Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 viewsAids
Aids
Uploaded by
Arnav DeshpandeAIDS was first reported in 1981 and detected in homosexual males in the US. It has resulted in over 25 million deaths globally. HIV is the virus that causes AIDS and was first identified in 1983. It is a retrovirus that attacks CD4+ T cells and progressively destroys the immune system. There is no cure for AIDS, but treatment with antiretroviral drugs can control the virus and prevent opportunistic infections. Prevention efforts focus on safe sex practices, sterile medical equipment, and education programs.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Cen-Tr 16999-2019Document75 pagesCen-Tr 16999-2019Muhammed Hasan GüçlüNo ratings yet
- BIO CBSE 12 PROJECT On HIV/AISDocument15 pagesBIO CBSE 12 PROJECT On HIV/AISAnonymous KdUrkMIyJQ72% (58)
- NationDocument88 pagesNationJustin Luu0% (1)
- Hiv and Prevention of Mother-To-Child Transmission (PMTCT) : by Gebremaryam TDocument100 pagesHiv and Prevention of Mother-To-Child Transmission (PMTCT) : by Gebremaryam THambal AhamedNo ratings yet
- Group 1 - HIV - Case StudyDocument30 pagesGroup 1 - HIV - Case StudyCONTRERAS, ALIANNA IRISHNo ratings yet
- AidsDocument11 pagesAidsroseannurakNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology: - Infertility - Dysmenorrhea - Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STD)Document22 pagesPathophysiology: - Infertility - Dysmenorrhea - Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STD)Om KambleNo ratings yet
- Hiv and Aids: ID Specialist Tamar KhuchuaDocument84 pagesHiv and Aids: ID Specialist Tamar KhuchuaMAMA LALANo ratings yet
- AidsDocument10 pagesAidsDaniela OxaniNo ratings yet
- World AIDS DayDocument41 pagesWorld AIDS DayAthira SureshNo ratings yet
- Insel11e - ppt18 Sex Transmit DiseaseDocument30 pagesInsel11e - ppt18 Sex Transmit DiseaseThalia SandersNo ratings yet
- Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) and Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS)Document6 pagesHuman Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) and Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS)Vanessa MolinaNo ratings yet
- N.B. HIV-1 and HIV-2 Are The Two Main Types of HIV. Most People With HIV Have HIV-1. HIV in This Document Refers To HIV-1Document4 pagesN.B. HIV-1 and HIV-2 Are The Two Main Types of HIV. Most People With HIV Have HIV-1. HIV in This Document Refers To HIV-1tenqbroNo ratings yet
- HIv FactsDocument5 pagesHIv Factslarrybeechey3792No ratings yet
- 162 Biology of HIVv2Document3 pages162 Biology of HIVv2gert16No ratings yet
- Typhoid Fever Human: ImmunodeficiencyDocument9 pagesTyphoid Fever Human: ImmunodeficiencyJOHN CARLO APATANNo ratings yet
- Immunologic Agents PDFDocument104 pagesImmunologic Agents PDFgherlethrNo ratings yet
- What Is HIV? - Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) Is A Virus That Attacks Cells That Help The Body FightDocument8 pagesWhat Is HIV? - Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) Is A Virus That Attacks Cells That Help The Body Fightdanica grace gubaNo ratings yet
- Bio Cbse 12 Project On Hiv AisDocument15 pagesBio Cbse 12 Project On Hiv Aishelo helium50% (2)
- Reproduction in HumanDocument61 pagesReproduction in HumanSunil YadavNo ratings yet
- Presentation of AIDSDocument16 pagesPresentation of AIDSZainab AbdullahiNo ratings yet
- AIDSDocument10 pagesAIDSFaris ShamimNo ratings yet
- HIV Patient Case - StudentDocument11 pagesHIV Patient Case - StudentNancy FNo ratings yet
- 13--AIDS-FINAL-PPT--------10062024-103852am (3)Document28 pages13--AIDS-FINAL-PPT--------10062024-103852am (3)laiqamalik09No ratings yet
- 1060 Module 1 - HIVDocument5 pages1060 Module 1 - HIVBrandi T.No ratings yet
- Hiv/Aids: by Aisha MansurDocument34 pagesHiv/Aids: by Aisha MansurMpanso Ahmad AlhijjNo ratings yet
