Professional Documents
Culture Documents
States of Matter Kinetic Theory of Matter Thermal Expansion Worksheet
States of Matter Kinetic Theory of Matter Thermal Expansion Worksheet
Uploaded by
Chua Hui LinOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
States of Matter Kinetic Theory of Matter Thermal Expansion Worksheet
States of Matter Kinetic Theory of Matter Thermal Expansion Worksheet
Uploaded by
Chua Hui LinCopyright:
Available Formats
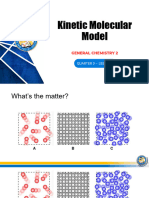
Task 1: States of Matter
Solid Liquid Gas
Arrangement Definite shape and Definite volume, no No definite volume, no
volume definite shape definite shape
Movement Do not move around, Move slowly, closer Big spaces between
packed together together particles
Energy Low energy - strong Moderate energy - loosely High energy - weak
bonds bonded attraction between
particles
Spaces between Packed together Closer together Big spaces between
particles particles
Particle Diagram
Task 2: Kinetic Molecular Theory
The kinetic molecular theory explains the forces between molecules and the energy they possess. This theory has 3
basic assumptions:
1. Matter is made up of small particles.
2. The molecules are always moving. The motion of the molecules increases as they gain kinetic energy as a
result of the change in temperature.
3. In solids, particles are tightly closed in a regular pattern. Particles in solids do not move around at a fixed
position as they have low energy. In liquids, particles are slightly apart. They have more energy to move around and
flow to follow the shape of the container. In gas, particles are furthest apart. Gas particles have the high energy and is
able to move around quickly.
Reflections:
Explain the relationship between temperature and energy of the particles.
When particles are heated and gain energy, they move faster and the spaces between them expand in size. When
particles are cooled and lose energy, they move slower and the spaces between hem contract in size. If the transfer
of energy is quite dramatic the state of matter changes.
Are you able to meet the objectives of this asynchronous task? What are the struggles you faced?
I am able to meet the objectives of this asynchronous task where I could recall the properties of different states of
matter that I learned in grade 8 until now, defining kinetic molecular theory, and understand the relationship
between temperature and energy of the particles.
Task 3: Thermal Expansion
Definition:
Thermal Expansion is the tendency of matter to expand on heating. This tendency of expansion can be observed in
solid, liquid, and gas.
Explanation:
When a matter is heated, particles gain kinetic energy and vibrates/moves faster. The increase in the motion of
particles causes the space between particles to increase. This results in an expansion in volume/area of the matter.
Likewise, when a matter is cooled down, particles lose kinetic energy and vibrate/moves slower. The decrease in the
motion of particles causes the space between particles to decrease. This results in a contraction in volume/area of
the matter.
You might also like
- Michael in The Bathroom - Lula Land EditDocument8 pagesMichael in The Bathroom - Lula Land EditKeishianna PetersonNo ratings yet
- Property 2 Notes&BriefsDocument48 pagesProperty 2 Notes&BriefsHaifaNo ratings yet
- Sofitel Philippine Plaza Manila Cultural Orientations FrameworkDocument3 pagesSofitel Philippine Plaza Manila Cultural Orientations FrameworkApril Jane EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Thermal Physics CIEDocument27 pagesUnit 2 Thermal Physics CIEShrirang ChandankhedeNo ratings yet
- The Particle Model Explains MatterDocument6 pagesThe Particle Model Explains MatterLoki PlushNo ratings yet
