Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Endocrine System Pt. 1
Endocrine System Pt. 1
Uploaded by
PD - 12ZZ 810951 The Woodlands SSOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Endocrine System Pt. 1
Endocrine System Pt. 1
Uploaded by
PD - 12ZZ 810951 The Woodlands SSCopyright:
Available Formats
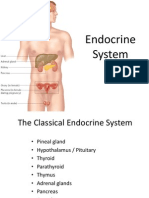
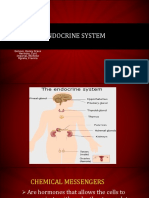
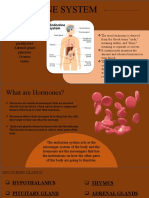
Endocrine System
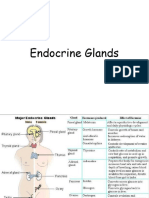
❖ Endocrine system: a network of glands/organs that secrete and produce hormones into
the bloodstream (maintains homeostasis in the body)
➢ Examples include: Pineal gland, hypothalamus, thyroid gland and the thymus
❖ Hypothalamus: Is a neuroendocrine system
➢ Link between the nervous system and endocrine system
❖ Regulates the pituitary gland
❖ Maintains homeostasis by controlling body temperature, hunger, etc
❖ Pituitary gland: Located at the base of the brain below the hypothalamus, regulates
many other endocrine glands
➢ Anterior pituitary produces and releases several hormones
➢ Posterior pituitary does not produce hormones itself but stores and releases
hormones
❖ The hypothalamic-pituitary portal system
➢ This connection allows the hypothalamus to control and regulate the release of
hormones from the pituitary gland.
❖ Thyroid Gland: Located in the front of the neck, just below the larynx
➢ Produces and releases hormones that regulate metabolism, growth and
development (thyroxine and calcitonin)
➢ Disorders
■ Hypothyroidism: insufficient thyroid hormones
■ Hyperthyroidism: excessive thyroid hormones
❖ Parathyroid Glands: Located in the neck, two on each side of the thyroid gland
➢ Mainly produces parathyroid hormone (PTH) which regulates calcium and
phosphate levels in the blood
➢ Disorders
■ Hyperparathyroidism: Excessive amounts of PTH (Kidney stones)
■ Hypoparathyroidism: insufficient amounts of PTH (Neurological symptoms)
❖ Adrenal Glands: located on top of each kidney
➢ Outer adrenal cortex: produces steroid hormones (corticosteroids) (cortisol, DHEA,
aldosterone)
➢ Inner adrenal medulla: produces catecholamines (fight or flight hormones)
➢ Regulated by the hypothalamus and pituitary gland
➢ Disorders
■ Addison’s disease: underproduction of cortisol
■ Cushingès syndrome: overproduction of cortisol
■ Hormone replacement therapy might be necessary
❖ Pancreas: Located behind the stomach
You might also like
- Endocrine SystemDocument96 pagesEndocrine SystemSandhya Kakkar100% (3)
- Endocrine System 2017Document28 pagesEndocrine System 2017cyber sec100% (1)
- Endocrine System PDFDocument59 pagesEndocrine System PDFHoney Grace GenoveNo ratings yet
- Ch2 NEW Anatomy of The Endocrine System - PPTX Updated - PPTX UpdatedDocument10 pagesCh2 NEW Anatomy of The Endocrine System - PPTX Updated - PPTX UpdatedAaysha NiyasNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System PPT Session 12-13Document35 pagesEndocrine System PPT Session 12-13Lawrence Genelago GamboaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System PPT Session 12-13Document35 pagesEndocrine System PPT Session 12-13LawrenceNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine System Lesson 1Document44 pagesThe Endocrine System Lesson 1Heaven Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Lesson 10 Endocrine SystemDocument12 pagesLesson 10 Endocrine SystemBai Donna S. AlimanNo ratings yet
- Endocrine and SecretionsDocument25 pagesEndocrine and SecretionsNelson Louie III RicerraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 Endocrine System NotesDocument12 pagesChapter 13 Endocrine System NotesJane XuNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine System GlandsDocument26 pagesThe Endocrine System Glandsidio valensiaNo ratings yet
- "Endocrine System": Human Anatomy and Physiology IiDocument74 pages"Endocrine System": Human Anatomy and Physiology IiJethro JasneyNo ratings yet
- Choral ReadingDocument2 pagesChoral ReadingDina GuitguitenNo ratings yet
- Lecture 20, Ch. 45Document12 pagesLecture 20, Ch. 45S. SpencerNo ratings yet
- EndocrineDocument70 pagesEndocrinehamidNo ratings yet
- Glands MDCAT PresentationDocument65 pagesGlands MDCAT PresentationGhulam zahraNo ratings yet
- Hormones (Basic+Advanced)Document30 pagesHormones (Basic+Advanced)Shubhasish KumarNo ratings yet
- 21 Endocrine SystemDocument66 pages21 Endocrine SystemAshok Kumar100% (1)
- Endocrine SystemDocument43 pagesEndocrine SystemJeanette RiosNo ratings yet
- Chemical Coordination and Integration by - Dr. Sunita SaxenaDocument66 pagesChemical Coordination and Integration by - Dr. Sunita SaxenaDivya AgarawalNo ratings yet
