Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ScE7.2.3 Booklet 2019 - ANSWERS
ScE7.2.3 Booklet 2019 - ANSWERS
Uploaded by
Backup UserCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Chapter 9 Heat Form 2 KSSMDocument7 pagesChapter 9 Heat Form 2 KSSMNadhirah Kamarudin80% (5)
- 2nd Year PhysicsDocument48 pages2nd Year PhysicsvenkyNo ratings yet
- Classification of Shear WallDocument23 pagesClassification of Shear WallShivkamal50% (2)
- Formative Assessment 8Document1 pageFormative Assessment 8bashadelacruz7No ratings yet
- ثرموDocument9 pagesثرموasmaaabdelkreem71No ratings yet
- 8th Science EM Term 2 Study Materials English Medium PDF DownloadDocument11 pages8th Science EM Term 2 Study Materials English Medium PDF DownloadE-tech EtecteraTechnologyNo ratings yet
- HeatDocument12 pagesHeatMayukh ChoudhuryNo ratings yet
- Earth Science Student Book - CPO Focus On-94-97Document4 pagesEarth Science Student Book - CPO Focus On-94-97jhonatanNo ratings yet
- Thermal Energy & HeatDocument28 pagesThermal Energy & Heatbisratbirhanu52No ratings yet
- S2Phy Unit 6-Transfer of Thermal EnergyDocument56 pagesS2Phy Unit 6-Transfer of Thermal EnergyAung Ye HtetNo ratings yet
- Form 2 Chapter 9 HeatDocument46 pagesForm 2 Chapter 9 HeatAmer MalekNo ratings yet
- PiXL Knowledge Test PowerPoint AQA P1 CORE Science Legacy 2016 and 2017Document19 pagesPiXL Knowledge Test PowerPoint AQA P1 CORE Science Legacy 2016 and 2017Isini sehansa amarathungaNo ratings yet
- Year7ScienceHomeLearning Cycle8Document10 pagesYear7ScienceHomeLearning Cycle8wg2xq8kddhNo ratings yet
- Heat Energy (GZ) 2017Document20 pagesHeat Energy (GZ) 2017kaviNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Conduction Convection and Radiation Gr. VDocument2 pagesDifference Between Conduction Convection and Radiation Gr. Vm.kadarfi26No ratings yet
- Heat TransferDocument24 pagesHeat TransferABEGAIL SOLIMANNo ratings yet
- Heat TransferDocument31 pagesHeat Transferlilixuxi53No ratings yet
- Las 7 Q3 Week 6Document2 pagesLas 7 Q3 Week 6Darven Cinchez100% (1)
- Science 7 Heat Transfer Learning Activity Sheets 6Document3 pagesScience 7 Heat Transfer Learning Activity Sheets 6fitz zamoraNo ratings yet
- P2.1 Energy Transfer by ConductionDocument17 pagesP2.1 Energy Transfer by ConductionchrisNo ratings yet
- Science 6 Q3 W4 LAS 2Document2 pagesScience 6 Q3 W4 LAS 2Ellen Jenneth PudaNo ratings yet
- G-8 Physics Unit 4 Note - 07-08-13796168803685 - Gobe - 3Document9 pagesG-8 Physics Unit 4 Note - 07-08-13796168803685 - Gobe - 3AbebechNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 HeatDocument6 pagesChapter 5 HeatRajesh JNo ratings yet
- Heat Exchanger Student HandoutDocument39 pagesHeat Exchanger Student HandoutkotiNo ratings yet
- Heat TransferDocument35 pagesHeat TransferUbaid Khan100% (2)
- Heat TransfersDocument16 pagesHeat Transfersrahayuutami30No ratings yet
- Example From Daily Life: - Why Does Mom Use Cloth To Take A Wok?Document23 pagesExample From Daily Life: - Why Does Mom Use Cloth To Take A Wok?Fauzan AkbarNo ratings yet
- Handout - Heat TransferDocument4 pagesHandout - Heat TransferRyerha RoldanNo ratings yet
- 1 HeatDocument1 page1 HeatpipelealNo ratings yet
- Transfer of Thermal Energy: ConductionDocument10 pagesTransfer of Thermal Energy: ConductionmelissaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 EXOTHERMIC AND ENDOTHERMIC REACTIONS AND HEAT TRANSFERDocument53 pagesChapter 5 EXOTHERMIC AND ENDOTHERMIC REACTIONS AND HEAT TRANSFERBrandon Lawy100% (1)