- PBH 101 - Hiv - SKMF-1Document22 pagesPBH 101 - Hiv - SKMF-1Zahin KhanNo ratings yet
- Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome or Acquired Immunodeficiency SyndromeDocument37 pagesAcquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome or Acquired Immunodeficiency SyndromeSumon ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Hiv 20infection 20 21 140104152057 Phpapp02Document43 pagesHiv 20infection 20 21 140104152057 Phpapp02Shyden Taghap Billones BordaNo ratings yet
- HIVDocument79 pagesHIVMehiella SatchiNo ratings yet
- Viral DiseasesDocument21 pagesViral Diseasesahmed29-551No ratings yet
- Human Immunodeficiency VirusDocument64 pagesHuman Immunodeficiency Virusmwambungup100% (2)
- Assignment AidsDocument11 pagesAssignment AidsYousaf ManzoorNo ratings yet
- AidsDocument5 pagesAidsBubblegumj Esus ChristNo ratings yet
- Virus Research AssignmentDocument7 pagesVirus Research AssignmentYvonne PangNo ratings yet
- Hiv PPDocument37 pagesHiv PPJitendra YadavNo ratings yet
- Hiv Aids PDFDocument16 pagesHiv Aids PDFМария КозловаNo ratings yet
- Hiv/AidsDocument130 pagesHiv/AidsRoline KarimiNo ratings yet
- HivDocument53 pagesHivReZa FriscaNo ratings yet
- Neuropsychiatric Aspects of HivDocument104 pagesNeuropsychiatric Aspects of HivPriyanka KoundinyaNo ratings yet
- What Is HIV?Document8 pagesWhat Is HIV?Quan ThieuNo ratings yet
- Hiv PresentationDocument10 pagesHiv Presentationapi-534814911No ratings yet
- HIV Case (Long Case)Document16 pagesHIV Case (Long Case)Max mitchyNo ratings yet
- Gulu Cohes Hiv Nelly MDDocument68 pagesGulu Cohes Hiv Nelly MDYIKI ISAACNo ratings yet
- Hiva IdsDocument28 pagesHiva IdsTinotenda TagariraNo ratings yet
- Nursing Clients With HIV Infection and AIDS: Learning ObjectivesDocument11 pagesNursing Clients With HIV Infection and AIDS: Learning Objectivesmorynayim-1No ratings yet
- Hiv AidsDocument14 pagesHiv Aidsapi-221532663No ratings yet
- Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) and Opperortunistic InfectionDocument54 pagesHuman Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) and Opperortunistic InfectionBikash SahNo ratings yet
- HIV Infection !: Dalal AlanaziDocument44 pagesHIV Infection !: Dalal AlanaziKarl Vincent SosoNo ratings yet
- Immunological DisordersDocument78 pagesImmunological DisordersAshwathy ThomasNo ratings yet
- Hiv Unit 1Document108 pagesHiv Unit 1Andrew NgairaNo ratings yet
- Stages of AidsDocument10 pagesStages of AidsHarshitha Gowda HarshiNo ratings yet
- HIV - AIDS PresentationDocument17 pagesHIV - AIDS PresentationphilNo ratings yet
- 8th Grade Health Powerpoint On Hiv and Aids (STDS)Document9 pages8th Grade Health Powerpoint On Hiv and Aids (STDS)Ryan JohnstonNo ratings yet
- End Stage AidsDocument33 pagesEnd Stage AidsMichael T GarciaNo ratings yet
- AIDS in The PhilippinesDocument29 pagesAIDS in The Philippinesjaninasuzette100% (1)
- Hiv/Aids: Mariano Marcos State University College of Health Sciences Department of Nursing Batac City, Ilocos NorteDocument10 pagesHiv/Aids: Mariano Marcos State University College of Health Sciences Department of Nursing Batac City, Ilocos NorteEyySiEffVee100% (1)
- What Is HIV.Document2 pagesWhat Is HIV.Chiranth ChandNo ratings yet
- UNIT 4 - New Challenges: Urja JoshiDocument72 pagesUNIT 4 - New Challenges: Urja JoshiRadhey RavalNo ratings yet
- Aidspptakki 141201102658 Conversion Gate01Document45 pagesAidspptakki 141201102658 Conversion Gate01Rahul DevNo ratings yet
- Spot Speed and Road InventoryDocument22 pagesSpot Speed and Road Inventoryleah yadaoNo ratings yet
- Subjective Tests vs. Objective Tests: Multiple-Choice TestDocument19 pagesSubjective Tests vs. Objective Tests: Multiple-Choice TestMuhammad Hidayatul RifqiNo ratings yet
