Professional Documents
Culture Documents
AKM 204E - Fluid Mechanics: 2 W 3 W 3 W - 6 2 Atm, Absolute
AKM 204E - Fluid Mechanics: 2 W 3 W 3 W - 6 2 Atm, Absolute
Uploaded by
Sude OğuzluOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
AKM 204E - Fluid Mechanics: 2 W 3 W 3 W - 6 2 Atm, Absolute
AKM 204E - Fluid Mechanics: 2 W 3 W 3 W - 6 2 Atm, Absolute
Uploaded by
Sude OğuzluCopyright:
Available Formats
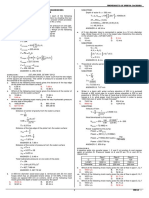
AKM 204E – Fluid Mechanics
Student ID Name-Surname Signature 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
Exam Duration 110 min.
SI Unit system is required.
For purpose; g=9.81 m/s2, w=1000 kg/m3, w=9810 N/m3, w=110-6 m2/s ve Patm,absolute=98.10 kPa
Question 1. Navier- Stokes equation is given for 3D flow of incompressible and real fluids at x direction as;
𝑑𝑢 𝜕𝑢 𝜕𝑢 𝜕𝑢 𝜕𝑢 1 𝜕𝑝 𝜕 𝑢 𝜕 𝑢 𝜕 𝑢
= +𝑢 +𝑣 +𝜔 =𝐾 − +𝜈 + +
𝑑𝑡 𝜕𝑡 𝜕𝑥 𝜕𝑦 𝜕𝑧 𝜌 𝜕𝑥 𝜕𝑥 𝜕𝑦 𝜕𝑧
a. Explain each term of the Equation.
b. How equation will change for ideal fluid condition?
c. Derive hydrostatic pressure by using this equation in vertical direction.
Question 2.
a. Write down the energy equation for real fluids.
b. Explain physical end geometrical meanings of each term of the equation.
c. Pressure was determined on the horizontal and constant diameter pipe with a certain distance. Could we determine
headloss between pressure measurement points by using this equation? Explain your answer.
FluidMechanics / Final Exam / 04.07.2018 / 1
AKM 204E – Fluid Mechanics
Final Exam
Question 3.
a. Show that rotational and irrotational flows on the figure.
b. Prove that stream and potential lines are perpendicular to each other.
c. Derive the Continuity Equation for two-dimensional flow of real fluid and write this equation for steady current
condition.
Question 4.
Calculate magnitude, direction and location of the resultant force exerted by the water on this rectangular tunnel plug for
unit width.
0.60 m
2.50 m
60
FluidMechanics / Final Exam / 04.07.2018 / 2
AKM 204E – Fluid Mechanics
Final Exam
Student ID Name-Surname Signature
g=9.81 m/s2; su=1000 kg/m3; su=9810 N/m3;
su=110-6 m2/s; Patm,mutlak=98.10 kPa
Question 5. For the flow of an ideal and incompressible fluid (water) in the system shown in the figure:
a. Describe the properties of the flow at the pipe AB (uniform/non-uniform and/or steady/unsteady).
b. Compute the discharge (Q) of the system.
c. Determine the mean velocities at the sections A, B, and C of the pipe.
d. Determine the flow type (laminar/turbulent) at the outlet point, i.e. section C (water =10-6 m²/s).
e. Determine the water surface levels in the mounted tubes and draw the relative energy and hydraulic grade lines.
f. Determine the minimum value of the pipe diameter at the section B (DB=DB,2=DB,min), provided that the discharge (Q)
remains constant and there is no vaporisation (Absolute vapour pressure of water, P vw, is 2,45 KN/m2).
Closed ended
Open ended
basin →∞
FluidMechanics / Final Exam / 04.06.2018 / 3
AKM 204E – Fluid Mechanics
Final Exam
Question6. That place (hatched area) covers 12,5 cm rectengular hole. What is the maximum H which can be maintained
without leaking (for 10 cm widh)?
3.3 m
15 cm, d1
12,5 cm, d2
Question 6. One of the velocity component of the flow in the x-y plate is u=2.x.t.
a) Determine the other component “ v ” of the velocity.
b) Determine the flow is steady or not.
c) Determine the stream function of the flow.
d) Find the flow is rotational or irrotational and determine the potential function of the flow if it is exist.
