Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Math 401 Midterms Formula Sheet
Math 401 Midterms Formula Sheet
Uploaded by
Hazel May MacalintalOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Math 401 Midterms Formula Sheet
Math 401 Midterms Formula Sheet
Uploaded by
Hazel May MacalintalCopyright:
Available Formats
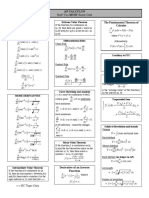
Differentiation
f(x1+Δ𝑥)−𝑓(𝑥1)
m= lim Δ𝑥
𝑥→0
𝑑𝑦 Δ𝑦 f(x+Δ𝑥)−𝑓(𝑥)
f’(x)= 𝑑𝑥 = lim Δ𝑥 = lim Δ𝑥
𝑥→0 𝑥→0
The Increment Method
Step 1: f(x+Δ) – f(x)
f(x+Δx)−f(x)
Step 2:
Δ𝑥
f(x+Δ𝑥)−𝑓(𝑥)
Step 3: lim
Δ𝑥→0 Δ𝑥
Theories on Differentiation of Algebraic Functions
The Constant Rule of Differentiation The Quotient Rule of Differentiation
d 𝑔(𝑥)∙
d d
[𝑓(𝑥)]− 𝑓(𝑥)∙ [𝑔(𝑥)]
dx
(c) =0 d 𝑓(𝑥)
[ ] = dx dx
dx 𝑔(𝑥) [g(x)]2
The Power Rule (for positive integer powers)
The General Power Rule of Differentiation
of Differentiation
d d
d [f(x)]n = n ∙ [f(x)]n-1 ∙ f(x)
(xn) =nxn-1 dx dx
dx
The Derivative of a Composite Function
The Constant Multiple Rule of Differentiation
d d (f ∙ g)’ (x)= f’(g(x))g’(x)
dx
[cf (x)] = c dx [f(x)]
The Chain Rule of Differentiation
The Sum Rule of Differentiation
𝑑𝑦 𝑑𝑦 𝑑𝑢
d d d = ∙
[f(x)±g(x)] =dx [f(x)] ± dx [g(x)] 𝑑𝑥 𝑑𝑢 𝑑𝑥
dx
If u is a differentiable function of x
The Product Rule of Differentiation
d d d
𝑑𝑢
[f(x)∙g(x)] = f(x) ∙ dx[g(x)] + g(x) ∙ dx [f(x)] d
dx (√𝑢) = 𝑑𝑥
dx 2√𝑢
Derivatives of Trigonometric Function
𝑑 𝑑
[ sin(𝑥) ] = cos(𝑥) [ cot(𝑥) ] = −𝑐𝑠𝑐 2 (𝑥)
𝑑𝑥 𝑑𝑥
𝑑 𝑑
[ cos(𝑥) ] = −sin (𝑥) [ sec(𝑥) ] = sec(𝑥) tan(𝑥)
𝑑𝑥 𝑑𝑥
𝑑 𝑑
[ tan(𝑥) ] = 𝑠𝑒𝑐 2 (𝑥) [ csc(𝑥) ] = −csc(𝑥) cot(𝑥)
𝑑𝑥 𝑑𝑥
Derivatives of Inverse Trigonometric Function
𝑑 𝑢′ 𝑑 −𝑢′
[ Arcsin(𝑢) ] = [ Arccos(𝑢) ] =
𝑑𝑥 √1 − 𝑢2 𝑑𝑥 √1 − 𝑢2
𝑑 𝑢′ 𝑑 −𝑢′
[ Arctan(𝑢) ] = [ Arccot(𝑢) ] =
𝑑𝑥 1 + 𝑢2 𝑑𝑥 1 + 𝑢2
𝑑 𝑢′ 𝑑 −𝑢′
[ Arcsec(𝑢) ] = [ Arccsc(𝑢) ] =
𝑑𝑥 |𝑢|√𝑢2 − 1 𝑑𝑥 |𝑢|√𝑢2 − 1
Trigonometric Identities
Pythagorean Identities cos 2𝑥 = 𝑐𝑜𝑠 2 𝑥 − 𝑠𝑖𝑛2 𝑥 = 2𝑐𝑜𝑠 2 𝑥 − 1
𝑠𝑖𝑛2 𝜃 + 𝑐𝑜𝑠 2 𝜃 = 1 = 1 − 2𝑠𝑖𝑛2 𝑥 =
1−𝑡𝑎𝑛2 𝑥
1+𝑡𝑎𝑛2 𝑥
𝑠𝑒𝑐 2 𝜃 = 1 + 𝑡𝑎𝑛2 𝜃
2 tan 𝑥
2 2 tan 2𝑥 =
𝑐𝑠𝑐 𝜃 = 1 + 𝑐𝑜𝑡 𝜃 1 − 𝑡𝑎𝑛2 𝑥
Half Angle Identities 𝑐𝑜𝑡 2 𝑥 − 1
cot 2𝑥 =
2 cot 𝑥
𝜃 1 − cos 𝜃 Product to Sum Formulas
sin ( ) = ±√
2 2
1
sin 𝑥 sin 𝑦 = [cos(𝑥 − 𝑦) − cos(𝑥 + 𝑦)]
2
𝜃 1 + cos 𝜃
cos ( ) = ±√ 1
2 2 cos 𝑥 cos 𝑦 = [cos(𝑥 − 𝑦) + cos(𝑥 + 𝑦)]
2
𝜃 1 − cos 𝜃 1
tan ( ) = sin 𝑥 cos 𝑦 = [sin(𝑥 + 𝑦) + sin(𝑥 − 𝑦)]
2 sin 𝜃 2
Double Angle Identities 1
cos 𝑥 sin 𝑦 = [sin(𝑥 + 𝑦) − sin(𝑥 − 𝑦)]
2 tan 𝑥 2
sin 2𝑥 = 2 sin 𝑥 cos 𝑥 =
1 + 𝑡𝑎𝑛2 𝑥
You might also like
- Calculus Cheat Sheet DerivativesDocument4 pagesCalculus Cheat Sheet Derivativeshyd arnes100% (5)
- Basic Differentiation FormulasDocument1 pageBasic Differentiation FormulasanakareninavrNo ratings yet
- DERIVATIVES (Formula)Document2 pagesDERIVATIVES (Formula)Geojanni PangibitanNo ratings yet
- Derivatives & Integrals FormulasDocument8 pagesDerivatives & Integrals Formulasdragon55knightNo ratings yet
- 1551 FinalExam ProblemBankDocument12 pages1551 FinalExam ProblemBankPedro TNo ratings yet
