ Allows you to turn your head
METATARSALS Gliding Joint
- the bones of the forefoot that connect - Allows one bone to slide over
the distal aspects of the cuneiform another.
- group of five long bones in the foot Ex. Knuckles,wrist, ankle
- allows your to bend and flex as well
PHALANGES as make limited side to side motions
- The 14 bones that are found in the
fingers of each hand and also in the LIGAMENTS
toes of each foot. - Connects bone to bone
TENDON
- Attaches muscles to bones
Nicole Andre Bautista
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM 1. Duodenum
organs that take in food and liquids and 2. Jejunum
break them down into substances that the 3. Ileum
body can use for energy, growth, and tissue
repair. & absorbs nutrients Large intestine
- long, tube-like organ that is
Mouth connected to the small intestine at
- Preliminary digestion one end and the anus at the othe
- water inaabsorbs
10-20x dapat ngumuya
Digestive System Processes
1. Chewing - masticating 1. Ingestion
2. Incisors - (front teeth/pustiso) - take in food through the
3. Canine - (Pangil) mouth.
4. Molar - flat teeth at the rear of the 2. Digestion
mouth - begins in the mouth with
5. Bicuspids - teeth located between chewing or mastication
your molars and canine teeth. 3. Chemical digestion
6. Hard palate - The front, bony part of - process called hydrolysis,
the roof of the mouth. (ngala-ngala) uses water and digestive
7. Soft palate - very flexible and does enzymes to break down the
not contain any bony structures complex molecules.
8. Uvula - little fleshy hanging ball in the 4. Absorption
back of your throat - simple molecules that result
9. Gum - tissue of the upper and lower from chemical digestion pass
jaws that surrounds the base of the through cell membranes
teeth 5. Elimination
10. Saliva - helps to lubricate food - food molecules that cannot be
digested or absorbed need to
Tongue be eliminated from the body.
- Very territorial The removal of indigestible
wastes through the anus, in
Pharynx (throat) the form of feces, is
- hollow tube inside the neck that starts defecation or elimination.
behind the nose and ends at the top
of the trachea (windpipe) and REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
esophagus (the tube that goes to the ● Argonauta Argo – Argonaut Octo
stomach). - Chop off
- Male argonauts use a
Bolus modified arm, known as a
- after bolus direct ng esophagus hectocotylus, to transfer their
(smooth muscles) sperm to the female
● Mantis religiosa
Esophagus - male praying mantis will leap
- muscular tube through which food onto the female
passes from the throat to the back—collapsing her thorax
stomach. and wing bases with his
forelegs. Once the collapsing
Stomach is done, he then bends his
- digest food by mixing it with digestive abdomen to place his sperm
juices and churning it into a thin into a cavity that is located on
liquid. the tip of the female's
abdomen.
Rugae - room for expansion ● Rana Pipiens
- Mating in frogs typically
Small intestine involves the male wrapping
- long tube-like organ that connects the his arms around female, the
stomach and the large intestine female depositing eggs and
the male fertilizing the eggs.
