Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Forces
Forces
Uploaded by
Alizeh Shoaib0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views4 pagesThis document discusses the concepts of force, balanced and unbalanced forces, Newton's laws of motion, and friction. The key points are:
- A force is a push or pull that can cause an object to change its motion or shape. Forces can be measured in Newtons.
- Balanced forces cause no change in an object's motion, while unbalanced forces cause acceleration or changes in speed or direction.
- Newton's laws state that an object's acceleration depends on the net force acting on it and its mass, and that for every action there is an equal and opposite reaction.
- Friction opposes motion between surfaces and can reduce efficiency. Its effects depend on factors like surface smooth
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses the concepts of force, balanced and unbalanced forces, Newton's laws of motion, and friction. The key points are:
- A force is a push or pull that can cause an object to change its motion or shape. Forces can be measured in Newtons.
- Balanced forces cause no change in an object's motion, while unbalanced forces cause acceleration or changes in speed or direction.
- Newton's laws state that an object's acceleration depends on the net force acting on it and its mass, and that for every action there is an equal and opposite reaction.
- Friction opposes motion between surfaces and can reduce efficiency. Its effects depend on factors like surface smooth
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views4 pagesForces
Forces
Uploaded by
Alizeh ShoaibThis document discusses the concepts of force, balanced and unbalanced forces, Newton's laws of motion, and friction. The key points are:
- A force is a push or pull that can cause an object to change its motion or shape. Forces can be measured in Newtons.
- Balanced forces cause no change in an object's motion, while unbalanced forces cause acceleration or changes in speed or direction.
- Newton's laws state that an object's acceleration depends on the net force acting on it and its mass, and that for every action there is an equal and opposite reaction.
- Friction opposes motion between surfaces and can reduce efficiency. Its effects depend on factors like surface smooth
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 4
Forces
Force is a push or a pull.
Changing the direct.
Acceleration.
Moves a stationary object.
Force can change the size, shape and motion of a body.
Unit of force is NEWTON (N).
Force can be measured with a spring balance.
Examples:
Friction,
Weight.
Air resistance due to matter is a contact force.
Electrostatic force.
Magnetic force is a non-contact force.
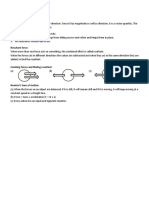
Balances Forces:
If the forces acts on a body is balanced:
it stay at rest
It moves with constant speed.
Lift + Gravity=
Resultant force
(Net)
Drag + Thrust=
Resultant force
(Net)
If the
forces acts on the body is balanced, then the
resultant force is zero (at rest or constant
speed.)
Resultant force = 6000 − 6000 = 0 N
Thrust means engine force (motion).
Contact Force:
Gravitational force is downward. Air resistence or frictional force is upward.
Decrease in speed.
Change in speed= change in air resistance Δ s= Δ ar
Speed increases every second of time.
Parachute increases S.A. decreases velocity.
Air resistance increases with S.A. – air resists.
Newton’s first law of motion:
If the forces acting on a body is balanced, then
If it is at rest, it will continue to stay at rest.
If it is moving, it will keep on moving at a constant speed in a straight line.
Unbalanced forces:
Unbalanced forces causes
a stationary body to move
a moving body to change its velocity
If the forces acts on a body is unbalanced, then there will be a resultant force.
Example:
Resultant force = 5000 − 1500 = 3500 N
The forces act on a car is unbalance, so it accelerates because forward force is greater than
backward force.
The forces act on a car is unbalance, so it decelerates because backward force is greater than
forward force.
Newton’s second law of motion
The acceleration of the body is directly proportional to the direction of force applied and
inversely proportional to the mass of the body.
The greater the mass of an object, the smaller acceleration it is given by a particular force.
The force, mass and acceleration can be combined into the following equation:
Force = mass × acceleration
F = ma
Newton’s third law of motion
To every action there is an equal but opposite reaction i.e. if object A exerts a force on object B
(action), then object B will exert an equal but opposite force on object A (reaction).
