Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bio Midterm Reviewer
Bio Midterm Reviewer
Uploaded by
CEEJAY P. PATAWARANCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- 1Q Reviewer General Biology 1Document9 pages1Q Reviewer General Biology 1Ruby May Regala100% (9)
- Product Data SummaryDocument11 pagesProduct Data SummaryLê CôngNo ratings yet
- Lec 3,4,5-Cell and Cell OrganellesDocument57 pagesLec 3,4,5-Cell and Cell OrganellesSatyam Arya100% (1)
- Thermoplastic Elastomeric (TPE) Gasket Materials For Drain, Waste, and Vent (DWV), Sewer, Sanitary and Storm Plumbing SystemsDocument2 pagesThermoplastic Elastomeric (TPE) Gasket Materials For Drain, Waste, and Vent (DWV), Sewer, Sanitary and Storm Plumbing SystemsĐường Nguyễn ThừaNo ratings yet
- Bio Chapter 2Document33 pagesBio Chapter 2Qistina MaisarahNo ratings yet
- f4 Chapter 2Document51 pagesf4 Chapter 2m-9476340No ratings yet
- Pre Found BioDocument334 pagesPre Found BioAARYAN SURESH V. X DNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Cell FunctionsDocument24 pagesModule 1 Cell FunctionsLady MeowNo ratings yet
- Sec 3Document28 pagesSec 3Jana Moataz Mohamed G02No ratings yet
- Plant Organology Theory PDFDocument24 pagesPlant Organology Theory PDFCaitlin SnymanNo ratings yet
- GS Biology 2Document70 pagesGS Biology 2LalruatdikiNo ratings yet
- CellDocument34 pagesCellSadaf JavedNo ratings yet
- 01 Introduction PDFDocument41 pages01 Introduction PDFpotatso02No ratings yet
- Reviewer in BiologyDocument16 pagesReviewer in BiologyAngel CastilloNo ratings yet
- Cells and TissuesDocument5 pagesCells and TissuesEARLRYAN TUMBALENo ratings yet
- Eukaryotic Cells - RuahDocument16 pagesEukaryotic Cells - RuahruahNo ratings yet
- 9.4. CellDocument88 pages9.4. CellTUĞRUL ERGÜLNo ratings yet
- B 160 PlantcellDocument30 pagesB 160 PlantcellJho AlpayNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio - First GradingDocument5 pagesGen Bio - First GradingCasey PedrayaNo ratings yet
- 1.mind Map - Cell - A Unit of LifeDocument100 pages1.mind Map - Cell - A Unit of LifeAyush KumarNo ratings yet
- Plant CellDocument22 pagesPlant CellAbenathi NolusuNo ratings yet
- B 160 Plant CellDocument30 pagesB 160 Plant CellJanina Ysabel ArosaNo ratings yet
- B 160 PlantcellDocument30 pagesB 160 PlantcellSamar JavedNo ratings yet
- Animal Cells and Bacterial CellsDocument40 pagesAnimal Cells and Bacterial CellsClarence CaparasNo ratings yet
- CellsDocument82 pagesCellsK.R. LiberosisNo ratings yet
- Cell Unit of Life Class NoteDocument36 pagesCell Unit of Life Class NoteKavana SNo ratings yet
- Bio NotesDocument10 pagesBio Noteschanhongyi16No ratings yet
- Cell Parts and Its Function DLLDocument62 pagesCell Parts and Its Function DLLRovelyn AlejoNo ratings yet
- Plasma MembraneDocument5 pagesPlasma MembraneNishi MenonNo ratings yet
- Introduction To CellsDocument87 pagesIntroduction To CellsLovely Ann LoyogoyNo ratings yet
- Plant Cell Structure and FunctionDocument29 pagesPlant Cell Structure and Functionihebunnaogochukwu24No ratings yet
- CellDocument23 pagesCellErdis MerepezaNo ratings yet
- CELLSDocument37 pagesCELLSsuggaballNo ratings yet
- CellsPart 1Document18 pagesCellsPart 1Angella Reece IsraelNo ratings yet
- SRM Institute of Science and Technology: Unit 1 - Cellular Components of PlantsDocument27 pagesSRM Institute of Science and Technology: Unit 1 - Cellular Components of PlantsABISHEK S (RA2012036010003)No ratings yet
- Cell OrganellesDocument2 pagesCell OrganellesSurminie Muksin100% (1)
