Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Group 3 - Case Presentation 3
Group 3 - Case Presentation 3
Uploaded by
MICHAEL GABRIEL JIMENEZ0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views37 pagesOriginal Title
GROUP-3_CASE-PRESENTATION-3
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views37 pagesGroup 3 - Case Presentation 3
Group 3 - Case Presentation 3
Uploaded by
MICHAEL GABRIEL JIMENEZCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 37
f contraception
methods oNCMA 217 RLE
presented by: group 3
GROUP MEMBERS
CALDERON, KRISTINE CAYE
LALOGO, DONNA
CALAMBA ROSELITO
MALLORCA, KENNETH
CASTRO, SHANNON MAURICE
MOISES, CHARLENE JOY
GONZALES, MIKAELA ANGELA
RAMOS, FRANCINE
JIMENEZ, MICHAEL GABRIEL
CASE SCENARIO
Eve, 27 years old, and Lamar, 33 years, are a young
couple who have just gotten married. They both are heavy
smokers. Eve had a miscarriage before marriage when they
were using a cervical mucus method of natural planning.
It’s important to her now not to become pregnant again for
2 years so she can finish a master’s degree in psychology.
Lamar wants a contraceptive that when discontinued will
allow fertility to return immediately. He also wants a
contraceptive that will prevent sexually transmitted
diseases.
What
contraceptive
would you
recommend as
best for Eve?
The most appropriate
contraceptive that
will be the best for
Eve is a
contraceptive
implant.
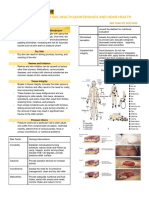
What is a Contraceptive Implant?
It is for long-term birth control. It is a
flexible plastic rod and it has a size like a
matchstick.
It is placed under the skin of a woman in the
upper arm.
Implants release a low, steady dose of
progestational hormone for it to thicken the
cervical mucus and to thin the lining of the
uterus of a woman.
It suppresses ovulation.
Effectiveness of Contraceptive Implant:
It is more than 99% effective and can last up to three
years.
Why it’s fits eve’s special request:
The implanted tube slowly releases low levels of hormone
progestin to prevent ovulation. Without ovulation, pregnancy
can’t happen because there is no egg for sperm to
fertilize.
Also Eve doesn’t want to be pregnant for two years to
focus on her studies. They also want to stop the
fertilization immediately and this implant can last for three
years. Also if they want to remove it, you can have
fertility immediately in one month.
Advantages and Disadvantages of contraceptive
implants:
Advantages
Very inexpensive method of long-term
contraception, comparable to intrauterine devices.
Contraceptive implants don’t interrupt sex
Contraceptive implants may reduce heavy periods or
period pain.
Users can easily remove contraceptive implants to
allow pregnancy to occur naturally.
Quick return of fertility within 21 days of implant
removal.
Advantages and Disadvantages of contraceptive
implants:
Disadvantages
Contraceptive implants don’t protect you against
sexually transmitted diseases (STDs)
Contraceptive implants make periods be irregular or stop
altogether.
Contraceptive implants need a minor procedure to have
it fitted and removed.
You may experience temporary side effects during the
first few months, like headaches, nausea, breast
tenderness and mood swings.
Lamar has special
requests. What
contraceptive
would best meet
his needs?
The most appropriate
contraceptive that
will likely meet
Lamar’s special
request is a male
condom.
What is a Male Condom?
It is a sheath rolled over the penis, acting
as a physical barrier, that prevents semen
from entering the vagina during coitus.
Its material could be made of latex,
polyurethane or lambskin.
It’s a one time use contraceptive that must
be disposed of after each use.
Effectiveness of Male Condom:
With typical use, a condom is 82%
effective at preventing pregnancy.
With perfect use, a condom is 98%
effective at preventing pregnancy.
Why it Fits Lamar’s Special Request
Fertility Return Concern:
The presence of latex or non-latex materials in male condoms will
not harm the chances of having babies later on.
Condoms solely act as physical blocks between the sperm and the
female reproductive system.
One’s innate fertility can be immediately restored by stopping
their usage.
Preventing STDs:
By using a condom, which essentially creates a barrier preventing
exchange of bodily fluids, many common sexually transmitted
diseases such as HIV can be avoided.
Condoms are only highly effective in preventing STDs when used
consistently and correctly by couples
Advantages and Disadvantages of Male Condoms:
Advantages:
Male condoms are easy to use, inexpensive, and
widely accessible.
Male condoms are purchasable without a
prescription
Male condoms do not alter the fertility of the
person using them
Male condoms do not cause any medical side
effects, unless you are allergic to latex
When used correctly and consistently, they are a
reliable method of preventing pregnancy and
protecting both partners from STDs
Advantages and Disadvantages of Male Condoms:
Disadvantages:
Individuals with latex allergies may not be able to use
regular condoms
There is reduced sensitivity during intercourse
Excessive friction during coitus may cause condom to tear
There is a need for male partners to pull out before penis
becomes flaccid
It places more responsibility on the male partner
Is it safe to use a
contraceptive method for as
long as 2 years? What if Eve
has another miscarriage,
making her over 30 years by
the time she’s pregnant for
the third time?
