Professional Documents
Culture Documents
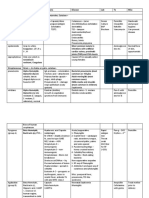
Chart - Gram Positive Bacteria
Chart - Gram Positive Bacteria
Uploaded by
RedOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chart - Gram Positive Bacteria
Chart - Gram Positive Bacteria
Uploaded by
RedCopyright:
Available Formats
Gram Positive Bacteria
Staphylococcus Coagulase negative Group A Streptococcus Viridans-group Enterococcus
S. aureus Staphylococcus S. pyogens streptococcus
Gram stain Gram + Gram + Gram + Diplococcus, Gram + Diplococcus, pairs Gram +
Shape/ Coccus, clusters Coccus, clusters chains Coccus, chains/pairs
Arrangement
Culture Yellow color, usually beta- Will grow in high [NaCl]
hemolytic Will hydrolyze esculin in presence
of high [bile]
Catalase & other Catalase + Catalase - Catalase Catalase - Catalase
tests PYR test
Normal body sites Mucosa and Skin Nose, intestine, skin Mucosa of upper Mouth, GI, vagina Large intestine
Nares (25%), hand, skin, respiratory system
vagina
Source/route of Contact (direct or fomites) Nasal secretions, droplets Contact Persontoperson via contact
acquisition Food ingestion Contact
Evasion of Protein A binds Fc domain of S. pyogenes: Lowvirulence organisms Highly
immune response IgG, blocking Ab opsonization M proteins access for antibiotic resistant
of bacterium complement and inh. Alt
Cytolytic toxins (hemolysins) pathway
Coagulase Capsules with selfantigens
How does bacteria Alterations in coagulase Associated with breaks in Streptolysin O and S Cause disease in compromised
damage host Enzymes digestion of host skin and mucosa Enzymes degrading host hosts
tissue tissues (streptokinase,
Cytolysins DNAse, hyaluronidase)
Pyogenic inflammation Strep. pyrogenic exotoxins
Enterotoxins* (Spe), aka superantigens
Exfoliative toxins (TSS and scarlet fever)
(keratinocytes)*
TSST-1*
Manifestations *specific
S. aureus: manifestations
staphylococcal S. saprophyticus: UTI in Group A strep: pharyngitis, Endocarditis UTI
scalded skin syndrome, women necrotizing fasciitis, otitis Meningitis Endocarditis
bullous impetigo, S. epidermidis: infections media, sinusitis, abscess, Pneumonia
folliculitis/carbuncle/furuncle, on foreign objects scarlet fever, rheumatoid
cellulitis, endocarditis, toxic Cause infections on arthritis, glomerulonephritis;
shock syndrome (TSST1) foreign objects (artificial erysipelas
heart valves, IV catheters,
prosthetics)
You might also like
- Dysarthria Evaluation ReportDocument3 pagesDysarthria Evaluation Reportapi-27281642067% (3)
- LeMone and Burke S Medical-Surgical Nurs PDFDocument1 pageLeMone and Burke S Medical-Surgical Nurs PDFRicardo Flores50% (2)
- Systemic BacteriologyDocument495 pagesSystemic BacteriologyAkash KaranwalNo ratings yet
- Bacteria Notes SketchyDocument3 pagesBacteria Notes SketchyJayNo ratings yet
- Brown (2001) PDFDocument13 pagesBrown (2001) PDFAna Catarina InácioNo ratings yet
- Gram Positive Bacteria TableDocument6 pagesGram Positive Bacteria Tables2128226No ratings yet
- Gram Positive Cocci - StaphylococcusDocument41 pagesGram Positive Cocci - StaphylococcusUMER AHMED KHAN DRAZNo ratings yet
- Staphylococcus & StreptococcusDocument100 pagesStaphylococcus & StreptococcusFahim NadvyNo ratings yet
