Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Metrology and Computer Aided Inspection
Metrology and Computer Aided Inspection
Uploaded by
ROOSSVELT PRABHU K A VOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Metrology and Computer Aided Inspection
Metrology and Computer Aided Inspection
Uploaded by
ROOSSVELT PRABHU K A VCopyright:
Available Formats
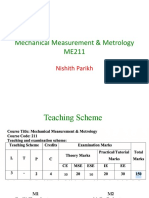
METROLOGY AND COMPUTER AIDED INSPECTION
OBJECTIVES:
To provide knowledge on various Metrological equipment available to measure the dimension
of the components.
To provide knowledge on the correct procedure to be adopted to measure the dimension of
the components.
UNIT I .BASICS OF METROLOGY 5
Introduction to Metrology – Need for measurement – Dimensional and Form tolerances – Elements –
Work piece, Instruments – Persons – Environment –their effect on Precision and Accuracy – Errors in
Measurements – Causes & Types – Control – Types of standards & Practice.
UNIT II LINEAR AND ANGULAR MEASUREMENTS 10
Linear Measuring Instruments – Evolution – Types – Classification – Limit gauges – gauge design –
terminology – procedure – concepts of interchange ability and selective assembly – Angular
measuring instruments – Types – Bevel protractor, Angle gauges, Spirit levels, Sine bar – Angle
alignment telescope – Autocollimator – Applications.
UNIT III FORM & LASER MEASUREMENT 10
Principles and Methods of straightness – Flatness measurement – Thread measurement, gear
measurement, surface finish measurement, Roundness measurement – Applications. Use of Lasers –
Principle – Laser Interferometer– Application in Linear and Angular measurements – Testing of
machine tools using Laser Interferometer.
UNIT IV CO-ORDINATE MEASURING MACHINE
10
Co-ordinate measuring machine (CMM) – Contact type CMM – Configurations, parts and its
features, types of probes, probe compensation. Non-Contact type CMM – Features, probes,
Specifications. Errors in CMM measurement – Calibration of CMM – measuring scales, accuracy
– Moire fringes – Applications of CMM for dimensional and form measurements.
UNIT V MACHINE VISION & NANO METROLOGY 10
Machine vision system – Methods for sensing objects, image processing, segmentation, pattern
recognition. Filters in image processing and analysis. Image histogram and processing.
Applications in metrology. Nanometrology – Introduction – Principles – Nanometer metrology
systems – Methods of measuring length and surfaces to nano scale result with interferometers and
other devices.
OUTCOMES:
Upon completion of this course, the Students can demonstrate different measurement
technologies and use of them in Industrial Components
TEXT BOOKS:
1. Jain R.K. “Engineering Metrology”, Khanna Publishers, 19th Edition, 2005.
2. Gupta. I.C., “Engineering Metrology”, Dhanpatrai Publications, 2005.
3. Whitehouse D.J., The Handbook of Surface and Nanometrology, CRC Press, 2011
REFERENCES:
1. Charles Reginald Shotbolt, “Metrology for Engineers”, 5th edition, Cengage Learning
EMEA, 1990.
