Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Final 11 Chemistry (Answersheet)
Final 11 Chemistry (Answersheet)
Uploaded by
Kedar GuravOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Final 11 Chemistry (Answersheet)
Final 11 Chemistry (Answersheet)
Uploaded by
Kedar GuravCopyright:
Available Formats
ST.
ARNOLD’S CENTRAL SCHOOL, PUNE
FINAL EXAMINATION (2022-23)
SUBJECT - CHEMISTRY
STD: XI __ ______ M.M:70
Read the following instructions carefully.
a) There are 35 questions in this question paper with internal choice.
b) SECTION A consists of 18 multiple-choice questions carrying 1 mark each.
c) SECTION B consists of 7 very short answer questions carrying 2 marks each.
d) SECTION C consists of 5 short answer questions carrying 3 marks each.
e) SECTION D consists of 2 case- based questions carrying 4 marks each.
f) SECTION E consists of 3 long answer questions carrying 5 marks each.
g) All questions are compulsory.
h) Use of log tables and calculators is not allowed.
____________________________________________________________________________________
SECTION-A
The following questions are multiple-choice questions with one correct answer. Each question carries
1 mark. There is no internal choice in this section.
1. What is the amount of water produced when 8g of hydrogen is reacted with 32g of oxygen?
(a) 2 mole
The chemical equation of water formation is 2H2 + O2 → 2H2O.
Though we have 8g of hydrogen, here oxygen is the limiting
reagent. So the only 4g of hydrogen can be used to produce water
i.e. 36g of water. That is 2 moles.
2. The four quantum numbers of the valence electron of potassium are
(a) 4,1,1,1/2 (b) 4,0,0,1/2
(c) 4,1,0,1/2 (d) 4,4,0,1/2
3. Which of the following molecules have trigonal planar geometry?
(a) BF3 (b) NH3
(c) PCl3 (d) IF3
4. An isolated system is a system in which
(a) there is no exchange of energy with the surrounding.
(b) there is exchange of mass and energy with the surrounding.
(c) there is no exchange of energy and mass with the surrounding.
(d) there is no exchange of mass with the surrounding.
Final Examination/2022-23/11-CHEMISTRY Page 1 of 7
5. Le Chatelier’s principle is applicable to:
(a) only homogeneous chemical reversible reactions
(b) only heterogeneous chemical reversible reactions
(c) only physical equilibrium
(d) all systems, chemical or physical in equilibrium.
6. The I.U.P.A.C. name of CH3COCH(CH3)2 is
(a) 3-methyl-2-butanone (b) Isopropyl methyl ketone
(c) 2-methyl-3-butanone (d) 4-methyl isopropyl ketone
7. A tertiary butyl carbocation is more stable than a secondary butyl carbocation due to which
of the following
(a) –I effect of -CH3 group (b) +R effect of -CH3 group
(c) Hyperconjugation (d) -R effect of -CH3 group
Correct option is C)
Tertiary carbocations are stable due to inductive effect (+I effect of alkyl groups) and hyperconjugation.
Tert. carbocation has greater number of alpha H in comparison to sec carbocation. This increases hyperconjugation which results to its
greater stability.
8. What acts as electrophile in Sulphonation of benzene?
(a) SO2 (b) SO3H+
(c) SO3 (d) SO3H–
Sulphur trioxide SO3 is active species in sulphonation of benzene.
SO3 acts as an electrophile and accepts a pair of pi electrons from benzene.
Note: Sulphonation of benzene is the substitution of the hydrogen atom of benzene molecule by −SO3H (sulphonic
acid) group.
9. The oxidation number of S in NaHSO4—————–
(a) 4 (b) +2
(c) -2 (d) +6
Oxidation number of S in NaHSO4:
⇒1+1+x+(4×−2)=0
⇒2+x−8=0
⇒x=+6.
Final Examination/2022-23/11-CHEMISTRY Page 2 of 7
10. Which of the following electron configurations is correct for iron, (atomic number 26)?
(a)[Kr]4s1 3d6 (b)[Kr]4s1 3d7
(c)[Ar]4s2 3d6 (d)[Kr]4s2 3d6
11. Which of the following is path function?
(a) Enthalpy (b) Heat
(c) Entropy (d) Gibb’s free energy
Path functions are those functions whose values or the properties depend on the initial and final states
of the system. The thermodynamic property which has the formulas as; PΔV depends on the initial and
the final states of the system. Now you can easily identify that property from the given thermodynamic
quantities.