- BacteriologyDocument20 pagesBacteriologyOj Alimbuyuguen100% (2)
- S. Aureus, Cons: S.Epidermidis, Cons: S.SaprophyticusDocument14 pagesS. Aureus, Cons: S.Epidermidis, Cons: S.SaprophyticusMugiNo ratings yet
- Tables of Gram PositiveDocument5 pagesTables of Gram PositiveLobna ElkilanyNo ratings yet
- Staph. Aureus Staph. Epidermidis Staph. SaprophyticusDocument5 pagesStaph. Aureus Staph. Epidermidis Staph. SaprophyticusTom PedersonNo ratings yet
- Streptococci and Enterococci and OthersDocument11 pagesStreptococci and Enterococci and OthersthedarkwingNo ratings yet
- Medmicronotes 3Document66 pagesMedmicronotes 3Lethal BaconNo ratings yet
- StaphylococcusDocument4 pagesStaphylococcusipad backupNo ratings yet
- Special MicrobiologyDocument68 pagesSpecial MicrobiologyrefuapalackyNo ratings yet
- Lecture1 Part2 (Gram Positive Cocci)Document49 pagesLecture1 Part2 (Gram Positive Cocci)mohamed2010.ibrahemNo ratings yet
- Streptococci: S. Pyogenes S. AgalactiaeDocument9 pagesStreptococci: S. Pyogenes S. AgalactiaeChristine BuenNo ratings yet
- Parasitology Table ProtozoaDocument10 pagesParasitology Table ProtozoaMae Rose Charlene MendozaNo ratings yet
- Finasls 1 Staph Strep PDFDocument50 pagesFinasls 1 Staph Strep PDFFrancis ValdezNo ratings yet
- Bacteriology Midterms GomezDocument20 pagesBacteriology Midterms GomezAive BelistaNo ratings yet
- Staphylococc I: Ni Nyoman Desi Bintari, S.Si.,M.SiDocument36 pagesStaphylococc I: Ni Nyoman Desi Bintari, S.Si.,M.SiDesi BintariNo ratings yet
- Staphylococci: MaheshyadavDocument36 pagesStaphylococci: MaheshyadavMuhammad IlhamNo ratings yet
- Parasitology Table: ProtozoaDocument10 pagesParasitology Table: ProtozoaKate Alyssa CatonNo ratings yet
- Veterinary MicrobiologyDocument206 pagesVeterinary MicrobiologyHomosapienNo ratings yet
- Bacteriology by Dhshan Hassan DhshanDocument48 pagesBacteriology by Dhshan Hassan Dhshanعلي الكوافي100% (1)
- Chap 13. StaphylococcusDocument40 pagesChap 13. StaphylococcusSHARON MARIA SUNNYNo ratings yet
- Staphylococcus 1Document8 pagesStaphylococcus 1JohnWangerNo ratings yet
- Med Micro BugsDocument16 pagesMed Micro BugsKaitlyn CabreraNo ratings yet
- Infectious-Disease Tables PDFDocument81 pagesInfectious-Disease Tables PDFMiguel CuevasNo ratings yet
- BacteriaDocument13 pagesBacteriathzone1986100% (1)
- Bacteria TableDocument4 pagesBacteria TableBrittany Lynn Myers100% (1)
- Taxonomy: Family StaphylococcaceaeDocument40 pagesTaxonomy: Family StaphylococcaceaeMarissa Terrado SorianoNo ratings yet
- Normal Flora of The Human BodyDocument37 pagesNormal Flora of The Human Bodyshahbaz100% (6)
- Micro by DR - Hesham (GIT)Document65 pagesMicro by DR - Hesham (GIT)abcde990075No ratings yet
- Staphylococcus MicrococcusDocument2 pagesStaphylococcus MicrococcusAyessa VillacorteNo ratings yet
- Microbiology and ParasitologyDocument157 pagesMicrobiology and ParasitologyNIKITIKITI100% (3)
- Reviewer - Bacteriology FINALS - ANGELES, ANGELICDocument38 pagesReviewer - Bacteriology FINALS - ANGELES, ANGELICAngelic AngelesNo ratings yet
- Staphylococcus LectureDocument66 pagesStaphylococcus LectureFarhan Azmain FahimNo ratings yet
- ENTEROBACTERIACEAE2Document14 pagesENTEROBACTERIACEAE2dokijoon100% (1)