2. Backwith, Marangoni, Lienhard, “Mechanical Measurements”, Pearson Education , 2006.
3. Galyer J.F.W. and Shotbolt C.R., “Metrology for Engineers”, O.R.Cassel, London,1993.
4. Thomas, “Engineering Metrology”, Butthinson & Co., 1984.
5. Bewoor A.K. and Kulkarni V.A., “Metrology and Measurements”, Tata McGraw-Hill, 2009.
You might also like
- SPM Manual Chapter 1Document4 pagesSPM Manual Chapter 1Jairo Andres Chavarria Alvarado20% (5)
- Phenomenological Research GuidelinesDocument4 pagesPhenomenological Research GuidelinesOxymoronic Blasphemy89% (9)
- Anti Bullying Act of 2013Document30 pagesAnti Bullying Act of 2013marjoerine100% (2)
- Public Admin Books PDFDocument3 pagesPublic Admin Books PDFNitinkiet1030% (1)
- SyllabusDocument1 pageSyllabusShankar NarayananNo ratings yet
- SyllubusDocument1 pageSyllubuskssudhagarNo ratings yet
- Me8501 SyllabusDocument1 pageMe8501 Syllabusk.l yuvarajNo ratings yet
- 070 - ME8501 Metrology and Measurements - Anna University 2017 Regulation Syllabus PDFDocument2 pages070 - ME8501 Metrology and Measurements - Anna University 2017 Regulation Syllabus PDFSidhu Vev Sidhu0% (1)
- Me6504 Metrology and Measurements L T P CDocument1 pageMe6504 Metrology and Measurements L T P CajitsssNo ratings yet
- 15hc04 Metrology and Computer Aided InspectionDocument1 page15hc04 Metrology and Computer Aided Inspectionarun2386No ratings yet
- MM SyllabusDocument2 pagesMM SyllabusS.Bharani KumarNo ratings yet
- State Board of Technical Education &training, Tamilnadu Diploma in Engineering / Technology Syllabus N - SchemeDocument15 pagesState Board of Technical Education &training, Tamilnadu Diploma in Engineering / Technology Syllabus N - SchemeIsrael Dharmaraj100% (1)
- 11me303 PDFDocument1 page11me303 PDFsumikannuNo ratings yet
- Me2304 Engineering Metrology and Measurements: Metrology Is The Science of Measurement. Metrology Includes AllDocument4 pagesMe2304 Engineering Metrology and Measurements: Metrology Is The Science of Measurement. Metrology Includes Allphb1986No ratings yet
- Metrology and Computer Aided InspectionDocument1 pageMetrology and Computer Aided Inspectionprincessaadhya29No ratings yet
- Nptel: Metrology - Video CourseDocument3 pagesNptel: Metrology - Video CourseLakshya MaletiNo ratings yet
- TE Mechanical and TE Automobile (2015 Course)Document7 pagesTE Mechanical and TE Automobile (2015 Course)A SNo ratings yet
- MetrologyDocument3 pagesMetrologySachi DhanandamNo ratings yet
- University of Pune: T.E. (Mechanical) - 2012 Course Metrology and Quality Control (302044)Document3 pagesUniversity of Pune: T.E. (Mechanical) - 2012 Course Metrology and Quality Control (302044)Arvind BhosaleNo ratings yet
- Measurements & Metrology BasicsDocument208 pagesMeasurements & Metrology BasicsPrabakaran Caleb0% (1)
- Cource Outline MeasuremntDocument3 pagesCource Outline Measuremntmuru0105No ratings yet
- CH 1 - Metrology and MeasurementDocument51 pagesCH 1 - Metrology and MeasurementRahul PathakNo ratings yet
- MQC SyllDocument2 pagesMQC SyllAandy KhasdarNo ratings yet
- Emm Question BankDocument19 pagesEmm Question BankbhuvansparksNo ratings yet
- M & IDocument12 pagesM & INenu Na RakshasiNo ratings yet
- Metrology and Surface EngineeringDocument2 pagesMetrology and Surface EngineeringnvemanNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Measurements & Metrology SyllabusDocument2 pagesMechanical Measurements & Metrology SyllabusThanka ElangoNo ratings yet
- Me6504 Metrology and Measurements Syllabus For 5th Sem Mech Reg 2013 - Anna University Internal Marks 2017Document2 pagesMe6504 Metrology and Measurements Syllabus For 5th Sem Mech Reg 2013 - Anna University Internal Marks 2017Mr.T.Barathan Assistant Professor100% (1)
- Engineering Metrology: 11UEK408 L T P C 3 0 0 3Document1 pageEngineering Metrology: 11UEK408 L T P C 3 0 0 3Aravind MohanNo ratings yet