12. What is the decreasing order of stability among the following alkenes:
(I) n-butene, (II) cis-2-butene (III) trans-2-butene
(a) III > II > I (b) III > I > II
(c) I > II > III (d) II > I > III
13. Butene-1 may be converted to butane by reaction with
(a) Pd/H2 (b) Zn/HCl
(c) Sn – HCl (d) Zn – Hg
Alkenes can be converted to alkanes by addition of hydrogen (H2).
In a hydrogenation reaction ( addition of H2), addition of two H2 atoms takes place across the double bond of
an alkene, forming an alkane. The reaction is carried out in the presence of Nickel , Platinum or Palladium.
From the above options only (Pd/H2) validates the condition.
14. Write IUPAC names of the products obtained by the ozonolysis of Pent-2-ene
(a) Product (I) is ethanal and Product (II)is propanal.
(b) Product (I) is ethanal and Product (II)is benzaldehyde
(c) Product (I)is benzaldehyde and Product (II)is propanal.
(d) Product (I) is ethanol and Product (II)is propanol.
For question number 9 and 10, two statements are given – one labelled Assertion (A) and the
other labelled as Reason (R). Select the correct answer to these questions from the codes (a), (b),
(c) and (d) as given below
a. Both A and R are true and R is correct explanation of the assertion.
b. Both A and R are true but R is not correct explanation of the assertion.
c. A is true but R is false.
d. A is false but R is true.
15. Assertion: Electron gain enthalpy can be exothermic or endothermic.
Reason: Electron gain enthalpy provides a measure of the ease with which an atom adds an
Final Examination/2022-23/11-CHEMISTRY Page 3 of 7
electron to form anion.(b) 1
16. Assertion: The bond order of helium is always zero.
Reason: The number of electrons in bonding molecular orbital and antibonding molecular
orbital is equal. (a) 1
17. Assertion: Pressure is an intensive property.
Reason: Pressure is defined as force by area. The ratio of two extensive properties is an
intensive property.(a) 1
18. Assertion: Chain isomerism is observed in compounds containing four or more than four carbon atoms.
Reason: Only alkanes show chain isomerism (c) 1
SECTION-B
This section contains 7 questions with internal choice in two questions. The following questions are very
short types and carry 2 marks each.
19. Draw Newman’s and Sawhorse projections of ethane and label them. 2
20. Derive the structure of the following compounds from their IUPAC names?
(a) Hexa-1,3dien-5-yne (b) 5-Oxohexanoic acid.
OR
Write the IUPAC names of the following compounds from their given structures.
(a) (b) 2
3-Nitrocyclohexene 2,4-Dinitrochlorobenzene
21. Write the main products when
(i) Alkynes are heated with mercuric sulphate and dilute sulphuric acid at 333 K (Ethanal)
(ii) Hydrogen halides (HCl, HBr, HI) added to alkynes.(gem dihalides)
OR
How would you convert the following:
(i) Sodium salt of benzoic acid to benzene.( Sodium salt of benzoic acid on heating with sodalime gives a
hydrocarbon benzene along with sodium carbonate.decarboxylation of aromatic acids)
(ii) Arenes to Haloarenes(halogenation) 2
22. (i)What is buffer solution.
Final Examination/2022-23/11-CHEMISTRY Page 4 of 7
Buffer Solution is a water solvent based solution which consists of a mixture containing a weak acid and the conjugate
base of the weak acid, or a weak base and the conjugate acid of the weak base.
(ii)Why does pH of blood not change despite of variety of food and spices we eat. 2
The pH of blood is maintained at ~ 7.4 by the carbonic acid – bicarbonate ion buffering system.
23. (i)Define enthalpy of fusion.( The amount of heat energy required to convert a unit mass of a solid at its
melting point into a liquid without an increase in temperature is called enthalpy of fusion.)
(ii) Is the enthalpy of neutrilisation of HCl is same as that of H 2SO4. Justify your answer 2
(Heat of neutralisation of strong acid with strong base is constant (−137 kcal. mol−1). Since HCl and H2SO4 are both
strong acid so the heat of neutralisation will be same.)
