Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lipids Summary Sheet
Lipids Summary Sheet
Uploaded by
monira alfadhilCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Clinical Questions: Histidine To HistamineDocument28 pagesClinical Questions: Histidine To HistamineNancy AkunnaNo ratings yet
- Parrillo Sports Nutrition Guide Part 2Document299 pagesParrillo Sports Nutrition Guide Part 2shawn hogan100% (2)
- Material Safety Data Sheet Jatropa Curcas DTZ 2009Document6 pagesMaterial Safety Data Sheet Jatropa Curcas DTZ 2009Arshita Wahyuning AtmokoNo ratings yet
- LipidDocument36 pagesLipidSina AgataNo ratings yet
- Hoy Ito Na Talaga Final LipidsDocument19 pagesHoy Ito Na Talaga Final LipidsJohn Daniel PangilinanNo ratings yet
- LipidsDocument12 pagesLipidsELOISA DELOS SANTOSNo ratings yet
- LIPIDSDocument6 pagesLIPIDSluzvi3110No ratings yet
- Lipids: o Dehydration Synthesis Is When TheDocument3 pagesLipids: o Dehydration Synthesis Is When TheKheza SuravillaNo ratings yet
- Metabolism Essential For Vital Processes.: Series of Chemical ReactionsDocument75 pagesMetabolism Essential For Vital Processes.: Series of Chemical ReactionsValeria RosasNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Biological Molecules: Santa Laurensia Senior High SchoolDocument45 pagesIntroduction To Biological Molecules: Santa Laurensia Senior High SchoolDeddy KismanaNo ratings yet
- LipidsDocument19 pagesLipidsShem Jenuelle SuarezNo ratings yet
- Biology Form 4 LipidsDocument14 pagesBiology Form 4 LipidsSofea RamieNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Lipids Copy 2Document23 pagesChapter 5 Lipids Copy 2gus peepNo ratings yet
- The Structure and Function of MacromoleculesDocument105 pagesThe Structure and Function of MacromoleculesJena-LynNo ratings yet
- Macromolecules: Concept 1: Macromolecules Are Polymers, Built From MonomersDocument8 pagesMacromolecules: Concept 1: Macromolecules Are Polymers, Built From MonomersLindsay GabrielNo ratings yet
- MacromolekulDocument85 pagesMacromolekultengku imamNo ratings yet
- UNIT 2 v3Document58 pagesUNIT 2 v3sampathjogipusala123No ratings yet
- BMS1011 Week3 L5Document25 pagesBMS1011 Week3 L5Arshaan ShaikhNo ratings yet
- LIPIDSDocument4 pagesLIPIDSJasper VillegasNo ratings yet
- Bio MoleculesDocument22 pagesBio MoleculesWinter BwiiNo ratings yet
- BioChem - LipidsDocument41 pagesBioChem - LipidsKYLE ANDREW SAWITNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry - Chapter 17Document3 pagesBiochemistry - Chapter 17Denise Mae DivinoNo ratings yet
- SBI4U Biochemistry NotesDocument13 pagesSBI4U Biochemistry NotesAli MalikNo ratings yet
- The Structure and Function of Macromolecules - Ihb.oktober 2015Document107 pagesThe Structure and Function of Macromolecules - Ihb.oktober 2015Nadya Hasna Rasyida DANo ratings yet
- Chapter 5-Macromolecules Part IDocument29 pagesChapter 5-Macromolecules Part Ijanardhan aghavNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 - Lipids and Proteins Are Associated in Biological Membranes - Part 1Document44 pagesChapter 8 - Lipids and Proteins Are Associated in Biological Membranes - Part 1Tommy RamazzottoNo ratings yet
- LipidsDocument9 pagesLipidssalbahenglotlotNo ratings yet
- FLASHCARDSDocument5 pagesFLASHCARDSAngel CalambaNo ratings yet
- SESE 115 Biochemistry: Don Mariano Marcos Memorial State University La Union PhilippinesDocument13 pagesSESE 115 Biochemistry: Don Mariano Marcos Memorial State University La Union PhilippinesVhenz MapiliNo ratings yet