Examples: firing gun, hammering a nail, book kept on a table and launching rocket.
Friction
Friction as the force between two surfaces that may impede motion and produce heating.
Friction is the force which opposes motion. i.e., stopping force
It always acts opposite to the direction of travel.
Friction (drag) acts on an object moving through a liquid
Friction (drag) acts on an object moving through a gas (e.g. air resistance)
Friction can be reduced by adding lubricants. E.g. lubricating oil, grease.
Sliding surfaces must be smooth. If they are rough or rusty there will be a lot of friction. Ball
bearings reduce friction because they roll rather than slide.
Cause of friction
1. Molecules in materials have a tendency to stick to each other when materials are pressed
or rubbed together.
2. Nature of the surface: rough surfaces have more friction due to up’s and down’s which
catch each other.
Advantages of friction:
Friction helps us to walk.
Friction helps us to hold the objects.
Friction helps us to stop a moving object.
Disadvantages of friction:
Machine parts rub together and become lose.
Shoes and clothes wear and tear.
It heats up the moving parts and some energy is wasted in the form of heat.
Effects of friction on the motion of a vehicle:
Tire surface:
If the vehicle is having more tyre surface, then the frictional force acting
on it will be more.
If tire surface of vehicle is less, then the frictional force acting on it will
be less.
Road conditions:
If the road is having rough surface, the frictional force will be more.
If the road is having smooth surface, the frictional force will be less.
Normal Reaction force:
Is the reaction force produced by an object holding another object has a limit. Balanced force.
When unbalanced, products fell.
Circular motion:
When any object is moving in a circular path, then the object is in circular motion.
Objects are moving in circular path due to constant force acting towards center of the circle. This
force is called centripetal force.
The centripetal force will increase:
If the mass of the object increased.
If the speed of the object increased.
If the radius of the circle reduced.
Pivot: fixed point around which moment takes place. M= F x d
Perpendicular Distance: right angled perpendicular distance between the pivot & the point where
the force is applied.
The planets are orbiting around the sun due to constant gravitational force acting towards the
sun.
The satellites are orbiting around the earth due to constant gravitational force acting towards the
earth.
The electrons are orbiting around the nucleus due to constant electrostatic force acting towards
nucleus of the atom.
You might also like
- CSP Exam Equation Fully Explained DEMODocument33 pagesCSP Exam Equation Fully Explained DEMOFff63% (8)
- Week 8 ForcesDocument38 pagesWeek 8 ForcesSALMA AREKATNo ratings yet
- Forceandmotion 181112055529Document36 pagesForceandmotion 181112055529FernandoNo ratings yet
- Definition of Tension ForceDocument12 pagesDefinition of Tension ForceWanderlust youtuberNo ratings yet
- 2.2.1 Forces and Dynamics Notes 3Document4 pages2.2.1 Forces and Dynamics Notes 39름No ratings yet
- What Is A ForceDocument12 pagesWhat Is A ForceSyed M HassanNo ratings yet