24. Define hydrogen bond. Why do compounds having hydrogen bonding have high melting
and boiling points? 2
Hydrogen bond is a electrostatic attraction between a hydrogen atom which is bond to a more electronegative atom such as
Nitrogen, Oxygen, fluorine.
Because hydrogen bonds are rather strong intermolecular interactions, breaking them requires a great deal of energy.
25. Explain the trends in following physical properties while moving across the period in a
periodic table.
a) Electron gain Enthalpy (On moving from left to right, atomic size decreases and effective nuclear
charge increases thus, electron gain enthalpy becomes more negative. On moving down the group,
atomic size increases thus, electron gain enthalpy becomes less negative.)
b) Electronegativity(electronegativity generally increases as you move from left to right across a
period and decreases as you move down a group)
2
SECTION-C
This section contains 5 questions with internal choice in two questions. The following questions are short
types and carry 3 marks each.
26. Give answers by pairing with correct statement: 3
(i) Hund’s Rule (a) determines the size and to large extent the
energy of the orbital.
(ii) Aufbau Principle (b)No two electrons in an atom can have the
same set of four quantum numbers
(iii) Pauli Exclusion Principle (c) pairing of electrons in the orbitals
belonging to the same subshell does not take
place until each orbital belonging to that
subshell has got one electron each.
(iv) Effective nuclear charge (d) In the ground state of atoms, orbitals are
filled in the order of their increasing energies.
(v) Principal quantum number (e) The attractive positive charge of nuclear
protons acting on valence electrons depends on
no.of protons and electrons in a polyelectronic
atom.
Final Examination/2022-23/11-CHEMISTRY Page 5 of 7
(vi) Magnetic quantum number (f) the spatial orientation of the orbital with
respect to standard set of co-ordinate axis.
(g) gives information about the spatial
orientation of the orbital with respect to
standard set of co-ordinate axis.
27. (i) If 10 volumes of dihydrogen gas react with five volumes of dioxygen gas,
how many volumes of water vapour would be produced?
H 2 +O 2 →H 2 O(g)
The balanced chemical equation for the reaction is,
2H2+O2→2H2O.
The volume of a gas is directly proportional to the number of moles
Thus, 2 volumes of dihydrogen react with 1 volume of oxygen to form 2 volumes of water.
Thus, 10 volumes of dihydrogen react with 5 volume of oxygen to form 10 volumes of water.
(ii) How many moles of methane are required to produce 22g CO2 (g) after combustion?
CH4 (g) + 2O2 (g) → CO2 (g) + 2H2O (g)
CH4+O2⟶CO2+2H2O
Gram molecular mass of CO2 = 12 +2(16) = 44g/mol
From the reaction it is clear that 1 mole of methane on complete combustion prod
uces 44g (1 mole) of carbon dioxide.
Therefore moles of CH4 required to produce 22g of CO2 are:
=441×22=0.5 mol
28. Dinitrogen and dihydrogen react with each other to produce ammonia according to the
following chemical equation: N 2 (g) + 3H 2 (g) 2NH 3 (g)
(i) Calculate the mass of ammonia produced if 2.00 × 103 g N2 reacts with 1.00 ×103 g of H2.
(ii) Will any of the two reactants remain unreacted?
(iii) If yes, which one and what would be its mass? 3
Final Examination/2022-23/11-CHEMISTRY Page 6 of 7
N2(g)+3H2(g)→2NH3(g)
(i) 28.0 g of N2 require 6.0 g of H2 to produce
=34.0 g of NH3
2.00×103g of N2 will produce
=2834×2.00×103g of NH3
=2.43×103g of NH3
=2430 g NH3
(ii) Yes, dihydrogen will remain unreacted to some extent
(iii) Amount of hydrogen that remains unreacted.
28.0 g of N2 require 6.0 g of H2
2.00 g×103g of N2 will require
=28.06.0×2.00×103 of H2=428.5 g of H2
∴ Amount of hydrogen that remains unreacted
=[1.00×103−428.5]g
=571.5 g.
29. Write the reactions showing preparation of alkenes from(Refer book)
(i) Alkyl halides
(ii) Vicinal dihalides
(iii) Alcohols 3
30. (i) Justify that the reaction: 2Cu 2 O(s) + Cu 2 S( s) → 6Cu(s) + SO 2 (g) is a redox reaction..