- F.Y. B.Tech. (Semester - I) (Revised) Examination, December - 2018 Fundamentals of Electronics and Computers (All Branches)Document2 pagesF.Y. B.Tech. (Semester - I) (Revised) Examination, December - 2018 Fundamentals of Electronics and Computers (All Branches)Saurabh BhiseNo ratings yet
- GMSH RefManualDocument396 pagesGMSH RefManualJosé Antonio MoríñigoNo ratings yet
- Extractor de Probetas DEMTECHDocument2 pagesExtractor de Probetas DEMTECHPaul Alex Quiroz BarrionuevoNo ratings yet
- Subject - Verb AgreementDocument12 pagesSubject - Verb AgreementRistaNo ratings yet
- Internship Report .....Document32 pagesInternship Report .....Santosh Thapa100% (1)
- Clinical Audit Where ToDocument13 pagesClinical Audit Where ToMulugeta DagneNo ratings yet
- Research Paper 1Document14 pagesResearch Paper 1Fatima SinghNo ratings yet
- 2023 California Model Year 1978 or Older Light-Duty Vehicle SurveyDocument10 pages2023 California Model Year 1978 or Older Light-Duty Vehicle SurveyNick PopeNo ratings yet
- Senfter Ernste Gedanken PDFDocument8 pagesSenfter Ernste Gedanken PDFthieves11No ratings yet
- Ensuring Ecological Integrity, Clean and Healthy EnvironmentDocument15 pagesEnsuring Ecological Integrity, Clean and Healthy EnvironmentJJNo ratings yet
- Us Nop Organic Compliant Materials 20171121Document3 pagesUs Nop Organic Compliant Materials 20171121LayfloNo ratings yet
- Astm D4Document3 pagesAstm D4Vijayan Munuswamy100% (1)
- Navya MVH HCQDocument13 pagesNavya MVH HCQhosur mvNo ratings yet
- Understanding Order ProcessDocument7 pagesUnderstanding Order ProcessfilipNo ratings yet
- UnivibeDocument1 pageUnivibePablo EspinosaNo ratings yet
- MonographDocument38 pagesMonographNicolocoNo ratings yet
- PNC Infratech Limited Bags Rs.233 Crore PWD Road Project in UP (Company Update)Document2 pagesPNC Infratech Limited Bags Rs.233 Crore PWD Road Project in UP (Company Update)Shyam SunderNo ratings yet
- MarketingDocument110 pagesMarketingriddhi0% (1)
- Widiastini, P.M.F and Et Al. (2023) - Prima Wiyata Health. 4 (2) : 47-56pDocument10 pagesWidiastini, P.M.F and Et Al. (2023) - Prima Wiyata Health. 4 (2) : 47-56pnayla nadrahNo ratings yet
- Ruppur Nuclear Power PlantDocument4 pagesRuppur Nuclear Power PlantShafi Muhammad IstiakNo ratings yet
- Artikel - Esensi Dan Urgensi Integritas Nasional Di Lingkungan Mahasiswa Universitas Sriwijaya Dalam Bhinneka Tunggal IkaDocument8 pagesArtikel - Esensi Dan Urgensi Integritas Nasional Di Lingkungan Mahasiswa Universitas Sriwijaya Dalam Bhinneka Tunggal IkaAkmal DwiNo ratings yet
- Linux IPv6 How ToDocument164 pagesLinux IPv6 How ToAri SetianiNo ratings yet
- International Trade TheoriesDocument38 pagesInternational Trade Theoriestrustme77No ratings yet
- Grundfosliterature 146014Document12 pagesGrundfosliterature 146014Mario Daniel MoreiraNo ratings yet
- Camera Control Pro 2 ManualDocument118 pagesCamera Control Pro 2 ManualBigHeadLittleFeetNo ratings yet
- DCS Slips PartsDocument2 pagesDCS Slips PartsCarlig Radu MihaiNo ratings yet
Aids
Aids
Uploaded by
Arnav Deshpande0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views3 pagesAIDS was first reported in 1981 and detected in homosexual males in the US. It has resulted in over 25 million deaths globally. HIV is the virus that causes AIDS and was first identified in 1983. It is a retrovirus that attacks CD4+ T cells and progressively destroys the immune system. There is no cure for AIDS, but treatment with antiretroviral drugs can control the virus and prevent opportunistic infections. Prevention efforts focus on safe sex practices, sterile medical equipment, and education programs.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentAIDS was first reported in 1981 and detected in homosexual males in the US. It has resulted in over 25 million deaths globally. HIV is the virus that causes AIDS and was first identified in 1983. It is a retrovirus that attacks CD4+ T cells and progressively destroys the immune system. There is no cure for AIDS, but treatment with antiretroviral drugs can control the virus and prevent opportunistic infections. Prevention efforts focus on safe sex practices, sterile medical equipment, and education programs.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views3 pagesAids