- AS Level Cells and Cell StructuresDocument54 pagesAS Level Cells and Cell StructuresRamya MalariniNo ratings yet
- The Cell: Cytoplasmic Organelles: Prepared By: Lenor M. Tunac MAED-BiologyDocument30 pagesThe Cell: Cytoplasmic Organelles: Prepared By: Lenor M. Tunac MAED-BiologyLenor TunacNo ratings yet
- Cell Structures and FunctionsDocument4 pagesCell Structures and FunctionsRaeson Amir ReyesNo ratings yet
- 1 Lec.1 (w1) Overview and Plant StructureDocument32 pages1 Lec.1 (w1) Overview and Plant StructureRabiatul AdawiyyahNo ratings yet
- Biology Unit Chapters 2 and 3 Plus IBDocument164 pagesBiology Unit Chapters 2 and 3 Plus IBallie3d100% (1)
- Bio Notes-Part-2Document8 pagesBio Notes-Part-2kreigblitz9801No ratings yet
- Cell UnitDocument7 pagesCell UnitParth GoyalNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure FunctionDocument30 pagesCell Structure FunctionAngelo GabrielNo ratings yet
- Plant CellsDocument28 pagesPlant CellsKent Lary TediosNo ratings yet
- FBS 31 - Lecture 1-4Document7 pagesFBS 31 - Lecture 1-4camillejv18No ratings yet
- The CellDocument59 pagesThe CellPrayl Hope NapanoNo ratings yet
- Topic 4 - Plant Structure and Function, Biodiversity and ConservationDocument21 pagesTopic 4 - Plant Structure and Function, Biodiversity and ConservationTheDarkSoulNo ratings yet
- SPT2 Cytology 2 Ergastic Substance Cell Wall 2019Document29 pagesSPT2 Cytology 2 Ergastic Substance Cell Wall 2019PutputNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3Document14 pagesLesson 3Kaizen100% (1)
- Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Cells: Distinguishing Their FeaturesDocument14 pagesProkaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Cells: Distinguishing Their FeaturesDaniella Pasilbas SabacNo ratings yet
- Pharmacognosy L02Document21 pagesPharmacognosy L02Youssef ElhamamyNo ratings yet
- Topic 4 Agr3101Document103 pagesTopic 4 Agr3101Sleeping BeautyNo ratings yet
- Ged CellDocument19 pagesGed CellKaung KhantNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Unit of Life: Cbse, Class Ix, BiologyDocument41 pagesFundamental Unit of Life: Cbse, Class Ix, BiologySmitha JayaprakashNo ratings yet
- CellsDocument24 pagesCellsapi-95529788100% (1)
- The Fundamental Unit of Life-IIDocument14 pagesThe Fundamental Unit of Life-IIPankaj VermaNo ratings yet
- Levels of Biological OrganizationsDocument23 pagesLevels of Biological OrganizationsYuu KieNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document15 pagesModule 2mycamariebeliot0508No ratings yet
- Transport in Plants: GCE Study Buddy BiologyDocument46 pagesTransport in Plants: GCE Study Buddy BiologyMaleeha HumayunNo ratings yet
- Antioxidant Capacity, Phenolic Content and Vitamin C in Pulp, Peel and Seed From 24 Exotic Fruits From ColombiaDocument8 pagesAntioxidant Capacity, Phenolic Content and Vitamin C in Pulp, Peel and Seed From 24 Exotic Fruits From ColombiaJuan Fernando Cano LarrotaNo ratings yet
- Product SIKADocument75 pagesProduct SIKAZan PerzadaNo ratings yet
- (23279834 - HortScience) Ammonium and Nitrate Accumulation in Containerized Southern Highbush Blueberry PlantsDocument4 pages(23279834 - HortScience) Ammonium and Nitrate Accumulation in Containerized Southern Highbush Blueberry PlantsFiorella EspinozaNo ratings yet
- Group-4 1121L Experiment-13Document5 pagesGroup-4 1121L Experiment-13Ezra Lee NgatiyonNo ratings yet
- Application Form For Textile Testing - Fabric: 1 U J C QDocument3 pagesApplication Form For Textile Testing - Fabric: 1 U J C QMd MasumNo ratings yet