- Introduction To EndocrinologyDocument53 pagesIntroduction To EndocrinologyAli ArainNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System Anatomy Hypothalamus, Pituitary, and Pineal GlandsDocument66 pagesEndocrine System Anatomy Hypothalamus, Pituitary, and Pineal GlandsdeeznutsnikkaballzNo ratings yet
- 3 HypothalamusDocument12 pages3 HypothalamusRana AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - The Endocrine System - FinalDocument57 pagesChapter 5 - The Endocrine System - FinalKharrel YballeNo ratings yet
- Anfis EndokrinDocument14 pagesAnfis Endokrinyolanda merinskyNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System GlandsDocument40 pagesEndocrine System GlandsSolita PorteriaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine DisordersDocument26 pagesEndocrine DisordersCrisia GungobNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument16 pagesEndocrine SystemJelyn Rose CuetoNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System/socialDocument33 pagesEndocrine System/socialrpant3165No ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument15 pagesEndocrine SystemNyakie MotlalaneNo ratings yet
- Chemical Coordination & Integration PowernotesDocument3 pagesChemical Coordination & Integration PowernotesSushmit SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Corticotropins and GonadotropinsDocument39 pagesCorticotropins and GonadotropinsSudhakar LakavathNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument15 pagesEndocrine Systemreema69929No ratings yet
- Control and Coordination Animal HormonesDocument46 pagesControl and Coordination Animal HormonesgolaNo ratings yet
- Primary Endocrine Organs Hypothalamus & Pituitary Gland: Regulate Many Body SystemsDocument5 pagesPrimary Endocrine Organs Hypothalamus & Pituitary Gland: Regulate Many Body SystemsGizem OsmanogluNo ratings yet
- HAPP Endocrine SystemDocument39 pagesHAPP Endocrine SystemDanes PaguioNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument14 pagesEndocrine SystemJhon AmorNo ratings yet
- Pituitary Gland: Prepared by Yousaf KhanDocument19 pagesPituitary Gland: Prepared by Yousaf KhanSalman KhanNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine System:: Chemical Signals in AnimalsDocument13 pagesThe Endocrine System:: Chemical Signals in AnimalsbobNo ratings yet
- HomeostasisDocument51 pagesHomeostasisKarla HyltonNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System IntroductionDocument8 pagesEndocrine System IntroductionAlchemi Mij PoolscanNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System - Class - 10 - Icse.Document2 pagesEndocrine System - Class - 10 - Icse.zoha afshanNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument16 pagesEndocrine SystemYoudonumeNo ratings yet
- Endocrine PhysiologyDocument26 pagesEndocrine Physiologysam bossaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1.2 The Endocrine System CompleteDocument71 pagesLesson 1.2 The Endocrine System CompletesoriamarheenakatrineNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System GlandsDocument40 pagesEndocrine System Glandsqty9jgkpnzNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Glands and Hormones2Document6 pagesEndocrine Glands and Hormones2sugandhdon77No ratings yet
- Farmacoendocrino 2008Document58 pagesFarmacoendocrino 2008Eduardo ValdezNo ratings yet
- ENDOCRINE Systems Ad Its DisordersDocument21 pagesENDOCRINE Systems Ad Its DisordersAmir PermitivoNo ratings yet
- EndocrineDocument3 pagesEndocrinePotato HeadNo ratings yet
- Review - Animal Endocrine SystemDocument3 pagesReview - Animal Endocrine SystemkjhNo ratings yet
- EndocrineDocument7 pagesEndocrineKharrel YballeNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument43 pagesEndocrine Systemwieka mawieNo ratings yet
- The Role of HormonesDocument22 pagesThe Role of HormonesHidayah Sanusi100% (1)
- Endocrine System-Made Up of Glands, Hormones Secretes & ProducersDocument2 pagesEndocrine System-Made Up of Glands, Hormones Secretes & ProducersLUISE DANIELLA DELOS REYES DOLOTALLASNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System PDFDocument86 pagesEndocrine System PDFsheryl dungogNo ratings yet
- Functional Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument38 pagesFunctional Anatomy and PhysiologyNawalNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine System NotesDocument6 pagesThe Endocrine System NotesRohit AnthuliaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument29 pagesEndocrine Systemcgkiran_kumarNo ratings yet
- TypesDocument2 pagesTypesPD - 12ZZ 810951 The Woodlands SSNo ratings yet
- Types of HoDocument2 pagesTypes of HoPD - 12ZZ 810951 The Woodlands SSNo ratings yet
- Hormones IntroDocument1 pageHormones IntroPD - 12ZZ 810951 The Woodlands SSNo ratings yet
- Feedback LoopsDocument1 pageFeedback LoopsPD - 12ZZ 810951 The Woodlands SSNo ratings yet