Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pharmmanuf. Transdermal Drug Delivery Systems
Pharmmanuf. Transdermal Drug Delivery Systems
Uploaded by
Denzyl Ann Laguit0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pagesTransdermal drug delivery systems (TDDS) are dosage forms designed to deliver drugs through the skin for systemic circulation. They consist of a drug reservoir between a backing layer and adhesive layer. Drugs are delivered across the stratum corneum at a controlled rate. TDDS offer advantages over oral routes like avoidance of gastrointestinal absorption/first pass effects and provide extended therapy with a single application but are only suitable for potent drugs. Examples of FDA approved TDDS include patches for scopolamine, nitroglycerin, clonidine, nicotine, and hormones.
Original Description:
Transdermal Drug Delivery Systems
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentTransdermal drug delivery systems (TDDS) are dosage forms designed to deliver drugs through the skin for systemic circulation. They consist of a drug reservoir between a backing layer and adhesive layer. Drugs are delivered across the stratum corneum at a controlled rate. TDDS offer advantages over oral routes like avoidance of gastrointestinal absorption/first pass effects and provide extended therapy with a single application but are only suitable for potent drugs. Examples of FDA approved TDDS include patches for scopolamine, nitroglycerin, clonidine, nicotine, and hormones.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pagesPharmmanuf. Transdermal Drug Delivery Systems
Pharmmanuf. Transdermal Drug Delivery Systems
Uploaded by
Denzyl Ann LaguitTransdermal drug delivery systems (TDDS) are dosage forms designed to deliver drugs through the skin for systemic circulation. They consist of a drug reservoir between a backing layer and adhesive layer. Drugs are delivered across the stratum corneum at a controlled rate. TDDS offer advantages over oral routes like avoidance of gastrointestinal absorption/first pass effects and provide extended therapy with a single application but are only suitable for potent drugs. Examples of FDA approved TDDS include patches for scopolamine, nitroglycerin, clonidine, nicotine, and hormones.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
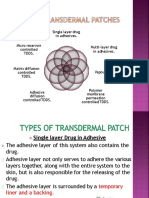
TRANSDERMAL DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEMS TYPES OF TDDS
Chapter 9 MONOLITHIC SYSTEM
Percutaneous Absorption A TDDS that incorporates a drug matrix between backing and
It refers to the direct penetration of the drug through the frontal layers
stratum corneum Examples
The stratum corneum is a 10-15 mm thick layer of flat, Salonpas
partially dessicated nonliving tissue. Band-aid
It is composed of approximately 40% protein [keratin], 40% MEMBRANE-CONTROLLED SYSTEM
water, with the balance being lipid [principally as A TTDS designed to contain a drug reservoir [or a pouch
triglycerides, free fatty acids, cholesterol and phospholipids]. usually in liquid or gel form], a rate-controlling membrane
FACTORS AFFECTING PERCUTANEOUS ABSORPTION and backing, adhesive and protective layer
Hydration of the skin generally favors percutaneous COMPONENTS OF TDDS
absorption. BACKING LAYER
Generally, the longer the TDDS is permitted to remain in An occlusive backing membrane to protect the system from
contact with the skin, the greater is the total drug absorption. environmental entry and from loss of drug from the system
More of the drug is absorbed when the TDDS is applied to a or moisture from the skin
large surface area. DRUG RESERVOIR/MATRIX SYSTEM
PERCUTANEOUS ABSORPTION ENHANCERS A system to store and release the drug at the skin site
CHEMICAL ENHANCERS RELEASE LINER/PROTECTIVE LINER
A chemical skin penetration enhancer increases skin It is removed from the system prior to application and
permeability by reversibly damaging or altering the enables drug release
physicochemical nature of the stratum corneum to reduce ADHESIVE LAYER
its diffusional resistance. A layer used to maintain contact with the skin after
IONTOPHORESIS application
