Professional Documents
Culture Documents
General Botany 3
General Botany 3
Uploaded by
Kin-Aleth Damiles Aragon0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views4 pagesThis document provides an introduction and overview of the field of botany. It discusses the main subdisciplines of botany including plant taxonomy, anatomy, morphology, physiology, genetics, cytology, and ecology. It also describes the gross structures of plants including root systems, shoot systems, and reproductive structures. Key aspects of plant cells are outlined such as cell walls, membranes, organelles, and specialization. The document provides definitions and examples to introduce foundational concepts in botany.
Original Description:
fea
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides an introduction and overview of the field of botany. It discusses the main subdisciplines of botany including plant taxonomy, anatomy, morphology, physiology, genetics, cytology, and ecology. It also describes the gross structures of plants including root systems, shoot systems, and reproductive structures. Key aspects of plant cells are outlined such as cell walls, membranes, organelles, and specialization. The document provides definitions and examples to introduce foundational concepts in botany.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views4 pagesGeneral Botany 3
General Botany 3
Uploaded by
Kin-Aleth Damiles AragonThis document provides an introduction and overview of the field of botany. It discusses the main subdisciplines of botany including plant taxonomy, anatomy, morphology, physiology, genetics, cytology, and ecology. It also describes the gross structures of plants including root systems, shoot systems, and reproductive structures. Key aspects of plant cells are outlined such as cell walls, membranes, organelles, and specialization. The document provides definitions and examples to introduce foundational concepts in botany.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 4
lOMoARcPSD|16836832
Lesson 1 - GENERAL BOTANY LECTURE (INTRODUCTION
TO BOTANY)
BS Biology (Pamantasan ng Lungsod ng Maynila)
Studocu is not sponsored or endorsed by any college or university
Downloaded by Kin-Aleth Aragon (niknogara05@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|16836832
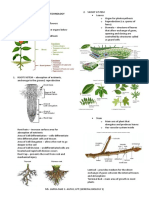
GENERAL BOTANY (LEC) Plant Ecology
LESSON 1 (INTRODUCTION TO BOTANY)
- Relationships of plants and environment
Botany – scientific study of plants’:
- Reaction of plants with certain conditions
- structures (internal [anatomical] & external
- Parasitic plants – get their food from host
[morphological])
Plant Pathology
- Factors that affect plant growth
(temperature, amt. of light/gas, type of soil, - Study of plant diseases
etc.) - (viral, bacterial, fungal)
- Development (from seeds, as well as Paleobotany
physical & chemical factors that affect
- Plant fossils and their importance
development)
- Obtain great info among plants that existed
Subsciences of Botany
a long time ago
Plant Taxonomy
- taxis – arrangement/order
Gross Structure of Plants
- naming, nomenclature
Root System
- One of the oldest sciences
- Important because it’s hard to study - Dicot: Tap root (main) & Lateral root
organisms w/out knowing their names
- Monocot: Fibrous root (no primary root)
Plant Anatomy
Shoot System
- More on internal
- Leaves – site of photosynthesis
- Microscope is required
- Petiole – attaches leaf to the stem
- Study of plants’ vessels, vascular system
- Blade
- (xylem, phloem, stomata)
- Apical bud – arises apex
Plant Morphology
- Axillary bud – develops between a leaf and
- More on external
stem
- Plant organs, types of fruit system, leaves
- Internode – space between 2 nodes
- (apex margins, etc.)