As long as the individual using the
contraceptive method is generally healthy, it
is safe to use it for an extended period of
time. There are a number of contraceptive
methods that are suggested for long-term
usage, including:
Contraceptive implants that last up to 3 years and intrauterine conceptions
e.g., intrauterine devices (IUD) that last for 3 to 5 years and intrauterine
system (IUS) that last for 5 to 10 years. The contraceptive implants and
intrauterine conceptions are 99% effective as a contraceptive method and
can be fitted immediately after a miscarriage or an abortion and the woman
would be protected against pregnancy straight away. It can also be removed
at any time, which makes it a top pick for people who know they may want
to get pregnant in the future. The bleeding pattern and fertility of the
woman can return immediately after the removal, so there is no waiting
period for trying to conceive after removal. Additionally, the ideal
contraceptive option to avoid sexually transmitted diseases is condom rubber,
which is quick to dispose of and simple to use. This is also useful for
preventing Eve from becoming pregnant while she is still studying. Also,
some contraceptives have an expiration date or may break over time, so it's
best to consult a doctor before switching because the majority of people can
safely utilize long-term birth control methods.
If Eve had another miscarriage, she can use all methods of
contraceptives without restrictions after the recurrent
miscarriage, and the doctor should choose what's the most
effective method of contraceptive for her. However, diaphragms
and caps should not be inserted in her before 6 weeks following
a second-trimester miscarriage to allow for total cervix
involution.
If Eve has another miscarriage and making her over 30 years by the
time, she’s pregnant for the third time is that she can still have a
safe, healthy pregnancy, according to Ellie Ragsdale, MD, the UH
Cleveland Medical Center's head of fetal intervention. However, they
do have a higher chance of some issues, such as difficulty
conceiving, because as women become older, their fertility declines
and it may take them longer to fall pregnant. Additionally, there
might be difficulties with birth, and they are more likely than
younger women to require a cesarean surgery. However, as Eve is
identified as a heavy smoker, there is a higher possibility of a
number of issues, such as miscarriage and early delivery. Last but
not least, I would advise the pair to have a medical checkup to
determine their health state and growth.
nursing care plan
ASSESSMENT
Subjective Data:
The patient verbalized that she had miscarriage before
and doesn’t want to get pregnant again for 2 years.
She also added that her husband wants a contraceptive
that when discontinued will allow fertility to return
immediately and will prevent sexually transmitted
diseases.
Both patients are heavy smokers.
DIAGNOSIS
Readiness for enhanced knowledge as
evidenced by enhanced interest /
involvement in meeting one's own health
needs.
PLANNING
Short-term:
After 1-2 hours of performing health education
and nursing interventions, the patient will be able
to:
Perform actions about individual needs.
Identify health needs and goals.
Identify quality informational resources to enhance
knowledge and support decision making.
PLANNING
Long-term:
Within 1 day of performing health education and
nursing interventions, the patient will be able to :
Verbalize understanding of health information that
they learn during health teaching and nursing
intervention.
Engage in preventive health practices.
Attain desired outcomes.
INTERVENTION
INTERVENTION RATIONALE
This provides an opportunity
Verify the client’s level of to ensure accuracy and
knowledge about a specific
topic. completeness of knowledge
base for future learning.
This provides insights useful
Determine motivation and
expectations for learning. in developing goals and
identifying information needs.
INTERVENTION RATIONALE
This helps to frame or focus
Assist the client to identify content to be learned and
learning goals and measurable
outcomes. provides a measure to
evaluate the learning process.
Identify and provide
information in varied formats
appropriate to the client's Use of multiple formats
learning style (e.g., increases learning and
audiotapes, print materials, retention of material.
videos, classes or seminars,
internet).
INTERVENTION RATIONALE
This encourages an independent
search for learning
Discuss ways to verify the opportunities while reducing
accuracy of informational the likelihood of acting on
resources. erroneous or unproven data
that could be detrimental to
the client’s well-being.
Observe and note existing Assessment provides an
misconceptions regarding important starting point in
material to be taught. education. Knowledge serves to
correct faulty ideas.
INTERVENTION RATIONALE
Questions facilitate open
communication between patient
Encourage questions and health care professionals
and allow verification of
understanding of given
information.
EVALUATION
Short-term:
After 1-2 hours of performing health education and
nursing interventions, the patient was able to:
Perform actions about individual needs.
Identify health needs and goals.
Identify quality informational resources to enhance
knowledge and support decision making.
EVALUATION
Long-term:
After 1 day of performing health education and nursing
interventions the patient was able to:
Verbalize understanding of health information that they
learn during health teaching and nursing intervention.
Engage in preventive health practices.
Attain desired outcomes
GOAL COMPLETELY MET
THANK YOU FOR
LISTENING!
references
ontraceptive
C implant - Mayo Clinic. (2021). Mayoclinic.org;
https://www.mayoclinic.org/tests-procedures/contraceptive-implant/about/pac-20393619
EL, G. (2022). The female condom: STD protection in the hands of women. The American
Journal of Gynecologic Health, 7(4).
