Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Click and Learn Computer Parts Assignment 1 1
Click and Learn Computer Parts Assignment 1 1
Uploaded by
api-6855427790 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
448 views13 pagesThe document describes the basic computer parts including the power supply, hard drive, optical drive, heat sink, motherboard, video card, processor, sound card, RAM memory, ROM memory, CMOS, and buses. Each part is defined in 1-3 sentences explaining its main functions within a computer system.
Original Description:
Original Title
click and learn computer parts assignment 1 1
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document describes the basic computer parts including the power supply, hard drive, optical drive, heat sink, motherboard, video card, processor, sound card, RAM memory, ROM memory, CMOS, and buses. Each part is defined in 1-3 sentences explaining its main functions within a computer system.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
448 views13 pagesClick and Learn Computer Parts Assignment 1 1
Click and Learn Computer Parts Assignment 1 1
Uploaded by
api-685542779The document describes the basic computer parts including the power supply, hard drive, optical drive, heat sink, motherboard, video card, processor, sound card, RAM memory, ROM memory, CMOS, and buses. Each part is defined in 1-3 sentences explaining its main functions within a computer system.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 13
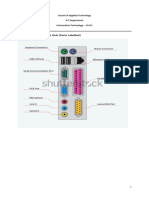
Basic Computer Parts
LABEL EACH OF THE FOLLOWING:
(Move the blocks around and draw an arrow to each part)
POWER
SUPPLY
13 15
HEAT SINK
14
HARD DRIVE (HDD)
ROM MEMORY
12
VIDEO CARD MOTHERBOARD
PROCESSOR BUSES
CMOS
SOUND CARD RAM MEMORY
Hard drive
self-contained storage device containing a read-
write mechanism plus one or more hard disks, inside
a sealed unit.
• was invented as a means of secondary storage
• Dutch scientists invented the world's smallest hard
drive
• the substances contained in a hard disk drive are
numerous.
Optical drive
allows you to use CDs, DVDs, and Blu-ray discs to
listen to music or watch a movie.
• provides greater memory capacity than
magnetic storage
• There are many different types of optical
drives
• The disks has microscopic codes written on it.
Heat sink
a device or substance for absorbing excessive or
unwanted heat.
• cools another part that is too hot
• it helps your CPU cool even if you use it for a
long period of time.
• is a heat reservoir that can absorb an arbitrary
amount of heat without significantly changing
temperature.
Power supply
an electrical device that supplies electric power to
an electrical load
• converts mains AC to low-voltage regulated DC
power for the internal components of a
computer
• personal computers always use switched-
mode power supplies
• Some power supplies have a manual switch for
selecting input voltage
Rom Memory
a type of storage medium that permanently stores data
on personal computers (PCs) and other electronic
devices.
• Its static nature means it does not require refreshing
• It is easy to test
• ROM is more reliable than RAM
Motherboard
a printed circuit board containing the principal
components of a computer or other device
• has connectors into which other circuit boards can
be slotted.
• Is attached with the daughterboard
• provides a single socket for CPU
Video Card
a printed circuit board controlling output to a
display screen.
• cards have their own processor called a
Graphics Processing Unit or GPU
• generates the video signal sent to a
computer display
• The memory on a video card is dedicated to
graphics tasks, and stores image data for
quick access.
Processor
the logic circuitry that responds to and
processes the basic instructions that drive a
computer
• Early CPUs were constructed from vacuum
tubes
• functions of a processor are fetch, decode,
execute and write back
• provides the instructions and processing
power the computer needs to do its work
Sound Card
a device which can be slotted into a computer to
allow the use of audio components for multimedia
applications.
• also called audio card
• generates an audio signal and sends it to a
computer's speakers
• The sound card can accept an analog sound
(as from a microphone or audio tape) and
convert it to digital data that can be stored in
an audio file
Ram Memory
Random Access Memory
• Data remains in RAM as long as the computer
is running
• RAM data gets wiped out on the computer
turned off
• other files get loaded into RAM from an HDD
or SSD
CMOS
a technology for making low power integrated
circuits.