Reproductive Shoot
Plant Physiology
- Modified leaves
- Functions of plants
- Petals – for attraction
- (photosynthesis, cellular respiration)
- Carpels – pistils
Plant Genetics
Angiosperms vs Gymnosperms
- Study of plants’ heredity, inheritance of
characteristics, variation. Gymno
- (off springs will have variations from
- Cones – made of scales, geen -> brown,
parents)
woody
- Application is important because of the
Genetically Modified Organisms (GMO), Pistillate – ovulate cone (female)
Cultivars were improved
Staminate – pollinate (male)
Plant Cytology
- Leaves – needle-likeS
- Study of plant cells
- (chromosome composition) Angio
- Plants are often polyploids (multiple sets of
- Flower
chromosomes)
DEANG, Yoko
Downloaded by Kin-Aleth Aragon (niknogara05@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|16836832
Ovules – embryosac (female) Cell wall – [prokaryotic: peptidoglycan-
carbohydrates, sugar, amino acids]
Pollen – germ nucleus, tube nucleus
- [eukaryotic: chemically simple]
(male)
Plasma membrane – sterols- kind of fats, have
- Haploid carbohydrates as receptors
- Except for sporophyte (2n) Cytoplasm – cytoskeleton – cell organelles
- Cytoplastic streaming – moving of plant
Parts of the Flower
parts under the microscope
1. Sepals – group: calyx
Ribosomes – sites of protein synthesis
2. Petals – group: corolla
- S (unit of measurement for sedimentation
3. Stamens – anther & filament (male) coefficient) – Svedberg
4. Carpels/Pistil – stigma, style, ovary (female) Chromosomes – (histones: wool & spool)
- female gametophyte – embryo Cell division – (conjugation)
sac
Cell Specialization
- ovule – becomes seeds
Guard cells – use osmotic pressure to open and
Characteristics of Plants close stomata
- Eukaryotic – nucleus enclosed w/ nuclear - Very important since in regulates the size of
membrane stoma
- Autotrophic – make their own food Brachyslereids – stone cells
- Multicellular - Specialized cells
- Cell walls are made of cellulose - Schlerenchyma (thick secondary cell wall)
- Contain chloroplasts (ch a & ch b; - (e.g. pear)
carotenoids (yellow, orange, brownish),
Astroclereids – star-shaped
anthocyanins (blue, red, violet)
- Found in nymphaea (aquatic plant) and
- Gives off oxygen
helps floatation
- Sessile – can’t move from one place to
Bulliform cells – very large compared to other
another (however, can perform tropism)
cells surrounding it
- Has stomata for gas exchange (mostly on
- Fan-shaped
leaves)
- Usually found in monocot leaves
- Cell specialization
- Sensitive to change humidity, makes leaves
- Alternation of generation – sporophyte
roll in adaptation or protection from heat
gen., gametophyte gen.
*phloem – carries sugar
Prokaryotic vs Eukaryotic cells
*xylem – carries water & nutrients
*some important notes only, kindly refer to the table
- Metaxylem
Cytoplasm - where cellular respiration takes place
(prokaryotic) - Protoxylem
Flagellum – 9+2 structure (universal to eukaryotes) – 2 Life Cycle of a Moss
pairs of microtubules [center], 9 pairs of microtubules *important notes only, kindly refer to the illustration
[outer]
Gametophyte – mature female plant – reproductive
Glycocalyx – capsule/ slime organs can be seen
- Present in animal cell Archegonium – the female reproductive organ in ferns,
- Important for cell recognition (serves as mosses & angiosperms (one egg only)
protection) Venther – expanded part (contains the egg)
Water – is required (mosses thrive in wet areas)
DEANG, Yoko
Downloaded by Kin-Aleth Aragon (niknogara05@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|16836832
Antheridium – male gametophyte (multiple cells)
Zygote – fertilized egg
Neck – narrow part
Calyptra – covers the young sporophyte for protection,
the only haploid.
Sporophyte – young plant
Seta – stalk
Sporangium
Foot – bottom
Operculum – covering (breaks open)
Economic Importance of Plants
Basic needs – food
Habitat – for birds, insects, etc.
Medicines – those that have been studied
Soil Integrity – monocots (grass) prevent erosion as well
as dicots.