- Thermal Physics States of Matter and Brownian MotionDocument27 pagesThermal Physics States of Matter and Brownian MotionSaad BBNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Theory of ParticlesDocument14 pagesKinetic Theory of ParticlesMenaga A/P IlangkovanNo ratings yet
- States of Matter Solids Liquids and GasesDocument3 pagesStates of Matter Solids Liquids and GasesMatipa DembureNo ratings yet
- CHM2 11 - 12 Q3 0101 AkDocument4 pagesCHM2 11 - 12 Q3 0101 AkKyla Dave LiganNo ratings yet
- TP1 Kinetic Theory of MatterDocument2 pagesTP1 Kinetic Theory of MatterThabang Sbo PhokontsiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Kinetic Particle TheoryDocument2 pagesChapter 1 - Kinetic Particle TheorymartynchekycNo ratings yet
- ACTIVITY 1 - KINETIC MOLECULAR MODEL - IngallaDocument4 pagesACTIVITY 1 - KINETIC MOLECULAR MODEL - Ingallajet tolintinoNo ratings yet
- Notre Dame of Dadiangas UniversityDocument17 pagesNotre Dame of Dadiangas UniversityGaylord M. VentoleroNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Particle Theory PDFDocument38 pagesKinetic Particle Theory PDFMuhammad Darrel Keefa100% (1)
- PHY111A 1.1.1 - Kinetic Particle Model PDFDocument28 pagesPHY111A 1.1.1 - Kinetic Particle Model PDFanton petrovNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Molecular TheoryDocument3 pagesKinetic Molecular TheorykimNo ratings yet
- 2.1.1 States of Matter CIE IGCSE Physics Revision Notes 2023 Save My ExamsDocument1 page2.1.1 States of Matter CIE IGCSE Physics Revision Notes 2023 Save My Examsyichenlin111No ratings yet
- Third Form Packet WorkDocument19 pagesThird Form Packet WorkLizbeth Chi100% (1)
- Kinetic Particle TheoryDocument53 pagesKinetic Particle TheoryAaditya MKNo ratings yet
- Class 9 - Chemistry HW - 18 April 2023Document3 pagesClass 9 - Chemistry HW - 18 April 2023Rishabh SinghNo ratings yet
- Mass Space Atoms Molecules Electrons Three Solid Liquid Gas: (Subatomic Particles: Protons, Electrons and Neutrons)Document2 pagesMass Space Atoms Molecules Electrons Three Solid Liquid Gas: (Subatomic Particles: Protons, Electrons and Neutrons)hajra chatthaNo ratings yet
- C07 Kinetic Model of Matter (Teacher)Document22 pagesC07 Kinetic Model of Matter (Teacher)a m i rNo ratings yet
- TP1 - Kinetic Theory of Matter 1Document2 pagesTP1 - Kinetic Theory of Matter 1wengiemotshegweNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 Manual 4th Edition Ver1 2023Document44 pagesTopic 1 Manual 4th Edition Ver1 2023Ha NaNo ratings yet
- Particulate Nature of Matter, Unit1Document15 pagesParticulate Nature of Matter, Unit1Keeertththana SaravananNo ratings yet
- Particle Theory & WorksheetsDocument6 pagesParticle Theory & WorksheetsaamarahyousafNo ratings yet
- 6resource 131602210601 53Document156 pages6resource 131602210601 53No ExcuseNo ratings yet
- Notes - Kinetic Theory of MatterDocument7 pagesNotes - Kinetic Theory of MatterAiney MaiNo ratings yet
- AQA Physics Topic 3 Particle Model of Matter Knowledge OrganiserDocument3 pagesAQA Physics Topic 3 Particle Model of Matter Knowledge OrganiserGabriel HoNo ratings yet
- SPM Chemistry Form 4 Chapter 2 Structure of AtomDocument23 pagesSPM Chemistry Form 4 Chapter 2 Structure of AtomTan YLunNo ratings yet
- Ngss Particle Model PDFDocument2 pagesNgss Particle Model PDFDarwinEspinoza100% (1)
- 01 Simple Kinetic ModelDocument4 pages01 Simple Kinetic ModelAli SalamehNo ratings yet
- G9 UK W15 - Kinetic Model of Matter 2Document35 pagesG9 UK W15 - Kinetic Model of Matter 2hk6sd6cf7vNo ratings yet
- 1 States of Matter Particle Model PowerpointDocument23 pages1 States of Matter Particle Model Powerpointloupoo80No ratings yet