• Unlike CCD's, CMOS sensors have circuitry at
the pixel level
• CMOS sensors are commonly designed with
rolling shutters, especially on commercial
applications
• CCD and CMOS are two types of image
sensors used in digital video cameras
Buses
a high-speed internal connection
• a high-speed internal connection
• Also called Data bus, Address bus, and
Control bus
• The data bus is a signal line for exchanging
the data between the CPU and the memory
You might also like
- Elex Event Log Explorer GuideDocument57 pagesElex Event Log Explorer GuideDragan StojanovicNo ratings yet
- SmartScope CNC-Flash 250 Service and Maintenance ManualDocument214 pagesSmartScope CNC-Flash 250 Service and Maintenance ManualTommyCasillas-Gerena100% (2)
- G10 ICT Lesson1 - Types and Parts of ComputerDocument4 pagesG10 ICT Lesson1 - Types and Parts of ComputerJOHN RIMMON TAQUISO50% (2)
- NCM 110 Lec Nursing Informatics Technology Part 1Document5 pagesNCM 110 Lec Nursing Informatics Technology Part 1Krizle Adaza0% (1)
- Computer Basics DefinitonDocument8 pagesComputer Basics DefinitonJeetender nath100% (1)
- Components of A MotherboardDocument114 pagesComponents of A Motherboarddeejhay14100% (1)
- 1.introduction To ComputersDocument29 pages1.introduction To ComputersPregathiNo ratings yet
- Itws 2Document33 pagesItws 2rg22No ratings yet
- MotherboardDocument41 pagesMotherboardjoseph rey ybiosaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Computer Hardware - Part 2Document44 pagesChapter 1 Computer Hardware - Part 2abinissri rajamuniswaranNo ratings yet
- ITWS Lab ManualDocument73 pagesITWS Lab Manualbharathsimha7465No ratings yet
- CHAPTER 2 - COMPUTER HARDWARE - IcsDocument70 pagesCHAPTER 2 - COMPUTER HARDWARE - Icsruzanna abu bakarNo ratings yet
- Comp IntroDocument85 pagesComp Introthecomputerminds2020No ratings yet
- Review Quiz 1Document160 pagesReview Quiz 1Luis SandovalNo ratings yet
- Computer Workshop Job 1Document19 pagesComputer Workshop Job 1ayushkumar77447No ratings yet
- Lab2 - Hardware-2Document24 pagesLab2 - Hardware-2Mohammed AlobaidyNo ratings yet
- Parts and Function of System UnitDocument48 pagesParts and Function of System UnitIvy ApolinarioNo ratings yet
- Parts of The System UnitDocument43 pagesParts of The System Unitroy nueraNo ratings yet
- System Unit & Boot SequenceDocument9 pagesSystem Unit & Boot SequenceEverton Evergreat RichardsNo ratings yet
- Computer Hardware ComponentDocument19 pagesComputer Hardware Componentrajibbarua2009100% (1)
- Computer Hardware ServicingDocument34 pagesComputer Hardware ServicingJhayden BlueNo ratings yet
- Motherboard and Other PartsDocument32 pagesMotherboard and Other PartsJom's Mijares100% (1)
- Perform Mensuration and CalculationDocument23 pagesPerform Mensuration and CalculationKaren Villapando LatNo ratings yet
- Midterm The Computer1Document42 pagesMidterm The Computer1NazireNo ratings yet
- Expansion SlotsDocument2 pagesExpansion SlotsABEGAIL CABIGTINGNo ratings yet
- 1.2 - Computer ComponentsDocument14 pages1.2 - Computer Componentsezedean.dahmanNo ratings yet
- Technical Lesson 1Document63 pagesTechnical Lesson 1PAUL GONZALESNo ratings yet
- PC Storage & Output Devices: Advanced Computer ApplicationsDocument22 pagesPC Storage & Output Devices: Advanced Computer ApplicationsQueenie Ann PaquitNo ratings yet