- Decomposing of organic matter
from plants also improve soil
Air quality & Humidity Levels – absorbs CO2 which is a
greenhouse gas and releases oxygen
Aesthetic Values
Regulates water cycle – through condensation of water
vapor and regulation of groundwater by preventing
erosion
DEANG, Yoko
Downloaded by Kin-Aleth Aragon (niknogara05@gmail.com)
You might also like
- Lesson 1 - Gen Bot LecDocument3 pagesLesson 1 - Gen Bot LecYoko DeangNo ratings yet
- NMAT Review 2018 Module - BiologyDocument34 pagesNMAT Review 2018 Module - BiologyRaf Lin DrawsNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio ReviewerDocument4 pagesGen Bio ReviewerRaphael Grant CastilloNo ratings yet
- Info 1Document1 pageInfo 1Adam HusseinNo ratings yet
- Plant Anatomy - NotesDocument7 pagesPlant Anatomy - Notesbeatrice acabadoNo ratings yet
- Plant Kingdom NotesDocument25 pagesPlant Kingdom NotesV 4UNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Biology of Agricultural CropsDocument8 pagesChapter 2: Biology of Agricultural CropsDwight Luciano T MendezNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7Document4 pagesLecture 7김j.kNo ratings yet
- Genetic Engineering: Ways To DisperseDocument4 pagesGenetic Engineering: Ways To DisperseBill McKillNo ratings yet
- Biological ClassDocument4 pagesBiological ClassVaibhav ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Biology 2 Plant Morphology and Biotechnology Plant SystemsDocument3 pagesBiology 2 Plant Morphology and Biotechnology Plant SystemslarraNo ratings yet
- 2 Biological Classification-Sample Notes 2021Document2 pages2 Biological Classification-Sample Notes 2021Pranavi MuthusamyNo ratings yet
- Biological Classification PDFDocument4 pagesBiological Classification PDFDanish UllahNo ratings yet
- GenBio (1st Long Exam Reviewer)Document20 pagesGenBio (1st Long Exam Reviewer)Ethan Erika BionaNo ratings yet
- GenBio (1st Long Exam Reviewer)Document20 pagesGenBio (1st Long Exam Reviewer)Ethan Erika BionaNo ratings yet
- Viruses: Lytic Cycle Lysogenic CycleDocument8 pagesViruses: Lytic Cycle Lysogenic CycleTài nguyễnNo ratings yet
- Different Tissue Types and Organ Systems in PlantsDocument6 pagesDifferent Tissue Types and Organ Systems in Plantsashleyjade.sundiam.sccNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Botany (PLANTS)Document10 pagesPharmaceutical Botany (PLANTS)yaoi yuri100% (1)
- Chapter 1 ClassificationDocument8 pagesChapter 1 Classificationyoura4203No ratings yet
- Plant Kingdom AlgaeDocument7 pagesPlant Kingdom AlgaeKhùśh NäùłákhāNo ratings yet
- Module 10: The Stem: Barrento, Mary Gabriele Bermudez, Helena Audrey Casia, Julia Marie Marquez, Francesca JulianneDocument16 pagesModule 10: The Stem: Barrento, Mary Gabriele Bermudez, Helena Audrey Casia, Julia Marie Marquez, Francesca JulianneJen AdvientoNo ratings yet
- Exam Guidelines Grade 11 Life SciencesDocument11 pagesExam Guidelines Grade 11 Life SciencesZwelihle BruheimNo ratings yet
- General BotanyDocument4 pagesGeneral BotanyAngela ParaynoNo ratings yet
- CM 4Document106 pagesCM 4Dawa NorbuNo ratings yet
- SBI3U:Plant Unit Review: Non-Vascular PlantsDocument2 pagesSBI3U:Plant Unit Review: Non-Vascular PlantsPavni ChandaniNo ratings yet
- PlantsDocument14 pagesPlantsnicoledearden7No ratings yet
- Core CH 19 BiodiversityDocument8 pagesCore CH 19 Biodiversitystudy.stkgNo ratings yet
- Lec 5. Plant Structure, Growth and DevelopmentDocument15 pagesLec 5. Plant Structure, Growth and DevelopmentLiana Rose MeregildoNo ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument7 pagesUntitled Documentmax.gabuteroocampoNo ratings yet
- Branches ListDocument3 pagesBranches ListSamantha RullaNo ratings yet
- Zoology Lecture: Transcript + NotesDocument35 pagesZoology Lecture: Transcript + NotesCharles GuillermoNo ratings yet
- Plant Structure, Growth, and Development: RootsDocument9 pagesPlant Structure, Growth, and Development: RootsHerlin MabalaNo ratings yet
- NIOS Biology CH 1 Origin and Evolution of Life Part 6Document4 pagesNIOS Biology CH 1 Origin and Evolution of Life Part 6Samuel OsuNo ratings yet