- Heat Booklet 2Document31 pagesHeat Booklet 2api-546418402No ratings yet
- 14-Revision Heat TransferDocument23 pages14-Revision Heat TransferYuichi AkasakaNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Y 10 Thermal Energy NotesDocument3 pagesGrade 9 Y 10 Thermal Energy NotesR4iDNo ratings yet
- Lecture No 1Document75 pagesLecture No 1Raza AnsariNo ratings yet
- Temperature and Heat Week6Document28 pagesTemperature and Heat Week6Marc Jenley MarqhitesNo ratings yet
- Form 2 Chapter 9 HeatDocument46 pagesForm 2 Chapter 9 HeatSiti Hajar Abd Hamid100% (1)
- 0 BooksDocument16 pages0 BooksRameen FatimaNo ratings yet
- Thermal Energy ReadingDocument5 pagesThermal Energy Readingapi-189616674No ratings yet
- Me412-Heat Transfer: Week 1-2:introduction & Fundamental ConceptsDocument34 pagesMe412-Heat Transfer: Week 1-2:introduction & Fundamental ConceptsKyroNo ratings yet
- Science 7 - 3rd Quarter (Week 6) Heat TransferDocument24 pagesScience 7 - 3rd Quarter (Week 6) Heat TransferLauro Hilario EsquilloNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer L 1 UsmiDocument1 pageHeat Transfer L 1 UsmiPathan KingNo ratings yet
- 4 Fundamentals of Heat TransferDocument36 pages4 Fundamentals of Heat TransferShaurya ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer TransesDocument2 pagesHeat Transfer TransesERICKA MAE CANTOSNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document23 pagesChapter 7Beevy GB100% (4)
- Energy TransferDocument6 pagesEnergy TransferSamin YasarNo ratings yet
- ENGI 273 Lec 2 - IspringDocument22 pagesENGI 273 Lec 2 - IspringHaidy T. SakrNo ratings yet
- Sci Oly 2.0Document12 pagesSci Oly 2.0arinaitwejoshua24No ratings yet
- Energy Transfer ConductionconvectionradiationDocument14 pagesEnergy Transfer Conductionconvectionradiationkumpul tugasNo ratings yet
- Energy Transfer ConductionconvectionradiationDocument14 pagesEnergy Transfer ConductionconvectionradiationalongsilatNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Methods 2017 Class Notes AutosavedDocument39 pagesHeat Transfer Methods 2017 Class Notes AutosavedItsMe SirMJNo ratings yet
- Conduction Convection and Radiation Lesson 2Document9 pagesConduction Convection and Radiation Lesson 2Ajeet KumarNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Heat TransferDocument65 pagesIntroduction To Heat TransferDivya DevhariNo ratings yet
- Silver Oak University: Mahirkhan I. PathanDocument26 pagesSilver Oak University: Mahirkhan I. PathanMahir Khan PathanNo ratings yet
- Heat CompleteDocument24 pagesHeat CompletePhilip MooreNo ratings yet
- Heat FlashcardsDocument3 pagesHeat Flashcardsapi-345686634No ratings yet
- Understanding Heat Transfer, Conduction, Convection and RadiationDocument25 pagesUnderstanding Heat Transfer, Conduction, Convection and RadiationMahir Khan PathanNo ratings yet
- David Physics s3Document12 pagesDavid Physics s3RUKUNDO OliveNo ratings yet
- 2nd QuartetrDocument3 pages2nd QuartetrCHERYL LOCSIN - VISAYANo ratings yet
- II. A. TemperatureDocument7 pagesII. A. TemperatureWă ÎłNo ratings yet
- 6.2 Transfer of Thermal EnergyDocument78 pages6.2 Transfer of Thermal EnergyHakim AbbasNo ratings yet
- Chapman 2018Document12 pagesChapman 2018Alexis Centeno CuellarNo ratings yet
- Calc Practice Problems Week 1Document4 pagesCalc Practice Problems Week 1api-374655242No ratings yet