Aids
Uploaded by
Arnav DeshpandeAIDS was first reported in 1981 and detected in homosexual males in the US. It has resulted in over 25 million deaths globally. HIV is the virus that causes AIDS and was first identified in 1983. It is a retrovirus that attacks CD4+ T cells and progressively destroys the immune system. There is no cure for AIDS, but treatment with antiretroviral drugs can control the virus and prevent opportunistic infections. Prevention efforts focus on safe sex practices, sterile medical equipment, and education programs.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 3
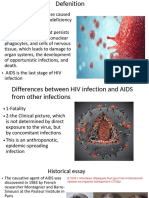
AIDS (Acquired Immuno Deficiency Syndrome)
y AIDS was first reported in 1981.
y It was first detected in homosexual males in USA at Centre for Disease Control, Atlanta.
y It has resulted to more than 25 million deaths.
y HIV I is more common in India and HIV II is more common in West Africa.
y It is characterized by decrease in number of helper T-cells.
y HIV (Human Immuno Deficiency Virus)
○ It is roughly spherical
○ It is around 60 times smaller than a red blood cell,
○ It is composed of two copies of single-stranded RNA
○ The RNAs are enclosed by a conical capsid composed of 2,000 copies of the viral protein p24.
○ The RNA is tightly bound to nucleocapsid proteins
○ A matrix composed of the viral protein p17 surrounds the capsid.
○ The matrix is surrounded by the viral envelope that is composed of two layers of phospholipids.
○ A viral protein and some host proteins are embedded in the envelope. This glycoprotein enables
the virus to attach to and fuse with target cells
Figure 8.5: Human Immuno-deficiency Virus
y Modes of transfer
○ Due to unprotected sexual intercourse with infected partners.
○ Contact of blood with infected tissue/blood.
○ Use of unsterilized material for tattooing or any practice that punctures the skin.
○ From mother to fetus during pregnancy.
○ From mother to child during lactation.
○ AIDS does not spread through mere touch, hugging, sharing meals, shaking hands, mosquito
bites, coughing, sneezing etc.
y Infection
○ After getting into the body of the person, the virus enters into macrophages.
○ Here the RNA genome of the virus replicates to form viral DNA and makes use of the cellular
machinery to produce more and more virus particles.
○ HIV enters T-helper cells and continue to multiply.
○ The progeny viruses are released in the blood. They attack other T-helper cells.
○ This leads to a progressive decrease in the number of T-helper cells.
○ The person suffers from fever, diarrhoea and weight loss.
○ Due to decrease in the number of T-helper cells, the person suffers from infections that the immune
system otherwise could have overcome.
○ The person becomes immuno-deficient.
Multiplication cycle of Retrovirus
Symptoms
y Asymptomatic phase
○ For 5-10 years antibodies are not produced against HIV.
○ There are no specific symptoms.
○ ELISA test comes out to be negative.
○ A fever and some illness may occur in 2-4 weeks after the infection.
y Full blown AIDS
○ The person suffers from fever, diarrhoea and weight loss.
○ The person becomes immunodeficient.
○ The person gets infected by opportunistic infections.
○ The person may suffer from Kaposi’s sarcoma, Burkitt’s lymphoma, primary central nervous
system lymphoma and cervical cancer.
○ Suffering from Pneumonia, TB is possible.
y Diagnosis
○ ELISA- Enzyme linked immunosorbent assay-
○ It is a sensitive test for detection of proteins.
○ Western Blot test for antibodies against HIV in the patient’s serum.
