Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Enzymes Notes For Mdcat
Enzymes Notes For Mdcat
Uploaded by
Brohi Nadeem0%(1)0% found this document useful (1 vote)
321 views3 pagesEnzymes are biocatalysts that speed up chemical reactions without being consumed. They do this by lowering the activation energy required for reactions to occur. Enzymes are mostly proteins that have specialized active sites that substrates can attach to, and they work through either the lock and key or induced fit models of catalysis. Some key characteristics of enzymes are that they are substrate and pH specific, work best at certain temperatures, and are needed only in small amounts to cause large changes.
Original Description:
Original Title
enzymes notes for mdcat
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentEnzymes are biocatalysts that speed up chemical reactions without being consumed. They do this by lowering the activation energy required for reactions to occur. Enzymes are mostly proteins that have specialized active sites that substrates can attach to, and they work through either the lock and key or induced fit models of catalysis. Some key characteristics of enzymes are that they are substrate and pH specific, work best at certain temperatures, and are needed only in small amounts to cause large changes.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0%(1)0% found this document useful (1 vote)
321 views3 pagesEnzymes Notes For Mdcat
Enzymes Notes For Mdcat
Uploaded by
Brohi NadeemEnzymes are biocatalysts that speed up chemical reactions without being consumed. They do this by lowering the activation energy required for reactions to occur. Enzymes are mostly proteins that have specialized active sites that substrates can attach to, and they work through either the lock and key or induced fit models of catalysis. Some key characteristics of enzymes are that they are substrate and pH specific, work best at certain temperatures, and are needed only in small amounts to cause large changes.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
CHAPTER 3 ENZYME
“Biocatalyst which speeds the rate of chemical reaction without
itself being consumed or utilized”
Activation energy is minimum energy required to initiate a
reaction
Enzyme speeds up rate of chemical reaction by lowering
Activation energy
1 min = 4 Trillion reactions
60 min = 240 Trillion reactions
Enzyme Characteristics
Proteinaceous mostly (Few made up of rRNA- Ribozyme)
Globular protein
High molecular weight
Macro - molecules
Temperature specific / sensitive (Labile)
pH Specific
Substrate specific
Water as absolute medium
Required in small quantities to bring a large amount of
change
Substrates are smaller in size than enzyme
They have specialized active site onto which substrate can
attach itself
Enzymes are of 2 types on the basis of site of action :
Exoenzyme – Functioning outside the cell
Endoenzyme – Functioning inside the cell
They are involved in a chemical reaction but not consumed
or utilized
They work under both acidic and alkaline medium –
amphoteric
Their activity can be accelerated by certain ions known as
activators. E.g Zn, Mg, Mn, Cl
Their activity can be inhibited by few FACTORS such as
substrate concentration, low Ph, High temp, enzyme
concentration.
Mode of action of Enzyme
1. Lock & Key Model – Fischer (1898)
2. Induce Fit Model – Koshland (1959)
Lock and Key Model
This model reflects the complimentary relationship
between substrate and enzyme in such a way that a specific
substrate can fit onto a specific active site of the enzyme
just like lock and key relation.
This model could not differentiate between actual substrate
and mimicking molecule known as competitive inhibitors.
Induce Fit Model
This model states that when a substrate fits onto its
respective active site, it undergoes charge verification with
active site to produce a conformational change in shape of
active site to proceed a reaction.
This model helps in determining between actual substrate
and mimicking molecules.
