Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Unit 3 Short Answer Questions BJT
Unit 3 Short Answer Questions BJT
Uploaded by
JSS0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
35 views3 pages1) A transistor is a three terminal semiconductor device that can amplify or switch electronic signals and electrical power. It consists of two PN junctions placed back-to-back.
2) There are two main types of transistors - NPN and PNP, depending on whether the majority charge carriers are electrons or holes.
3) Transistors can be connected in three main configurations - common base (CB), common emitter (CE), or common collector (CC) - depending on which terminal is common to both the input and output circuits.
Original Description:
Original Title
UNIT 3 SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS BJT
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1) A transistor is a three terminal semiconductor device that can amplify or switch electronic signals and electrical power. It consists of two PN junctions placed back-to-back.
2) There are two main types of transistors - NPN and PNP, depending on whether the majority charge carriers are electrons or holes.
3) Transistors can be connected in three main configurations - common base (CB), common emitter (CE), or common collector (CC) - depending on which terminal is common to both the input and output circuits.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
35 views3 pagesUnit 3 Short Answer Questions BJT
Unit 3 Short Answer Questions BJT
Uploaded by
JSS1) A transistor is a three terminal semiconductor device that can amplify or switch electronic signals and electrical power. It consists of two PN junctions placed back-to-back.
2) There are two main types of transistors - NPN and PNP, depending on whether the majority charge carriers are electrons or holes.
3) Transistors can be connected in three main configurations - common base (CB), common emitter (CE), or common collector (CC) - depending on which terminal is common to both the input and output circuits.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
UNIT 3 SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS
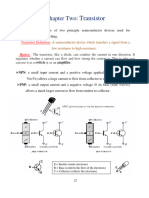
Question-1.What is a transistor?or Define BJT
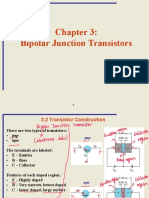
A junction transistor or BJT is simply a sandwich of one type of semiconductor material
between two layers of the other type. A transistor is a three terminal current controlled device. It
can be looked upon as two pn junction placed back to back. The three terminals are named as
emitter base & collector.
Question-2. What are the types of transistor?
The transistor may be NPN or PNP type. An NPN bipolar transistor is so called because the
outer layers are N-type semiconductors, while the base is a P-type. N stands for negative charge
carriers or electrons, and P for positive charge carriers or holes.
Question-3. What are the different configurations of transistor?
A transistor may be connected in three configurations namely: 1) Common Emitter (CE) 2)
Common Base (CB) 3) Common collector (CC)
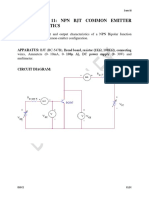
Question-4 What is Common Base configuration?
The common-base configuration (CB), base is common between input and output circuits. In
emitter-base terminal input signal is applied and in collector-base terminal output is taken from
it.
Question-5. What are the characteristics of CB?
since it has a low input resistance (30 ohms-160 ohms) and a high output resistance (250
kilohms-550 kilohms). However, two factors limit its usefulness in some circuit applications: (1)
its low input resistance and (2) its current gain of less than 1. Since the CB configuration will
give voltage amplification, and use in some microphone amplifiers. The input and output signals
in the common-base circuit are in phase.
Question-6 What is current gain for CB?
The current gain in the common-base circuit is the ratio of change in collector current(output
current ) to the change in emitter current(input current) at constant VCB . The term ALPHA (a)
is used for gain.
Question-7. What is input characteristic of CB?
Input Characteristics is , a graph of the base current IE versus VBE with constant VCB , which
is the voltage between the base and the collector, looks like that of an ordinary diode. IE
increases rapidly with small increase in VBE. The IE is almost independent of VCB.
Question-8. Output Characteristics of CB configuration?
Output characteristics are found by considering the collector loop. A graph of the collector
current IC versus the collector-base voltage VCB with constant IE. The IC varies with VCB only
at very low voltages (< 1 v). Beyond this value IC became constant and dependent upon only IE.
Question-9. What are the characteristics of CE configuration?
CE configuration has following characteristics: i) High voltage gain; ii) High current gain; iii)
Medium input impendence; and iV) Output impendence equal too the load resistance.
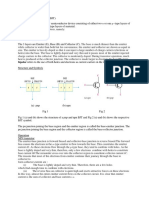
Question-10 What is CE configuration?
In common emitter or CE circuit, the base terminal of the transistor serves as the input, the
collector is the output, and the emitter is common to both, hence its name. It is used for
amplification. A small signal introduced into the base produces a larger signal at the output.
Question-11. What is transistor gain for CE configuration?
The transistor gain, or ?, is the ratio of the change of collector current IC to the change of base
current IB. The gain tells how much the input signal is amplified. It is a constant that depends on
the transistor type.