○ PCR based test.
y Treatment
○ Reverse transcriptase inhibitors- Zidovudine (previously called AZT), Stavudine, Trizivir, Foscarnet,
DDI (Didexymidine) etc.
○ Protease inhibitors-Ritonavir, Nelfinavir etc.
○ HAART (Highly Active Anti-Retroviral Therapy) includes both reverse transcriptase inhibitors and
protease inhibitor drugs.
○ Treatment does not cure. Only helps to reduce viral load.
y Prevention
○ Use of appropriate contraceptives/protection (condoms) during sexual intercourse.
○ Proper sterilization of surgical equipment.
○ Use of disposable instruments for any body puncture practice.
○ Avoiding intra-venous drug use and sharing of needles, razors etc.
○ Creating social awareness.
You might also like
- Cen-Tr 16999-2019Document75 pagesCen-Tr 16999-2019Muhammed Hasan GüçlüNo ratings yet
- BIO CBSE 12 PROJECT On HIV/AISDocument15 pagesBIO CBSE 12 PROJECT On HIV/AISAnonymous KdUrkMIyJQ72% (58)
- NationDocument88 pagesNationJustin Luu0% (1)
- Hiv and Prevention of Mother-To-Child Transmission (PMTCT) : by Gebremaryam TDocument100 pagesHiv and Prevention of Mother-To-Child Transmission (PMTCT) : by Gebremaryam THambal AhamedNo ratings yet
- Group 1 - HIV - Case StudyDocument30 pagesGroup 1 - HIV - Case StudyCONTRERAS, ALIANNA IRISHNo ratings yet
- AidsDocument11 pagesAidsroseannurakNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology: - Infertility - Dysmenorrhea - Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STD)Document22 pagesPathophysiology: - Infertility - Dysmenorrhea - Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STD)Om KambleNo ratings yet
- Hiv and Aids: ID Specialist Tamar KhuchuaDocument84 pagesHiv and Aids: ID Specialist Tamar KhuchuaMAMA LALANo ratings yet
- AidsDocument10 pagesAidsDaniela OxaniNo ratings yet
- World AIDS DayDocument41 pagesWorld AIDS DayAthira SureshNo ratings yet
- Insel11e - ppt18 Sex Transmit DiseaseDocument30 pagesInsel11e - ppt18 Sex Transmit DiseaseThalia SandersNo ratings yet
- Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) and Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS)Document6 pagesHuman Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) and Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS)Vanessa MolinaNo ratings yet
- N.B. HIV-1 and HIV-2 Are The Two Main Types of HIV. Most People With HIV Have HIV-1. HIV in This Document Refers To HIV-1Document4 pagesN.B. HIV-1 and HIV-2 Are The Two Main Types of HIV. Most People With HIV Have HIV-1. HIV in This Document Refers To HIV-1tenqbroNo ratings yet
- HIv FactsDocument5 pagesHIv Factslarrybeechey3792No ratings yet
- 162 Biology of HIVv2Document3 pages162 Biology of HIVv2gert16No ratings yet
- Typhoid Fever Human: ImmunodeficiencyDocument9 pagesTyphoid Fever Human: ImmunodeficiencyJOHN CARLO APATANNo ratings yet
- Immunologic Agents PDFDocument104 pagesImmunologic Agents PDFgherlethrNo ratings yet
- What Is HIV? - Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) Is A Virus That Attacks Cells That Help The Body FightDocument8 pagesWhat Is HIV? - Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) Is A Virus That Attacks Cells That Help The Body Fightdanica grace gubaNo ratings yet
- Bio Cbse 12 Project On Hiv AisDocument15 pagesBio Cbse 12 Project On Hiv Aishelo helium50% (2)
- Reproduction in HumanDocument61 pagesReproduction in HumanSunil YadavNo ratings yet
- Presentation of AIDSDocument16 pagesPresentation of AIDSZainab AbdullahiNo ratings yet
- AIDSDocument10 pagesAIDSFaris ShamimNo ratings yet
- HIV Patient Case - StudentDocument11 pagesHIV Patient Case - StudentNancy FNo ratings yet