- Actylis LAB PL Jan-2024 Low ResDocument144 pagesActylis LAB PL Jan-2024 Low ResKaushik hazarikaNo ratings yet
- Ch.4 Pile FoundationsDocument13 pagesCh.4 Pile FoundationsAhmed2No ratings yet
- 701.114 730 008 00 Technology and OperationDocument48 pages701.114 730 008 00 Technology and OperationmohamedqadiNo ratings yet
- Hydrogen Sulfide (0.0001% - 0.05 %) in Nitrogen: Safety Data Sheet 50248Document9 pagesHydrogen Sulfide (0.0001% - 0.05 %) in Nitrogen: Safety Data Sheet 50248pcatruongNo ratings yet
- Introduction To The Structure and The Structural Role of Elements in GlassesDocument84 pagesIntroduction To The Structure and The Structural Role of Elements in GlassesBiswanath senNo ratings yet
- Determination of Toxicity of Spinosad Against The Pulse Beetle, CallosobruchusDocument6 pagesDetermination of Toxicity of Spinosad Against The Pulse Beetle, CallosobruchustofazzalhNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice AssessmentDocument10 pagesMultiple Choice Assessmentgrace ongNo ratings yet
- Titanium Tube Failures-Power PlantsDocument11 pagesTitanium Tube Failures-Power PlantsgshdavidNo ratings yet
- High Shrink Sleeves: Product DescriptionDocument2 pagesHigh Shrink Sleeves: Product DescriptionCristobal Leal ArandaNo ratings yet
- Class - Xii Subject - ChemistryDocument70 pagesClass - Xii Subject - ChemistryYash TandonNo ratings yet
- GPX Assay KitDocument6 pagesGPX Assay KitRodrigo OliveiraNo ratings yet
- Analisis de Fallas en Ingenieria de MaterialesDocument88 pagesAnalisis de Fallas en Ingenieria de MaterialesMarjorie BlossiersNo ratings yet
- Ijisr 15 072 02 PDFDocument10 pagesIjisr 15 072 02 PDFKima MadNo ratings yet
- CoAs... Hidroxipropilmetilcelulosa (HPMC) (Methocel K100M Premium-2208) - CoA L-1EF0909 (Spectrum)Document1 pageCoAs... Hidroxipropilmetilcelulosa (HPMC) (Methocel K100M Premium-2208) - CoA L-1EF0909 (Spectrum)Maikel Perez NavarroNo ratings yet
- Coatings and Construction Components (EU)Document20 pagesCoatings and Construction Components (EU)Shahid MirzaNo ratings yet
- Thermo-Hygrometer-Air Quality: Data SheetDocument4 pagesThermo-Hygrometer-Air Quality: Data Sheetabhe prasetyaNo ratings yet
- CHY1701-M4 - Dr. Krishnendu BiswasDocument58 pagesCHY1701-M4 - Dr. Krishnendu Biswaslalithkumaran LNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE 9 EXAM (2nd Quarter) QuestionsDocument3 pagesSCIENCE 9 EXAM (2nd Quarter) QuestionsKert Cyrel RomeroNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 1-To Study Cochran and Babcock and Wilcox BoilersDocument8 pagesExperiment No. 1-To Study Cochran and Babcock and Wilcox BoilersShahedNo ratings yet
- Stock 16042022Document81 pagesStock 16042022NeetuNo ratings yet
- Production of BioplasticDocument5 pagesProduction of BioplasticNatsu DragoneelNo ratings yet
- Section 1 GeneralDocument612 pagesSection 1 GeneralM Ramzi100% (2)
- Wood Biodeterioration and PreservationDocument3 pagesWood Biodeterioration and Preservationthelostboy undomielNo ratings yet
Bio Midterm Reviewer
Bio Midterm Reviewer
Uploaded by
CEEJAY P. PATAWARANOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Bio Midterm Reviewer
Bio Midterm Reviewer
Uploaded by
CEEJAY P. PATAWARANCopyright:
Available Formats
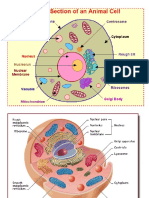
Quiz 1 Mitochondria - Membrane-bound cell organelles that
Golgi Bodies - A cell organelle that helps process and generate most of the chemical energy needed to power the
package proteins and lipid molecules, especially proteins cell's biochemical reactions.