- M & I PDFDocument13 pagesM & I PDFvirendraNo ratings yet
- Text Books:: 2. Ansel Ugural, "Mechanical Design - An Integral Approach", 1 Edition, Tata Mcgraw-Hill Book Co, 2003Document6 pagesText Books:: 2. Ansel Ugural, "Mechanical Design - An Integral Approach", 1 Edition, Tata Mcgraw-Hill Book Co, 2003Liaqat ahmedNo ratings yet
- MEPR205C - El 1 Metrology & Computer Aided InspectionDocument3 pagesMEPR205C - El 1 Metrology & Computer Aided Inspectionዘረአዳም ዘመንቆረርNo ratings yet
- Engineering Metrology and Measurements Unit 1 2Document82 pagesEngineering Metrology and Measurements Unit 1 2scorpionarnold100% (1)
- Subject: Metrology: Academic Year:2017-2018 Branch: Mechanical Engineering Subject: Metrology Year / Sem: Iii / IDocument2 pagesSubject: Metrology: Academic Year:2017-2018 Branch: Mechanical Engineering Subject: Metrology Year / Sem: Iii / IMech DeptNo ratings yet
- ME312 Metrology and instrumentationKTUNOTES - IN PDFDocument4 pagesME312 Metrology and instrumentationKTUNOTES - IN PDFpraphultmenonNo ratings yet
- Metrology BasicsDocument113 pagesMetrology Basicsavutu_kunduru100% (1)
- Sardar Raja College of Engineering, AlangulamDocument5 pagesSardar Raja College of Engineering, AlangulammayilsamythangarajuNo ratings yet
- Metrology and Mechanical MeasurementsDocument118 pagesMetrology and Mechanical MeasurementsNihar ApteNo ratings yet
- Metrology & Quality ControlDocument127 pagesMetrology & Quality ControlArnav PandeyNo ratings yet
- Me Manufacturing Curriculum-2Document11 pagesMe Manufacturing Curriculum-2Arun KumarNo ratings yet
- Engineering Metrology and MeasurementsDocument128 pagesEngineering Metrology and MeasurementsArvind Bhosale100% (7)
- Toaz - Info Engineering Metrology PRDocument129 pagesToaz - Info Engineering Metrology PRB05Vedant BarpandeNo ratings yet
- Viime - Sy - 290613040916Document17 pagesViime - Sy - 290613040916Vivek RajakNo ratings yet
- Bit Sindri, Dhanbad: NAMEOFDEPTT. /CENTRE: Department of Production EngineeringDocument1 pageBit Sindri, Dhanbad: NAMEOFDEPTT. /CENTRE: Department of Production Engineeringtalk2sumantaNo ratings yet
- Engineering Metrology and Measurements - 5th Sem Mechanical & Automobile SyllabusDocument1 pageEngineering Metrology and Measurements - 5th Sem Mechanical & Automobile Syllabuspriyo21jwNo ratings yet
- SyllabusDocument1 pageSyllabusGnaneswaran NarayananNo ratings yet
- 5TH 6TH Final As Per Bos Adjuen Meetin On 21-08-21 210824 164803Document28 pages5TH 6TH Final As Per Bos Adjuen Meetin On 21-08-21 210824 164803DigvijayNo ratings yet
- 9097 - Metrology & Quality ControlDocument7 pages9097 - Metrology & Quality ControlAhmed Abu-SinnaNo ratings yet
- IP5SEMSYLLABUSDocument6 pagesIP5SEMSYLLABUSAditya RaoNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Engineering VI Sem SyllabusDocument25 pagesMechanical Engineering VI Sem Syllabussaurabh1116No ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological University - MeasurementDocument4 pagesGujarat Technological University - MeasurementA SNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Measurement and MetrologyDocument2 pagesMechanical Measurement and MetrologyNarayanarao PalagaraNo ratings yet
- Metrology: ME3190 Machine Tools and MetrologyDocument64 pagesMetrology: ME3190 Machine Tools and MetrologySujit MuleNo ratings yet
- Engineering Metrology 2Document3 pagesEngineering Metrology 2Manu RavuriNo ratings yet
- MEC601 Metrology and Quality Engineering 3+1: ObjectivesDocument1 pageMEC601 Metrology and Quality Engineering 3+1: ObjectivesHoney SinghNo ratings yet
- MEC601 Metrology and Quality Engineering 3+1: ObjectivesDocument1 pageMEC601 Metrology and Quality Engineering 3+1: Objectivesnavneetkpatil8409No ratings yet