- Dynamics: What Is A Force?Document13 pagesDynamics: What Is A Force?TorettoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Forces & Turning Effect of ForcesDocument24 pagesChapter 4 - Forces & Turning Effect of ForcesSafwan MahmudNo ratings yet
- CH#2: ForcesDocument3 pagesCH#2: ForcesdetNo ratings yet
- Physics - Force and MotionDocument10 pagesPhysics - Force and MotionÅBanDonNo ratings yet
- Phys 1011 - Dynamic NotesDocument10 pagesPhys 1011 - Dynamic Notesnigusayele06No ratings yet
- Newton's Laws of Motion by JoyDocument49 pagesNewton's Laws of Motion by JoyMjoyTibayNo ratings yet
- 1.5newton's LawDocument39 pages1.5newton's LawEaintNo ratings yet
- Contact Versus Action-at-a-Distance ForcesDocument5 pagesContact Versus Action-at-a-Distance ForcesAna Marie RentonNo ratings yet
- 7th Lesson Newtons Laws of MotionDocument27 pages7th Lesson Newtons Laws of MotionMRmister123No ratings yet
- ForcesDocument1 pageForcestasnimNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes Chapter 5 FrictionDocument5 pagesLecture Notes Chapter 5 FrictionNguyễn Sơn LâmNo ratings yet
- Newton'S Laws of Motion: Mark Anthony C. Burgonio, MSCDocument37 pagesNewton'S Laws of Motion: Mark Anthony C. Burgonio, MSCChristel GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Force and Pressure NotesDocument11 pagesForce and Pressure Notesmatho logyNo ratings yet
- Resultant of Forces:: Maintaining Equilibrium or Changing MotionDocument68 pagesResultant of Forces:: Maintaining Equilibrium or Changing MotionRandy NatalNo ratings yet
- Force - A Push or A Pull: Pulling, Lifting, Stretching, Twisting and PressingDocument11 pagesForce - A Push or A Pull: Pulling, Lifting, Stretching, Twisting and PressingAbhiveerdahiya08No ratings yet
- FORCESDocument4 pagesFORCESNirvana SuggieNo ratings yet
- Dynamics 2Document49 pagesDynamics 2Zubair FarooqNo ratings yet
- Hit TerDocument29 pagesHit TerSai-Min Thit-KoNo ratings yet
- Science Notes To PrintDocument1 pageScience Notes To Printmatt.ryan.mcnallyNo ratings yet
- Eastern Cape Revision P1 Combine 2017 2019 - 240122 - 174513Document225 pagesEastern Cape Revision P1 Combine 2017 2019 - 240122 - 174513owaratoamalingaNo ratings yet
- Paper 1 PhysicsDocument106 pagesPaper 1 Physics77xzs8njzzNo ratings yet
- ForcesDocument23 pagesForcesNancy Kawilarang100% (1)
- Every Day ForcesDocument40 pagesEvery Day ForcesHaneen DweikatNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 CH 11 NotesDocument9 pagesGrade 8 CH 11 NotesNikhat SiddiqueNo ratings yet
- Laws of Motion: - Dynamics Is The Branch of Physics in Which We StudyDocument18 pagesLaws of Motion: - Dynamics Is The Branch of Physics in Which We StudyVipeen BendaleNo ratings yet
- Law of Motion Class 11 Notes Physics Chapter 5Document13 pagesLaw of Motion Class 11 Notes Physics Chapter 5pujal dabasNo ratings yet
- Note Applicationas of Newton's Laws and Conservation of MomentumDocument16 pagesNote Applicationas of Newton's Laws and Conservation of MomentumWatr SatNo ratings yet
- Forces:: Maintaining Equilibrium or Changing MotionDocument69 pagesForces:: Maintaining Equilibrium or Changing MotionPuneetNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 PhysicDocument5 pagesChapter 4 PhysicWaleska MendezNo ratings yet
- Class 8 Physics Sample FounationDocument25 pagesClass 8 Physics Sample FounationPraveen MaramNo ratings yet