FluidMechanics / Final Exam / 04.07.2018 / 4
You might also like
- Best Practices For SAP BTP: Public 2023-03-22Document110 pagesBest Practices For SAP BTP: Public 2023-03-22Rosario CastañedaNo ratings yet
- HYDRAULICS GEOTECH CE REFRESHER PART 3 2019 Answers PDFDocument11 pagesHYDRAULICS GEOTECH CE REFRESHER PART 3 2019 Answers PDFkisshot100% (1)
- Open Book/Notes: First Page of Your Submission and Sign It ThereDocument5 pagesOpen Book/Notes: First Page of Your Submission and Sign It ThereRobert BuiNo ratings yet
- Ewsd OverviewDocument0 pagesEwsd Overviewpratham_svnitNo ratings yet
- 2 W 3 W 3 W - 6 2 Atm, Absolute: Fluidmechanics / Final Exam / 22.05.2013 / 1Document3 pages2 W 3 W 3 W - 6 2 Atm, Absolute: Fluidmechanics / Final Exam / 22.05.2013 / 1Sude OğuzluNo ratings yet
- Institute of Aeronautical Engineering: Hall Ticket No. Question Paper Code: ACE005Document4 pagesInstitute of Aeronautical Engineering: Hall Ticket No. Question Paper Code: ACE005Praveen Reddy ReddyNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Lect Notes With Sample QuesDocument96 pagesFluid Mechanics Lect Notes With Sample QuesMahin Samuel John 74No ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Lab: ST Mary'S Institute of Science and TechnologyDocument36 pagesFluid Mechanics Lab: ST Mary'S Institute of Science and TechnologysidNo ratings yet
- Final FMHM LAB MANUAL Manual of 1Document67 pagesFinal FMHM LAB MANUAL Manual of 1Motee SinghNo ratings yet
- 2020 Dec. MET203-ADocument3 pages2020 Dec. MET203-Ared18ggmuNo ratings yet
- Group Assignment IIIDocument7 pagesGroup Assignment IIIlelisagetachew90No ratings yet
- Dsy B.tech Mech Sem IVDocument2 pagesDsy B.tech Mech Sem IViplauction006No ratings yet
- Ce8394 FMMDocument2 pagesCe8394 FMMsyed1188No ratings yet
- Practice C SolutionDocument5 pagesPractice C Solutionrahouo devNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2023-10-09 at 3.54.38 AMDocument5 pagesScreenshot 2023-10-09 at 3.54.38 AMhnsm9bwtqrNo ratings yet
- A Simplified Approach To Water-Hammer Analysis PDFDocument0 pagesA Simplified Approach To Water-Hammer Analysis PDFbtjajadi100% (1)
- Mech280final 2013Document14 pagesMech280final 2013manrabrarNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics2Document6 pagesFluid Mechanics2cemaliNo ratings yet
- ChE 2O04 Winter 2016 - Midterm R3Document10 pagesChE 2O04 Winter 2016 - Midterm R3kmcNo ratings yet
- FE Fluids Review - Notes and Problems113pdfDocument25 pagesFE Fluids Review - Notes and Problems113pdfMahmoud HelmyNo ratings yet
- Marine Hydrodynamics 1: Sheets BookletDocument13 pagesMarine Hydrodynamics 1: Sheets BookletKhalid BaragaNo ratings yet
- NR RR 211401 ThermodynamicsDocument4 pagesNR RR 211401 ThermodynamicsVenkatesh AluriNo ratings yet
- Ce 8381 - Strength of Materials and Fluid Mechanics and Machinery Laboratory ManualDocument38 pagesCe 8381 - Strength of Materials and Fluid Mechanics and Machinery Laboratory ManualManivannan JeevaNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics - 1661429347Document10 pagesFluid Mechanics - 1661429347hussain lunawadiNo ratings yet
- S. H. M. Engineering College, Kadakkal: (Answer Any 4 Questions. Each Carries 5 Marks)Document1 pageS. H. M. Engineering College, Kadakkal: (Answer Any 4 Questions. Each Carries 5 Marks)Vijeesh VijayalayamNo ratings yet
- Department of Mechanical Engineering: Laboratory ManualDocument66 pagesDepartment of Mechanical Engineering: Laboratory ManualKrishna SinghNo ratings yet
- 07a3ec02 Fluid Mechanics and Hydraulic MachineryDocument8 pages07a3ec02 Fluid Mechanics and Hydraulic MachineryandhracollegesNo ratings yet
- Numerical Simulation of Aerodynamic Performances of Wet Compression Compressor CascadeDocument9 pagesNumerical Simulation of Aerodynamic Performances of Wet Compression Compressor CascadeDeepakNarayananNo ratings yet