Nucleus - The largest organelle inside the cell taking up Antoni van Leeuwenhoek - FIRST PERSON to see a
about a tenth. BACTERIA.
Cytoplasm - A thick solution that fills each cell and is Protoplasm - Composed of a mixture of small molecules
enclosed by the cell membrane. such as ions, amino acids, monosaccharides and water,
and macromolecules such as nucleic acids, proteins, lipids
Ribosomes - Particles consisting of RNA and associated
and polysaccharides.
proteins.
Cell Wall - Provides the cell with both structural support and
Plastids - Types of pigments that can change the color of
protection.
the cell.
TRUE
Cilia - Small hair-like protuberances on the outside of
• CAROTENOIDS – yellow pigment
eukaryotic cells.
• Tonoplast is a membrane enclosing vacuoles.
Sogaerisines - Filled with hydrolytic enzymes for fat • Secondary Wall is impermeable to water and other
synthesis. substances which results to the death of cells.
• CaCO₃ crystals which are grape-like (crystolith) may
Glyoxysomes - Contains enzymes involved in the
conversion of fats to carbohydrates during germination. be found within the cell hanging from the cell wall
Plasmodesma - Are microscopic channels which traverse False
the cell walls of plant cells and some algal cells. • In plants, golgi bodies are connected and scattered.
These are called dictyosomes.
Endoplasmic Reticulum - A continuous membrane system • Suberin – renders the cell permeable to water and
that forms a series of flattened sacs within the cytoplasm gases.
of eukaryotic cells and serves multiple functions. • In eukaryotic cells, the protoplasm includes all of the
Microtubules - Polymers of tubulin that form part of the material inside the cell and outside of the nucleus.
cytoskeleton and provide structure and shape. • Cutin is a fatty material usually found as a layer, the
cuticle, on outer walls of cells forming the exterior
Spindle Fibers - Involved in moving and segregating the surfaces of land plants; is permeable to water and
chromosomes during nuclear division. protect leaves and stems against water loss.
• Anthoxanthins are the pigments that give red, • Building foods from the materials and light energy it
purple, and blue plants their rich coloring. absorbs through as process called of
• Plant cells are the basic unit of life in organisms of photosynthesis.
the kingdom Plantae. They are prokaryotic cells, • Monosaccharides aka simple sugars.
which have a true nucleus along with specialized • Cytolysis, can occur if the cell is in a hypotonic
structures called organelles that carry out different solution resulting in a lower external osmotic
functions. pressure and a net flow of water into the cell.
• CELL THEORY states that “the bodies of plants and • After telophase, the daughter cells go through the
animals are composed of cells and their products interphase and cell cycle is repeated.
and these cells came from existing cells. False
• Cytoplasm is part of the protoplasm found outside • Anaphase-the spindle has captured all the
the cell membrane and inside the nucleus. chromosomes and lined them up at the middle of
Quiz 2 the cell, ready to divide.
True • First 3 phases of the cycle are referred to as
• Suberin and cutin – protect leaves and stem against prophase.
water loss. • Neurons are chemical messengers present in very
• Interphase-chromosomes duplicate, and copies small amounts that bring about important changes
remain attached to each other. in growth and development.
• Lipid-soluble pigments – found in the plastids like • Normally when a cell divides, the nucleus divides
chlorophyll, carotenes and xanthophylls. first, followed by the division of the cytoplasm or
• Releasing the energy in the food for its varied mitosis.
activities through a process called respiration. • Phytochromes are found in the cytoplasm and
• Enzymes – composed primarily of proteins together concerned with certain steps in respiration and
with other substances. photosynthesis.