- Biological Molecules: Prepared By: Mrs. Eden C. SanchezDocument62 pagesBiological Molecules: Prepared By: Mrs. Eden C. SanchezBernard D. Fajardo Jr.No ratings yet
- Water PH and Biological MoleculesDocument39 pagesWater PH and Biological MoleculesSrdjanNo ratings yet
- Lipids Sample BrochureDocument2 pagesLipids Sample BrochureCaryl Alvarado Silang0% (1)
- LIPIDS ReviewerDocument4 pagesLIPIDS ReviewermayiachiqtNo ratings yet
- LipidsDocument11 pagesLipidsbingbong2231No ratings yet
- Lipids Friends or Foes-1121Document57 pagesLipids Friends or Foes-1121ywnrmgp9fxNo ratings yet
- Bio MoleculesDocument39 pagesBio MoleculesMilani ReyesNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 Lipids PbeDocument51 pagesLecture 6 Lipids PbeCeylin BaykoçNo ratings yet
- Macro Tech BrochureDocument2 pagesMacro Tech BrochureaznpowerNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - Biochemistry - LipidsDocument25 pagesLecture 3 - Biochemistry - LipidsKim Bryan A. JavierNo ratings yet
- Brochure 22Document2 pagesBrochure 22danielle stephanieNo ratings yet
- Note - LipidsDocument17 pagesNote - Lipids705458No ratings yet
- Lipids: StructureDocument42 pagesLipids: Structurecream oNo ratings yet
- LIPIDS D PharmDocument65 pagesLIPIDS D PharmMadhuri poulkarNo ratings yet
- The FOUR Classes of Large Biomolecules الجزيئات الاربع الحيوية الاكبر في تركيب الكائناتDocument29 pagesThe FOUR Classes of Large Biomolecules الجزيئات الاربع الحيوية الاكبر في تركيب الكائناتIraqiNo ratings yet
- BIOL BCHM 111 BiomoleculesDocument49 pagesBIOL BCHM 111 BiomoleculeshavenNo ratings yet
- CP511 - Food Chemistry - Lipids - Lecture NoteDocument9 pagesCP511 - Food Chemistry - Lipids - Lecture NoteAD DNo ratings yet
- MTChem2 Lab Module 3 Exp 5Document3 pagesMTChem2 Lab Module 3 Exp 511stem2.enriquemariajulianaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document60 pagesChapter 5EhazNo ratings yet
- Lipid ChemistryDocument53 pagesLipid ChemistryMayuri DhanushwarNo ratings yet
- LIPIDS PRESENTATION Second Discussion BSNDocument13 pagesLIPIDS PRESENTATION Second Discussion BSNkesheeestopaNo ratings yet
- Biological MacromoleculesDocument103 pagesBiological MacromoleculesEuniceNo ratings yet
- Lipids: Important Secondary Source of Energy in The BodyDocument4 pagesLipids: Important Secondary Source of Energy in The BodyAshley UmNo ratings yet
- Notes3 - LipidsKey (Clean)Document7 pagesNotes3 - LipidsKey (Clean)Lanz MoenNo ratings yet
- BIOMOLECULESDocument2 pagesBIOMOLECULESKeith Chastine MiraballesNo ratings yet
- Lipids and CarbohydratesDocument27 pagesLipids and CarbohydratesbogattjeffNo ratings yet
- Week 3 - LipidsDocument32 pagesWeek 3 - LipidsNICOLE KAYE MANALANGNo ratings yet
- Physical Science Biological MacromoleculesDocument49 pagesPhysical Science Biological MacromoleculesHannah Lee JudillaNo ratings yet
- BIOCHEMISTRYDocument11 pagesBIOCHEMISTRYebaadmalik653No ratings yet
- Unit 5 TransDocument11 pagesUnit 5 TransGrace FernandoNo ratings yet
- Structure and Classification of Lipids: Lipids Are Naturally Occurring MoleculesDocument19 pagesStructure and Classification of Lipids: Lipids Are Naturally Occurring MoleculesKomic WebtoonNo ratings yet
- Lipids ReportDocument33 pagesLipids ReportCaryl Ann C. SernadillaNo ratings yet
- Week 3 Lipids ProteinsDocument21 pagesWeek 3 Lipids Proteinssabeera.ahmadNo ratings yet
- A-level Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Act 1 - Final Term - BIOCHEMDocument7 pagesAct 1 - Final Term - BIOCHEMHatol, Rommel ArangelNo ratings yet
- 9-15 CHDocument108 pages9-15 CHShubham SharmaNo ratings yet