- 5.1 Particle ModelDocument4 pages5.1 Particle ModelKris_14No ratings yet
- Thermal Transfer IDocument6 pagesThermal Transfer Iashane dwightNo ratings yet
- Igcse Chemistry-Notes UNIT-1 The Nature of Matter: SolidsDocument5 pagesIgcse Chemistry-Notes UNIT-1 The Nature of Matter: SolidsCHIO SHEUNG YONGNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 2Document194 pagesGeneral Chemistry 2BEANo ratings yet
- 2024 - Chapter 2 - KPTDocument11 pages2024 - Chapter 2 - KPTkaylamok3No ratings yet
- MATTERDocument4 pagesMATTERRajiv BiswasNo ratings yet
- Name - Class - : Year 7 C2 ParticlesDocument33 pagesName - Class - : Year 7 C2 Particleskrista100717No ratings yet
- Key Terms Definitions Particle Theory: Properties Properties PropertiesDocument3 pagesKey Terms Definitions Particle Theory: Properties Properties PropertiesShimaa ElsharnobyNo ratings yet
- VIII Chemistry HO 01Document9 pagesVIII Chemistry HO 01AINo ratings yet
- Kinetic Particle TheoryDocument39 pagesKinetic Particle Theoryh8alfred100% (1)
- Chapter 10Document31 pagesChapter 10oninNo ratings yet
- Three States of MatterDocument36 pagesThree States of MatterFozia ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Changes in The States of Matter: Chapter 4 Matter and Substance 4.1Document11 pagesChanges in The States of Matter: Chapter 4 Matter and Substance 4.1Jia JiaNo ratings yet
- Resource 1Document13 pagesResource 1eeren41789No ratings yet
- MELC 1 Kinetic Molecular Model of Solids and LiquidsDocument27 pagesMELC 1 Kinetic Molecular Model of Solids and Liquidsreemm pascualNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Molecular Model: General Chemistry 2Document34 pagesKinetic Molecular Model: General Chemistry 2Cielo GatdulaNo ratings yet
- Matter: Science 9 Ms. WhiteDocument11 pagesMatter: Science 9 Ms. WhiteAlvin U. DumdumaNo ratings yet
- 1.2 States of Matter PowerPointDocument13 pages1.2 States of Matter PowerPointwil.whiteNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document2 pagesLecture 1Gabriel JocsonNo ratings yet
- Notes - Matter in Our Surroundings - ExpDocument6 pagesNotes - Matter in Our Surroundings - Expdeborah hildaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Matters Chapter 1Document7 pagesChemistry Matters Chapter 1Ayan AhmedNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Molecular Theory Sept.17Document1 pageKinetic Molecular Theory Sept.17Clint ArranchadoNo ratings yet
- Lesson No1 GC1 Substane Are Made of Smaller ParticlesDocument53 pagesLesson No1 GC1 Substane Are Made of Smaller Particlesmarinette batasNo ratings yet
- Dungca, Catherine D. Gen Chem Worksheet 1Document2 pagesDungca, Catherine D. Gen Chem Worksheet 1Dungca, Catherine D.No ratings yet
- UntitledDocument14 pagesUntitledNana MinNo ratings yet
- Understanding Kinetic Particle TheoryDocument50 pagesUnderstanding Kinetic Particle TheoryozmanNo ratings yet
- Expansion 19Document7 pagesExpansion 19davisdavion831No ratings yet
- Greenhouse GasesDocument2 pagesGreenhouse GasesChua Hui LinNo ratings yet
- Sacrificial ProtectionDocument1 pageSacrificial ProtectionChua Hui LinNo ratings yet
- Air PollutionDocument2 pagesAir PollutionChua Hui LinNo ratings yet
- Chem Energetics, Acids Bases, Rates of ReactionsDocument12 pagesChem Energetics, Acids Bases, Rates of ReactionsChua Hui LinNo ratings yet
- Carbon CycleDocument2 pagesCarbon CycleChua Hui LinNo ratings yet
- Balanced Diet Worksheet 2Document2 pagesBalanced Diet Worksheet 2Chua Hui LinNo ratings yet
- Reversible Reactions WorksheetDocument5 pagesReversible Reactions WorksheetChua Hui LinNo ratings yet