- Retaining Wall Excel SheetDocument6 pagesRetaining Wall Excel SheetJohn Nixt100% (1)
- MS-1H Epoxy PDSDocument2 pagesMS-1H Epoxy PDSAndre CalmonNo ratings yet
- 11 - 12 Sedimentation Tank - Design-1 PDFDocument34 pages11 - 12 Sedimentation Tank - Design-1 PDFAwais MemonNo ratings yet
- Cross Section Shape of Bias Tire1Document9 pagesCross Section Shape of Bias Tire1siritapeNo ratings yet
- Problem Sheet No 5Document2 pagesProblem Sheet No 5akbarNo ratings yet
- Determining Gear EfficiencyDocument56 pagesDetermining Gear EfficiencyPetrescu FlorianNo ratings yet
- Instruction and Manual: Unit 2Document5 pagesInstruction and Manual: Unit 2Elva DevyantiNo ratings yet
- Formula f4 KSSMDocument2 pagesFormula f4 KSSMSukHarunNo ratings yet
- CBL Experiment WorkbookDocument94 pagesCBL Experiment WorkbookdavecNo ratings yet
- PrecisaDocument24 pagesPrecisaAlan MartinezNo ratings yet
- UMG80BS-41 SPMDocument111 pagesUMG80BS-41 SPMDmitriy SemakovNo ratings yet
- Compressor Catalogue 2015 PDFDocument29 pagesCompressor Catalogue 2015 PDFGazmend Krasniqi50% (2)
- Day 2 - TestDocument3 pagesDay 2 - Testsanand110% (1)
- Greenhouse Effect Lueddecke - v49n3p274Document6 pagesGreenhouse Effect Lueddecke - v49n3p274Yadav NitinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 PDFDocument14 pagesChapter 5 PDFCarlos CahuanaNo ratings yet
- Measurements 1 PDFDocument164 pagesMeasurements 1 PDFgiangNo ratings yet
- Sensoplan GMBH - Englisch 2014Document2 pagesSensoplan GMBH - Englisch 2014ternerinNo ratings yet
- Delrin 100P NC010Document4 pagesDelrin 100P NC010Keshav JhanwarNo ratings yet
- Graphs of Quadratic EquationsDocument10 pagesGraphs of Quadratic EquationsROSLINA BINTI ABDUL RASHID MoeNo ratings yet
- Electric Motors Catalogue en 2019-2020 Low PDFDocument80 pagesElectric Motors Catalogue en 2019-2020 Low PDFAlex PumneaNo ratings yet
- Apparent Viscosity of Engine Oils and Base Stocks Between - 10 °C and - 35 °C Using Cold-Cranking SimulatorDocument12 pagesApparent Viscosity of Engine Oils and Base Stocks Between - 10 °C and - 35 °C Using Cold-Cranking SimulatormanojballaNo ratings yet
- Ote Psi300i Particle Size Analyzer Eng PDFDocument8 pagesOte Psi300i Particle Size Analyzer Eng PDFjuanNo ratings yet
- Modes of TurbineDocument20 pagesModes of Turbinenabil160874100% (1)
- Tests, Codes and Frequency of Tests-2Document8 pagesTests, Codes and Frequency of Tests-2nitinNo ratings yet
- S Chaw Low and TownesDocument5 pagesS Chaw Low and TownesAgnivesh SharmaNo ratings yet
ScE7.2.3 Booklet 2019 - ANSWERS
ScE7.2.3 Booklet 2019 - ANSWERS
Uploaded by
Backup UserOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
ScE7.2.3 Booklet 2019 - ANSWERS
ScE7.2.3 Booklet 2019 - ANSWERS
Uploaded by
Backup UserCopyright:
Available Formats
Science Grade 7 Name : ___________________________ HR : _____
ScE7.2.3 : Heat Transfers - ANSWERS
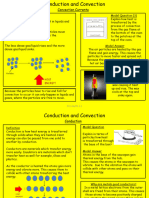
1. Three Modes of Heat Transfer
a) Conduction, Convection, Radiation
b) Convection Currents
c) Lab 6-1D Absorption of Radiation
2. Conductors and Insulators
Terms
Heat Convection Heat insulator
Heat conductor Radiation Heat transfer
Conduction Convection current
1. Heat : the type of energy that moves from hot things to cold things.
2. Heat transfer : when heat moves from one place to another
3. Conduction : a kind of heat transfer in solids, where heat is passed by collisions between
molecules that are not free to move around.