Is a delivery of a charged chemical compound across the skin Types
membrane using an electric field Peripheral adhesive
Examples - Contains adhesive around the outer edges of the TDDS
Lidocaine Face adhesive
- Covers the entire face of the TDDS
Dexamethasone
Polybutyl acrylate is the commonly used adhesive in TDDS
Amino acids, peptides and insulin
ADVANTAGES OF TDDS
Verapamil
Can avoid gastrointestinal absorption difficulties
Propranolol Can substitute for oral administration of medication when
Percutaneous Absorption that route is unsuitable
Enhancers Avoid first pass effect
SONOPHORESIS Non-invasive
Involves the use of high-frequency ultrasound to enhance Provide extended therapy with a single application
DISADVANTAGES OF TDDS
transdermal drug delivery
o Only relatively potent drugs are suitable candidates for
Examples
transdermal delivery
Hydrocortisone
o Some patients may develop contact dermatitis at the site of
Lidocaine
application
Salicylic acid
EXAMPLES OF TDDS
TRANSDERMAL DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEMS
TDDS OR TRANSDERMAL PATCHES Transdermal Scopolamine
Are dosage forms designed to support the passage of drug The first TDDS to receive FDA approval
substances from the surface of the skin through its various A belladonna alkaloid used to prevent travel-related motion
layers and into the systemic circulation sickness and the nausea and vomiting that result from the
use of certain anesthetics and analgesics in surgery
It is worn in a hairless area behind the ear
Transdermal Nitroglycerin
Used widely in the prophylactic treatment of angina
Placed in the chest, back, upper arms or shoulders
The site should be free of hair, clean and dry
Transdermal Clonidine
The first TDDS for hypertension
It is applied to a hairless area of intact skin on the upper
outer arm or chest
Transdermal Nicotine
Are used as adjuncts in smoking cessation programs
It is applied to the arm or upper front torso
Transdermal Estradiol
It is indicated for the treatment of moderate to severe
vasomotor symptoms associated with menopause, female
hypogonadism, female castration, primary ovarian failure and
atrophic conditions caused by deficient estrogen production
It is applied to a clean, dry area of the skin on the body trunk,
either the abdomen or upper quadrant of the buttocks
Transdermal Testosterone
Used as hormone replacement therapy in men who have an
absence or deficiency of testosterone
It is applied to a clean, dry scrotal skin that has been dry-
shaved
It is also applied to a clean, dry, unbraided area of the skin of
the back, abdomen, upper arms or thighs
Transdermal Contraceptive System
It contains norelgestromin and ethinyl estradiol indicated for
family planning
Other TransdermalTherapeutic Systems
Diltiazem, ISDN, propranolol, nifedipine, mepindololand
verapamil for cardiovascular problems
Levenorgestrel with estradiol for hormonal contraception
Physostigmine and xanomeline for Alzheimer’s disease
Naltrexone and methadone for substance addiction
Buspirone for anxiety
Bupropion for smoking cessation
Papaverine for male impotence
GENERAL CONSIDERATIONS IN THE USE OF TDDS
There is a preferred site of application for every TDDS
product
They are applied to clean, dry skin areas, relatively
free from hair, oil, irritation, inflammation, abrasion or
callous
Use of skin lotions should be avoided at the application site
TDDS should not be physically altered by cutting
A TDDS should be removed from its protective package, being
careful not to tear or cut-off the unit
It should be placed at a site that is not subject to being
rubbed off by clothing or movement
It should be worn for the full period of time stated in the
product’s instructions
The user’s should clean their hands thoroughly before and
after applying a TDDS
If the patient exhibits sensitivity or intolerance to the TDDS,
he should seek reevaluation
Upon removal, a used TDDS should be folded in half with the
adhesive layer together so that it cannot be re-used
You might also like
- Chapter 11 - Transdermal Drug Delivery SystemDocument4 pagesChapter 11 - Transdermal Drug Delivery SystemYoreeNo ratings yet
