Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Discovering Cells - GR 7 Lesson Notes
Discovering Cells - GR 7 Lesson Notes
Uploaded by
Jung Ahn HongOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Discovering Cells - GR 7 Lesson Notes
Discovering Cells - GR 7 Lesson Notes
Uploaded by
Jung Ahn HongCopyright:
Available Formats
CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION TO CELLS
LESSON 1: DISCOVERING CELLS
Learning Objectives
1. Tell what cells are.
2. Describe how scientists first observed cells and developed the cell theory
3. Describe how microscopes produce magnified images
What Are Cells?
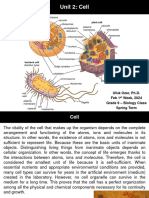
Cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things.
Every organism is made up of one or more cells, and each cell can carry out the
basic functions that let it live, grow, and reproduce.
Those functions can include obtaining food, water, and oxygen, secreting wastes,
and reproducing by division.
What Is the Cell Theory?
The cell theory explains the relationship between cells and living things.
It was developed about two hundred years after the invention of the microscope.
The cell theory states the following:
1. All living things are made up of cells.
2. Cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things.
3. All cells are produced from other cells.
How Do Microscopes Work?
Most cells are too small to be seen by the human eye, so the development of the
cell theory depended on observations made through microscopes.
Some microscopes focus light through lenses to produce a magnified image, and
other microscopes use beams of electrons.
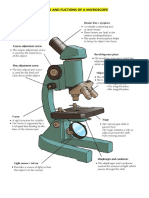
A compound microscope uses two lenses and focuses light from a lamp or
reflected from a mirror.
This type of microscope is often used in classrooms.
You can estimate the true size of an enlarged object by measuring the width of
the circular field visible through the microscope and comparing the size of the
object to the width of the field.
Objects viewed through a microscope are also more detailed than when viewed
with the naked eye.
Microscopes improve resolution, the ability to distinguish separate structures that
are close together.
Electron microscopes have better resolution and magnification than light
microscopes.
You might also like
- Cell StructureDocument16 pagesCell StructureExequiel Macalisang Ramientos Jr.No ratings yet
- B 10 VRV 3071Document24 pagesB 10 VRV 3071api-283593849No ratings yet
- 7 1powerpointeDocument25 pages7 1powerpointeapi-261447125No ratings yet
- Organic CompondsDocument55 pagesOrganic CompondsHappy Monamaladi Sibahle MoepyaNo ratings yet
- Class IX Biology Book Chapter 02Document21 pagesClass IX Biology Book Chapter 02myNoteslibrary50% (2)
- GS Group WorkDocument26 pagesGS Group Worknathanwolle.njnjNo ratings yet
- Estructura de La Celula1Document61 pagesEstructura de La Celula1Williams AlexanderNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document16 pagesChapter 1Anis PuadahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Cell StructureDocument7 pagesChapter 1 Cell StructureMerimaNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology: Science Explorer - Cells and HeredityDocument242 pagesCell Biology: Science Explorer - Cells and HeredityZeinab ElkholyNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument2 pagesBiologylishaleo3No ratings yet
- Mad21975 ch03Document22 pagesMad21975 ch03Aulia AmaniNo ratings yet
- IB Biology Microscope Cell LabDocument3 pagesIB Biology Microscope Cell LabJustin Closet Boy VargheseNo ratings yet
- Cell and Cell TheoryDocument13 pagesCell and Cell TheoryAnaJeanJumawidMaranan100% (1)
- Science Chapter 1Document13 pagesScience Chapter 1Asia BibiNo ratings yet
- BSB 113 Biology of Cells-notes-August 2018Document47 pagesBSB 113 Biology of Cells-notes-August 2018Thabo ChuchuNo ratings yet
- Significance of Microscopy in Cell BiologyDocument10 pagesSignificance of Microscopy in Cell BiologyAbeer FatimaNo ratings yet
- READING Chapter 7.1 Life Is CellularDocument3 pagesREADING Chapter 7.1 Life Is Cellularkathryn_bruyère100% (1)
- Chapter 1 (Introduction To Cell)Document38 pagesChapter 1 (Introduction To Cell)hilmanNo ratings yet