Question-12 Define Input Characteristics of CE configuration.
Input Characteristics, a graph of the base current IB versus VBE with constant VCE , which is
the voltage between the base and the emitter, looks like that of an ordinary diode. The current is
zero until VBE reaches 0.7 volts, where it then increases very suddenly.
Question-15. Define Output Characteristics of CE configuration?
Output characteristics are found by considering the collector loop. A graph of the collector
current IC versus the collector-emitter voltage VCE with constant IB. As VCE increases, IC will
remain zero and then suddenly shoot up when the voltage reaches a certain value, much the same
way as IB. Unlike IB, IC will remain constant as VCE increases.
Question-16. Define gain?
The term GAIN is used to describe the amplification capabilities of the amplifier. It is basically
a ratio of output versus input. Each transistor configuration gives a different value of gain even
though the same transistor is used.
Question-18. Applications of CE configuration?
In Low frequency voltage amplifier, in Radio, as a low-noise amplifiers, as a switch etc.
Question-19. What is the advantage of CE configuration?
The common-emitter configuration (CE) is the arrangement most frequently used in practical
amplifier circuits, since it provides good voltage, current, and power gain.
Question-20. What is the property of CE transistor?
The input signal to the common emitter goes positive when the output goes negative; the two
signals (input and output) are 180 degrees out of phase. The common-emitter circuit is the only
configuration that provides a phase reversal.
Question-21. Difference among CB, CE, and CC in terms of gain?
The current gain of CC is higher than that in the common emitter, but it has a lower power gain
than either the common base or common emitter. Like the common base, the output signal from
the common collector is in phase with the input signal
You might also like
- Flash Memories: Detlev RichterDocument287 pagesFlash Memories: Detlev RichterdarNo ratings yet
- Experiment: 5: AIM: Study of CB & CE Characteristics of Transistor TheoryDocument5 pagesExperiment: 5: AIM: Study of CB & CE Characteristics of Transistor TheorysanjuNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 - BJTDocument17 pagesLesson 5 - BJTPavan G MNo ratings yet
- BJTDocument34 pagesBJTPratik BhattNo ratings yet
- Course Code & Title - 19ecc03/ Analog ElectronicsDocument122 pagesCourse Code & Title - 19ecc03/ Analog ElectronicsSarinNo ratings yet
- Bipolar Junction TransistorDocument115 pagesBipolar Junction TransistorVince Silva100% (1)
- National University of Modern Languages: BJT As An Amplifier (Common Emitter)Document7 pagesNational University of Modern Languages: BJT As An Amplifier (Common Emitter)artistryrivalNo ratings yet
- Physics TransistorDocument11 pagesPhysics TransistorMajid KhanNo ratings yet
- CE, CB, CC Characteristics of TransistorDocument39 pagesCE, CB, CC Characteristics of TransistorMERUGA UDAYANo ratings yet
- Bee C4Document15 pagesBee C4ruchitaNo ratings yet
- BE Unit-II PDFDocument21 pagesBE Unit-II PDFJagadeesh KaruturiNo ratings yet
- الفصل 2tDocument23 pagesالفصل 2tmustafaasaad020No ratings yet
- 8 - Bipolar Junction TransistorDocument38 pages8 - Bipolar Junction TransistorShahnail MemonNo ratings yet
- Common Emitter ConfigurationDocument5 pagesCommon Emitter ConfigurationMoiz SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Experiment 11: NPN BJT Common Emitter CharacteristicsDocument7 pagesExperiment 11: NPN BJT Common Emitter CharacteristicsMalikAlrahabiNo ratings yet
- Taylor & Francis TemplateDocument25 pagesTaylor & Francis TemplateOlatomide OlaosebikanNo ratings yet
- BJT Written Report Group 8Document11 pagesBJT Written Report Group 8Jayvee GusenalemNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 10:: Biploar TransistorDocument21 pagesLecture - 10:: Biploar TransistorGEORGENo ratings yet
- Experiment 5Document5 pagesExperiment 5dummy008No ratings yet
- Transistor PPT ElecttronicsDocument77 pagesTransistor PPT ElecttronicsAnjali KumbharNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4. BJTPPTDocument52 pagesLecture 4. BJTPPTjthanikNo ratings yet