- Principle of Topical Agent-FzpDocument16 pagesPrinciple of Topical Agent-FzpMurwani LatifahNo ratings yet
- 03.transdermal Drug Delivery SystemsDocument56 pages03.transdermal Drug Delivery SystemsMoganaa LakshmiNo ratings yet
- Transdermal Drug Delivery SystemsDocument6 pagesTransdermal Drug Delivery SystemsKim Manlangit100% (1)
- Transdermal Drug Delivery SystemDocument45 pagesTransdermal Drug Delivery Systemphd0780No ratings yet
- Poonam PPT FinalDocument15 pagesPoonam PPT Finalpooam_rktNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Transdermal Drug Delivary System (1)Document42 pagesUnit 4 Transdermal Drug Delivary System (1)Randa OmdaNo ratings yet
- Formulation and Evaluation of Transdermal PatchDocument4 pagesFormulation and Evaluation of Transdermal PatchMelissa STanNo ratings yet
- A Basic Overview On Transdermal Drug Delivery SystemDocument9 pagesA Basic Overview On Transdermal Drug Delivery SystemEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Transdermal Drug DeliveryDocument38 pagesTransdermal Drug DeliveryJhansi SattiNo ratings yet
- 1.topical and Transdermal Drug Delivery SystemDocument101 pages1.topical and Transdermal Drug Delivery SystemRao Salman LatifNo ratings yet
- Formulation and Evaluation of Transdermal Patch of Diclofenac SodiumDocument4 pagesFormulation and Evaluation of Transdermal Patch of Diclofenac SodiumM Dwiyan RilandiNo ratings yet
- Transdermal Drug Delivery System: Shirode Rahul ADocument37 pagesTransdermal Drug Delivery System: Shirode Rahul AFrancisco MarcanoNo ratings yet
- Transdermal: Drug Delivery SystemsDocument33 pagesTransdermal: Drug Delivery SystemsRazda RangrageNo ratings yet
- Transdermal Drug Delivery System: A Review: The Pharma InnovationDocument10 pagesTransdermal Drug Delivery System: A Review: The Pharma InnovationAlfiyana YuniarNo ratings yet
- 40 Oct 9507Document22 pages40 Oct 9507bipasha rayNo ratings yet
- Introductio N: Transdermal Drug Delivery SystemDocument15 pagesIntroductio N: Transdermal Drug Delivery SystemsahilmunjalpharmaNo ratings yet
- Phardose - Transdermal Drug Delivery SystemDocument25 pagesPhardose - Transdermal Drug Delivery SystemEdrick RamoranNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Transdermal Drug Delivery SystemDocument3 pagesChapter 11 Transdermal Drug Delivery SystemluisynonNo ratings yet
- Transdermal Drug Delivery SystemsDocument28 pagesTransdermal Drug Delivery Systemsvalentine mhuteNo ratings yet
- Thesis 2Document49 pagesThesis 2Kalyan Reddy AnuguNo ratings yet
- Transdermal OpoidsDocument6 pagesTransdermal OpoidsSau Yee ChowNo ratings yet
- Transdermal Drug Delivery System: A Review: The Pharma InnovationDocument10 pagesTransdermal Drug Delivery System: A Review: The Pharma InnovationdianNo ratings yet
- The Structure of Skin and Transdermal Drug Delivery System-A ReviewDocument7 pagesThe Structure of Skin and Transdermal Drug Delivery System-A ReviewTira MaharaniNo ratings yet
- Development and Characterization of Transdermal Therapeutics System of Tramadol HydrochlorideDocument5 pagesDevelopment and Characterization of Transdermal Therapeutics System of Tramadol HydrochlorideMuhammad SikandarNo ratings yet
- Transdermal Drug Delivery System: Shirode Rahul ADocument37 pagesTransdermal Drug Delivery System: Shirode Rahul Aنور الهدىNo ratings yet
- Ijresm V2 I11 23Document6 pagesIjresm V2 I11 23Prema SenthilkumarNo ratings yet
- PatchesDocument50 pagesPatches2zxhy7mngkNo ratings yet
- Transdermal Drug Delivery System A RevieDocument12 pagesTransdermal Drug Delivery System A RevieMrunali Porete CSE-11No ratings yet
- Formulation and Characterization of Naproxen Transdermal Patch For Sustained Drug Delivery SystemDocument5 pagesFormulation and Characterization of Naproxen Transdermal Patch For Sustained Drug Delivery SystemBang AthanNo ratings yet
- Trans Dermal Drug DeliveryDocument47 pagesTrans Dermal Drug Deliverysouvik maitiNo ratings yet
- Biofar 2 PDFDocument7 pagesBiofar 2 PDFFadilah Mode JemberNo ratings yet
- Dermatologic Pharmacology 1Document7 pagesDermatologic Pharmacology 1Nikko Angelo AlcalaNo ratings yet
- Dermatological Pharmacology Topical AgentsDocument5 pagesDermatological Pharmacology Topical AgentsYilianeth Mena DazaNo ratings yet