Factors Affecting Enzyme Activity
Concentration of Substrate
Effect of Temp
Effect of pH
Effect of Co enzyme, activators and inhibitors
Effect of water
Effect of Radiation
You might also like
- 2-14 Epoxidation of AlkenesDocument2 pages2-14 Epoxidation of AlkenesMohd Zulhelmi AzmiNo ratings yet
- Biocatalysts and Enzyme TechnologyDocument9 pagesBiocatalysts and Enzyme TechnologyMichelle Santillán0% (1)
- Gas Chromatography Mass SpectrometryDocument20 pagesGas Chromatography Mass SpectrometryNirmal SharmaNo ratings yet
- 2016 BCH223 PracticalsDocument7 pages2016 BCH223 PracticalsvictorNo ratings yet
- Ontario HOT2000 PDFDocument138 pagesOntario HOT2000 PDFelish_agrawalNo ratings yet
- COCO Help TEADocument43 pagesCOCO Help TEAPedro Milton ChibulachoNo ratings yet
- Enzymes: A Practical Introduction to Structure, Mechanism, and Data AnalysisFrom EverandEnzymes: A Practical Introduction to Structure, Mechanism, and Data AnalysisRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Enzymes:: The Nature's CatalystsDocument51 pagesEnzymes:: The Nature's Catalystskrk100% (1)
- Comparison of GC MS and FTIR Methods ForDocument7 pagesComparison of GC MS and FTIR Methods ForIan RidzuanNo ratings yet
- Chemical Vs Enzyme Catalydasis AdvantageDocument10 pagesChemical Vs Enzyme Catalydasis AdvantageDavid AntonitoNo ratings yet
- CalorimeterDocument2 pagesCalorimeterUrvi MaruNo ratings yet
- General Principles of CatalysisDocument12 pagesGeneral Principles of CatalysisOLUWASEGUN K AfolabiNo ratings yet
- Microcarrier Cell Culture ScaleUp Procedures HandbookDocument32 pagesMicrocarrier Cell Culture ScaleUp Procedures HandbookDolphingNo ratings yet
- Measurement of Cellulase ActivitiesDocument12 pagesMeasurement of Cellulase ActivitiesJanaina LimaNo ratings yet
- Determination of Intrinsic Viscosity and MW OF PolystyreneDocument19 pagesDetermination of Intrinsic Viscosity and MW OF PolystyreneNouran ShedidNo ratings yet
- Gel FiltrationDocument123 pagesGel FiltrationZulfikri Asmardi RaufNo ratings yet
- Sem 3 Bt8303 Basic Industrial Biot Question BankDocument59 pagesSem 3 Bt8303 Basic Industrial Biot Question BankarchanaNo ratings yet
- Docko MaticDocument86 pagesDocko MaticAbdurrahman Olğaç0% (1)
- Ion Exchange Chromatography Research PaperDocument6 pagesIon Exchange Chromatography Research Papergz8xbnex100% (1)
- BiotechDocument486 pagesBiotechDertySulistyowatiNo ratings yet
- Shuguang Zhang Et Al - Design of Nanostructured Biological Materials Through Self-Assembly of Peptides and ProteinsDocument8 pagesShuguang Zhang Et Al - Design of Nanostructured Biological Materials Through Self-Assembly of Peptides and ProteinsGmewop30m100% (1)
- 03.affinity Efficacy PotencyDocument33 pages03.affinity Efficacy PotencyelitechemsNo ratings yet
- Strain Improvement TechniquesDocument28 pagesStrain Improvement TechniqueselaiyarajaNo ratings yet
- NIH Public Access: Introduction To Peptide SynthesisDocument17 pagesNIH Public Access: Introduction To Peptide SynthesisStella AguirreNo ratings yet
- कालनिर्णय २०१८ PDFDocument12 pagesकालनिर्णय २०१८ PDFAjinkya JogiNo ratings yet
- The SQA Unit and Other Actors in The SQA SystemDocument14 pagesThe SQA Unit and Other Actors in The SQA SystemAli RazaNo ratings yet
- CatalysisDocument6 pagesCatalysisNaveen PalaNo ratings yet
- Enzyme AssayDocument23 pagesEnzyme AssayTanvir JawadNo ratings yet
- SCH 421 Reactor Design WEEK 1 & 2 Notes-1Document15 pagesSCH 421 Reactor Design WEEK 1 & 2 Notes-1vivaline AchiengNo ratings yet
- 2014 - Enzyme Assays PDFDocument15 pages2014 - Enzyme Assays PDFJason ParsonsNo ratings yet
- Live Webinar: A Better Understanding Causes, Control Strategy and Regulatory ApproachesDocument44 pagesLive Webinar: A Better Understanding Causes, Control Strategy and Regulatory ApproachesBen ClarkeNo ratings yet
- Protein Biocatalyst (Enzyme)Document3 pagesProtein Biocatalyst (Enzyme)Khairul RidwanNo ratings yet
- Nzymes: By: Mrs. Kalaivani Sathish. M. Pharm, Assistant Professor, Pims - PanipatDocument63 pagesNzymes: By: Mrs. Kalaivani Sathish. M. Pharm, Assistant Professor, Pims - Panipaturmila pandeyNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Chemcad 5.1Document34 pagesIntroduction To Chemcad 5.1Kennie Ntege LubwamaNo ratings yet