- Rr410801 Transport PhenomenaDocument8 pagesRr410801 Transport PhenomenaSrinivasa Rao GNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Fluids RR 212101Document8 pagesMechanics of Fluids RR 212101Nizam Institute of Engineering and Technology LibraryNo ratings yet
- Spe 99Document2 pagesSpe 99tomk2220No ratings yet
- ACFrOgAhFbiyYPelIiyOI-D3Vp6Bk5hqs0vz3B2JavNSJCsN1H5bx5P2mcatw 8ojy xDeWw6uLXzl H0wgry9Z3MQc-NFw4WQ6o5rKERm Nh6hgcOysonQWrCj2OZt hmfLO4lMBM0uUiMRFxd6Document10 pagesACFrOgAhFbiyYPelIiyOI-D3Vp6Bk5hqs0vz3B2JavNSJCsN1H5bx5P2mcatw 8ojy xDeWw6uLXzl H0wgry9Z3MQc-NFw4WQ6o5rKERm Nh6hgcOysonQWrCj2OZt hmfLO4lMBM0uUiMRFxd6Natália SantosNo ratings yet
- Sheet 4Document3 pagesSheet 4الطيب كمالNo ratings yet
- r5220303 Mechanics of Fluids r5 2-2Document4 pagesr5220303 Mechanics of Fluids r5 2-2sivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- ENGR 2343 - Fluid Mechanics Chapter 7: Dimensional Analysis & Modeling Homework #8 - Due 10/22/14 at Beginning of ClassDocument10 pagesENGR 2343 - Fluid Mechanics Chapter 7: Dimensional Analysis & Modeling Homework #8 - Due 10/22/14 at Beginning of ClassKarthik_BondaNo ratings yet
- Yaqub 2018 IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 458 012078Document10 pagesYaqub 2018 IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 458 012078Daniel MoraesNo ratings yet
- ME2109 Fluid May2012Document7 pagesME2109 Fluid May2012Hafsa KhanNo ratings yet
- International Institute of Management & Technical Studies: Subject Name: Fluid Mechanics - II (GPME2002)Document3 pagesInternational Institute of Management & Technical Studies: Subject Name: Fluid Mechanics - II (GPME2002)hussain lunawadiNo ratings yet
- Ce 411 MeDocument1 pageCe 411 MeJames Llamera ArgenteNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics - Unit 6 - Week 5 - APPLICATIONS OF FLUID STATICS AND DYNAMICSDocument4 pagesFluid Mechanics - Unit 6 - Week 5 - APPLICATIONS OF FLUID STATICS AND DYNAMICShemaruthrra.rNo ratings yet
- Revision FluidDocument4 pagesRevision FluidPrince VinceNo ratings yet
- FLM360S Tut 1Document3 pagesFLM360S Tut 1bluenode02No ratings yet
- Civil Engg Q Papers 2019Document12 pagesCivil Engg Q Papers 2019Surjit Kumar GandhiNo ratings yet
- Study of Numerical Simulation Applying To The Design of An Orifice With High-Velocity WaterjetDocument10 pagesStudy of Numerical Simulation Applying To The Design of An Orifice With High-Velocity WaterjetYu HuiNo ratings yet
- Exam. On Fluid Mechanics - No.2: Tip: You Can Refer To This ExampleDocument1 pageExam. On Fluid Mechanics - No.2: Tip: You Can Refer To This ExampleNg Lay HoonNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Sessional CE 262Document28 pagesFluid Mechanics Sessional CE 262মোঃমেহেদী হাসান শরীফNo ratings yet
- 7636fluid Mechanics and Hydralics MachinesDocument8 pages7636fluid Mechanics and Hydralics MachinesNitin GuptaNo ratings yet
- XII To XIV PDFDocument33 pagesXII To XIV PDFAmira RamleeNo ratings yet
- Syllabus MET203Document12 pagesSyllabus MET203Sudeesh SudevanNo ratings yet
- XI Physics Sample PaperDocument4 pagesXI Physics Sample Paperprem TNo ratings yet
- XI Physics Sample PaperDocument4 pagesXI Physics Sample Paperprem TNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics: Instructions To CandidatesDocument2 pagesFluid Mechanics: Instructions To CandidatesZamaan JanNo ratings yet
- Sheet 2Document2 pagesSheet 2abdoharfosh1710No ratings yet
- Candidates Are Required To Give Their Answers in Their Own Words As Far As Practicable. The Figures in The Margin Indicate Full MarksDocument2 pagesCandidates Are Required To Give Their Answers in Their Own Words As Far As Practicable. The Figures in The Margin Indicate Full MarksAdhikari SushilNo ratings yet