4. Convection : a kind of heat transfer in liquids and gases, where the heat is carried by a flow
of molecules moving through.
5. Radiation : a kind of heat transfer without direct contact, by heat rays travelling through
empty space or transparent substances.
6. Convection current : a circulation current that happens when a hotter liquid or gas floats
up because it is less dense, while the cooler liquid or gas sinks because
it is denser.
7. Heat conductor : a substance through which heat moves easily.
8. Heat insulator : a substance that does not allow heat to pass easily.
ScE7.2.3 Heat Transfers 2019 –p.1
Heat Transfers
9. Define heat transfer: when heat moves from one place to another
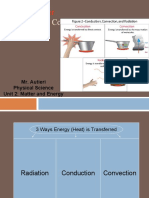
Name the three modes of heat transfer :
Conduction, convection, radiation.
Complete the table :
Conduction Convection Radiation
heat transfer
heat transfer in heat transfer in
without direct
solids, where heat is liquids and gases,
contact, by heat
passed by collisions where the heat is
Definition rays travelling
between molecules carried by a flow of
through empty space
that are not free to molecules moving
or transparent
move around through
substances
Molecules stay in
Molecules circulate
place but vibrate
through the
What are the faster and collide, Does not involve
substance, carrying
molecules doing? passing on heat molecules
the heat energy
energy from one to
throughout.
the next.
Which states of
Mostly solids Liquids and gases No matter required
matter do this?
Heat from hot soup Heat from the sun
Water heating on
Examples moving through a warming the earth
stove
metal spoon
ScE7.2.3 Heat Transfers 2019 –p.2
Application Exercise
Classify the examples of heat transfer, according to which type (conduction,
convection, radiation).
Description Classification
The hot water flows up and the
Convection
cold water flows down.
Stir-frying veggies Conduction
Wind currents Convection
Using a microwave Radiation
The warm glow from a campfire Radiation
The heat from a lightbulb Radiation
Using cold water to cool a hot pan Convection/conduction
ScE7.2.3 Heat Transfers 2019 –p.3
The basement is cooler, the attic
Convection
is warmer.
Frying an egg Conduction
Steaming veggies Convection
ScE7.2.3 Heat Transfers 2019 –p.4
Convection Currents
Explain what is a convection current :
When a liquid or gas is heated unevenly, the warmer gas/liquid expands and
becomes less dense, so it floats up. The part of the gas/liquid that is cooler is
denser, so it sinks. This creates a flow in the substance called convection currents
that carry the heat throughout. When the substance is all the same temperature,
the convection currents stop.
Explain the convection currents when water is heated on a stove.
We often hear the phrase “heat rises”. This is a quick way to remember what is happening, but it
is not quite accurate as an explanation. Explain why not.
It’s not “heat” that rises, otherwise a hot stove would float up in your kitchen,
which would not be good! We could say “hot liquids/gases float up in cooler
liquids/gases”, and that would be more correct, but harder to remember.
ScE7.2.3 Heat Transfers 2019 –p.5
Heat Conductors and Insulators
Heat Conductor Heat Insulator
a substance through which heat a substance that does not allow
Definition
moves easily. heat to pass easily.
Wood, styrofoam, fiberglass,
Examples Metals
cork.
Activity : Observe the objects in the lab. Complete the table below.
Substance it Conductor or What heat do we want to keep in or
Object
is made of Insulator ? transfer in this use?
Wool mitts Wool I To keep in the heat from your hands
Wooden To stop the heat from hot food from
spoon
Wood I burning your hand.
To let the heat from the element
Metal frying
pan
Metal C transfer through the pan to cook your
food
Plastic
To stop the heat from the pan from
handle on Plastic I burning your hands.
frying pan
ScE7.2.3 Heat Transfers 2019 –p.6
Substance it Conductor or What heat transfer do we want to
Object
is made of Insulator ? happen or avoid in this use?