- IntegralDocument3 pagesIntegralAkshit BansalNo ratings yet
- Derivatives: Basic Properties/Formulas/RulesDocument4 pagesDerivatives: Basic Properties/Formulas/RulesjonahNo ratings yet
- Introduction To IntegrationDocument6 pagesIntroduction To Integrationsatinath GhoshNo ratings yet
- DifferentiationFormulas HandoutDocument2 pagesDifferentiationFormulas Handoutyodel23957No ratings yet
- (Sin (X) ) : Find The Derivative - D/DXDocument2 pages(Sin (X) ) : Find The Derivative - D/DXKatherine MoleNo ratings yet
- Common Derivatives IntegralsDocument4 pagesCommon Derivatives IntegralsPhilanderGereenPiniliNo ratings yet
- Formulario para Integrales - SymbolabDocument3 pagesFormulario para Integrales - SymbolabAbraham CandiaNo ratings yet
- Differentiation Formulas & Rules - Various Derivative Formulas of Trigonometric, Hyperbolic, Logarithmic & MoreDocument4 pagesDifferentiation Formulas & Rules - Various Derivative Formulas of Trigonometric, Hyperbolic, Logarithmic & Moreambresh.09No ratings yet
- Materi Turunan (Derivatif)Document1 pageMateri Turunan (Derivatif)Jefri ArdiansahNo ratings yet
- Techniques of Differentiation-1Document3 pagesTechniques of Differentiation-1lqmandyNo ratings yet
- Skills in Mathematics Integral Calculus For JEE Main and Advanced 2022Document319 pagesSkills in Mathematics Integral Calculus For JEE Main and Advanced 2022Harshil Nagwani100% (3)
- PRINT5 - Integrals Cheat Sheet - SymbolabDocument2 pagesPRINT5 - Integrals Cheat Sheet - SymbolabPamela Ricaforte100% (1)
- Common Derivatives Integrals PDFDocument4 pagesCommon Derivatives Integrals PDFMeysem Tamaar MalikNo ratings yet
- Integrals Cheat SheetDocument3 pagesIntegrals Cheat SheetVaishnav VIPANCHIKANo ratings yet
- Formulario para Derivadas - SymbolabDocument2 pagesFormulario para Derivadas - SymbolabAbraham CandiaNo ratings yet
- Derivadas Folha de Apoio - SymbolabDocument2 pagesDerivadas Folha de Apoio - SymbolabLeonardo AlmadaNo ratings yet
- T2 - IntegrationDocument100 pagesT2 - IntegrationMahmudNo ratings yet
- Common Derivatives IntegralsDocument4 pagesCommon Derivatives Integralsjaytech O. kerim100% (1)
- Tabla de DerivadasDocument2 pagesTabla de DerivadasJorge Luis Osorio MurilloNo ratings yet
- Integral Calculus Formula SheetDocument4 pagesIntegral Calculus Formula Sheetdaphnegrace villaralvoNo ratings yet
- 1551 FinalExam ProblemBank SolDocument54 pages1551 FinalExam ProblemBank SolPedro TNo ratings yet
- CalculusDocument4 pagesCalculusabhishek sinhaNo ratings yet
- Formulario para Derivadas - SymbolabDocument2 pagesFormulario para Derivadas - SymbolabJose CondoriNo ratings yet
- MA103 Lab 4 NotesDocument2 pagesMA103 Lab 4 Notessubway9113No ratings yet
- PRINT4 - Derivatives Cheat Sheet - SymbolabDocument2 pagesPRINT4 - Derivatives Cheat Sheet - SymbolabPamela RicaforteNo ratings yet
- Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesCheat SheetMaxfield QuayleNo ratings yet
- Derivatives: Definition and NotationDocument4 pagesDerivatives: Definition and NotationHarsh VyasNo ratings yet