- Bacteria PDFDocument13 pagesBacteria PDFJohn Christopher LucesNo ratings yet
- Nutrition and DiseasesDocument2 pagesNutrition and DiseasessanskarforblissNo ratings yet
- Common Cause: Staphylococcus Spp. Streptococcus Spp. Enterococcus SPPDocument8 pagesCommon Cause: Staphylococcus Spp. Streptococcus Spp. Enterococcus SPPAdel mohammadNo ratings yet
- Aerobic Small GR Negative Rods.23-24Document56 pagesAerobic Small GR Negative Rods.23-24Sra Nk?❗️No ratings yet
- 10 Bacillus & ClostridiumDocument11 pages10 Bacillus & ClostridiumASECO LISHNo ratings yet
- Gram Positive BacteriaDocument88 pagesGram Positive BacteriaRonelene GatoNo ratings yet
- Staph - 2020 Nov - PDocument14 pagesStaph - 2020 Nov - PHUỲNH QUỐC KHÁNHNo ratings yet
- Streptococcus and EnterococcusDocument91 pagesStreptococcus and EnterococcusAllyah Ross DuqueNo ratings yet
- Thermobacteriology I: Food Microbiology and Public HealthDocument28 pagesThermobacteriology I: Food Microbiology and Public HealthHasan TheMcNo ratings yet
- Staphylococci AtfDocument22 pagesStaphylococci Atftahaijaz89No ratings yet
- Gram Positive Cocci: Two GeneraDocument31 pagesGram Positive Cocci: Two GeneraGeorgeNecoară100% (1)
- Complete Bacteriology Notes From Levinson by Medical Study CenterDocument13 pagesComplete Bacteriology Notes From Levinson by Medical Study CenterUsama HameedNo ratings yet
- Parasitology TableDocument15 pagesParasitology TableJohn Benedict BondocNo ratings yet
- Microbiology TablesDocument19 pagesMicrobiology TablesRebecca MarshallNo ratings yet
- 2023.pedia - Trans24.-Bacterial-Infections - Gram Postitive (Part 1)Document6 pages2023.pedia - Trans24.-Bacterial-Infections - Gram Postitive (Part 1)Adrian CaballesNo ratings yet
- Bacteria of Medical Importance 1Document21 pagesBacteria of Medical Importance 1Tshepang MohlahloNo ratings yet
- Bakteri Yang Menginfeksi Muskuloskeletal: Oleh NurrokhmanDocument42 pagesBakteri Yang Menginfeksi Muskuloskeletal: Oleh NurrokhmanRiris SutrisnoNo ratings yet
- Staphylococcus Aureus Infiection Thang 1 2007Document44 pagesStaphylococcus Aureus Infiection Thang 1 2007Nguyễn Tấn BìnhNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2021-06-04 at 23.19.29Document72 pagesScreenshot 2021-06-04 at 23.19.29Amina Mohamed AbdikeirNo ratings yet
- Staphylococci - Ref - Canvas PDFDocument5 pagesStaphylococci - Ref - Canvas PDFacademics pdfNo ratings yet
- Notes on Diseases of Cattle: Cause, Symptoms and TreatmentFrom EverandNotes on Diseases of Cattle: Cause, Symptoms and TreatmentNo ratings yet
- 911 Pigeon Disease & Treatment Protocols!From Everand911 Pigeon Disease & Treatment Protocols!Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Notes on Diseases of Swine, Sheep, Poultry and the Dog: Cause, Symptoms and TreatmentsFrom EverandNotes on Diseases of Swine, Sheep, Poultry and the Dog: Cause, Symptoms and TreatmentsNo ratings yet
- PDF Clinical Guide To Cardiology 1St Edition Christian Fielder Camm Ebook Full ChapterDocument53 pagesPDF Clinical Guide To Cardiology 1St Edition Christian Fielder Camm Ebook Full Chapternolan.gold619100% (3)
- Postural DrainageDocument19 pagesPostural Drainagenkarthikraj100% (1)
- Modified Rives StoppaDocument8 pagesModified Rives StoppaAndrei SinNo ratings yet