Nicole Andre Bautista
Gynecologist - a specialist doctor who Female reproductive system (INTERNAL)
manages conditions that affect the female 1. Uterine/fallopian tube - transport
reproductive system ova
2. Recto & Vesico-uterine Pouch -
Urologist - diagnosing and treating diseases hallow space
of the urinary system of the male. 3. Cervix - passage for menstrual fluid
4. Fornix - catch & retain ejaculated
Male Reproductive system semen
1. Bulbourethral Glands (Cowper's 5. Greater Vestibular Glan - lubrication
glands) of vagina
- produce a thick mucus
2. Corpus Cavernosum and Corpus ● Ovary - transport ova
Spongiosum ● Uterus - hallow space
- Erection ● Fimbriae - catches ovum
3. Ejaculatory Ducts ● Ovarian Ligament - attachment
- Spermatozoa and semen ● Broad Ligament - support
fluids channel
4. Epididymis Hormonal Control of Male Physiology
- storage for spermatids
5. External Urethral Orifice
- Exit point
6. Glans Penis
- Covered with prepuce
(movable sheath of skin that
covers the head of the penis)
7. Membranous & Prostatic Urethra
- Passage way
8. Prostate Gland
- Contributes 26% to the
volume of semen
9. Scrotum
- Protection of testis
10. Seminal Vesicles
- Seminal fluid contains a lot of
fructose
Parts of Testis
● Testis - spermatozoa and
testosterone
● Rete Testis - helps move sperm cells
● Vas Deferens - passage for
ejaculation
● Seminiferous Tubules - site for
spermatogenesis
● Tunica Albuginea - connective
tissue capsule / “white tunic”
Female reproductive system (EXTERNAL)
1. Clitoris - sensitive bulbous erectile
structure
2. Labia Majora - sudoriferous &
sebaceous glands
3. Labia Minora - sebaceous glands
but no hair
4. Mons Pubis - cushions & protects
pubic symphysis
5. Vulva - removal of urine, copulation,
childbirth
Nicole Andre Bautista
Hormonal Regulation of Reproductive
Cycle
Gametes
1. Oogenesis - process of the formation
of a mature ovum from the oogonia in
females
2. Spermatogenesis - process by
which sperm cell production occurs
Circumcision - foreskin is removed just
behind the head of the penis using a scalpel
or surgical scissors
Female Genital Circumcision - (FGC)
involves the cutting or altering of the external
female genital organs
Sexually Trandsmitted Infection (STDs)
1. Chlamydia
2. Gonorrhea
3. Syphillis
4. Trichomoniasis
5. HSV (herpes simplex virus)
6. HPV (Human Papilloma virus)
Pubic Lice - lice attach eggs to the pubic
hair & feed on human blood
Human Papilomavirus (HPV) - Cause by
Herpes, spread thru skin-to-skin & oral,
vaginal sex
Nicole Andre Bautista
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5825)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (903)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (541)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (823)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (403)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Miller and Harley Zoology 11ed Ch02Document50 pagesMiller and Harley Zoology 11ed Ch02KEANNA RUBIANo ratings yet
- Ancient Invention Stone ToolsDocument1 pageAncient Invention Stone ToolsKEANNA RUBIANo ratings yet
- STATISTICS ReviewerDocument4 pagesSTATISTICS ReviewerKEANNA RUBIANo ratings yet
- Developmental Psychology ReviewerDocument2 pagesDevelopmental Psychology ReviewerKEANNA RUBIANo ratings yet
- Human AnatomyDocument10 pagesHuman AnatomyKEANNA RUBIANo ratings yet
- Early Adulthood Development TasksDocument2 pagesEarly Adulthood Development TasksKEANNA RUBIANo ratings yet
- ETECHDocument2 pagesETECHKEANNA RUBIANo ratings yet
- 2a - Electric FieldDocument39 pages2a - Electric FieldKEANNA RUBIANo ratings yet
- Itp Reflection PapersDocument20 pagesItp Reflection PapersKEANNA RUBIANo ratings yet
- Lesson 9Document16 pagesLesson 9KEANNA RUBIANo ratings yet
- Concepts of Self.Document12 pagesConcepts of Self.KEANNA RUBIANo ratings yet
- 8 - Practice Problem Solutions - Light As An Electromagnetic WaveDocument5 pages8 - Practice Problem Solutions - Light As An Electromagnetic WaveKEANNA RUBIANo ratings yet
- Arts PromotionDocument17 pagesArts PromotionKEANNA RUBIANo ratings yet
- 2ND Quarter ReviewerDocument46 pages2ND Quarter ReviewerKEANNA RUBIANo ratings yet
- 6 - Complete Solutions - Direct-Current CircuitsDocument45 pages6 - Complete Solutions - Direct-Current CircuitsKEANNA RUBIANo ratings yet