- Classification of Lipids and Their ExamplesDocument2 pagesClassification of Lipids and Their ExamplesA C100% (1)
- Biochemistry - Chapter 17Document3 pagesBiochemistry - Chapter 17Denise Mae DivinoNo ratings yet
- BIO 121 Tutorial 14-07-2021Document19 pagesBIO 121 Tutorial 14-07-2021PARVATHY ANIL - IMS20211No ratings yet
- Metabolism LipidsDocument23 pagesMetabolism LipidsYuli MuliyaniNo ratings yet
- Lab Exercise 6Document3 pagesLab Exercise 6clarence manegdegNo ratings yet
- Understandings, Applications and Skills (This Is What You Maybe Assessed On)Document14 pagesUnderstandings, Applications and Skills (This Is What You Maybe Assessed On)Big CinemaNo ratings yet
- Sit - Intern PresentationDocument43 pagesSit - Intern PresentationBhinitha ChandrasagaranNo ratings yet
- Oil Crops For Energy: G Koc Ar, Ege University Solar Energy Institute, Izmir, TurkeyDocument10 pagesOil Crops For Energy: G Koc Ar, Ege University Solar Energy Institute, Izmir, TurkeyDiegoVasqzNo ratings yet
- A Fully Automated Clinical Chemistry Analyser With Unrivalled PerformanceDocument16 pagesA Fully Automated Clinical Chemistry Analyser With Unrivalled PerformanceBadmus AdeyemiNo ratings yet
- Quiz 6Document2 pagesQuiz 6Lam NhậtNo ratings yet
- Pcog Lec Midterms PDFDocument18 pagesPcog Lec Midterms PDFMikaela YumulNo ratings yet
- 2013EC Source-Extraction-And-Constituents-Of-Fats-And-OilsDocument8 pages2013EC Source-Extraction-And-Constituents-Of-Fats-And-OilsĜĭdęŷ KîřöşNo ratings yet
- Ws MoleculesDocument96 pagesWs Moleculessalahuddin_md5935No ratings yet
- CXS 234e PDFDocument77 pagesCXS 234e PDFAlief AzizahNo ratings yet
- Infrared Spectroscopy Differences Between Biodiesel Prepared From Rapeseed and The Edible Rapaseed OilDocument2 pagesInfrared Spectroscopy Differences Between Biodiesel Prepared From Rapeseed and The Edible Rapaseed Oilrgx1120% (1)
- Brochure-MakatiMed Health Packages 2015Document2 pagesBrochure-MakatiMed Health Packages 2015Mikee FelipeNo ratings yet
- Williams Basic Nutrition and Diet Therapy 14th Edition Nix Test BankDocument10 pagesWilliams Basic Nutrition and Diet Therapy 14th Edition Nix Test Bankjonathanmelendezscpjzgfikb100% (12)
- Vitamins & LipidsDocument64 pagesVitamins & LipidsShimmering MoonNo ratings yet
- Digestion PDFDocument15 pagesDigestion PDFPandat JiNo ratings yet
- 1.5 LipidsDocument19 pages1.5 Lipidsasifh76543No ratings yet
- MilkDocument35 pagesMilkBorja Bueno GarciaNo ratings yet
- Biochem Midterm ReviewerDocument22 pagesBiochem Midterm Reviewerrentachin18No ratings yet
- Edible Oils, Fat, and WaxesDocument37 pagesEdible Oils, Fat, and WaxesNur LaelahNo ratings yet
- Palm Oil Standard MethodDocument3 pagesPalm Oil Standard MethodUswatul HasanahNo ratings yet
- Coconut OilDocument18 pagesCoconut OilEniabire Ayodeji67% (3)
Lipids Summary Sheet
Lipids Summary Sheet
Uploaded by
monira alfadhilOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lipids Summary Sheet
Lipids Summary Sheet
Uploaded by
monira alfadhilCopyright:
Available Formats
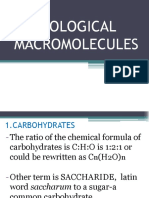
Chapter 23.
3 - Lipids
• Large molecules but not polymers
• Non-polar, hydrophobic, so they don’t dissolve in water
• Their main functions (store energy & make up most of the cell structure membranes
• The major building blocks are fatty acids.
Fatty acids:
• Long chain carboxylic acid could be saturated or unsaturated.
• Saturated: Stearic acid – all bonds are single, Unsaturated: Oleic acid (has low melting point) – at least one double bond.
• Unsaturated converted into saturated through hydrogenation reaction.