- CALENG2 Quiz 1: FX X FX XDocument11 pagesCALENG2 Quiz 1: FX X FX XRocelle Andrea BelandresNo ratings yet
- Derivatives FormulasDocument5 pagesDerivatives FormulasAnudeep ReddyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document13 pagesLecture 2James Karen100% (1)
- Basics of Integration: FX FXDocument17 pagesBasics of Integration: FX FXcikguhafidzuddinNo ratings yet
- Arihant Integral CalculusDocument82 pagesArihant Integral CalculusAbhi100% (1)
- Integrals Cheat SheetDocument3 pagesIntegrals Cheat SheetFrostDevs GTNo ratings yet
- Stuff You MUST Know Cold: Ap CalculusDocument2 pagesStuff You MUST Know Cold: Ap CalculusChen LiNo ratings yet
- 185 Derivs Ints From Calc IDocument1 page185 Derivs Ints From Calc Idata worksNo ratings yet
- Calculus Formula Sheet:: Sin X Cos XDocument4 pagesCalculus Formula Sheet:: Sin X Cos X17090 Ashikur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Derivatives: 1. Definition & NotationDocument6 pagesDerivatives: 1. Definition & NotationVivek GuptaNo ratings yet
- CalculusDocument2 pagesCalculusdissipog1932No ratings yet
- 7.methods of Differentiation and Applications of DerivativesTheoryDocument27 pages7.methods of Differentiation and Applications of DerivativesTheoryDevansh ParasharNo ratings yet
- Derivatives Cheat SheetDocument3 pagesDerivatives Cheat SheetalexNo ratings yet
- Formulas of Integration - CalDocument9 pagesFormulas of Integration - Calsamraarshad76No ratings yet
- Hand Out Continuity and DifferentiabilityDocument3 pagesHand Out Continuity and DifferentiabilityKriti SinghNo ratings yet
- RSimpson Lecture10Document9 pagesRSimpson Lecture10Ali Najim AbdullahNo ratings yet
- MATH 2170: Table of Derivatives and IntegralsDocument5 pagesMATH 2170: Table of Derivatives and IntegralsspacejuyNo ratings yet
- Sec3 3solutionsDocument18 pagesSec3 3solutionsRayun ChoiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Indefinite Integration OnlyDocument7 pagesChapter 8 Indefinite Integration Onlyapi-3728615No ratings yet
- Integration of Function: D DX D DXDocument10 pagesIntegration of Function: D DX D DXYeoh HanNo ratings yet
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- Green's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and Applications. (AM-158)From EverandGreen's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and Applications. (AM-158)No ratings yet
- Mathematical Formulas for Economics and Business: A Simple IntroductionFrom EverandMathematical Formulas for Economics and Business: A Simple IntroductionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
- Actualizar Dspace 5 A 6Document8 pagesActualizar Dspace 5 A 6Miguel AHNo ratings yet
- C++ - STD - Wstring Vs STD - String - Stack OverflowDocument16 pagesC++ - STD - Wstring Vs STD - String - Stack Overflowlbio9103No ratings yet
- Principles of Public Speaking 1-2-17Document384 pagesPrinciples of Public Speaking 1-2-17MgNo ratings yet