- Assaiment of Hardware: course:DITM BatchDocument6 pagesAssaiment of Hardware: course:DITM BatchItmahedi HasanNo ratings yet
- NOTA DKB1022-K1 1.1-2 (2-4) DoneDocument46 pagesNOTA DKB1022-K1 1.1-2 (2-4) DoneMohdHaris Pelajar KVNo ratings yet
- Parts of A Mother BoardDocument28 pagesParts of A Mother BoardReilina KylaNo ratings yet
- Different Parts and Function of System UnitDocument12 pagesDifferent Parts and Function of System UnitHaidhar HusinNo ratings yet
- Bab-1 Pengantar Personal Computer (PC) 1Document30 pagesBab-1 Pengantar Personal Computer (PC) 1haniNo ratings yet
- CP SirDocument238 pagesCP SirKaran SharmaNo ratings yet
- System UnitDocument24 pagesSystem UnitWindy Rose Gamao DeliquiñaNo ratings yet
- Computer Acronyms and AbbreviationsDocument5 pagesComputer Acronyms and AbbreviationsJeian Ashley A. MaasinNo ratings yet
- 9626 CHP 2Document184 pages9626 CHP 2nahid.ibrahim.shaikhNo ratings yet
- Hard Ware Note BookDocument22 pagesHard Ware Note BookSrini VasuluNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1-5Document66 pagesLesson 1-5Gian Andrei BenaguaNo ratings yet
- System Unit and Their FunctionsDocument30 pagesSystem Unit and Their Functionslex jhonNo ratings yet
- Computer HardwareDocument56 pagesComputer HardwareKenneth BautistaNo ratings yet
- Chapter2 Hardware ComponentsDocument48 pagesChapter2 Hardware ComponentsUntouchable Monster 2No ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument79 pagesIntroductionAka RadhikaNo ratings yet
- Parts of A ComputerDocument15 pagesParts of A ComputerAnnie Rose MahinayNo ratings yet
- Computer Hardware-Related AcronymsDocument3 pagesComputer Hardware-Related Acronymsghoul ciprianoNo ratings yet
- PC Assembling WorkshopDocument51 pagesPC Assembling Workshopkitty8200No ratings yet
- Computer ICTDocument20 pagesComputer ICTmobilelegendshelpcenter2022No ratings yet
- Chs 11 LessonDocument8 pagesChs 11 LessonMaverick Borres Romo ChoiiNo ratings yet
- Parts of System Unit & MotherboardDocument6 pagesParts of System Unit & MotherboardNonoy Enopena100% (2)
- Parts of Computer 2Document10 pagesParts of Computer 2tinaNo ratings yet
- BIOS InstallationDocument5 pagesBIOS InstallationArif ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Itwork ShopDocument63 pagesItwork ShopSai KumarNo ratings yet
- Basic Computer Structure and KnowledgeDocument22 pagesBasic Computer Structure and KnowledgeCyril Jay G. OrtegaNo ratings yet
- IT Chapter 1Document10 pagesIT Chapter 1Alice HovsepyanNo ratings yet
- Maxim Nyansa I.T Solution (Nigeria) : Note On Computer RepairsDocument16 pagesMaxim Nyansa I.T Solution (Nigeria) : Note On Computer RepairsOlúwaṣẹ́gunNo ratings yet
- Hardware Components of The System UnitDocument2 pagesHardware Components of The System UnitRebecca EjandraNo ratings yet
- To Study MOTHERBOARD.: HistoryDocument6 pagesTo Study MOTHERBOARD.: Historyshyam ranaNo ratings yet
- External and Internal Hardware: Vansh Shukla EDocument13 pagesExternal and Internal Hardware: Vansh Shukla EVansh ShuklaNo ratings yet
- The Cpu The Bus: VDU (Monitor) KeyboardDocument9 pagesThe Cpu The Bus: VDU (Monitor) Keyboardsaksham111No ratings yet
- Hardware Components SADocument46 pagesHardware Components SAEm Cee PerezNo ratings yet