- 13--AIDS-FINAL-PPT--------10062024-103852am (3)Document28 pages13--AIDS-FINAL-PPT--------10062024-103852am (3)laiqamalik09No ratings yet
- 1060 Module 1 - HIVDocument5 pages1060 Module 1 - HIVBrandi T.No ratings yet
- Hiv/Aids: by Aisha MansurDocument34 pagesHiv/Aids: by Aisha MansurMpanso Ahmad AlhijjNo ratings yet
- PBH 101 - Hiv - SKMF-1Document22 pagesPBH 101 - Hiv - SKMF-1Zahin KhanNo ratings yet
- Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome or Acquired Immunodeficiency SyndromeDocument37 pagesAcquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome or Acquired Immunodeficiency SyndromeSumon ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Hiv 20infection 20 21 140104152057 Phpapp02Document43 pagesHiv 20infection 20 21 140104152057 Phpapp02Shyden Taghap Billones BordaNo ratings yet
- HIVDocument79 pagesHIVMehiella SatchiNo ratings yet
- Viral DiseasesDocument21 pagesViral Diseasesahmed29-551No ratings yet
- Human Immunodeficiency VirusDocument64 pagesHuman Immunodeficiency Virusmwambungup100% (2)
- Assignment AidsDocument11 pagesAssignment AidsYousaf ManzoorNo ratings yet
- AidsDocument5 pagesAidsBubblegumj Esus ChristNo ratings yet
- Virus Research AssignmentDocument7 pagesVirus Research AssignmentYvonne PangNo ratings yet
- Hiv PPDocument37 pagesHiv PPJitendra YadavNo ratings yet
- Hiv Aids PDFDocument16 pagesHiv Aids PDFМария КозловаNo ratings yet
- Hiv/AidsDocument130 pagesHiv/AidsRoline KarimiNo ratings yet
- HivDocument53 pagesHivReZa FriscaNo ratings yet
- Neuropsychiatric Aspects of HivDocument104 pagesNeuropsychiatric Aspects of HivPriyanka KoundinyaNo ratings yet
- What Is HIV?Document8 pagesWhat Is HIV?Quan ThieuNo ratings yet
- Hiv PresentationDocument10 pagesHiv Presentationapi-534814911No ratings yet
- HIV Case (Long Case)Document16 pagesHIV Case (Long Case)Max mitchyNo ratings yet
- Gulu Cohes Hiv Nelly MDDocument68 pagesGulu Cohes Hiv Nelly MDYIKI ISAACNo ratings yet
- Hiva IdsDocument28 pagesHiva IdsTinotenda TagariraNo ratings yet
- Nursing Clients With HIV Infection and AIDS: Learning ObjectivesDocument11 pagesNursing Clients With HIV Infection and AIDS: Learning Objectivesmorynayim-1No ratings yet
- Hiv AidsDocument14 pagesHiv Aidsapi-221532663No ratings yet
- Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) and Opperortunistic InfectionDocument54 pagesHuman Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) and Opperortunistic InfectionBikash SahNo ratings yet
- HIV Infection !: Dalal AlanaziDocument44 pagesHIV Infection !: Dalal AlanaziKarl Vincent SosoNo ratings yet
- Immunological DisordersDocument78 pagesImmunological DisordersAshwathy ThomasNo ratings yet
- Hiv Unit 1Document108 pagesHiv Unit 1Andrew NgairaNo ratings yet
- Stages of AidsDocument10 pagesStages of AidsHarshitha Gowda HarshiNo ratings yet
- HIV - AIDS PresentationDocument17 pagesHIV - AIDS PresentationphilNo ratings yet
- 8th Grade Health Powerpoint On Hiv and Aids (STDS)Document9 pages8th Grade Health Powerpoint On Hiv and Aids (STDS)Ryan JohnstonNo ratings yet
- End Stage AidsDocument33 pagesEnd Stage AidsMichael T GarciaNo ratings yet
- AIDS in The PhilippinesDocument29 pagesAIDS in The Philippinesjaninasuzette100% (1)
- Hiv/Aids: Mariano Marcos State University College of Health Sciences Department of Nursing Batac City, Ilocos NorteDocument10 pagesHiv/Aids: Mariano Marcos State University College of Health Sciences Department of Nursing Batac City, Ilocos NorteEyySiEffVee100% (1)
- What Is HIV.Document2 pagesWhat Is HIV.Chiranth ChandNo ratings yet