(ii) Balance the following redox reactions by ion – electron method:
MnO 4 – (aq) + I – (aq) → MnO 2 ( s) + I 2 (s) (in basic medium)
OR
(i) Calculate the oxidation number of Sulphur and Nitrogen in
a. S2O3 2 − b.NO3 - 1
(ii) Balance the following equation by half reaction method
Fe 2 + ( aq) + Cr 2 O 7 2 – (aq) → Fe 3 + (aq) + Cr 3 + (aq) 2
SECTION-D
The following questions are case-based questions and carries 4 (1+1+2) marks each. Read the
passage carefully and answer the questions that follow.
31.When a liquid evaporates in a closed container, molecules with relatively higher kinetic energy
escape the liquid surface into the vapour phase and number of liquid molecules from the vapour
Final Examination/2022-23/11-CHEMISTRY Page 7 of 7
phase strike the liquid surface and are retained in the liquid phase. It gives rise to a constant
vapour pressure because of an equilibrium in which the number of molecules leaving the liquid
equals the number returning to liquid from the vapour. We say that the system has reached
equilibrium state at this stage. At equilibrium, the rate of evaporation is equal to the
rate of condensation. It may be represented by
H 2 O (l) ⇌ H 2 O (vap)
The mixture of reactants and products in the equilibrium state is called an equilibrium mixture.
Equilibrium can be established for both physical processes and chemical reactions. When the reactants
in a closed vessel at a particular temperature react to give products, the concentrations of the reactants
keep on decreasing, while those of products keep on increasing for some time after which there is no
change in the concentrations of either of the reactants or products. This stage of the system is the
dynamic equilibrium. It is seen that acid (or base) dissociation equilibrium is dynamic involving a
transfer of proton in forward and reverse directions. The concept of conjugate acid-base pair is related
to Bronsted -Lowry acid-base theory and according to this theory, acid is a proton donor while base is a
proton acceptor.
(a) The ionisation of hydrochloric in water is given below:
HCI(aq) + H2O (l) ⇋ H3O+ (aq) + CI– (aq)
Label two conjugate acid-base pairs in this ionisation. HCl(acid)→ Cl− (Conjugate base)
H2O(base)→ H3O+ (Conjugate acid) 1
(b) In a given acidic buffer solution (CH3COOH +CH3COONa), What ionic species are mainly
present in the solution.( CH 3 COO – ( aq ) Acetate ion , H 3 O + ( aq ) Hydronium ion, Na+) 1
(c) On basis of Le-Chatelier’s principle explain how can the temperature and pressure
be adjusted to increase the yield of ammonia in the following reaction.
N 2 (g)+3H 2 (g) ⇌ 2NH 3 (g), ΔH=−92.38kJ mo l
i) Since △H is negative that means forward reaction is exothermic.
ii) Now according to Le Chatelier’s principle, for an exothermic reaction decrease in temperature favors the forward reaction.
For more yield of ammonia, temperature should be kept low, and if the temperature is increased, the reaction will move in bac kward direction and yield of Ammonia
will be less.
iii) According to Le Chatelier’s principle, if the pressure is increased the equilibrium will shift in the direction having less number of gaseous moles. In
N2(g)+3H2(g)⇋2NH3(g) reaction,
No. of moles of gaseous reactants =1+3=4
No. of moles of gaseous product =2
This means, on increasing the pressure, equilibrium will shift to forward direction yielding more ammonia.
Therefore, low temperature and high pressure are favorable conditions to increase the yield of ammonia
OR
PCl5, PCl3 and Cl2 are at equilibrium at 500K in a closed container and their concentrations are 0.8 ×
10–3 mol L–1 , 1.2 × 10–3 mol L–1 and 1.2 × 10–3 mol L–1 respectively. The value of Kc for the reaction
PCl3 (g) + Cl2 (g) → PCl5 (g)
Final Examination/2022-23/11-CHEMISTRY Page 8 of 7
The correct option is B 1.8×10−3
PCl5(g)⇌PCl3(g)+Cl2(g)
At equilibrium,
Kc=[PCl3][Cl2][PCl5] -----------(1)
Kc=[PCl5][Cl2][PCl5]molL×mol/Lmol/L
=1.2×10−3×1.2×10−30.8×10−3mol/L
Kc=1.8×10−3mol/L
Therefore, the correct options is (B) 1.8×10−3mol/L
32. Molecular orbitals are formed by the overlap of atomic orbitals. Two atomic orbitals combine to form
two molecular orbitals called bonding molecular orbital (BMO) and anti bonding molecular
orbital (ABMO). Energy of anti-bonding orbital is raised above the parent atomic orbitals that
have combined and the energy of the bonding orbital is lowered than the parent atomic orbitals.