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12288250/#:~:text=PIP%3A%20In%201993%2C%20the%20U
S,vagina%2C%20cervix%2C%20and%20vulva
ale
M Condom. (2019). Alberta.ca. https://myhealth.alberta.ca/HealthTopics/sexual-
reproductive-health/Pages/male-condom.aspx
ews-Medical. (2017, May 5). Condoms - Advantages and Disadvantages. News-Medical.net.
N
https://www.news-medical.net/health/Condoms-Advantages-and-Disadvantages.aspx
HS
N Choices. (2022). Condoms - Your contraception guide.
https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/contraception/male-condoms/
HS
N Choices. (2022). Contraceptive implant - Your contraception guide.
https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/contraception/contraceptive-
implant/#:~:text=The%20implant%20is%20more%20than,the%20same%20time%20every%20d
ay
references
NHS Choices. (2022). Intrauterine device (IUD) - Your contraception guide.
https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/contraception/iud-coil/?
fbclid=IwAR1Zkct_MPl6bFQF3eTYaqQ17xyBwAjcNKyXUkOwszr5Y10l2GkFYE1qVaQ#:~:text=When%
20inserted%20correctly%2C%20IUDs%20are,as%20you’re%20not%20pregnant
HS Choices. (2022). Intrauterine system (IUS) - Your contraception guide.
N
https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/contraception/ius-intrauterine-system/?
fbclid=IwAR0JZK8TtGpe03uqBuXd_agp_9S5Th60Qw6g34Bh2hvs79FM13_eM3Yla08#:~:text=An%2
0IUS%20is%20a%20small,years%2C%20depending%20on%20the%20brand
Planned Parenthood. (2022). Plannedparenthood.org.
https://www.plannedparenthood.org/learn/birth-control/birth-control-vaginal-ring-
nuvaring/how-do-i-use-nuvaring
T eam DN. (2021, January 28). Contraceptive Implant (Implanon) - SHINE SA. SHINE SA.
https://shinesa.org.au/health-information/contraception/contraceptive-implant-implanon/?
fbclid=IwAR2X00rnuoOIwKPR5yd3HVZo2nwGNETj4KBuocbUY5gjtc8vFMxiT0QNgYc
T horpe, J. (2016, March 31). 5 Things That Happen To Your Body When You Use Condoms.
Bustle; Bustle. https://www.bustle.com/articles/148539-5-things-that-happen-to-your-body-
when-you-use-condoms
references
UHBlog. (2021, July 20). Thinking About Pregnancy After Age 30? 3 Issues to Consider.
Uhhospitals.org; University Hospitals. https://www.uhhospitals.org/Healthy-at-
UH/articles/2021/07/thinking-about-pregnancy-after-age-30-3-issues-to-consider?
fbclid=IwAR3jARdw2H9JqXQN5jT3Go-_tBPaIC5dMaG9qZPL5-
TqOaJRoFT9p7YFqV4#:~:text=Women%20who%20become%20pregnant%20in,higher%20risk%20o
f%20some%20problems
What Kinds of Birth Control Work Best Against Pregnancy and STDs? - Connecticut
Children’s. (2020). Connecticut Children’s. https://www.connecticutchildrens.org/health-
library/en/teens/bc-
stds/#:~:text=Condoms%20are%20the%20only%20type,IUD%2C%20or%20birth%20control%20s
hot
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5824)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (903)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (541)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (823)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (403)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- NCMB314 - Week 4Document4 pagesNCMB314 - Week 4MICHAEL GABRIEL JIMENEZNo ratings yet
- Week 10 MS Responses To Altered Perception Neurological Dysfunctions IntroductionDocument8 pagesWeek 10 MS Responses To Altered Perception Neurological Dysfunctions IntroductionMICHAEL GABRIEL JIMENEZNo ratings yet
- NCMB 312 Review Questions Week 14-17 Only (Finals)Document12 pagesNCMB 312 Review Questions Week 14-17 Only (Finals)MICHAEL GABRIEL JIMENEZNo ratings yet
- NamalignoDocument2 pagesNamalignoMICHAEL GABRIEL JIMENEZNo ratings yet
- TCWD111 - Week 7Document2 pagesTCWD111 - Week 7MICHAEL GABRIEL JIMENEZNo ratings yet
- Movie ReviewDocument3 pagesMovie ReviewMICHAEL GABRIEL JIMENEZNo ratings yet
- HW1 PharmacologyDocument3 pagesHW1 PharmacologyMICHAEL GABRIEL JIMENEZNo ratings yet
- HW#4 PaharmacologyDocument5 pagesHW#4 PaharmacologyMICHAEL GABRIEL JIMENEZNo ratings yet
- HW3 PharmacologyDocument8 pagesHW3 PharmacologyMICHAEL GABRIEL JIMENEZNo ratings yet
- HW2 PharmacologyDocument6 pagesHW2 PharmacologyMICHAEL GABRIEL JIMENEZNo ratings yet