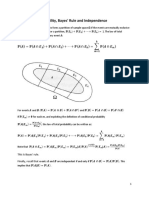
Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Truth Table Examples
Truth Table Examples
Uploaded by
Tshepang Radingoanis0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views11 pagesThe document summarizes logical operators including NOT, AND, OR, implication, biconditional. It provides truth tables for the operators and examples of combinations including A AND NOT B, NOT (C OR D), E OR (F AND G), H implies NOT I OR J, K biconditional NOT L OR M, N biconditional O implies P AND N, and determines if two expressions are logically equivalent. It asks the reader to complete the truth tables.
Original Description:
Original Title
Truth table examples
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document summarizes logical operators including NOT, AND, OR, implication, biconditional. It provides truth tables for the operators and examples of combinations including A AND NOT B, NOT (C OR D), E OR (F AND G), H implies NOT I OR J, K biconditional NOT L OR M, N biconditional O implies P AND N, and determines if two expressions are logically equivalent. It asks the reader to complete the truth tables.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views11 pagesTruth Table Examples
Truth Table Examples
Uploaded by
Tshepang RadingoanisThe document summarizes logical operators including NOT, AND, OR, implication, biconditional. It provides truth tables for the operators and examples of combinations including A AND NOT B, NOT (C OR D), E OR (F AND G), H implies NOT I OR J, K biconditional NOT L OR M, N biconditional O implies P AND N, and determines if two expressions are logically equivalent. It asks the reader to complete the truth tables.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 11
Summary of logical operators:
¬ NOT. Opposite ¬𝑇 = 𝐹
(~) ¬𝐹 = 𝑇
⋀ AND. Only a true and a true gives a true; all 𝑇⋀𝑇 =𝑇
others are false 𝑇⋀𝐹 =𝐹
𝐹⋀𝑇 =𝐹
𝐹⋀𝐹 =𝐹
⋁ OR. Just need at least one true for a true 𝑇⋁𝑇 = 𝑇
result or the only way to get a false result is if 𝑇⋁𝐹 = 𝑇
there are two false values. 𝐹⋁𝑇 = 𝑇
𝐹⋁𝐹 = 𝐹
→ Implication. If…then. Only false result if a true 𝑇→𝐹=𝐹
‘is followed’ by a false; all others are true 𝑇→𝑇=𝑇
𝑷 → 𝑸 ≡ ¬𝑷⋁𝑸 𝐹→𝑇=𝑇
𝐹→𝐹=𝑇
↔ Biconditional. If and only if (iff). True if both 𝑇↔𝑇=𝑇
have the same value 𝐹↔𝐹=𝑇
𝑇↔𝐹=𝐹
𝐹↔𝑇=𝐹
Complete the truth tables for the following:
1. 𝐴⋀¬𝐵
2. ¬(𝐶⋁𝐷)
3. 𝐸⋁𝐹⋀𝐺
4. 𝐻 → ¬𝐼⋁𝐽
5. 𝐾 ↔ ¬𝐿⋁𝑀
6. 𝑁 ↔ 𝑂 → 𝑃⋀𝑁
7. Determine if 𝑄⋀(𝑅⋁𝑆) is logically equivalent to (𝑄⋀𝑅)⋁(𝑄⋀𝑆)
8. ((𝑇⋀𝑈) → ¬(𝑉 ↔ 𝑈))
1. 𝐴⋀¬𝐵
2. ¬(𝐶⋁𝐷)
3. 𝐸⋁𝐹⋀𝐺
4. 𝐻 → ¬𝐼⋁𝐽
5. 𝐾 ↔ ¬𝐿⋁𝑀
6. 𝑁 ↔ 𝑂 → 𝑃⋀𝑁
7. Determine if 𝑄⋀(𝑅⋁𝑆) is logically equivalent to (𝑄⋀𝑅)⋁(𝑄⋀𝑆)
8. ((𝑇⋀𝑈) → ¬(𝑉 ↔ 𝑈))
You might also like
- 7and 8th Semester SCJan5Document48 pages7and 8th Semester SCJan5Maharghya BiswasNo ratings yet
- 21 MleDocument24 pages21 MlealexpaulirunguNo ratings yet
- Algebra Set 1Document2 pagesAlgebra Set 1Albert PangilinanNo ratings yet
- Improper Integrals FinalDocument26 pagesImproper Integrals FinalKhokon GayenNo ratings yet
- Average VelocityDocument3 pagesAverage VelocitybatazaiNo ratings yet