- Lead Optimization PDFDocument22 pagesLead Optimization PDFMoh Zulkifli SyarifuddinNo ratings yet
- Brochure BPS-200 EnglishDocument8 pagesBrochure BPS-200 Englishpls509sNo ratings yet
- 11 Bioprocess Design Consideration PDFDocument21 pages11 Bioprocess Design Consideration PDFsodgoweisjdNo ratings yet
- CatalysisDocument54 pagesCatalysisRajatSonkarNo ratings yet
- Biochem HNDDocument130 pagesBiochem HNDCHIEMEZIEM NJOKU100% (1)
- QC in Clinical LaboratoriesDocument28 pagesQC in Clinical LaboratoriesMustafa KhandgawiNo ratings yet
- ArticA Multistep Synthesis Incorporating A Green Bromination of An Aromatic RinguloDocument3 pagesArticA Multistep Synthesis Incorporating A Green Bromination of An Aromatic Ringuloitz_19No ratings yet
- Inhibitor Sourcebook Third EditionDocument234 pagesInhibitor Sourcebook Third Editionchristina_finkeNo ratings yet
- Char Point and Bloom - Physicochemical and AnalyticalDocument2 pagesChar Point and Bloom - Physicochemical and AnalyticalKhanh NguyenNo ratings yet
- Classification of BioreactorsDocument2 pagesClassification of BioreactorsisabelelmhNo ratings yet
- Problems Associates With Edible Coating 16008Document25 pagesProblems Associates With Edible Coating 16008Sahil MujawarNo ratings yet
- PapainDocument3 pagesPapainMohamed0% (1)
- Agglutination and PrecipitationDocument28 pagesAgglutination and PrecipitationRohith GunduNo ratings yet
- Optimization of Cellulase Enzyme From Vegetable Waste by Using Trichoderma Atroviride in Solid State FermentationDocument6 pagesOptimization of Cellulase Enzyme From Vegetable Waste by Using Trichoderma Atroviride in Solid State FermentationIOSRjournalNo ratings yet
- GC AASGasChromatography AtomicAbsorptionspectrometry Advancedspectralanalysis MPHARMACYMPCTDocument9 pagesGC AASGasChromatography AtomicAbsorptionspectrometry Advancedspectralanalysis MPHARMACYMPCTSubhasish DashNo ratings yet
- Mechanism of Enzyme ActionDocument2 pagesMechanism of Enzyme ActionBlazy InhumangNo ratings yet
- Bottel Filling ReportDocument6 pagesBottel Filling ReportUdaya InduwaraNo ratings yet
- Nano Structured HydrogelsDocument11 pagesNano Structured HydrogelsMarina MelencuNo ratings yet
- Data Biostataplus Sbi2014-EDocument4 pagesData Biostataplus Sbi2014-ELucila Milagros PinillosNo ratings yet
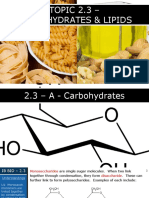
- 09 - IB Biology (2016) - 2.3 - Carbohydrates & LipidsDocument29 pages09 - IB Biology (2016) - 2.3 - Carbohydrates & LipidsSamuel French RojasNo ratings yet
- Steric Stabilizers For Cubic Phase Lyotropic Liquid Crystal Nanodispersions (Cubosomas)Document57 pagesSteric Stabilizers For Cubic Phase Lyotropic Liquid Crystal Nanodispersions (Cubosomas)Karla PooleyNo ratings yet
- Cleland Nomenclature For Enzymes (Bi-Bi) Enzymatic Reactions, Which Make Up 60% of All EnzymaticDocument25 pagesCleland Nomenclature For Enzymes (Bi-Bi) Enzymatic Reactions, Which Make Up 60% of All EnzymatictsanusaNo ratings yet
- Enzyme Catalysis: Salahaddin-University-Erbil College of Education Chemistry DepartmentDocument11 pagesEnzyme Catalysis: Salahaddin-University-Erbil College of Education Chemistry DepartmentZana EdrisNo ratings yet
- L8 EnzymesDocument26 pagesL8 Enzymesayaanali.voraNo ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument3 pagesEnzymesArabela SimanganNo ratings yet
- Enzymes Mode of Action of EnzymesDocument6 pagesEnzymes Mode of Action of EnzymesNamra MazherNo ratings yet
- CHEM-XII Chap-8 Bullet Points (Sir Fakhir)Document2 pagesCHEM-XII Chap-8 Bullet Points (Sir Fakhir)Brohi NadeemNo ratings yet
- Entry Test For Pharm-D Exam-2024 (Session-2023-24) Date (11-02-2024)Document27 pagesEntry Test For Pharm-D Exam-2024 (Session-2023-24) Date (11-02-2024)Brohi NadeemNo ratings yet
- Novel Mcqs With Answer KeyDocument53 pagesNovel Mcqs With Answer KeyBrohi NadeemNo ratings yet
- CHP-19 WORKSHEET (1) For MdcatDocument2 pagesCHP-19 WORKSHEET (1) For MdcatBrohi NadeemNo ratings yet