Heat Heat-
To stop the heat from the hot object
resistant resistant I from burning your hand.
gloves fabric
Double-
The air between the glass walls stops
walled
Glass and the heat of the coffee from passing
coffee cup
air I through the walls of the cup, so your
(glass and
coffee stays hot longer.
air)
Double-
The air between the metal walls stops
walled travel
Metal and the heat of the coffee from passing
coffee mug
air I through the walls of the cup, so your
(metal and
coffee stays hot longer.
air)
Metal To let the heat transfer from the
“beaker”
Steel C hotplate to the water.
Pick Styrofoam
styrofoam (contains
home lots of tiny I To keep the heat inside your house.
insulation air bubbles)
So the heat from a hot dish doesn’t
Cork trivet Cork I burn your table.
ScE7.2.3 Heat Transfers 2019 –p.7
You might also like
- Chapter 9 Heat Form 2 KSSMDocument7 pagesChapter 9 Heat Form 2 KSSMNadhirah Kamarudin80% (5)
- 2nd Year PhysicsDocument48 pages2nd Year PhysicsvenkyNo ratings yet
- Classification of Shear WallDocument23 pagesClassification of Shear WallShivkamal50% (2)
- Formative Assessment 8Document1 pageFormative Assessment 8bashadelacruz7No ratings yet
- ثرموDocument9 pagesثرموasmaaabdelkreem71No ratings yet
- 8th Science EM Term 2 Study Materials English Medium PDF DownloadDocument11 pages8th Science EM Term 2 Study Materials English Medium PDF DownloadE-tech EtecteraTechnologyNo ratings yet
- HeatDocument12 pagesHeatMayukh ChoudhuryNo ratings yet
- Earth Science Student Book - CPO Focus On-94-97Document4 pagesEarth Science Student Book - CPO Focus On-94-97jhonatanNo ratings yet
- Thermal Energy & HeatDocument28 pagesThermal Energy & Heatbisratbirhanu52No ratings yet
- S2Phy Unit 6-Transfer of Thermal EnergyDocument56 pagesS2Phy Unit 6-Transfer of Thermal EnergyAung Ye HtetNo ratings yet
- Form 2 Chapter 9 HeatDocument46 pagesForm 2 Chapter 9 HeatAmer MalekNo ratings yet
- PiXL Knowledge Test PowerPoint AQA P1 CORE Science Legacy 2016 and 2017Document19 pagesPiXL Knowledge Test PowerPoint AQA P1 CORE Science Legacy 2016 and 2017Isini sehansa amarathungaNo ratings yet
- Year7ScienceHomeLearning Cycle8Document10 pagesYear7ScienceHomeLearning Cycle8wg2xq8kddhNo ratings yet
- Heat Energy (GZ) 2017Document20 pagesHeat Energy (GZ) 2017kaviNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Conduction Convection and Radiation Gr. VDocument2 pagesDifference Between Conduction Convection and Radiation Gr. Vm.kadarfi26No ratings yet
- Heat TransferDocument24 pagesHeat TransferABEGAIL SOLIMANNo ratings yet
- Heat TransferDocument31 pagesHeat Transferlilixuxi53No ratings yet
- Las 7 Q3 Week 6Document2 pagesLas 7 Q3 Week 6Darven Cinchez100% (1)
- Science 7 Heat Transfer Learning Activity Sheets 6Document3 pagesScience 7 Heat Transfer Learning Activity Sheets 6fitz zamoraNo ratings yet
- P2.1 Energy Transfer by ConductionDocument17 pagesP2.1 Energy Transfer by ConductionchrisNo ratings yet
- Science 6 Q3 W4 LAS 2Document2 pagesScience 6 Q3 W4 LAS 2Ellen Jenneth PudaNo ratings yet
- G-8 Physics Unit 4 Note - 07-08-13796168803685 - Gobe - 3Document9 pagesG-8 Physics Unit 4 Note - 07-08-13796168803685 - Gobe - 3AbebechNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 HeatDocument6 pagesChapter 5 HeatRajesh JNo ratings yet
- Heat Exchanger Student HandoutDocument39 pagesHeat Exchanger Student HandoutkotiNo ratings yet