Different atomic orbitals of one atom combine with those atomic orbitals of the second atom which
have comparable energies and proper orientation. Further, if the overlapping is head on, the
molecular orbital is called ‘Sigma’, (σ) and if the overlap is lateral, the molecular orbital is called ‘pi’,
(π). The molecular orbitals are filled with electrons according to the same rules as followed for filling
of atomic orbitals. However, the order for filling is not the same for all molecules or their ions.
Bond order is one of the most important parameters to compare the strength of bonds.
(a)Which bond is more polar in the following pairs of molecules?
(i)H3C−H and H3C−Br (ii) H3C−NH2 and H3C−OH 1
(b) Describe the hybridisation in case of BCl3 1
(c) What is the total number of sigma and pi bonds in the following molecules?
(i) C2H2 (ii) C2H4
OR
(i) Draw molecular orbital diagram for Cl2 molecule and calculate its bond order. . 2
SECTION-E
The following questions are long answer type and carry 5 marks each. Two questions have an internal
choice.
33. (a) Explain the following with one example in each case of covalent bonds.
(i) Homolytic fission
(ii) Heterolytic fission 2
(b) What are nucleophiles? Give 2 example of nucleophiles.( Methyl carbanion, chloride ion.) 2
(c) Give two points of difference between inductive effect and resonance effect. 1
OR
(a) What is homologous series? Write first four homologous of alcohols and give their IUPAC names. 2
Final Examination/2022-23/11-CHEMISTRY Page 9 of 7
(b) Explain the following isomerism by giving one example in each case.
(i) position isomerism (ii) functional isomerism 2
(c) Show the electron shift for C6H5OH molecule using curved arrow notation. 1
34.(a) Calculate the enthalpy change for the reaction H 2 +Br 2 →2HBr
The bond enthalpies of H-H, Br-Br and H-Br are 435 kJ mol-1, 192 kJ mol-1
and 364 kJ mol-1 respectively. 2
Δr H = ∑B.E. (Reactants) – ∑B.E. (Products) = [B.E. (H2) + B.E. (Br2 )] – 2 B.E. (HBr) = 435 + 192 – 2 ×
364 =
– 101 kJ
(b) What do you mean by thermodynamics state functions. Give two examples. 2
(c) State Hess’s Law of Constant Heat Summation. 1
If a reaction takes place in several steps then its standard reaction enthalpy is the sum of the
standard enthalpies of the intermediate reactions into which the overall reaction may be divided
at the same temperature.
OR
(a) Define specific heat capacity and molar heat capacity. 2
(b) Write mathematical equations of first law of thermodynamics for the following processes
(i) Adiabatic process (ii) Isochoric process
(a) In adiabatic process, there is no exchange of heat thus q=0. So First law becomes ΔU=W.
(b) Isochoric process, as it is carried in closed vessel ΔV=0 thus W=0. So first law becomes ΔU=q.
(c) Calculate the ΔH of the following reaction:
CO2 (g) + H2O (g) → H2CO3 (g)
If the standard values of ΔHf are 1. ΔHº = ∑Δvp ΔHºf(products) - ∑Δ vr ΔHºf(reactants) so this means that you
CO2 (g): -393.509 KJ /mol, add up the sum of the ΔH's of the products and subtract away the ΔH of the
H2O (g) : -241.83 KJ/mol, and products: (-275.2kJ) - (-393.509kJ + -241.83kJ) = (-275.2) - (-635.339) =
H2CO3(g) : -275.2 KJ/mol. +360.139 kJ.
2
35. (a) Why the energy of 2s orbital of hydrogen atom is greater than that of 2s orbital of lithium 1
Energies of the orbitals in the same subshell decrease with increase in the atomic
number
(b) Write the electronic configurations of the following ions:
(i) Na + (ii) O2– 1
(c) Identify the iso-electronic ions from the following pairs?