• Prophase - chromatin begins to condense and • Diffusion is the spontaneous net movement of
thicken, coiling up into bodies referred to as solvent molecules through a partially permeable
chromosomes. membrane into a region of higher solute
• Mineral salts are compound formed when an acid is concentration, in the direction that tends to equalize
neutralized by a base. the solute concentrations on the two sides.
• Plasmolysis the process in which cells lose water in
a hypotonic solution.
• The G 2 phase start as the cell begins division. Collenchyma - Composed of cells with unevenly thickened
• Cytokinesis : Division of the nucleus during the cell walls.
cycle
Cork - Cell walls impregnated with suberin
• Protein- carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms with
general formula (CH2O)n. ROOTS - Cylindrical structures which are usually located
• DNA molecule is duplicated by a process called beneath the surface of the soil.
duplication. PRIMARY, SECONDARY, TERTIARY, ADVENTITOUS –
• Inorganic substances are compounds that contain Types of roots based on origin.
carbon.
• Metaphase cell starts to break down some TAP ROOTS SYSTEM - Consists of one main root which
structures and build others up, setting the stage for arises lateral roots.
division of the chromosomes. FIBROUS SYSTEM - Consists of several main roots that
• O2 – raw material for photosynthesis branch to form a dense mass of intermeshed lateral roots.
Quiz 3 Support – Creeping Ivy, Old Trees
Xylem Food Storage – Ube Beets, Radish
• They are dead with hollow cells, which consist of only
Photosynthesis – Orchids
cell wall.
Protection – Yam
• Is mainly responsible for the conduction of water
and mineral salts from roots to other parts of the Nitrogen Fixation – Peanuts, Soybeans
plant. Aeration – Mangrove
Phloem Reproduction - Purple Yam
• Also called as sugar.
• They transport the nutrients in the downward
direction.
Quiz 4
Permanent Tissues - Contain nondividing cells.
ROOTING - Stem cuttings are placed in moist sand or peat
INTERCALARY MERISTEM - Responsible for the rapid mass until adventitious root develop.
growth of stems.
Photosynthesis - Stick plant.
LATERAL MERISTEM - Responsible for the increase in the
diameter or width of the roots and stems.
PRUNING - the removal of a diseased, broken, or otherwise Storage - Fleshy, underground stems.
undesired branch. BRANCH - A stem that is more than 1 year old, typically
Bulbs - Very small piece of the stem tissue surrounded by with lateral stems radiating from it.
numerous fleshy leaves HEARTWOOD - Center part of the wood.
SAP WOOD/ALBURNUM - Outer part of the wood, which Interphase
is paler in color • 46 Chromosomes.
VASCULAR BUNDLE - Inner region composed of the • Divided into three phases: G1 (first gap), S
primary vascular tissue made up of primary xylem and (synthesis), and G2 (second gap).
primary phloem. Prophase
• Cell starts to break down some structures and
CORTEX - Middle region composed of an outer zone of build others up.
collenchyma, an inner zone of parenchyma. • Chromosomes doubled
NODES - An area on a stem where buds are located. • Nuclear membrane dissolves
GIRDLING - The removal of the complete ring of the bark Metaphase - Chromosomes align at the middle of cell.
to shop the downward passage of food. Anaphase
SCION - stem piece which is grafted to the stock. • The sister chromatids separate from each other
and are pulled towards opposite ends of the cell.
Balloon vine - Unusual method of support • Separated chromosomes pulled apart
STOCK - Basal rooted stem used in a graft Telophase
Digman - Uncutinized epidermis. • Microtubules disappear cell division begins.
• Cytokinesis or the partitioning of the cell may also
Tubers - Short, swollen, terminal portions of an begin during this stage
underground stems.
TWIG - A young stem (1 year old or less) that is in the
dormant winter stage (has no leaves).
stems + leaves - SHOOTS
BUDS - An undeveloped shoot from which leaves or
flowers grow.