- Math 9 Module Week14Document3 pagesMath 9 Module Week14Destiny Fiona Peralta PilarNo ratings yet
- AER602 SummaryDocument2 pagesAER602 Summarymuhammad.shibl.imamNo ratings yet
- The Laplace TransformDocument3 pagesThe Laplace TransformRenaldoNo ratings yet
- The Formal Rules of Algebra PDFDocument4 pagesThe Formal Rules of Algebra PDFFranco NfonNo ratings yet
- List of EquationsDocument8 pagesList of EquationsxadoogarNo ratings yet
- Q2 Week1 Quadratic InequalitiesDocument22 pagesQ2 Week1 Quadratic InequalitiesGONZALES, RINOA GABRIELLE S.No ratings yet
- CASINILLO LogicAct1Document3 pagesCASINILLO LogicAct1Jhon Ryzel LagubisNo ratings yet
- L17: Quasi-Fermi Levels and Steady State: EE203 Semiconductor DevicesDocument19 pagesL17: Quasi-Fermi Levels and Steady State: EE203 Semiconductor Devicesabdul ahadNo ratings yet
- Basic of LogicDocument41 pagesBasic of Logicyoudy012No ratings yet
- Topic 4 - Power Series - Q&A - Q1-Q6Document12 pagesTopic 4 - Power Series - Q&A - Q1-Q6deivasigamaniNo ratings yet
- Proving Lagrange EquationDocument5 pagesProving Lagrange Equationأحمد علي الفاخريNo ratings yet
- Lectute 1 - Instrumental Variable MethodDocument32 pagesLectute 1 - Instrumental Variable MethodHưng PhạmNo ratings yet
- Unit-III Probability and Random VariablesDocument10 pagesUnit-III Probability and Random VariablesYogi kalisettiNo ratings yet
- EE221 Part8FT A DrYazidDocument13 pagesEE221 Part8FT A DrYazidIbrahim GhunaimNo ratings yet
- Statistical InferenceDocument55 pagesStatistical Inferenceshamilabdulazeez9No ratings yet
- All Concepts in Linear Differential EquationDocument3 pagesAll Concepts in Linear Differential Equationpranaybhandare765No ratings yet
- STAT 6100 - MATH 6180 Lecture 24 - The Exponential Distribution (Continued)Document20 pagesSTAT 6100 - MATH 6180 Lecture 24 - The Exponential Distribution (Continued)Ramana NimaiNo ratings yet
- All Formulae CH # 03Document2 pagesAll Formulae CH # 03abbas ZafarNo ratings yet
- Unit-Iiic DevcDocument14 pagesUnit-Iiic Devc464-JALLA GANESHNo ratings yet
- 9 CLTDocument19 pages9 CLTrsmyrsmy14No ratings yet
- Dependent Event Formula: Derive The Equation ofDocument18 pagesDependent Event Formula: Derive The Equation ofTheKnow04No ratings yet
- 6-Continuous Random VariableDocument14 pages6-Continuous Random Variableadamoh62No ratings yet
- MAM1019H NotesDocument10 pagesMAM1019H NotesRendani TshikovhiNo ratings yet
- EE221 Part8FT B DrYazidDocument22 pagesEE221 Part8FT B DrYazidIbrahim GhunaimNo ratings yet
- Lecture PPT ProbabilityDocument16 pagesLecture PPT ProbabilityMohamed AlgilyNo ratings yet
- DRS 113 Probability Theory Lecture Notes CollectionDocument246 pagesDRS 113 Probability Theory Lecture Notes CollectionNay AungNo ratings yet
- Measurement and Instrumentation Lab: Experiment 1Document44 pagesMeasurement and Instrumentation Lab: Experiment 1Pranay DumbhareNo ratings yet
- APDEs Lec 6Document16 pagesAPDEs Lec 6Mohammad YarNo ratings yet
- Summary (ES) أ. احمد الزريعيDocument7 pagesSummary (ES) أ. احمد الزريعيLilian AlkordyNo ratings yet