Final Examination/2022-23/11-CHEMISTRY Page 10 of
7
(i) Na+ and Mg2+ (ii) Al3+and O– 1
(d) What are the atomic numbers of elements whose outermost electrons are represented by
(i) 2p 3 (ii) 3p 5 1
(e) How many electrons will be present in the sub-shells having ms value of –1 for n=4 ? 1
The number of orbitals will be =n2
The number of orbitals =16.
Two electrons will go to each orbital with spins -1/2and+1/2
∴ Hence the number of electrons having spin -1/2 will be 16
Final Examination/2022-23/11-CHEMISTRY Page 11 of
7
You might also like
- Modern Chemistry (1st) - HoltMcDougallDocument926 pagesModern Chemistry (1st) - HoltMcDougallAlonso Llacsahuache Tomas92% (13)
- HL Biology IA 20/24Document14 pagesHL Biology IA 20/24dev0% (1)
- 2017-18 T.Y.B.Sc. Chemistry PDFDocument47 pages2017-18 T.Y.B.Sc. Chemistry PDFAkshay Khambare0% (1)
- Chemistry Mock PaperDocument7 pagesChemistry Mock PaperKedar GuravNo ratings yet
- Bodhi Anup XII CHEMISTRY - 4Document8 pagesBodhi Anup XII CHEMISTRY - 4mitra cbseNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Chemistry Sample PaperDocument8 pagesClass 12 Chemistry Sample Paperabhinavdahiya77No ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Chemistry 14 Apr Sample Paper 2023 24Document8 pagesCBSE Class 12 Chemistry 14 Apr Sample Paper 2023 24aknishad71385No ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Chemistry 14 Apr Sample Paper 2023 24Document8 pagesCBSE Class 12 Chemistry 14 Apr Sample Paper 2023 24Vinoth RNo ratings yet
- AnasDocument6 pagesAnasradiant boyNo ratings yet
- Cblechpu 04Document8 pagesCblechpu 04Aawesh BackupsNo ratings yet
- CLASS 12 Chem Practice Sample QP CHEM SET 1Document20 pagesCLASS 12 Chem Practice Sample QP CHEM SET 1Minecraft NoobsNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Set 1Document7 pagesChemistry Set 1krish.meghashriNo ratings yet
- Chemistry SQP 1Document8 pagesChemistry SQP 1Purnima PandaNo ratings yet
- Half Yearly Exam Paper 1Document7 pagesHalf Yearly Exam Paper 1AëNo ratings yet
- Q7 S YSRXX4 Ovcbo Ky Y2 LJDocument24 pagesQ7 S YSRXX4 Ovcbo Ky Y2 LJYashveer RaiNo ratings yet
- SET 2 Question PaperDocument8 pagesSET 2 Question PaperKrityapriya BhaumikNo ratings yet
- Chem Xii PB 1 QP Set ADocument6 pagesChem Xii PB 1 QP Set Aharshitapawar3010No ratings yet
- 12 Chemistry23 24 sp11Document14 pages12 Chemistry23 24 sp11Babur HussainNo ratings yet
- Chem 4Document8 pagesChem 4vishwasoni01No ratings yet
- XII QP Chemistry2022-2023Document8 pagesXII QP Chemistry2022-2023Akash Kumar UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Sample Papers Class XiDocument26 pagesChemistry Sample Papers Class Xijayanti obcNo ratings yet
- Chem Set 1Document6 pagesChem Set 1ALOK RANJANNo ratings yet
- Sample PapersDocument65 pagesSample PapersKatara BittuNo ratings yet
- Chemistry SQP 2Document11 pagesChemistry SQP 2ACHAL PATILNo ratings yet
- CLASS XII Chemistry-SQP 22-23Document16 pagesCLASS XII Chemistry-SQP 22-23Yug GandhiNo ratings yet
- Chemistry SQPDocument11 pagesChemistry SQPMohd Zaid KhanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry SQPDocument11 pagesChemistry SQPSariska MehraNo ratings yet
- QP 4 Xi Chem Paper 4Document5 pagesQP 4 Xi Chem Paper 4technical SiteNo ratings yet