- Solid Friction TheoryDocument11 pagesSolid Friction TheorySoham NayakNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Physics - Newton's Laws of MotionDocument9 pagesIGCSE Physics - Newton's Laws of MotionKasunDilshanNo ratings yet
- FORCESDocument11 pagesFORCESJennieNo ratings yet
- Newton's Laws of Motion (Force A Recall)Document79 pagesNewton's Laws of Motion (Force A Recall)Quenie Balanay AgaNo ratings yet
- What Are Forces in PhysicsDocument3 pagesWhat Are Forces in PhysicsJessNo ratings yet
- ForcesDocument56 pagesForcesMais MarwanNo ratings yet
- Force Causes Change in Motion By: Avigael MarayaDocument18 pagesForce Causes Change in Motion By: Avigael MarayaHazel LiporadaNo ratings yet
- FORCESDocument6 pagesFORCESlemoniteNo ratings yet
- CH-5 Laws of MotionDocument12 pagesCH-5 Laws of MotionSaransh KumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 NotesDocument3 pagesChapter 11 NotesChahat SanataniNo ratings yet
- Force and PressureDocument90 pagesForce and PressureAzra BaigNo ratings yet
- Types of ForcesDocument10 pagesTypes of ForcesAbdulrahman RadeefNo ratings yet
- Esc 17 1Document21 pagesEsc 17 1elaco56No ratings yet
- Forces and Newton's Laws of MotionDocument38 pagesForces and Newton's Laws of MotionfarismohNo ratings yet
- What Is Force?: DefinitionDocument5 pagesWhat Is Force?: Definitionمحمد ایمانNo ratings yet
- EebodydiagramDocument41 pagesEebodydiagramTechhhniniNo ratings yet
- CIE IGCSE ForcesDocument62 pagesCIE IGCSE ForcesRudi HartonoNo ratings yet
- Force and PressureDocument6 pagesForce and PressureRaj KumarNo ratings yet
- Newton's First Law of Motion: ExampleDocument4 pagesNewton's First Law of Motion: ExampleligmaNo ratings yet
- Force (Hand Out)Document2 pagesForce (Hand Out)merlindaNo ratings yet
- Physics-Group 4 ProjectDocument13 pagesPhysics-Group 4 ProjectSwastick PaliwalNo ratings yet
- Forces: Force Can Cause An Object To Change Its Velocity or ShapeDocument8 pagesForces: Force Can Cause An Object To Change Its Velocity or ShapeLabeenaNo ratings yet
- Physics Key Terms and Meaning-Semester-1Document6 pagesPhysics Key Terms and Meaning-Semester-1techzealNo ratings yet
- Physics DefinitionDocument6 pagesPhysics DefinitionMin Aung KyawNo ratings yet
- EnergyDocument45 pagesEnergyAlizeh ShoaibNo ratings yet
- Physical Quantities and Measurement TechniquesDocument5 pagesPhysical Quantities and Measurement TechniquesAlizeh ShoaibNo ratings yet
- General Properties of WavesDocument4 pagesGeneral Properties of WavesAlizeh ShoaibNo ratings yet
- MomentumDocument1 pageMomentumAlizeh ShoaibNo ratings yet
- Revision WSDocument3 pagesRevision WSAlizeh ShoaibNo ratings yet
- ElectricityDocument10 pagesElectricityAlizeh ShoaibNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Model of MatterDocument3 pagesKinetic Model of MatterAlizeh ShoaibNo ratings yet
- Experiment To Measure The Center of GravityDocument1 pageExperiment To Measure The Center of GravityAlizeh ShoaibNo ratings yet
- MotionDocument2 pagesMotionAlizeh ShoaibNo ratings yet
- Experiment To Measure The Center of Gravity of An Irregular Lamina (Forces)Document1 pageExperiment To Measure The Center of Gravity of An Irregular Lamina (Forces)Alizeh ShoaibNo ratings yet
- Elastic DeformationDocument9 pagesElastic DeformationAlizeh ShoaibNo ratings yet
- Momentum WsDocument2 pagesMomentum WsAlizeh ShoaibNo ratings yet
- Past Paper Question of ForcesDocument6 pagesPast Paper Question of ForcesAlizeh ShoaibNo ratings yet