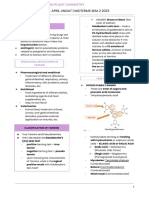
Triglycerides Phospholipids Waxes Steroids
• Three fatty acids with one glycerol, synthesized through condensation • Triglyceride (fatty acid) and phosphate group, a Waxes are lipids • lipids that have multiple cyclic rings in their
reaction, form ester bond. triglyceride in which a fatty acid is replaced by formed by combining structures
• Triglyceride could be solid at room temperature (Fat) or liquid (Oil). a phosphate group. a fatty acid with a • No fatty acids)
• Make up all the cell membrane bilayer, called long-chain alcohol, • All are made from the basic four-ring steroid.
lipid bilayer. both plants and Examples:
• Connection real life: Venom of some snakes animals make waxes. ✓ Vitamin D: plays a role in the formation of bones.
contains the enzyme phospholipase that ✓ Sex hormones: such as estrogen and testosterone,
breaks down the phospholipids, once it enters regulate metabolic process.
the blood stream it destroys the phospholipids ✓ Cholesterol: important structural component of cell
of blood cells and causes death. membranes.
Saponification
Connection to real life:
You might also like
- Clinical Questions: Histidine To HistamineDocument28 pagesClinical Questions: Histidine To HistamineNancy AkunnaNo ratings yet
- Parrillo Sports Nutrition Guide Part 2Document299 pagesParrillo Sports Nutrition Guide Part 2shawn hogan100% (2)
- Material Safety Data Sheet Jatropa Curcas DTZ 2009Document6 pagesMaterial Safety Data Sheet Jatropa Curcas DTZ 2009Arshita Wahyuning AtmokoNo ratings yet
- LipidDocument36 pagesLipidSina AgataNo ratings yet
- Hoy Ito Na Talaga Final LipidsDocument19 pagesHoy Ito Na Talaga Final LipidsJohn Daniel PangilinanNo ratings yet
- LipidsDocument12 pagesLipidsELOISA DELOS SANTOSNo ratings yet
- LIPIDSDocument6 pagesLIPIDSluzvi3110No ratings yet
- Lipids: o Dehydration Synthesis Is When TheDocument3 pagesLipids: o Dehydration Synthesis Is When TheKheza SuravillaNo ratings yet
- Metabolism Essential For Vital Processes.: Series of Chemical ReactionsDocument75 pagesMetabolism Essential For Vital Processes.: Series of Chemical ReactionsValeria RosasNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Biological Molecules: Santa Laurensia Senior High SchoolDocument45 pagesIntroduction To Biological Molecules: Santa Laurensia Senior High SchoolDeddy KismanaNo ratings yet
- LipidsDocument19 pagesLipidsShem Jenuelle SuarezNo ratings yet
- Biology Form 4 LipidsDocument14 pagesBiology Form 4 LipidsSofea RamieNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Lipids Copy 2Document23 pagesChapter 5 Lipids Copy 2gus peepNo ratings yet
- The Structure and Function of MacromoleculesDocument105 pagesThe Structure and Function of MacromoleculesJena-LynNo ratings yet
- Macromolecules: Concept 1: Macromolecules Are Polymers, Built From MonomersDocument8 pagesMacromolecules: Concept 1: Macromolecules Are Polymers, Built From MonomersLindsay GabrielNo ratings yet
- MacromolekulDocument85 pagesMacromolekultengku imamNo ratings yet
- UNIT 2 v3Document58 pagesUNIT 2 v3sampathjogipusala123No ratings yet
- BMS1011 Week3 L5Document25 pagesBMS1011 Week3 L5Arshaan ShaikhNo ratings yet
- LIPIDSDocument4 pagesLIPIDSJasper VillegasNo ratings yet
- Bio MoleculesDocument22 pagesBio MoleculesWinter BwiiNo ratings yet
- BioChem - LipidsDocument41 pagesBioChem - LipidsKYLE ANDREW SAWITNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry - Chapter 17Document3 pagesBiochemistry - Chapter 17Denise Mae DivinoNo ratings yet
- SBI4U Biochemistry NotesDocument13 pagesSBI4U Biochemistry NotesAli MalikNo ratings yet