- Highly-Branched: General Biology 1 Basic Plant Cell and Tissue Types 1. ParenchymaDocument8 pagesHighly-Branched: General Biology 1 Basic Plant Cell and Tissue Types 1. ParenchymaAlfonso PlantillaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in BotanyDocument13 pagesReviewer in BotanyIrish MartinezNo ratings yet
- Morphology of Flowering Plants - Structure of Flowering PlantDocument5 pagesMorphology of Flowering Plants - Structure of Flowering Plantmohammed amaan paNo ratings yet
- BOT 109 Lecture 1Document3 pagesBOT 109 Lecture 1Japi TorratoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To General Botany PDFDocument14 pagesIntroduction To General Botany PDFnathaniel80% (5)
- 1 Botlec ReviewerDocument7 pages1 Botlec ReviewerKamille PobleteNo ratings yet
- Plant Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument14 pagesPlant Anatomy and PhysiologyRana Muhammad HuzaifNo ratings yet
- Branches of BotanyDocument5 pagesBranches of BotanyBianca RamirezNo ratings yet
- Botany - Prelims NotesDocument30 pagesBotany - Prelims NotesKier PanugaoNo ratings yet
- PK Notes Ncert Detail ExplnDocument33 pagesPK Notes Ncert Detail Explnarjun shindeNo ratings yet
- Unfurling Fern Biology in The Genomics AgeDocument9 pagesUnfurling Fern Biology in The Genomics AgeRetno NovvitasariNo ratings yet
- Plant-Physiology-Intro.-pptx - SDocument19 pagesPlant-Physiology-Intro.-pptx - SJego ManloloNo ratings yet
- BIO100 LE2ReviewerDocument2 pagesBIO100 LE2ReviewerMariel De Leon GinesNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio Ii FinalsDocument4 pagesGen Bio Ii Finalskenjia814No ratings yet
- Malaluan, M.M. Summary Notes PDFDocument5 pagesMalaluan, M.M. Summary Notes PDFAngel MalaluanNo ratings yet
- Botany - A Branch of Biology That StudiesDocument3 pagesBotany - A Branch of Biology That StudiesTom CuencaNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 7: Diversity in Living OrganismsDocument32 pagesChapter - 7: Diversity in Living OrganismsSrikant SubramanianNo ratings yet
- The Living World: Mind MapDocument12 pagesThe Living World: Mind MapPrince100% (1)
- Theories of The Origin of Solar SystemDocument18 pagesTheories of The Origin of Solar SystemGWYNETH REIN CARI�ONo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Biological ClassificationDocument9 pagesChapter 2 Biological ClassificationYashiNo ratings yet
- BIOCHEM Mid - Short QuestionsDocument13 pagesBIOCHEM Mid - Short QuestionsMazhar FarNo ratings yet
- 4th Sem Botany P IVDocument83 pages4th Sem Botany P IVRaushan varmaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Botany: Botany Is The Branch of Biology Concerned With The Scientific Study of PlantsDocument39 pagesIntroduction To Botany: Botany Is The Branch of Biology Concerned With The Scientific Study of PlantsHazelClaveNo ratings yet
- TH THDocument12 pagesTH THnayandeep080No ratings yet
- Chapter - 7-Diversity in Living Organisms - Class Ix - ScienceDocument32 pagesChapter - 7-Diversity in Living Organisms - Class Ix - ScienceMadhav DayareNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 7: Diversity in Living OrganismsDocument33 pagesChapter - 7: Diversity in Living Organismsuma mishraNo ratings yet
- Academic CommissionsDocument8 pagesAcademic CommissionsKin-Aleth Damiles AragonNo ratings yet
- Aragon, Katrina HRDM 2B Mission Vission. Environmental PolicyDocument2 pagesAragon, Katrina HRDM 2B Mission Vission. Environmental PolicyKin-Aleth Damiles AragonNo ratings yet
- GEC 7 MODULE 3 Science and Technology and Nation BuildingDocument17 pagesGEC 7 MODULE 3 Science and Technology and Nation BuildingKin-Aleth Damiles AragonNo ratings yet
- Effective Verbal and Nonverbal CommunicationDocument21 pagesEffective Verbal and Nonverbal CommunicationKin-Aleth Damiles AragonNo ratings yet
- Filipino ArtistDocument4 pagesFilipino ArtistKin-Aleth Damiles AragonNo ratings yet