- Heat TransferDocument35 pagesHeat TransferUbaid Khan100% (2)
- Heat TransfersDocument16 pagesHeat Transfersrahayuutami30No ratings yet
- Example From Daily Life: - Why Does Mom Use Cloth To Take A Wok?Document23 pagesExample From Daily Life: - Why Does Mom Use Cloth To Take A Wok?Fauzan AkbarNo ratings yet
- Handout - Heat TransferDocument4 pagesHandout - Heat TransferRyerha RoldanNo ratings yet
- 1 HeatDocument1 page1 HeatpipelealNo ratings yet
- Transfer of Thermal Energy: ConductionDocument10 pagesTransfer of Thermal Energy: ConductionmelissaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 EXOTHERMIC AND ENDOTHERMIC REACTIONS AND HEAT TRANSFERDocument53 pagesChapter 5 EXOTHERMIC AND ENDOTHERMIC REACTIONS AND HEAT TRANSFERBrandon Lawy100% (1)
- Heat Booklet 2Document31 pagesHeat Booklet 2api-546418402No ratings yet
- 14-Revision Heat TransferDocument23 pages14-Revision Heat TransferYuichi AkasakaNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Y 10 Thermal Energy NotesDocument3 pagesGrade 9 Y 10 Thermal Energy NotesR4iDNo ratings yet
- Lecture No 1Document75 pagesLecture No 1Raza AnsariNo ratings yet
- Temperature and Heat Week6Document28 pagesTemperature and Heat Week6Marc Jenley MarqhitesNo ratings yet
- Form 2 Chapter 9 HeatDocument46 pagesForm 2 Chapter 9 HeatSiti Hajar Abd Hamid100% (1)
- 0 BooksDocument16 pages0 BooksRameen FatimaNo ratings yet
- Thermal Energy ReadingDocument5 pagesThermal Energy Readingapi-189616674No ratings yet
- Me412-Heat Transfer: Week 1-2:introduction & Fundamental ConceptsDocument34 pagesMe412-Heat Transfer: Week 1-2:introduction & Fundamental ConceptsKyroNo ratings yet
- Science 7 - 3rd Quarter (Week 6) Heat TransferDocument24 pagesScience 7 - 3rd Quarter (Week 6) Heat TransferLauro Hilario EsquilloNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer L 1 UsmiDocument1 pageHeat Transfer L 1 UsmiPathan KingNo ratings yet
- 4 Fundamentals of Heat TransferDocument36 pages4 Fundamentals of Heat TransferShaurya ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer TransesDocument2 pagesHeat Transfer TransesERICKA MAE CANTOSNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document23 pagesChapter 7Beevy GB100% (4)
- Energy TransferDocument6 pagesEnergy TransferSamin YasarNo ratings yet
- ENGI 273 Lec 2 - IspringDocument22 pagesENGI 273 Lec 2 - IspringHaidy T. SakrNo ratings yet
- Sci Oly 2.0Document12 pagesSci Oly 2.0arinaitwejoshua24No ratings yet
- Energy Transfer ConductionconvectionradiationDocument14 pagesEnergy Transfer Conductionconvectionradiationkumpul tugasNo ratings yet
- Energy Transfer ConductionconvectionradiationDocument14 pagesEnergy Transfer ConductionconvectionradiationalongsilatNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Methods 2017 Class Notes AutosavedDocument39 pagesHeat Transfer Methods 2017 Class Notes AutosavedItsMe SirMJNo ratings yet
- Conduction Convection and Radiation Lesson 2Document9 pagesConduction Convection and Radiation Lesson 2Ajeet KumarNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Heat TransferDocument65 pagesIntroduction To Heat TransferDivya DevhariNo ratings yet
- Silver Oak University: Mahirkhan I. PathanDocument26 pagesSilver Oak University: Mahirkhan I. PathanMahir Khan PathanNo ratings yet