- Synectics SeligmannDocument19 pagesSynectics SeligmannCroco latoz100% (1)
- Reportdbms 1Document22 pagesReportdbms 1Shivam SinghNo ratings yet
- Articles: Definite Indefinite The A, AnDocument12 pagesArticles: Definite Indefinite The A, AnAndré RodriguesNo ratings yet
- Japanese Guide For BeginnersDocument27 pagesJapanese Guide For BeginnersNihon GoNo ratings yet
- Elliott Waves in MQL5Document87 pagesElliott Waves in MQL5Jorge Ivan100% (2)
- The Concept of Manopavicāra in Vasubandhu's Exposition of Pratītyasamutpāda in Chapter Three of The Abhidharmakośabhā YaDocument19 pagesThe Concept of Manopavicāra in Vasubandhu's Exposition of Pratītyasamutpāda in Chapter Three of The Abhidharmakośabhā Ya张晓亮No ratings yet
- Vol 25 1Document227 pagesVol 25 1Lucía Carmona FernándezNo ratings yet
- Course Syllabus 2020 Fundamentals of Computing 1Document6 pagesCourse Syllabus 2020 Fundamentals of Computing 1Wit Excelsior PañaNo ratings yet
- Logic Gate - UnicodeDocument12 pagesLogic Gate - UnicodeshreyaxchauhanNo ratings yet
- Aatmiyaa ( ) - The SoulmateDocument5 pagesAatmiyaa ( ) - The SoulmateArunabha DeyNo ratings yet
- What Is An Informal LetterDocument10 pagesWhat Is An Informal LetterJoko SukarionoNo ratings yet
- Composed Upon Westminster Bridge, September 3, 1802: William WordsworthDocument9 pagesComposed Upon Westminster Bridge, September 3, 1802: William WordsworthSowmithra ThulasimaniNo ratings yet
- ListofwotdDocument5 pagesListofwotdHarvey MoralesNo ratings yet
- How Long Can A Human Survive Without Water and Food?Document3 pagesHow Long Can A Human Survive Without Water and Food?michelleNo ratings yet
- Syslib Rm018 en e (P AInAdv)Document56 pagesSyslib Rm018 en e (P AInAdv)carbono980No ratings yet
- No Splash KeralaDocument265 pagesNo Splash KeralaadeeshmidasNo ratings yet
- The Christian Understanding of TimeDocument13 pagesThe Christian Understanding of Timeinterregnum. roNo ratings yet
- The Secret Cave of The HeartDocument19 pagesThe Secret Cave of The HeartkatburnerNo ratings yet
- If Everyone Cared LyricsDocument1 pageIf Everyone Cared LyricsMuhammad AliNo ratings yet
- Multiview ProjectionDocument21 pagesMultiview Projectionjaderic buisingNo ratings yet
- Object Oriented Programming and Java (MC221) July 2007Document16 pagesObject Oriented Programming and Java (MC221) July 2007amitukumarNo ratings yet
- Why Do Accordions Have A Counter BassDocument1 pageWhy Do Accordions Have A Counter BassRobbie PieNo ratings yet
- Exercitii Recapitulative Present PerfectDocument2 pagesExercitii Recapitulative Present PerfectCami CerneanuNo ratings yet
- Report-Anthro Educ 302Document97 pagesReport-Anthro Educ 302Gel VelasquezcauzonNo ratings yet
- ACC-224L Week-4-5 ULOb NewDocument13 pagesACC-224L Week-4-5 ULOb NewDivine Grace PatrimonioNo ratings yet
- The Sanctuary Honor AnswersDocument5 pagesThe Sanctuary Honor AnswersMPUNDU MWAPENo ratings yet
- Supernaturalism in Kubla Khan 1Document1 pageSupernaturalism in Kubla Khan 1Manish Kumar Dubey100% (3)