- Xii Chem QPDocument8 pagesXii Chem QPOMKAR Singh RaghuvanshiNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 1Document19 pagesChemistry 1SAHIL SINGHNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument7 pagesChemistryrjakrithiNo ratings yet
- SQP 20 Sets ChemistryDocument144 pagesSQP 20 Sets Chemistrypoornima9739100% (1)
- 11 Chemistry23 24sp 01Document13 pages11 Chemistry23 24sp 01AbhishekNo ratings yet
- Chem PreboardDocument13 pagesChem Preboardvirender.pinghalNo ratings yet
- XII Chemistry Sample Question Paper - FinalDocument65 pagesXII Chemistry Sample Question Paper - Finalkrishnapradhani091No ratings yet
- PB 2 Question PaperDocument8 pagesPB 2 Question PaperabhilashNo ratings yet
- Set 1 Pre-Board 1 Class Xii 2023-24Document4 pagesSet 1 Pre-Board 1 Class Xii 2023-24opppsiyiNo ratings yet
- 12 ChemDocument6 pages12 ChemMohammed AmmaarNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 12thDocument5 pagesChemistry 12thvidushiinksNo ratings yet
- SP Chem PB GurugramDocument14 pagesSP Chem PB Gurugramkomalkapri156No ratings yet
- 12 Chemistry23 24 sp10Document14 pages12 Chemistry23 24 sp10Babur HussainNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbon 1Document6 pagesHydrocarbon 1VK CREATIONNo ratings yet
- 12TH ChemistryDocument11 pages12TH ChemistryAkshatNo ratings yet
- Sample PaperDocument6 pagesSample PaperBhumisht JatiNo ratings yet
- QP Chemistry Pb2 Xii Set2Document13 pagesQP Chemistry Pb2 Xii Set2Yug GandhiNo ratings yet
- 12thchemistrysamplepaper1 291223044313Document9 pages12thchemistrysamplepaper1 291223044313aditikharb2020No ratings yet
- SQP 20 Sets ChemistryDocument145 pagesSQP 20 Sets ChemistrySky Sir50% (4)
- 12 Chemistry23 24 sp03Document14 pages12 Chemistry23 24 sp03bhattkrrish339No ratings yet
- Practise Paper - Chemistry - Class XI 2023-24Document6 pagesPractise Paper - Chemistry - Class XI 2023-24mysixthidisNo ratings yet
- Xii Chemistry - 1Document10 pagesXii Chemistry - 1M A T T H Y D E NNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Chemistry Sample Paper 01Document15 pagesClass 12 Chemistry Sample Paper 01milanraj9148No ratings yet
- Chem 001Document22 pagesChem 001Yashveer RaiNo ratings yet
- Chem e TermDocument6 pagesChem e TermchituNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Pre Board SQP Chemistry 02Document19 pagesClass 12 Pre Board SQP Chemistry 02akpavan72No ratings yet
- Chem 2Document8 pagesChem 2vishwasoni01No ratings yet
- Kvs Sample Paper Chemistry Page 2 - 6Document5 pagesKvs Sample Paper Chemistry Page 2 - 6Rohan BaghelNo ratings yet
- ChandigarhXII PB1 QP CHEM2023Document8 pagesChandigarhXII PB1 QP CHEM2023harshitapawar3010No ratings yet
- SQP1Document10 pagesSQP1The. Daksh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Class 11 CHEMISTRY - Term2 Exam Question Paper (1) - 2020-21 2Document8 pagesClass 11 CHEMISTRY - Term2 Exam Question Paper (1) - 2020-21 2moiiifitbituserNo ratings yet
- Chemistry PaperDocument7 pagesChemistry Papersharanakash06No ratings yet
- Xi Chemistry QPDocument5 pagesXi Chemistry QPDamodar KasukurthiNo ratings yet
- Cblechpu 09Document7 pagesCblechpu 09anushdonkingNo ratings yet
- Plasma Chemistry: International Symposium on Plasma ChemistryFrom EverandPlasma Chemistry: International Symposium on Plasma ChemistryD. E. JensenNo ratings yet
- Determining The Rate Law From Experimental DataDocument45 pagesDetermining The Rate Law From Experimental Datasospeter barasaNo ratings yet