TRUNK - A woody plant’s main stem.
You might also like
- 1Q Reviewer General Biology 1Document9 pages1Q Reviewer General Biology 1Ruby May Regala100% (9)
- Product Data SummaryDocument11 pagesProduct Data SummaryLê CôngNo ratings yet
- Lec 3,4,5-Cell and Cell OrganellesDocument57 pagesLec 3,4,5-Cell and Cell OrganellesSatyam Arya100% (1)
- Thermoplastic Elastomeric (TPE) Gasket Materials For Drain, Waste, and Vent (DWV), Sewer, Sanitary and Storm Plumbing SystemsDocument2 pagesThermoplastic Elastomeric (TPE) Gasket Materials For Drain, Waste, and Vent (DWV), Sewer, Sanitary and Storm Plumbing SystemsĐường Nguyễn ThừaNo ratings yet
- Bio Chapter 2Document33 pagesBio Chapter 2Qistina MaisarahNo ratings yet
- f4 Chapter 2Document51 pagesf4 Chapter 2m-9476340No ratings yet
- Pre Found BioDocument334 pagesPre Found BioAARYAN SURESH V. X DNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Cell FunctionsDocument24 pagesModule 1 Cell FunctionsLady MeowNo ratings yet
- Sec 3Document28 pagesSec 3Jana Moataz Mohamed G02No ratings yet
- Plant Organology Theory PDFDocument24 pagesPlant Organology Theory PDFCaitlin SnymanNo ratings yet
- GS Biology 2Document70 pagesGS Biology 2LalruatdikiNo ratings yet
- CellDocument34 pagesCellSadaf JavedNo ratings yet
- 01 Introduction PDFDocument41 pages01 Introduction PDFpotatso02No ratings yet
- Reviewer in BiologyDocument16 pagesReviewer in BiologyAngel CastilloNo ratings yet
- Cells and TissuesDocument5 pagesCells and TissuesEARLRYAN TUMBALENo ratings yet
- Eukaryotic Cells - RuahDocument16 pagesEukaryotic Cells - RuahruahNo ratings yet
- 9.4. CellDocument88 pages9.4. CellTUĞRUL ERGÜLNo ratings yet
- B 160 PlantcellDocument30 pagesB 160 PlantcellJho AlpayNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio - First GradingDocument5 pagesGen Bio - First GradingCasey PedrayaNo ratings yet
- 1.mind Map - Cell - A Unit of LifeDocument100 pages1.mind Map - Cell - A Unit of LifeAyush KumarNo ratings yet
- Plant CellDocument22 pagesPlant CellAbenathi NolusuNo ratings yet
- B 160 Plant CellDocument30 pagesB 160 Plant CellJanina Ysabel ArosaNo ratings yet
- B 160 PlantcellDocument30 pagesB 160 PlantcellSamar JavedNo ratings yet
- Animal Cells and Bacterial CellsDocument40 pagesAnimal Cells and Bacterial CellsClarence CaparasNo ratings yet
- CellsDocument82 pagesCellsK.R. LiberosisNo ratings yet
- Cell Unit of Life Class NoteDocument36 pagesCell Unit of Life Class NoteKavana SNo ratings yet
- Bio NotesDocument10 pagesBio Noteschanhongyi16No ratings yet
- Cell Parts and Its Function DLLDocument62 pagesCell Parts and Its Function DLLRovelyn AlejoNo ratings yet
- Plasma MembraneDocument5 pagesPlasma MembraneNishi MenonNo ratings yet
- Introduction To CellsDocument87 pagesIntroduction To CellsLovely Ann LoyogoyNo ratings yet
- Plant Cell Structure and FunctionDocument29 pagesPlant Cell Structure and Functionihebunnaogochukwu24No ratings yet
- CellDocument23 pagesCellErdis MerepezaNo ratings yet
- CELLSDocument37 pagesCELLSsuggaballNo ratings yet
- CellsPart 1Document18 pagesCellsPart 1Angella Reece IsraelNo ratings yet
- SRM Institute of Science and Technology: Unit 1 - Cellular Components of PlantsDocument27 pagesSRM Institute of Science and Technology: Unit 1 - Cellular Components of PlantsABISHEK S (RA2012036010003)No ratings yet