- UNIT 4 - New Challenges: Urja JoshiDocument72 pagesUNIT 4 - New Challenges: Urja JoshiRadhey RavalNo ratings yet
- Aidspptakki 141201102658 Conversion Gate01Document45 pagesAidspptakki 141201102658 Conversion Gate01Rahul DevNo ratings yet
- Spot Speed and Road InventoryDocument22 pagesSpot Speed and Road Inventoryleah yadaoNo ratings yet
- Subjective Tests vs. Objective Tests: Multiple-Choice TestDocument19 pagesSubjective Tests vs. Objective Tests: Multiple-Choice TestMuhammad Hidayatul RifqiNo ratings yet
- F.Y. B.Tech. (Semester - I) (Revised) Examination, December - 2018 Fundamentals of Electronics and Computers (All Branches)Document2 pagesF.Y. B.Tech. (Semester - I) (Revised) Examination, December - 2018 Fundamentals of Electronics and Computers (All Branches)Saurabh BhiseNo ratings yet
- GMSH RefManualDocument396 pagesGMSH RefManualJosé Antonio MoríñigoNo ratings yet
- Extractor de Probetas DEMTECHDocument2 pagesExtractor de Probetas DEMTECHPaul Alex Quiroz BarrionuevoNo ratings yet
- Subject - Verb AgreementDocument12 pagesSubject - Verb AgreementRistaNo ratings yet
- Internship Report .....Document32 pagesInternship Report .....Santosh Thapa100% (1)
- Clinical Audit Where ToDocument13 pagesClinical Audit Where ToMulugeta DagneNo ratings yet
- Research Paper 1Document14 pagesResearch Paper 1Fatima SinghNo ratings yet
- 2023 California Model Year 1978 or Older Light-Duty Vehicle SurveyDocument10 pages2023 California Model Year 1978 or Older Light-Duty Vehicle SurveyNick PopeNo ratings yet
- Senfter Ernste Gedanken PDFDocument8 pagesSenfter Ernste Gedanken PDFthieves11No ratings yet
- Ensuring Ecological Integrity, Clean and Healthy EnvironmentDocument15 pagesEnsuring Ecological Integrity, Clean and Healthy EnvironmentJJNo ratings yet
- Us Nop Organic Compliant Materials 20171121Document3 pagesUs Nop Organic Compliant Materials 20171121LayfloNo ratings yet
- Astm D4Document3 pagesAstm D4Vijayan Munuswamy100% (1)
- Navya MVH HCQDocument13 pagesNavya MVH HCQhosur mvNo ratings yet
- Understanding Order ProcessDocument7 pagesUnderstanding Order ProcessfilipNo ratings yet
- UnivibeDocument1 pageUnivibePablo EspinosaNo ratings yet
- MonographDocument38 pagesMonographNicolocoNo ratings yet
- PNC Infratech Limited Bags Rs.233 Crore PWD Road Project in UP (Company Update)Document2 pagesPNC Infratech Limited Bags Rs.233 Crore PWD Road Project in UP (Company Update)Shyam SunderNo ratings yet
- MarketingDocument110 pagesMarketingriddhi0% (1)
- Widiastini, P.M.F and Et Al. (2023) - Prima Wiyata Health. 4 (2) : 47-56pDocument10 pagesWidiastini, P.M.F and Et Al. (2023) - Prima Wiyata Health. 4 (2) : 47-56pnayla nadrahNo ratings yet
- Ruppur Nuclear Power PlantDocument4 pagesRuppur Nuclear Power PlantShafi Muhammad IstiakNo ratings yet
- Artikel - Esensi Dan Urgensi Integritas Nasional Di Lingkungan Mahasiswa Universitas Sriwijaya Dalam Bhinneka Tunggal IkaDocument8 pagesArtikel - Esensi Dan Urgensi Integritas Nasional Di Lingkungan Mahasiswa Universitas Sriwijaya Dalam Bhinneka Tunggal IkaAkmal DwiNo ratings yet
- Linux IPv6 How ToDocument164 pagesLinux IPv6 How ToAri SetianiNo ratings yet
- International Trade TheoriesDocument38 pagesInternational Trade Theoriestrustme77No ratings yet
- Grundfosliterature 146014Document12 pagesGrundfosliterature 146014Mario Daniel MoreiraNo ratings yet
- Camera Control Pro 2 ManualDocument118 pagesCamera Control Pro 2 ManualBigHeadLittleFeetNo ratings yet
- DCS Slips PartsDocument2 pagesDCS Slips PartsCarlig Radu MihaiNo ratings yet