- Lec 3Document116 pagesLec 3Cheng Chao HanNo ratings yet
- Physical Pharmacy Lect of KineticsDocument20 pagesPhysical Pharmacy Lect of KineticsFaizNo ratings yet
- Chap 1 CREDocument24 pagesChap 1 CREtuansyafiqNo ratings yet
- CHM 358 Wi 02Document145 pagesCHM 358 Wi 02Akpa KenechukwuNo ratings yet
- Membrane ReactorDocument9 pagesMembrane ReactorAzharuddin Ehtesham FarooquiNo ratings yet
- Chemical Kinetics RevisedDocument56 pagesChemical Kinetics RevisedCacey Daiwey CalixtoNo ratings yet
- Quiz 4.2Document3 pagesQuiz 4.2Annabelle Cebrero Paulo AlbaoNo ratings yet
- Chemcad 5 Services To Visual Basic ApplicationsDocument41 pagesChemcad 5 Services To Visual Basic ApplicationsFrancoNo ratings yet
- Gas Phase Boudouard Reaction RateDocument9 pagesGas Phase Boudouard Reaction RatePiyush AgarwalNo ratings yet
- I. Introductory Concept: SHS-Physical Science (Rates of Chemical Reaction)Document9 pagesI. Introductory Concept: SHS-Physical Science (Rates of Chemical Reaction)Jane182004No ratings yet
- Assignment 2 3Document3 pagesAssignment 2 3Sandeep Challa0% (1)
- SPM Chemistry Revision Module On The BasicsDocument64 pagesSPM Chemistry Revision Module On The Basicssuritanu96No ratings yet
- Antimony Production by Carbothermic Reduction of Stibnite in The Presence of LimeDocument9 pagesAntimony Production by Carbothermic Reduction of Stibnite in The Presence of LimeStefany Michelle Huanca ChoqueNo ratings yet
- LAS Gen - Chem2 - MELC - 20 22 - Q3 Week 8Document11 pagesLAS Gen - Chem2 - MELC - 20 22 - Q3 Week 8JV Subang PatindolNo ratings yet
- Chemical KineticsDocument31 pagesChemical KineticsAnonymous LnQ4lBXiPjNo ratings yet
- Lecture 11 Reaction EquilbruimDocument24 pagesLecture 11 Reaction EquilbruimMostafa BayoumyNo ratings yet
- FTPDocument5 pagesFTPSurendar Vejayan100% (1)
- Bio 150-Experiment 1Document8 pagesBio 150-Experiment 1Aina MaisarahNo ratings yet
- Applied Catalysis A: General: F. Frusteri, F. Arena, G. Bonura, C. Cannilla, L. Spadaro, O. Di BlasiDocument7 pagesApplied Catalysis A: General: F. Frusteri, F. Arena, G. Bonura, C. Cannilla, L. Spadaro, O. Di Blasibearzy94No ratings yet
- Vulcan CFD Code OverviewDocument28 pagesVulcan CFD Code OverviewRay LuoNo ratings yet
- Exp 13 Kinetics of Crystal Violet InstructionsDocument13 pagesExp 13 Kinetics of Crystal Violet InstructionsEzekielNo ratings yet
- JEE MAIN AND ADVANCED Chapterwise PYQ Chemistry Prabhat Publication PDFDocument413 pagesJEE MAIN AND ADVANCED Chapterwise PYQ Chemistry Prabhat Publication PDFk p rathour100% (4)
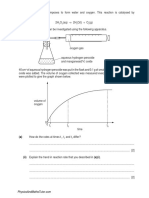
- 1 Hydrogen Peroxide Decomposes To Form Water and Oxygen. This Reaction Is Catalysed byDocument9 pages1 Hydrogen Peroxide Decomposes To Form Water and Oxygen. This Reaction Is Catalysed byKelvin DenhereNo ratings yet
- 8.3 Factors Affecting RXN RateDocument36 pages8.3 Factors Affecting RXN RateNur AleyaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Kinetics & Stability: Final CoverageDocument2 pagesChemical Kinetics & Stability: Final CoverageVanessa QuintoNo ratings yet
- Determination of The Activation Energy of The Reaction Between Oxalic Acid and Potassium Permanganate.Document7 pagesDetermination of The Activation Energy of The Reaction Between Oxalic Acid and Potassium Permanganate.刘象58% (19)