- Cell OrganellesDocument2 pagesCell OrganellesSurminie Muksin100% (1)
- AS Level Cells and Cell StructuresDocument54 pagesAS Level Cells and Cell StructuresRamya MalariniNo ratings yet
- The Cell: Cytoplasmic Organelles: Prepared By: Lenor M. Tunac MAED-BiologyDocument30 pagesThe Cell: Cytoplasmic Organelles: Prepared By: Lenor M. Tunac MAED-BiologyLenor TunacNo ratings yet
- Cell Structures and FunctionsDocument4 pagesCell Structures and FunctionsRaeson Amir ReyesNo ratings yet
- 1 Lec.1 (w1) Overview and Plant StructureDocument32 pages1 Lec.1 (w1) Overview and Plant StructureRabiatul AdawiyyahNo ratings yet
- Biology Unit Chapters 2 and 3 Plus IBDocument164 pagesBiology Unit Chapters 2 and 3 Plus IBallie3d100% (1)
- Bio Notes-Part-2Document8 pagesBio Notes-Part-2kreigblitz9801No ratings yet
- Cell UnitDocument7 pagesCell UnitParth GoyalNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure FunctionDocument30 pagesCell Structure FunctionAngelo GabrielNo ratings yet
- Plant CellsDocument28 pagesPlant CellsKent Lary TediosNo ratings yet
- FBS 31 - Lecture 1-4Document7 pagesFBS 31 - Lecture 1-4camillejv18No ratings yet
- The CellDocument59 pagesThe CellPrayl Hope NapanoNo ratings yet
- Topic 4 - Plant Structure and Function, Biodiversity and ConservationDocument21 pagesTopic 4 - Plant Structure and Function, Biodiversity and ConservationTheDarkSoulNo ratings yet
- SPT2 Cytology 2 Ergastic Substance Cell Wall 2019Document29 pagesSPT2 Cytology 2 Ergastic Substance Cell Wall 2019PutputNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3Document14 pagesLesson 3Kaizen100% (1)
- Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Cells: Distinguishing Their FeaturesDocument14 pagesProkaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Cells: Distinguishing Their FeaturesDaniella Pasilbas SabacNo ratings yet
- Pharmacognosy L02Document21 pagesPharmacognosy L02Youssef ElhamamyNo ratings yet
- Topic 4 Agr3101Document103 pagesTopic 4 Agr3101Sleeping BeautyNo ratings yet
- Ged CellDocument19 pagesGed CellKaung KhantNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Unit of Life: Cbse, Class Ix, BiologyDocument41 pagesFundamental Unit of Life: Cbse, Class Ix, BiologySmitha JayaprakashNo ratings yet
- CellsDocument24 pagesCellsapi-95529788100% (1)
- The Fundamental Unit of Life-IIDocument14 pagesThe Fundamental Unit of Life-IIPankaj VermaNo ratings yet
- Levels of Biological OrganizationsDocument23 pagesLevels of Biological OrganizationsYuu KieNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document15 pagesModule 2mycamariebeliot0508No ratings yet
- Transport in Plants: GCE Study Buddy BiologyDocument46 pagesTransport in Plants: GCE Study Buddy BiologyMaleeha HumayunNo ratings yet
- Antioxidant Capacity, Phenolic Content and Vitamin C in Pulp, Peel and Seed From 24 Exotic Fruits From ColombiaDocument8 pagesAntioxidant Capacity, Phenolic Content and Vitamin C in Pulp, Peel and Seed From 24 Exotic Fruits From ColombiaJuan Fernando Cano LarrotaNo ratings yet
- Product SIKADocument75 pagesProduct SIKAZan PerzadaNo ratings yet
- (23279834 - HortScience) Ammonium and Nitrate Accumulation in Containerized Southern Highbush Blueberry PlantsDocument4 pages(23279834 - HortScience) Ammonium and Nitrate Accumulation in Containerized Southern Highbush Blueberry PlantsFiorella EspinozaNo ratings yet