- PHY PROJ - SynopsisDocument13 pagesPHY PROJ - SynopsisPiyush HarlalkaNo ratings yet
- AP Lab 12Document7 pagesAP Lab 12muhammad arslanNo ratings yet
- Transistors and MOSFETDocument28 pagesTransistors and MOSFETUtkarsh ShuklaNo ratings yet
- 3.1 BJTransistors pt1 Rev2.3 LectDocument37 pages3.1 BJTransistors pt1 Rev2.3 LectShudermawan JarumanNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7 BJTTransistorsDocument15 pagesLesson 7 BJTTransistorsBlueprint MihNo ratings yet
- CH 3Document25 pagesCH 3avishek aviNo ratings yet
- ET 212 Electronics: Bipolar Junction TransistorsDocument29 pagesET 212 Electronics: Bipolar Junction TransistorsPaula JaneNo ratings yet
- BJTDocument22 pagesBJTAliyan TahirNo ratings yet
- Experiment 3: Common Emitter CharacteristicsDocument6 pagesExperiment 3: Common Emitter CharacteristicsAhmed SalehNo ratings yet
- Bipolar Junction TransistorsDocument38 pagesBipolar Junction TransistorsMuhammad AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Unit IIDocument18 pagesUnit IInagarajudbpNo ratings yet
- CH 1 Rev1 - Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJTS) - Syed PDFDocument53 pagesCH 1 Rev1 - Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJTS) - Syed PDFMuhammad Anaz'sNo ratings yet
- 20013122-034-EDC Lab Manual#10Document7 pages20013122-034-EDC Lab Manual#10Usama MughalNo ratings yet
- Slide 4 - Electronics (Transistors)Document48 pagesSlide 4 - Electronics (Transistors)Priyatharshan ViswanathanNo ratings yet
- Chapter Three32Document64 pagesChapter Three32mamoabera012No ratings yet
- Chapter ThreeDocument38 pagesChapter ThreeTolesa ShoreNo ratings yet
- Introduction To BJTDocument38 pagesIntroduction To BJTDave Harvey VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 BJTDocument5 pagesChapter 4 BJTBRIGHT TZZZY CHINGWENANo ratings yet
- Lesson On TransistorsDocument8 pagesLesson On TransistorsMalika BowlegNo ratings yet
- AE Unit - 2Document13 pagesAE Unit - 2aamirnasirNo ratings yet
- Transistor CharacteristicsDocument44 pagesTransistor Characteristicsnidhi100% (1)
- 1.5 Bipolar Junction TransistorDocument65 pages1.5 Bipolar Junction Transistor727723euee070No ratings yet
- Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJTS) Questions and AnswersDocument5 pagesBipolar Junction Transistors (BJTS) Questions and AnswersSuresh LNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 BJT2Document32 pagesLecture 3 BJT2MegaHertz_92No ratings yet
- Chapter Three ElectronicsDocument96 pagesChapter Three Electronicsamanuelfitsum589No ratings yet
- Theory For BJTDocument7 pagesTheory For BJTBenita AgbagwaraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Msbte Asked QuestionsDocument10 pagesChapter 3 Msbte Asked Questionsrutu surve (Ru.)No ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document45 pagesChapter 4api-394738731No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 2.1Document85 pagesChapter 3 2.1vipar snikeNo ratings yet
- 1-4 Coen 309Document20 pages1-4 Coen 309mahmoud sadiqNo ratings yet
- 3a BJT IntroductionDocument20 pages3a BJT IntroductionSyahmi AkmalNo ratings yet
- ECE 201 ch3Document56 pagesECE 201 ch3Senay MehariNo ratings yet
- Unit 6. Introduction To Bi-Polar Junction Transistor (BJT)Document9 pagesUnit 6. Introduction To Bi-Polar Junction Transistor (BJT)Gunjan GuptaNo ratings yet
- Analogue Electronic Design Module E EEE2039 / EEE2026 / EEE2042Document36 pagesAnalogue Electronic Design Module E EEE2039 / EEE2026 / EEE2042Arvish RamseebaluckNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2-BJT Applics and Feedback AmpliDocument37 pagesChapter 2-BJT Applics and Feedback Ampliramya hegdeNo ratings yet
- TransistorsDocument6 pagesTransistorsshuvrobhattacharya01No ratings yet
- Bipolar Junction TransistorDocument6 pagesBipolar Junction TransistorPadirikuppam PavithraNo ratings yet
- Publication 12 4449 82Document10 pagesPublication 12 4449 82Samz AdrianNo ratings yet
- Three Terminal, Three-Layered, Two-JunctionDocument61 pagesThree Terminal, Three-Layered, Two-JunctionGetahun shankoNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- LBYEC3P - Exp04 - Prelim ReportDocument6 pagesLBYEC3P - Exp04 - Prelim ReportJob BumanlagNo ratings yet