- Numerical Modelling of Transient Flow in Long Oil Pipe Line SystemDocument33 pagesNumerical Modelling of Transient Flow in Long Oil Pipe Line SystemlsaishankarNo ratings yet
- CVNG 1001 Orifice Lab 2015Document3 pagesCVNG 1001 Orifice Lab 2015Harrington HaynesNo ratings yet
- Mech Sylabus 19Document1 pageMech Sylabus 19Nishikant KulkarniNo ratings yet
- L4C1 Examiner Report March 2022Document7 pagesL4C1 Examiner Report March 2022Nadaa28No ratings yet
- Reservoir Engineering in Modern Oilfields: Vertical, Deviated, Horizontal and Multilateral Well SystemsFrom EverandReservoir Engineering in Modern Oilfields: Vertical, Deviated, Horizontal and Multilateral Well SystemsNo ratings yet
- Mac ShiftDocument2 pagesMac ShiftanoopsreNo ratings yet
- Organization and Management Module 2: Quarter 1 - Week 2Document15 pagesOrganization and Management Module 2: Quarter 1 - Week 2juvelyn luegoNo ratings yet
- Homemade RicottaDocument3 pagesHomemade RicottaJules PaulkNo ratings yet
- Inspection ChecklistDocument2 pagesInspection ChecklistBerp OnrubiaNo ratings yet
- Finman MidtermDocument4 pagesFinman Midtermmarc rodriguezNo ratings yet
- Pega 7 - Pega PRPC Basic Concepts V 0.1Document13 pagesPega 7 - Pega PRPC Basic Concepts V 0.1Vijay Kori100% (1)
- Economics Grade 9 & 10 (Quiz 2)Document2 pagesEconomics Grade 9 & 10 (Quiz 2)Nofel AmeenNo ratings yet
- Pindex System InstructionsDocument6 pagesPindex System InstructionsJASPREETKAUR0410No ratings yet
- (Toni) TX MS W Chinese Scalp AcupDocument16 pages(Toni) TX MS W Chinese Scalp AcupAngelaNo ratings yet
- Barney Smca6 Tif 05Document31 pagesBarney Smca6 Tif 05p astelNo ratings yet
- HSE Plan For RoadsDocument75 pagesHSE Plan For RoadsEtienne NWNo ratings yet
- COA RulesDocument22 pagesCOA RulesNoraiza Mae Keith TalbinNo ratings yet
- State Transition Diagram To PLC Ladder Logic Translation WhitepaperDocument15 pagesState Transition Diagram To PLC Ladder Logic Translation WhitepapermhrahbNo ratings yet
- Blue Chips Bags 4 Gold, 15 Silver, 1 Bronze Medals in ArcheryDocument1 pageBlue Chips Bags 4 Gold, 15 Silver, 1 Bronze Medals in ArcheryRodel Novesteras ClausNo ratings yet
- Serv1862 TXTDocument40 pagesServ1862 TXTlalo11715100% (1)
- Concept BoardDocument5 pagesConcept BoardMelvin AlarillaNo ratings yet
- Module 4 Environmental Protection and Mngt. Isu AngadananDocument9 pagesModule 4 Environmental Protection and Mngt. Isu AngadananWild RiftNo ratings yet
- IMCI PX John Booysen and Shannon MilehamDocument6 pagesIMCI PX John Booysen and Shannon Mileham1330658No ratings yet
- CHAPTER 4 (Review Questions) : Direction: Read Each Question Carefully. Encircle The Letter of The Correct AnswerDocument11 pagesCHAPTER 4 (Review Questions) : Direction: Read Each Question Carefully. Encircle The Letter of The Correct AnswerChery PerialdeNo ratings yet
- 1000 Puzzle Series Set - 1 To 25 Merged PDFDocument417 pages1000 Puzzle Series Set - 1 To 25 Merged PDFSangam ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Exercises About Reported Speech (Questions)Document6 pagesExercises About Reported Speech (Questions)Len Đinh ThịNo ratings yet
- MICE Brochure For U.S.A. by Cox and KingsDocument19 pagesMICE Brochure For U.S.A. by Cox and KingsCox and Kings IndiaNo ratings yet
- Adce Parameter of 2gDocument4 pagesAdce Parameter of 2gAmit DevNo ratings yet
- Congress Program - Updated 09.05.2018Document4 pagesCongress Program - Updated 09.05.2018Booker DewittNo ratings yet
- Anh 12-WORD FORM & WORD ORDER-HSDocument6 pagesAnh 12-WORD FORM & WORD ORDER-HSTuan Anh Nguyen100% (1)
- 521 Lesson 2Document4 pages521 Lesson 2api-322060627No ratings yet
- Counter AffidavitDocument6 pagesCounter Affidavitkong pagulayanNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual FEB 9Document67 pagesLab Manual FEB 9kingraajaNo ratings yet