- Lecture Seven: 1.derivatives of Exponential and Logarithm Functions 2. Applied OptimizationDocument8 pagesLecture Seven: 1.derivatives of Exponential and Logarithm Functions 2. Applied OptimizationEdi MuhammNo ratings yet
- Moment Generating FunctionDocument13 pagesMoment Generating FunctionSagar PandeyNo ratings yet
- Final Exam Study Guide (5 Problems A Day)Document5 pagesFinal Exam Study Guide (5 Problems A Day)strijelaš MuminovićNo ratings yet
- WTW 238 English SummaryDocument30 pagesWTW 238 English Summarykotjanekarabo1No ratings yet
- Law of ExponentsDocument7 pagesLaw of ExponentsDe GuzmanNo ratings yet
- EXAM FormulaSheetDocument9 pagesEXAM FormulaSheetAbood RainNo ratings yet
- Solving Quads by Factorization FinalDocument8 pagesSolving Quads by Factorization Finalchelsea correaNo ratings yet
- 1.quality of Tests and EstimatorsDocument51 pages1.quality of Tests and Estimators加赛 郭No ratings yet
- Lecture 6. Random Variable and Its DistributionDocument7 pagesLecture 6. Random Variable and Its Distributionkatherineoden14No ratings yet
- Gen Math Module 6 Solving Exponential Equation and Inequalities - 112920Document18 pagesGen Math Module 6 Solving Exponential Equation and Inequalities - 112920MGrace P. VergaraNo ratings yet
- Gen Math Module 6 Solving Exponential Equation and Inequalities - 112920 PDFDocument18 pagesGen Math Module 6 Solving Exponential Equation and Inequalities - 112920 PDFMGrace P. VergaraNo ratings yet
- Exposición TG 12Document11 pagesExposición TG 12MOISES DAVID HUAMAN TORRESNo ratings yet
- Selective Review - ProbabilityDocument30 pagesSelective Review - ProbabilityNouman KhanNo ratings yet
- Module 6: Analysis of Algorithms: Reading From The Textbook: Chapter 4 AlgorithmsDocument19 pagesModule 6: Analysis of Algorithms: Reading From The Textbook: Chapter 4 AlgorithmsDejing KongNo ratings yet
- Wuolah Free Apuntes Parte 2Document4 pagesWuolah Free Apuntes Parte 2José Manuel Santiago ToscanoNo ratings yet
- Unit - V: Statistical Technique & DistributionDocument20 pagesUnit - V: Statistical Technique & DistributionGirraj DohareNo ratings yet
- Important Properties in AlgebraDocument47 pagesImportant Properties in AlgebraRohclem Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Discrete Probability Distributions: Variance Mean Probability Distribution NameDocument7 pagesDiscrete Probability Distributions: Variance Mean Probability Distribution NamemustafaNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Methods SYMBOL of SUM, Double SUM and MultiplicationDocument24 pagesQuantitative Methods SYMBOL of SUM, Double SUM and MultiplicationCasper DarkusNo ratings yet
- Kinetic and Ideal Reactors (Lecture 2)Document61 pagesKinetic and Ideal Reactors (Lecture 2)Ratta VattaNo ratings yet
- Methods of ProofDocument13 pagesMethods of ProofIsmailNo ratings yet
- Radically Elementary Probability Theory. (AM-117), Volume 117From EverandRadically Elementary Probability Theory. (AM-117), Volume 117Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)