- The Structure and Function of Macromolecules - Ihb.oktober 2015Document107 pagesThe Structure and Function of Macromolecules - Ihb.oktober 2015Nadya Hasna Rasyida DANo ratings yet
- Chapter 5-Macromolecules Part IDocument29 pagesChapter 5-Macromolecules Part Ijanardhan aghavNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 - Lipids and Proteins Are Associated in Biological Membranes - Part 1Document44 pagesChapter 8 - Lipids and Proteins Are Associated in Biological Membranes - Part 1Tommy RamazzottoNo ratings yet
- LipidsDocument9 pagesLipidssalbahenglotlotNo ratings yet
- FLASHCARDSDocument5 pagesFLASHCARDSAngel CalambaNo ratings yet
- SESE 115 Biochemistry: Don Mariano Marcos Memorial State University La Union PhilippinesDocument13 pagesSESE 115 Biochemistry: Don Mariano Marcos Memorial State University La Union PhilippinesVhenz MapiliNo ratings yet
- Biological Molecules: Prepared By: Mrs. Eden C. SanchezDocument62 pagesBiological Molecules: Prepared By: Mrs. Eden C. SanchezBernard D. Fajardo Jr.No ratings yet
- Water PH and Biological MoleculesDocument39 pagesWater PH and Biological MoleculesSrdjanNo ratings yet
- Lipids Sample BrochureDocument2 pagesLipids Sample BrochureCaryl Alvarado Silang0% (1)
- LIPIDS ReviewerDocument4 pagesLIPIDS ReviewermayiachiqtNo ratings yet
- LipidsDocument11 pagesLipidsbingbong2231No ratings yet
- Lipids Friends or Foes-1121Document57 pagesLipids Friends or Foes-1121ywnrmgp9fxNo ratings yet
- Bio MoleculesDocument39 pagesBio MoleculesMilani ReyesNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 Lipids PbeDocument51 pagesLecture 6 Lipids PbeCeylin BaykoçNo ratings yet
- Macro Tech BrochureDocument2 pagesMacro Tech BrochureaznpowerNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - Biochemistry - LipidsDocument25 pagesLecture 3 - Biochemistry - LipidsKim Bryan A. JavierNo ratings yet
- Brochure 22Document2 pagesBrochure 22danielle stephanieNo ratings yet
- Note - LipidsDocument17 pagesNote - Lipids705458No ratings yet
- Lipids: StructureDocument42 pagesLipids: Structurecream oNo ratings yet
- LIPIDS D PharmDocument65 pagesLIPIDS D PharmMadhuri poulkarNo ratings yet
- The FOUR Classes of Large Biomolecules الجزيئات الاربع الحيوية الاكبر في تركيب الكائناتDocument29 pagesThe FOUR Classes of Large Biomolecules الجزيئات الاربع الحيوية الاكبر في تركيب الكائناتIraqiNo ratings yet
- BIOL BCHM 111 BiomoleculesDocument49 pagesBIOL BCHM 111 BiomoleculeshavenNo ratings yet
- CP511 - Food Chemistry - Lipids - Lecture NoteDocument9 pagesCP511 - Food Chemistry - Lipids - Lecture NoteAD DNo ratings yet
- MTChem2 Lab Module 3 Exp 5Document3 pagesMTChem2 Lab Module 3 Exp 511stem2.enriquemariajulianaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document60 pagesChapter 5EhazNo ratings yet
- Lipid ChemistryDocument53 pagesLipid ChemistryMayuri DhanushwarNo ratings yet
- LIPIDS PRESENTATION Second Discussion BSNDocument13 pagesLIPIDS PRESENTATION Second Discussion BSNkesheeestopaNo ratings yet
- Biological MacromoleculesDocument103 pagesBiological MacromoleculesEuniceNo ratings yet
- Lipids: Important Secondary Source of Energy in The BodyDocument4 pagesLipids: Important Secondary Source of Energy in The BodyAshley UmNo ratings yet
- Notes3 - LipidsKey (Clean)Document7 pagesNotes3 - LipidsKey (Clean)Lanz MoenNo ratings yet
- BIOMOLECULESDocument2 pagesBIOMOLECULESKeith Chastine MiraballesNo ratings yet
- Lipids and CarbohydratesDocument27 pagesLipids and CarbohydratesbogattjeffNo ratings yet
- Week 3 - LipidsDocument32 pagesWeek 3 - LipidsNICOLE KAYE MANALANGNo ratings yet