- Heat CompleteDocument24 pagesHeat CompletePhilip MooreNo ratings yet
- Heat FlashcardsDocument3 pagesHeat Flashcardsapi-345686634No ratings yet
- Understanding Heat Transfer, Conduction, Convection and RadiationDocument25 pagesUnderstanding Heat Transfer, Conduction, Convection and RadiationMahir Khan PathanNo ratings yet
- David Physics s3Document12 pagesDavid Physics s3RUKUNDO OliveNo ratings yet
- 2nd QuartetrDocument3 pages2nd QuartetrCHERYL LOCSIN - VISAYANo ratings yet
- II. A. TemperatureDocument7 pagesII. A. TemperatureWă ÎłNo ratings yet
- 6.2 Transfer of Thermal EnergyDocument78 pages6.2 Transfer of Thermal EnergyHakim AbbasNo ratings yet
- Chapman 2018Document12 pagesChapman 2018Alexis Centeno CuellarNo ratings yet
- Calc Practice Problems Week 1Document4 pagesCalc Practice Problems Week 1api-374655242No ratings yet
- Retaining Wall Excel SheetDocument6 pagesRetaining Wall Excel SheetJohn Nixt100% (1)
- MS-1H Epoxy PDSDocument2 pagesMS-1H Epoxy PDSAndre CalmonNo ratings yet
- 11 - 12 Sedimentation Tank - Design-1 PDFDocument34 pages11 - 12 Sedimentation Tank - Design-1 PDFAwais MemonNo ratings yet
- Cross Section Shape of Bias Tire1Document9 pagesCross Section Shape of Bias Tire1siritapeNo ratings yet
- Problem Sheet No 5Document2 pagesProblem Sheet No 5akbarNo ratings yet
- Determining Gear EfficiencyDocument56 pagesDetermining Gear EfficiencyPetrescu FlorianNo ratings yet
- Instruction and Manual: Unit 2Document5 pagesInstruction and Manual: Unit 2Elva DevyantiNo ratings yet
- Formula f4 KSSMDocument2 pagesFormula f4 KSSMSukHarunNo ratings yet
- CBL Experiment WorkbookDocument94 pagesCBL Experiment WorkbookdavecNo ratings yet
- PrecisaDocument24 pagesPrecisaAlan MartinezNo ratings yet
- UMG80BS-41 SPMDocument111 pagesUMG80BS-41 SPMDmitriy SemakovNo ratings yet
- Compressor Catalogue 2015 PDFDocument29 pagesCompressor Catalogue 2015 PDFGazmend Krasniqi50% (2)
- Day 2 - TestDocument3 pagesDay 2 - Testsanand110% (1)
- Greenhouse Effect Lueddecke - v49n3p274Document6 pagesGreenhouse Effect Lueddecke - v49n3p274Yadav NitinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 PDFDocument14 pagesChapter 5 PDFCarlos CahuanaNo ratings yet
- Measurements 1 PDFDocument164 pagesMeasurements 1 PDFgiangNo ratings yet
- Sensoplan GMBH - Englisch 2014Document2 pagesSensoplan GMBH - Englisch 2014ternerinNo ratings yet
- Delrin 100P NC010Document4 pagesDelrin 100P NC010Keshav JhanwarNo ratings yet
- Graphs of Quadratic EquationsDocument10 pagesGraphs of Quadratic EquationsROSLINA BINTI ABDUL RASHID MoeNo ratings yet
- Electric Motors Catalogue en 2019-2020 Low PDFDocument80 pagesElectric Motors Catalogue en 2019-2020 Low PDFAlex PumneaNo ratings yet
- Apparent Viscosity of Engine Oils and Base Stocks Between - 10 °C and - 35 °C Using Cold-Cranking SimulatorDocument12 pagesApparent Viscosity of Engine Oils and Base Stocks Between - 10 °C and - 35 °C Using Cold-Cranking SimulatormanojballaNo ratings yet
- Ote Psi300i Particle Size Analyzer Eng PDFDocument8 pagesOte Psi300i Particle Size Analyzer Eng PDFjuanNo ratings yet
- Modes of TurbineDocument20 pagesModes of Turbinenabil160874100% (1)
- Tests, Codes and Frequency of Tests-2Document8 pagesTests, Codes and Frequency of Tests-2nitinNo ratings yet
- S Chaw Low and TownesDocument5 pagesS Chaw Low and TownesAgnivesh SharmaNo ratings yet