- Group-4 1121L Experiment-13Document5 pagesGroup-4 1121L Experiment-13Ezra Lee NgatiyonNo ratings yet
- Application Form For Textile Testing - Fabric: 1 U J C QDocument3 pagesApplication Form For Textile Testing - Fabric: 1 U J C QMd MasumNo ratings yet
- Actylis LAB PL Jan-2024 Low ResDocument144 pagesActylis LAB PL Jan-2024 Low ResKaushik hazarikaNo ratings yet
- Ch.4 Pile FoundationsDocument13 pagesCh.4 Pile FoundationsAhmed2No ratings yet
- 701.114 730 008 00 Technology and OperationDocument48 pages701.114 730 008 00 Technology and OperationmohamedqadiNo ratings yet
- Hydrogen Sulfide (0.0001% - 0.05 %) in Nitrogen: Safety Data Sheet 50248Document9 pagesHydrogen Sulfide (0.0001% - 0.05 %) in Nitrogen: Safety Data Sheet 50248pcatruongNo ratings yet
- Introduction To The Structure and The Structural Role of Elements in GlassesDocument84 pagesIntroduction To The Structure and The Structural Role of Elements in GlassesBiswanath senNo ratings yet
- Determination of Toxicity of Spinosad Against The Pulse Beetle, CallosobruchusDocument6 pagesDetermination of Toxicity of Spinosad Against The Pulse Beetle, CallosobruchustofazzalhNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice AssessmentDocument10 pagesMultiple Choice Assessmentgrace ongNo ratings yet
- Titanium Tube Failures-Power PlantsDocument11 pagesTitanium Tube Failures-Power PlantsgshdavidNo ratings yet
- High Shrink Sleeves: Product DescriptionDocument2 pagesHigh Shrink Sleeves: Product DescriptionCristobal Leal ArandaNo ratings yet
- Class - Xii Subject - ChemistryDocument70 pagesClass - Xii Subject - ChemistryYash TandonNo ratings yet
- GPX Assay KitDocument6 pagesGPX Assay KitRodrigo OliveiraNo ratings yet
- Analisis de Fallas en Ingenieria de MaterialesDocument88 pagesAnalisis de Fallas en Ingenieria de MaterialesMarjorie BlossiersNo ratings yet
- Ijisr 15 072 02 PDFDocument10 pagesIjisr 15 072 02 PDFKima MadNo ratings yet
- CoAs... Hidroxipropilmetilcelulosa (HPMC) (Methocel K100M Premium-2208) - CoA L-1EF0909 (Spectrum)Document1 pageCoAs... Hidroxipropilmetilcelulosa (HPMC) (Methocel K100M Premium-2208) - CoA L-1EF0909 (Spectrum)Maikel Perez NavarroNo ratings yet
- Coatings and Construction Components (EU)Document20 pagesCoatings and Construction Components (EU)Shahid MirzaNo ratings yet
- Thermo-Hygrometer-Air Quality: Data SheetDocument4 pagesThermo-Hygrometer-Air Quality: Data Sheetabhe prasetyaNo ratings yet
- CHY1701-M4 - Dr. Krishnendu BiswasDocument58 pagesCHY1701-M4 - Dr. Krishnendu Biswaslalithkumaran LNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE 9 EXAM (2nd Quarter) QuestionsDocument3 pagesSCIENCE 9 EXAM (2nd Quarter) QuestionsKert Cyrel RomeroNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 1-To Study Cochran and Babcock and Wilcox BoilersDocument8 pagesExperiment No. 1-To Study Cochran and Babcock and Wilcox BoilersShahedNo ratings yet
- Stock 16042022Document81 pagesStock 16042022NeetuNo ratings yet
- Production of BioplasticDocument5 pagesProduction of BioplasticNatsu DragoneelNo ratings yet
- Section 1 GeneralDocument612 pagesSection 1 GeneralM Ramzi100% (2)
- Wood Biodeterioration and PreservationDocument3 pagesWood Biodeterioration and Preservationthelostboy undomielNo ratings yet