- Measurements & Metrology PracticalDocument91 pagesMeasurements & Metrology PracticalAU Aalim Muhammed Salegh Polytechnic CollegeNo ratings yet
- Jntuh Mech Engg R16 SyllabusDocument7 pagesJntuh Mech Engg R16 SyllabusAqib syedNo ratings yet
- ME334 Manufacturing Technology Laboratory - IIDocument5 pagesME334 Manufacturing Technology Laboratory - IInandan144No ratings yet
- Mechanical Measurement & Metrology ME211: Nishith ParikhDocument18 pagesMechanical Measurement & Metrology ME211: Nishith ParikhDrMohamed MansourNo ratings yet
- M.E. Mechatronics SyllabusDocument38 pagesM.E. Mechatronics SyllabusJoswa CaxtonNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Particle Inspection: Techniques, Applications, Interviews Q&A, and GlossaryFrom EverandMagnetic Particle Inspection: Techniques, Applications, Interviews Q&A, and GlossaryNo ratings yet
- Final Internship ReportDocument53 pagesFinal Internship Reportsrabon_sh63% (8)
- Balance Score CardDocument3 pagesBalance Score CardMuhammad SohailNo ratings yet
- Presented by Denise Tarlinton: Pupil Free Day Monday 14 July, 2003Document58 pagesPresented by Denise Tarlinton: Pupil Free Day Monday 14 July, 2003Mclin Jhon Marave MabalotNo ratings yet
- Non Engg InstituteDocument157 pagesNon Engg InstituteshekharavacNo ratings yet
- IELTS Application FormDocument8 pagesIELTS Application FormAnand RasaneNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Rational Algebraic ExpressionsDocument4 pagesLesson Plan in Rational Algebraic ExpressionsDaneman GasdelNo ratings yet
- Sas2 - Filipino Values and TraditionsDocument5 pagesSas2 - Filipino Values and TraditionsCharlene MananapNo ratings yet
- Playtime BDocument19 pagesPlaytime BTeff PsomotragosNo ratings yet
- HE6 W6a PDFDocument4 pagesHE6 W6a PDFK TIRINo ratings yet
- RA-095630 - PROFESSIONAL TEACHER - Elementary - CAUAYAN, ISABELA - 10-2022Document37 pagesRA-095630 - PROFESSIONAL TEACHER - Elementary - CAUAYAN, ISABELA - 10-2022Liean Gumaru Angui-BodolloNo ratings yet
- Participatory DevelopmentDocument20 pagesParticipatory DevelopmentFranditya UtomoNo ratings yet
- ABC's of KindergartenDocument14 pagesABC's of Kindergartenaking60No ratings yet
- SpeechDocument4 pagesSpeechMohammed AtifNo ratings yet
- How To Build The Right Team For Your Self-Directed FilmDocument2 pagesHow To Build The Right Team For Your Self-Directed FilmJay-anCastillonNo ratings yet
- Proposal Writing A Practical Guide For Writing ProposalsDocument4 pagesProposal Writing A Practical Guide For Writing Proposalsyesuplus2No ratings yet
- Chapter 15 SummaryDocument2 pagesChapter 15 Summaryapi-610839184No ratings yet
- 2022 Best Undergraduate Business Programs - US News RankingsDocument69 pages2022 Best Undergraduate Business Programs - US News RankingsHòa NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 - Cell ModificationDocument3 pagesLesson 5 - Cell ModificationEarl Caesar Quiba PagunsanNo ratings yet
- Alvin123: Jan 18, 2012, 10:32am #2 (Moderator)Document11 pagesAlvin123: Jan 18, 2012, 10:32am #2 (Moderator)Silence ForteNo ratings yet
- CVDocument5 pagesCVSuzzanne JobaibeesNo ratings yet
- Disability HandbookDocument29 pagesDisability Handbookapi-662162360No ratings yet
- School ConsultationDocument235 pagesSchool ConsultationmazfamuratNo ratings yet
- Nisha ValviDocument11 pagesNisha ValviAnonymous CwJeBCAXpNo ratings yet
- Welcome To Slauele: It's An Online Learning Management System (LMS) - It's An Online (LMS)Document12 pagesWelcome To Slauele: It's An Online Learning Management System (LMS) - It's An Online (LMS)St. Lawrence University SLAUNo ratings yet
- Bangladesh Agricultural University ThesisDocument8 pagesBangladesh Agricultural University Thesisdnnvbpvh100% (2)
- Staying Relevant in The WorkplaceDocument41 pagesStaying Relevant in The WorkplaceMiguel MartínNo ratings yet