- SND Kod Dt2Document12 pagesSND Kod Dt2arturshenikNo ratings yet
- Cross Reference Mofset DSA0018459 PDFDocument6 pagesCross Reference Mofset DSA0018459 PDFDENIS_STARCOMNo ratings yet
- Bipolar TransistorDocument8 pagesBipolar TransistorfcmandiNo ratings yet
- Chittagong University of Engineering and TechnologyDocument8 pagesChittagong University of Engineering and Technologyirfan khanNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 10 Fundamentals of The Metal - Oxide - Semiconductor Field Effect TransistorDocument57 pagesCHAPTER 10 Fundamentals of The Metal - Oxide - Semiconductor Field Effect TransistorTAMILSELVI S S TAMILSELVI S SNo ratings yet
- ELEC 310: Microelectronic Circuits and Devices: LAB # 03: Bipolar Junction Transistor CharacteristicsDocument6 pagesELEC 310: Microelectronic Circuits and Devices: LAB # 03: Bipolar Junction Transistor CharacteristicsBerke KadıoğluNo ratings yet
- Bipolar Junction TransistorDocument20 pagesBipolar Junction TransistorChandra ReddyNo ratings yet
- 65Nm Logic Technology Featuring 35Nm Gate Lengths, Enhanced Channel Strain, 8 Cu Interconnect Layers, Low-K Ild and 0.57 PMZ Sram CellDocument4 pages65Nm Logic Technology Featuring 35Nm Gate Lengths, Enhanced Channel Strain, 8 Cu Interconnect Layers, Low-K Ild and 0.57 PMZ Sram CellVLSISD36 Edwin DominicNo ratings yet
- Central: CXT2907A Surface Mount PNP Silicon Transistor DescriptionDocument2 pagesCentral: CXT2907A Surface Mount PNP Silicon Transistor DescriptionJuan HernándezNo ratings yet
- Exam: MST - III - Nov-2021 - CS3CO29 - Digital ElectronicsDocument17 pagesExam: MST - III - Nov-2021 - CS3CO29 - Digital ElectronicsNikhil MahajanNo ratings yet
- Datasheet 2N7000Document11 pagesDatasheet 2N7000Sergio HernandezNo ratings yet
- P75N02LDG: N-Channel Enhancement Mode MOSFETDocument5 pagesP75N02LDG: N-Channel Enhancement Mode MOSFETAriel Rodrigo MuñozNo ratings yet
- 7.1 The MOSFET - Introduction: 7.1.1 Basic Structure and Principle of OperationDocument4 pages7.1 The MOSFET - Introduction: 7.1.1 Basic Structure and Principle of OperationManoj VatsNo ratings yet
- VLSI Design Interview QuestionsDocument11 pagesVLSI Design Interview QuestionsRohit SomkuwarNo ratings yet
- HRF3205 100A, 55V, 0.008 Ohm, N-Channel, PowerDocument9 pagesHRF3205 100A, 55V, 0.008 Ohm, N-Channel, PowerZxdIaminxXzlovewithzxXzyouzxNo ratings yet
- Implementation of 1-Bit Full Adder Circuit Using Pass Transistor LogicDocument11 pagesImplementation of 1-Bit Full Adder Circuit Using Pass Transistor LogicIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Read-Only Memory - WikipediaDocument17 pagesRead-Only Memory - WikipediaMuhammad usamaNo ratings yet
- 05 Internal MemoryDocument33 pages05 Internal MemoryfikaduNo ratings yet
- SS8050 SMD Transistor NPN Y1 40V 1.5aDocument6 pagesSS8050 SMD Transistor NPN Y1 40V 1.5adinh vinh nguyenNo ratings yet
- Mosfet: Presented by Vivek Krishna Kannan Siddarth Ram Mohan ArunDocument15 pagesMosfet: Presented by Vivek Krishna Kannan Siddarth Ram Mohan ArunMushaim AfreenNo ratings yet
- Magna: BUZ900 BUZ901Document4 pagesMagna: BUZ900 BUZ901rory957No ratings yet
- UNIT-2 Stick Diagrams and LayoutDocument54 pagesUNIT-2 Stick Diagrams and LayoutVenkateswara ReddyNo ratings yet
- Electronic Devices and Circuits Questions and AnswersDocument9 pagesElectronic Devices and Circuits Questions and AnswersUIT pravinkumar.eceNo ratings yet
- Silicon NPN Power Transistors: BUW13 BUW13ADocument3 pagesSilicon NPN Power Transistors: BUW13 BUW13ADJALMA MOREIRANo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document38 pagesChapter 2Arife AbdulkerimNo ratings yet
- Assignment 5 MOS & MOSFET Problem 1:: W C V I V VV V V V LDocument2 pagesAssignment 5 MOS & MOSFET Problem 1:: W C V I V VV V V V LhansrajNo ratings yet
- 2SC5586Document24 pages2SC5586Laarabi FouadNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Questions and Answers On Power Electronics... PART-1Document5 pagesMultiple Choice Questions and Answers On Power Electronics... PART-1Anonymous LcKoptl6miNo ratings yet