- Transdermal BioavalibilityDocument13 pagesTransdermal BioavalibilityRizqon MukhaddamNo ratings yet
- Transdermal Drug Delivery System A ReviewDocument6 pagesTransdermal Drug Delivery System A ReviewEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Transdermal Drug Delivery Systems: By: Tsegaye N (B. Pharm., MSC)Document62 pagesTransdermal Drug Delivery Systems: By: Tsegaye N (B. Pharm., MSC)Tsegaye NigussieNo ratings yet
- Transdermal Drug Delivery - TaggedDocument39 pagesTransdermal Drug Delivery - TaggedHadeelNo ratings yet
- Get The Edge in A Competitive Environment.: Transdermal Drug DeliveryDocument11 pagesGet The Edge in A Competitive Environment.: Transdermal Drug DeliverysmswamyNo ratings yet
- Transdermal Drug Delivery System - PendahuluanDocument18 pagesTransdermal Drug Delivery System - PendahuluanRizqon MukhaddamNo ratings yet
- Transdermal Drug Delivery System (TDDS) : Advanced Pharmaceutics Chapter No. 6Document74 pagesTransdermal Drug Delivery System (TDDS) : Advanced Pharmaceutics Chapter No. 6SHAHIQNo ratings yet
- Transdermal Drug DeliveryDocument37 pagesTransdermal Drug Deliveryabdullah2020No ratings yet
- Transdermal Drug Delivery System ReviewDocument8 pagesTransdermal Drug Delivery System ReviewParth SahniNo ratings yet
- TDDS #Document52 pagesTDDS #britoraj100% (2)
- Transdermal Drug Delivery System1Document38 pagesTransdermal Drug Delivery System1shobhitNo ratings yet
- Transdermal Drug Delivery SystemDocument47 pagesTransdermal Drug Delivery SystemMridul AroraNo ratings yet
- Yadav 2012Document8 pagesYadav 2012Fhyrdha Slaluw ZetiaaNo ratings yet
- Geeta AggarwalDocument9 pagesGeeta Aggarwalkhanaijaza129397No ratings yet
- Transdermal Drug Delivery System: A Review: IJPSR (2016), Vol. 7, Issue 6 (Review Article)Document17 pagesTransdermal Drug Delivery System: A Review: IJPSR (2016), Vol. 7, Issue 6 (Review Article)Rashmii BoppunaNo ratings yet
- 7 Transdermal Drug Delivery SystemDocument59 pages7 Transdermal Drug Delivery Systemwikako9357No ratings yet
- A Novel Approach Transdermal GelDocument10 pagesA Novel Approach Transdermal GelTira MaharaniNo ratings yet
- Semisolid Dosage FormDocument77 pagesSemisolid Dosage FormMonyratanak LimNo ratings yet
- Pharma - SkinDocument8 pagesPharma - Skinreference books100% (1)
- Single Layer Drug in Adhesives. Multi-Layer Drug in Adhesives. Micro Reservoir Controlled TddsDocument47 pagesSingle Layer Drug in Adhesives. Multi-Layer Drug in Adhesives. Micro Reservoir Controlled Tddsshamma shahulhameedNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument18 pagesIntroductionsai projectNo ratings yet
- PHD211 Plaster and PatchesDocument2 pagesPHD211 Plaster and Patches2022823764No ratings yet
- Transdermal Drug Delivery Patches: A ReviewDocument9 pagesTransdermal Drug Delivery Patches: A ReviewAnii VoierfflichhNo ratings yet
- Hyper-Pigmentation Of The Skin A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment, And Related ConditionsFrom EverandHyper-Pigmentation Of The Skin A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment, And Related ConditionsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Pharmmanuf. Formulation of Sterile ProductsDocument2 pagesPharmmanuf. Formulation of Sterile ProductsDenzyl Ann LaguitNo ratings yet
- Pharmmanuf. Formulation of Liquids and SuspensionDocument6 pagesPharmmanuf. Formulation of Liquids and SuspensionDenzyl Ann LaguitNo ratings yet
- Pharmmanuf. Formulation of TabletsDocument3 pagesPharmmanuf. Formulation of TabletsDenzyl Ann LaguitNo ratings yet
- Hospitalpharm. The Hospital Pharmacy DepartmentDocument3 pagesHospitalpharm. The Hospital Pharmacy DepartmentDenzyl Ann LaguitNo ratings yet
- Pharmmanuf. Formulationof Medicated ApplicationsDocument4 pagesPharmmanuf. Formulationof Medicated ApplicationsDenzyl Ann LaguitNo ratings yet
- Pharmmanuf. Formulation of Pharmaceutical AerosolsDocument3 pagesPharmmanuf. Formulation of Pharmaceutical AerosolsDenzyl Ann LaguitNo ratings yet
- Pharmmanuf. Formulation of CapsulesDocument2 pagesPharmmanuf. Formulation of CapsulesDenzyl Ann LaguitNo ratings yet