- Three Year Projected Comprehensive Income StatementDocument3 pagesThree Year Projected Comprehensive Income StatementKin-Aleth Damiles AragonNo ratings yet
- Corn Growth StagesDocument33 pagesCorn Growth StagesAthar Vegas Al JaggadNo ratings yet
- Planting Trees and Shrubs in The Landscape: Washington State University Extension Fact Sheet - Fs047eDocument10 pagesPlanting Trees and Shrubs in The Landscape: Washington State University Extension Fact Sheet - Fs047eroh009No ratings yet
- Full Guide On Cactus Diseases, Pests and TreatmentsDocument18 pagesFull Guide On Cactus Diseases, Pests and TreatmentsPurple CrystalNo ratings yet
- Effect of Rooting Media and IBA (Indole Butyric Acid) Levels On Rooting and Survival of AIR Layering in Fig (Ficus Carica L.) Cv. Under Middle Gujarat Agro-Climatic ConditionsDocument5 pagesEffect of Rooting Media and IBA (Indole Butyric Acid) Levels On Rooting and Survival of AIR Layering in Fig (Ficus Carica L.) Cv. Under Middle Gujarat Agro-Climatic ConditionsFaten AbdallahNo ratings yet
- Class 9 Bio PracticalsDocument23 pagesClass 9 Bio PracticalsRaj PandeyNo ratings yet
- GB1Q1W2L2Document5 pagesGB1Q1W2L2StephNo ratings yet
- Killling On A Tree Quetion AnswarsDocument3 pagesKillling On A Tree Quetion AnswarsAnjan BasakNo ratings yet
- Mangrove - Ecosystems - PowerPoint TechniquesDocument26 pagesMangrove - Ecosystems - PowerPoint TechniquesPhyo Aung HeinNo ratings yet
- Tratamento Com SilicioDocument9 pagesTratamento Com SilicioGabriel SpigariolNo ratings yet
- USA Vetiver Installation Guide 2012Document16 pagesUSA Vetiver Installation Guide 2012MANJURUL ANAMNo ratings yet
- GraftingDocument38 pagesGraftingISHITA GUPTANo ratings yet
- Subhan Danish Soil Sci 2020 BzuDocument177 pagesSubhan Danish Soil Sci 2020 BzuKhadijaNo ratings yet
- 42 Home Improvement ProjectsDocument24 pages42 Home Improvement ProjectsSreenivas ReddyNo ratings yet
- Microbial Inoculants in Sustainable Agricultural Productivity Vol. 1Document354 pagesMicrobial Inoculants in Sustainable Agricultural Productivity Vol. 1PekkaSwamplordNo ratings yet
- Nilam Module F5 Biology AnswersDocument34 pagesNilam Module F5 Biology Answerskazin yuen kah zingNo ratings yet
- PlantDocument28 pagesPlantNovelinda RenataNo ratings yet
- Topic Economic Importance of Bryophytes: Course Title: BryologyDocument31 pagesTopic Economic Importance of Bryophytes: Course Title: BryologywertyuiodfghjklNo ratings yet
- Benghalensis) (B) Still Roots - Delicate Steam Develops Shot and Thick Supporting Roots From The Basal Portion ofDocument2 pagesBenghalensis) (B) Still Roots - Delicate Steam Develops Shot and Thick Supporting Roots From The Basal Portion ofAni Oo SamaNo ratings yet
- AFA With AnswersDocument17 pagesAFA With AnswersLovely day ybanezNo ratings yet
- MEC10 Moisture&Temperature&EC Sensor InstructionsDocument35 pagesMEC10 Moisture&Temperature&EC Sensor InstructionspablogepsaNo ratings yet
- Grade 5 Science Weeks 9-12 Worksheets - Term 1Document25 pagesGrade 5 Science Weeks 9-12 Worksheets - Term 1Latchmini DyalNo ratings yet
- Biostimulants From By-Products of Anaerobic Digestion PDFDocument17 pagesBiostimulants From By-Products of Anaerobic Digestion PDFVassilis TziakasNo ratings yet
- Botanical Pharmacognosy of AndrographisDocument4 pagesBotanical Pharmacognosy of AndrographisNongton DeBitNo ratings yet
- PothosDocument9 pagesPothosPra TamaNo ratings yet
- Socioeconomic Benefits of Shade TreesDocument18 pagesSocioeconomic Benefits of Shade TreesMulatu SimeonNo ratings yet
- 1 An Illustrated Guide To AgroforestryDocument28 pages1 An Illustrated Guide To AgroforestryJam ColasNo ratings yet
- 2022-2023-Class VI-General Science-Part 13-AWDocument13 pages2022-2023-Class VI-General Science-Part 13-AWyoshidxbNo ratings yet
- Site Plan GarwoodDocument6 pagesSite Plan Garwoodarchvizatelier920No ratings yet
- Alfalfa Germination & GrowthDocument22 pagesAlfalfa Germination & GrowthINES BAZANNo ratings yet
- B.SC BOTANY Semester 3-4 Syllabus June 2018Document18 pagesB.SC BOTANY Semester 3-4 Syllabus June 2018Barnali DuttaNo ratings yet