- Essay Topics 2021Document2 pagesEssay Topics 2021Alizeh ShoaibNo ratings yet
- EnergyDocument5 pagesEnergyAlizeh ShoaibNo ratings yet
- Symmetry Analysis of Differential EquationsDocument88 pagesSymmetry Analysis of Differential EquationsShabbir ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure Assignment-3Document20 pagesAtomic Structure Assignment-3VARSHITHNo ratings yet
- Kerosene OilDocument7 pagesKerosene OilSadain ZafarNo ratings yet
- Tolerance Map Models For Design and Manufacturing: MotivationDocument9 pagesTolerance Map Models For Design and Manufacturing: MotivationCahyono IriawanNo ratings yet
- Electric Potential in A Uniform Electric Field: PhysicsDocument1 pageElectric Potential in A Uniform Electric Field: PhysicsHermanNo ratings yet
- Instruction Manual of Capacitor Voltage TransformersDocument22 pagesInstruction Manual of Capacitor Voltage Transformerst.o.i.n.gNo ratings yet
- Applied Physics NTCDocument2 pagesApplied Physics NTCFasih Khan DurraniNo ratings yet
- Lab 1 Center of GravityDocument5 pagesLab 1 Center of GravityWaqas Muneer KhanNo ratings yet
- Recursive Newton-Euler Formulation Manipulator DynamicsDocument10 pagesRecursive Newton-Euler Formulation Manipulator DynamicsbontacccNo ratings yet
- Geas Iecep PDFDocument26 pagesGeas Iecep PDFMichael Cabrera RabinoNo ratings yet
- Quantum Theory: Von Neumann vs. DiracDocument20 pagesQuantum Theory: Von Neumann vs. DiracsonirocksNo ratings yet
- D.K.Pandey: Acceleration Due To Gravity G' by Kater's PendulumDocument2 pagesD.K.Pandey: Acceleration Due To Gravity G' by Kater's PendulumPrashantNo ratings yet
- OLGA 2014 New Functionalities For Well and DrillingDocument26 pagesOLGA 2014 New Functionalities For Well and DrillingAkin MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Quantum Cryptography Chap 1Document21 pagesQuantum Cryptography Chap 1Anees Ur RehmanNo ratings yet
- SM ch1 Mat Meyers 2Document37 pagesSM ch1 Mat Meyers 2infinity_azNo ratings yet
- M 3Document5 pagesM 3Varunan VarunNo ratings yet
- Formal Report Exp6Document7 pagesFormal Report Exp6Rachel CajilesNo ratings yet
- Science Focus 4 CBDocument343 pagesScience Focus 4 CBmusic_stefan98100% (2)
- Exp 2 ChemistryDocument6 pagesExp 2 Chemistryhasmar67% (3)
- MJC 2010 H2 Physics Prelim Paper 3xDocument21 pagesMJC 2010 H2 Physics Prelim Paper 3xcjcsucksNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Solution To Sample ProblemDocument22 pagesLecture 1 Solution To Sample ProblemJohn Carlo CortezNo ratings yet
- Inter 1 Physics Success Series 2019 by Ambitious Academy ShahdaraDocument22 pagesInter 1 Physics Success Series 2019 by Ambitious Academy Shahdaraashfaq4985No ratings yet
- Ferrite Magnets-Ceramic Magnets Datasheet v1Document4 pagesFerrite Magnets-Ceramic Magnets Datasheet v1GILBERTO YOSHIDANo ratings yet
- Calcite ReviewDocument12 pagesCalcite ReviewIsrarul HaqueNo ratings yet
- University Physics: Waves and Electricity: Dr.-Ing. Erwin SitompulDocument37 pagesUniversity Physics: Waves and Electricity: Dr.-Ing. Erwin SitompulAliNo ratings yet
- RPT Add Math Form 5Document9 pagesRPT Add Math Form 5Suziana MohamadNo ratings yet
- Multiphase FlowDocument15 pagesMultiphase FlowvictorvikramNo ratings yet
- Errors in MeasurementDocument2 pagesErrors in MeasurementSuantak TuangNo ratings yet
- AreaDocument13 pagesAreaamitjustamitNo ratings yet