- Globalisation & Trade WorksheetDocument3 pagesGlobalisation & Trade WorksheetChua Hui LinNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Theory Summary WorksheetDocument1 pageKinetic Theory Summary WorksheetChua Hui LinNo ratings yet
- Mixed Questions GeneticsDocument12 pagesMixed Questions GeneticsChua Hui LinNo ratings yet
- Heart WorksheetDocument1 pageHeart WorksheetChua Hui LinNo ratings yet
- W1L2 - Causes of World War 1Document1 pageW1L2 - Causes of World War 1Chua Hui LinNo ratings yet
- PSY - Paper 3Document11 pagesPSY - Paper 3Chua Hui LinNo ratings yet
- PDF Created With Pdffactory Pro Trial VersionDocument152 pagesPDF Created With Pdffactory Pro Trial Versionسري موتيك يوليانيNo ratings yet
- S4-4 Damping Paper TakedaDocument26 pagesS4-4 Damping Paper TakedaRonald Omar García RojasNo ratings yet
- Partial Differential Equations PDFDocument126 pagesPartial Differential Equations PDFManoj Bisht100% (1)
- Pressure Relief Valve Scenario Summary: General Job DataDocument6 pagesPressure Relief Valve Scenario Summary: General Job DatajorgekarlosprNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument58 pagesUntitledArun KumarNo ratings yet
- GrandStream GXV-3175 - User Manual EnglishDocument130 pagesGrandStream GXV-3175 - User Manual Englishซิสทูยู ออนไลน์No ratings yet
- An Empirical Analysis of The Antecedents and Performance Consequences of Using The Moodle PlatformDocument5 pagesAn Empirical Analysis of The Antecedents and Performance Consequences of Using The Moodle Platformsamas7480No ratings yet
- QuadEquations PPT Alg2Document16 pagesQuadEquations PPT Alg2Kenny Ann Grace BatiancilaNo ratings yet
- Table Box TitleDocument53 pagesTable Box TitleRoland Calubiran MayaNo ratings yet
- Dawson 2002Document10 pagesDawson 2002sofia merNo ratings yet
- Analgesics in ObstetricsDocument33 pagesAnalgesics in ObstetricsVeena KaNo ratings yet
- International Journal of Pharmtech Research: Formulation of Aloe Juice (Aloe Vera (L) Burm.F.) Sheet Mask As Anti-AgingDocument10 pagesInternational Journal of Pharmtech Research: Formulation of Aloe Juice (Aloe Vera (L) Burm.F.) Sheet Mask As Anti-AgingAzri RahmadiNo ratings yet
- SAp QM OverviewDocument80 pagesSAp QM OverviewAlfonso Herrera RojasNo ratings yet
- Praise Be To Allah: Mymona HendricksDocument37 pagesPraise Be To Allah: Mymona HendricksRulytta MimiNo ratings yet
- 1st Quarter Exam in Math9Document3 pages1st Quarter Exam in Math9Robert Jay Mejorada100% (4)
- School Form 5A (SF 5A)Document3 pagesSchool Form 5A (SF 5A)Ijherafel Baliola YusophNo ratings yet
- Bentley Software Installation and ActivationDocument2 pagesBentley Software Installation and ActivationSaifur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Music LP OrchestraDocument11 pagesMusic LP OrchestraCybi MethueneNo ratings yet
- De Thi Thu TN THPT 2024 Tieng Anh So GD Ha NoiDocument23 pagesDe Thi Thu TN THPT 2024 Tieng Anh So GD Ha NoiQuang Lê Hồ DuyNo ratings yet
- Final - Thesis Quantum Study Silicon NanowiresDocument154 pagesFinal - Thesis Quantum Study Silicon NanowiresChandra Bhal SinghNo ratings yet
- GeoseaDocument9 pagesGeoseaArthur WakashimasuNo ratings yet
- Light and Geometric OpticsDocument53 pagesLight and Geometric OpticsLeah May Tamayo ManayonNo ratings yet
- Biology WaterDocument22 pagesBiology WaternurhanisahmohamadnorNo ratings yet
- Low-Cost Arrival Assistance Service Vietnam AirportDocument9 pagesLow-Cost Arrival Assistance Service Vietnam AirportvietnamfasttrackserviceNo ratings yet
- The Best Classical Music For New YearDocument10 pagesThe Best Classical Music For New Yeardane franolicNo ratings yet
- Carasuc Form 2 GalleryDocument2 pagesCarasuc Form 2 GalleryJohn Henry TampoyNo ratings yet
- Quantum Tunneling and Spin 14Document14 pagesQuantum Tunneling and Spin 14plfratarNo ratings yet