- Dr. Rabindra Tamang Junior Resident BPKIHS, Dharan NepalDocument56 pagesDr. Rabindra Tamang Junior Resident BPKIHS, Dharan NepalOmar Zaman KhanNo ratings yet
- CC - Liver FunctionDocument5 pagesCC - Liver FunctionOrhan AsdfghjklNo ratings yet
- PEDIA 20Idiot20Notes 1Document76 pagesPEDIA 20Idiot20Notes 1Aljon S. TemploNo ratings yet
- 06 Luka Kanker 2022Document34 pages06 Luka Kanker 2022mesi purnamaNo ratings yet
- Sepsis in Post Transplant Patients: DR - Hina Aamir Abbasi SiutDocument33 pagesSepsis in Post Transplant Patients: DR - Hina Aamir Abbasi SiutSandhi PrabowoNo ratings yet
- Triglyceride Ratio With Total Cholesterol PPT IbanDocument9 pagesTriglyceride Ratio With Total Cholesterol PPT IbanGoez Aditya NugrahaNo ratings yet
- 0 - MDI-P (Precursor ASEA) - Studiu Efect Germeni Agresivi - Baltch 2000Document7 pages0 - MDI-P (Precursor ASEA) - Studiu Efect Germeni Agresivi - Baltch 2000andrushkkutzaNo ratings yet
- Cagayan Valley Medical Center Department of RadiologyDocument72 pagesCagayan Valley Medical Center Department of RadiologySofia Kezia Apostol CabaroNo ratings yet
- J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry-2000-Newton-433-41Document10 pagesJ Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry-2000-Newton-433-41Joy SanjayaNo ratings yet
- Oks Na To Thank U Aubs!!: Okiii!!! Wuv U All!Document10 pagesOks Na To Thank U Aubs!!: Okiii!!! Wuv U All!CiaraNo ratings yet
- Mengapa Biosecurity Menjadi Penting Pada Laboratorium Penyakit Infeksi ?Document10 pagesMengapa Biosecurity Menjadi Penting Pada Laboratorium Penyakit Infeksi ?AndyNo ratings yet
- Nejmoa1700089 AppendixDocument42 pagesNejmoa1700089 Appendixwigrha 98No ratings yet
- Psychiatry Made Easy: History Taking Technique Using Life Event ChartDocument14 pagesPsychiatry Made Easy: History Taking Technique Using Life Event ChartvelanganniNo ratings yet
- Community Health Nursing: Arby James Abonalla, RN, MSN, PHDN (C)Document237 pagesCommunity Health Nursing: Arby James Abonalla, RN, MSN, PHDN (C)Roshie Kaye AbalorioNo ratings yet
- Statement On Practice Recommendations For Pediatric AnesthesiaDocument5 pagesStatement On Practice Recommendations For Pediatric AnesthesiaAnonymous tG35SYROzENo ratings yet
- AcinobacterDocument2 pagesAcinobacterAllyson Layaoen CollierNo ratings yet
- Effect of Corticosteroids On Pain Relief Following Root Canal Treatment: A Systematic ReviewDocument8 pagesEffect of Corticosteroids On Pain Relief Following Root Canal Treatment: A Systematic ReviewJorge OrbeNo ratings yet
- He Respiratory System in BabiesDocument16 pagesHe Respiratory System in BabiesWidiya Nur FatinahNo ratings yet
- CHN Quizzes FinalsDocument10 pagesCHN Quizzes FinalsSTUDENTNURSESOONRN2024No ratings yet
- Williams PDFDocument18 pagesWilliams PDFEmilioHernándezNo ratings yet
- Enteral Nutrition: Sanja KolačekDocument5 pagesEnteral Nutrition: Sanja KolačekManuela MontesNo ratings yet
- SONOACE X4 Product CatalogDocument6 pagesSONOACE X4 Product Catalogdoctorviet1979No ratings yet
- Blood Pressure Tracker 1Document3 pagesBlood Pressure Tracker 1Yu HasNo ratings yet
- Hypersensitivity Reaction TypesDocument1 pageHypersensitivity Reaction TypesTom MallinsonNo ratings yet