- Physical Science Biological MacromoleculesDocument49 pagesPhysical Science Biological MacromoleculesHannah Lee JudillaNo ratings yet
- BIOCHEMISTRYDocument11 pagesBIOCHEMISTRYebaadmalik653No ratings yet
- Unit 5 TransDocument11 pagesUnit 5 TransGrace FernandoNo ratings yet
- Structure and Classification of Lipids: Lipids Are Naturally Occurring MoleculesDocument19 pagesStructure and Classification of Lipids: Lipids Are Naturally Occurring MoleculesKomic WebtoonNo ratings yet
- Lipids ReportDocument33 pagesLipids ReportCaryl Ann C. SernadillaNo ratings yet
- Week 3 Lipids ProteinsDocument21 pagesWeek 3 Lipids Proteinssabeera.ahmadNo ratings yet
- A-level Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Act 1 - Final Term - BIOCHEMDocument7 pagesAct 1 - Final Term - BIOCHEMHatol, Rommel ArangelNo ratings yet
- 9-15 CHDocument108 pages9-15 CHShubham SharmaNo ratings yet
- Classification of Lipids and Their ExamplesDocument2 pagesClassification of Lipids and Their ExamplesA C100% (1)
- Biochemistry - Chapter 17Document3 pagesBiochemistry - Chapter 17Denise Mae DivinoNo ratings yet
- BIO 121 Tutorial 14-07-2021Document19 pagesBIO 121 Tutorial 14-07-2021PARVATHY ANIL - IMS20211No ratings yet
- Metabolism LipidsDocument23 pagesMetabolism LipidsYuli MuliyaniNo ratings yet
- Lab Exercise 6Document3 pagesLab Exercise 6clarence manegdegNo ratings yet
- Understandings, Applications and Skills (This Is What You Maybe Assessed On)Document14 pagesUnderstandings, Applications and Skills (This Is What You Maybe Assessed On)Big CinemaNo ratings yet
- Sit - Intern PresentationDocument43 pagesSit - Intern PresentationBhinitha ChandrasagaranNo ratings yet
- Oil Crops For Energy: G Koc Ar, Ege University Solar Energy Institute, Izmir, TurkeyDocument10 pagesOil Crops For Energy: G Koc Ar, Ege University Solar Energy Institute, Izmir, TurkeyDiegoVasqzNo ratings yet
- A Fully Automated Clinical Chemistry Analyser With Unrivalled PerformanceDocument16 pagesA Fully Automated Clinical Chemistry Analyser With Unrivalled PerformanceBadmus AdeyemiNo ratings yet
- Quiz 6Document2 pagesQuiz 6Lam NhậtNo ratings yet
- Pcog Lec Midterms PDFDocument18 pagesPcog Lec Midterms PDFMikaela YumulNo ratings yet
- 2013EC Source-Extraction-And-Constituents-Of-Fats-And-OilsDocument8 pages2013EC Source-Extraction-And-Constituents-Of-Fats-And-OilsĜĭdęŷ KîřöşNo ratings yet
- Ws MoleculesDocument96 pagesWs Moleculessalahuddin_md5935No ratings yet
- CXS 234e PDFDocument77 pagesCXS 234e PDFAlief AzizahNo ratings yet
- Infrared Spectroscopy Differences Between Biodiesel Prepared From Rapeseed and The Edible Rapaseed OilDocument2 pagesInfrared Spectroscopy Differences Between Biodiesel Prepared From Rapeseed and The Edible Rapaseed Oilrgx1120% (1)
- Brochure-MakatiMed Health Packages 2015Document2 pagesBrochure-MakatiMed Health Packages 2015Mikee FelipeNo ratings yet
- Williams Basic Nutrition and Diet Therapy 14th Edition Nix Test BankDocument10 pagesWilliams Basic Nutrition and Diet Therapy 14th Edition Nix Test Bankjonathanmelendezscpjzgfikb100% (12)
- Vitamins & LipidsDocument64 pagesVitamins & LipidsShimmering MoonNo ratings yet
- Digestion PDFDocument15 pagesDigestion PDFPandat JiNo ratings yet
- 1.5 LipidsDocument19 pages1.5 Lipidsasifh76543No ratings yet
- MilkDocument35 pagesMilkBorja Bueno GarciaNo ratings yet
- Biochem Midterm ReviewerDocument22 pagesBiochem Midterm Reviewerrentachin18No ratings yet
- Edible Oils, Fat, and WaxesDocument37 pagesEdible Oils, Fat, and WaxesNur LaelahNo ratings yet
- Palm Oil Standard MethodDocument3 pagesPalm Oil Standard MethodUswatul HasanahNo ratings yet
- Coconut OilDocument18 pagesCoconut OilEniabire Ayodeji67% (3)