- Biology Laboratory Lab ReportDocument6 pagesBiology Laboratory Lab ReportNURUL AZZAHNo ratings yet
- Unit C-Chapter 8 PowerpointDocument66 pagesUnit C-Chapter 8 Powerpointm_frajman100% (1)
- Cell and OrganellesDocument49 pagesCell and Organellesbiri.melisa.105No ratings yet
- Lab Report 2 by Xheni KuqoDocument8 pagesLab Report 2 by Xheni KuqoXheniNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY AL - Cell StructureDocument44 pagesBIOLOGY AL - Cell StructureSmile4 UNo ratings yet
- EukaryotaDocument5 pagesEukaryotaMartina BugejaNo ratings yet
- 1 The Light MicroscopeDocument16 pages1 The Light Microscopeapi-335157422No ratings yet
- Bio Adv CC CH 03 - Cell Biology - Answer Keys (10.03.15)Document29 pagesBio Adv CC CH 03 - Cell Biology - Answer Keys (10.03.15)Margie OpayNo ratings yet
- Histo CompilationDocument217 pagesHisto CompilationNico LokoNo ratings yet
- The Discovery of Cells: Cell Theory EmergesDocument53 pagesThe Discovery of Cells: Cell Theory EmergesRohunGuptaNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and Function NotesDocument8 pagesCell Structure and Function NotesShiloh FrederickNo ratings yet
- L 6 GP CX 5 U IFCf Wod DX 38 WDocument22 pagesL 6 GP CX 5 U IFCf Wod DX 38 WAradhana GuptaNo ratings yet
- D. Chapter 2 - Life in A Cell (Lesson 2.1 and 2.2)Document66 pagesD. Chapter 2 - Life in A Cell (Lesson 2.1 and 2.2)klayncantos543No ratings yet
- Sci7 Q2Document3 pagesSci7 Q2Choco YeyNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1 Module FinalDocument56 pagesGeneral Biology 1 Module FinaldautongjonathanjoseNo ratings yet
- Pastel Yellow Simple Illustrative English Word Choice and Connotations PresentationDocument15 pagesPastel Yellow Simple Illustrative English Word Choice and Connotations PresentationKeerthi SureshNo ratings yet
- BIO Lab 5Document10 pagesBIO Lab 5Antonio WilloughbyNo ratings yet
- Taller Microscopia 1Document46 pagesTaller Microscopia 1Erika PereaNo ratings yet
- Discovering Cells NotesDocument14 pagesDiscovering Cells Notesava nortonNo ratings yet
- Cell TheoryDocument6 pagesCell TheorySiang KeeNo ratings yet
- Module 3A: Cell Structure: 3.1 Studying CellsDocument22 pagesModule 3A: Cell Structure: 3.1 Studying CellsDiane Balaba OsingNo ratings yet
- Week 15 StudentDocument9 pagesWeek 15 StudentSilviya HongNo ratings yet
- Lab Report Boi206Document21 pagesLab Report Boi206Ainul BatrisyiaNo ratings yet
- Laporan Cara Menggunakan MikroskopDocument12 pagesLaporan Cara Menggunakan MikroskopTya AmaliahNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Cell BiologyDocument7 pagesUnit 3 Cell BiologyQaran PrintingNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER1 CellBiologyDocument59 pagesCHAPTER1 CellBiologymhrathodNo ratings yet
- The CellDocument8 pagesThe CellCasielle KyroffNo ratings yet
- How To Use A MicroscopeDocument1 pageHow To Use A MicroscopeSweetchoco 101No ratings yet
- Cell and MicroscopeDocument17 pagesCell and MicroscopeEsad ZlaticNo ratings yet
- Chap 4 Long QA Bio 9thDocument17 pagesChap 4 Long QA Bio 9thSub2 PromoteNo ratings yet
- Gen. ZoologyDocument13 pagesGen. ZoologyJulia ReignNo ratings yet
- Chapter6 - A Tour of The CellDocument20 pagesChapter6 - A Tour of The CellOsannah IrishNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Cells - 241023Document70 pagesUnit 1 Cells - 241023DAN DNANo ratings yet
- Table of ContentsDocument9 pagesTable of ContentsTSha MeunierNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 1 - IB Biology Cell LabDocument15 pagesLab Report 1 - IB Biology Cell LabNada SalmanNo ratings yet
- Basic Microscopy: Are There Aliens Among Us?Document11 pagesBasic Microscopy: Are There Aliens Among Us?cormacNo ratings yet
- Biology: The CellDocument55 pagesBiology: The CellMa'am AnjNo ratings yet
- Class 10th CELL CHAPTR Biology NotesDocument27 pagesClass 10th CELL CHAPTR Biology NotesBlue RaysNo ratings yet
- Bio 6 Chapter Notes FSC IstDocument151 pagesBio 6 Chapter Notes FSC IstThe QuestNo ratings yet
- Different Kinds of Microscopes and Their UsesDocument9 pagesDifferent Kinds of Microscopes and Their UsesJhon Carlo Bataller Monleon100% (1)