- ITI&MDocument12 pagesITI&MDebanshu MohantyNo ratings yet
- Computer HardwareDocument87 pagesComputer HardwareLutfiNo ratings yet
- PlayStation 2 Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #12From EverandPlayStation 2 Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #12No ratings yet
- Al Ict Competency 1 APEX Education CenterDocument7 pagesAl Ict Competency 1 APEX Education CenterShirani BalasuriyaNo ratings yet
- Multimedia Class 5Document3 pagesMultimedia Class 5gsudeep918No ratings yet
- Plan Training Sessions DaumarDocument38 pagesPlan Training Sessions DaumarJames DaumarNo ratings yet
- Grafoplast 2006 PDFDocument28 pagesGrafoplast 2006 PDFavfarzar27No ratings yet
- Ics 2101 Computer OrganizationDocument3 pagesIcs 2101 Computer Organization123 321No ratings yet
- BBC Mitteilungen 1973 e 10-11Document62 pagesBBC Mitteilungen 1973 e 10-11Pedro PizzoqueroNo ratings yet
- Year 10 Computer Science November 2020Document21 pagesYear 10 Computer Science November 2020Mahmud RahmanNo ratings yet
- Living in The IT Era - Reviewer Guide - MidTerm 1st Sem. 2022-2023 (Drill)Document10 pagesLiving in The IT Era - Reviewer Guide - MidTerm 1st Sem. 2022-2023 (Drill)Daennise Louiseanna SebastianNo ratings yet
- Circuit Diagram Eng 5582-2-01Document95 pagesCircuit Diagram Eng 5582-2-01edolzaNo ratings yet
- RTS Lec1Document11 pagesRTS Lec1Suraj KandpalNo ratings yet
- Combined Sept 2015 HELPV2Document92 pagesCombined Sept 2015 HELPV2Ounna PechNo ratings yet
- Media and Information SOURCESDocument89 pagesMedia and Information SOURCESAlyssa Dee VillenaNo ratings yet
- BEL Trainee Engineer SyllabusDocument3 pagesBEL Trainee Engineer SyllabusGanesh balikaiNo ratings yet
- Tools of MS Word With DescriptionDocument7 pagesTools of MS Word With DescriptionTaliya MuraadNo ratings yet
- Self - Assessment Guide - CHS NC IIDocument3 pagesSelf - Assessment Guide - CHS NC IIMichael V. MagallanoNo ratings yet
- Downloaded From Manuals Search EngineDocument17 pagesDownloaded From Manuals Search EngineJesús Rafael Méndez NateraNo ratings yet
- Daley7 PPT 02Document40 pagesDaley7 PPT 02Tanafe100% (1)
- Digital Forensics: Processing Crime and Incident ScenesDocument25 pagesDigital Forensics: Processing Crime and Incident ScenesABCNo ratings yet
- The Information Technology Act 2000Document9 pagesThe Information Technology Act 2000Birendra PushpakarNo ratings yet
- Artemis: Owner's ManualDocument101 pagesArtemis: Owner's ManualWolfgang Wolgy ErešNo ratings yet
- Assignment # 4: Muhammad Saad Ayub MBA (Evening) 14488Document11 pagesAssignment # 4: Muhammad Saad Ayub MBA (Evening) 14488Semra RaheelNo ratings yet
- Embedded SystemsDocument24 pagesEmbedded SystemsDileep KumarNo ratings yet
- Syllabus Semester 1Document8 pagesSyllabus Semester 1Eng Abdulkadir MahamedNo ratings yet
- Bit 101 Reviewer Group 1-5Document10 pagesBit 101 Reviewer Group 1-5Cleofe Jane PatnubayNo ratings yet
- Cloud: Figure - The Symbol Used To Denote The Boundary of A Cloud EnvironmentDocument27 pagesCloud: Figure - The Symbol Used To Denote The Boundary of A Cloud Environmentαηαητ αφπαωαΙNo ratings yet
- Computer Programming E Balagurusamy Full ChapterDocument67 pagesComputer Programming E Balagurusamy Full Chaptererin.hakimian447100% (6)