Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Biology G9 Q1 W8 D4
Biology G9 Q1 W8 D4
Uploaded by
MARIANNE OPADAOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Biology G9 Q1 W8 D4
Biology G9 Q1 W8 D4
Uploaded by
MARIANNE OPADACopyright:
Available Formats
Grade: 9 Subject: Science-Biology
Quarter/ 1st Quarter Week 8 Day: 4
Semester: No:
I. OBECTIVES
Content Standard The students demonstrate an understanding of the structure
and function of plant parts and organelles involved in
photosynthesis
Performance Standard The learners should be able to design and conduct an
investigation to provide evidence that plants can manufacture
their own food
Learning Competency Differentiate basic features and importance of photosynthesis
and respiration. (S9LT-lg-j31)
Knowledge Identify the major steps that occur during Calvin cycle
Skills Write the molecules used and produced during the different
phases of Calvin cycle
Attitude Cite other importance of photosynthesis aside from food and
oxygen production
II. CONTENT PHOTOSYNTHESIS – CALVIN CYCLE
III. LEARNING
RESOURCES
References Science 9-Learners Manual pp:72-85
Other Learning https://www.biologydiscussion.com/photosynthesis/raw-
Resources materials-used-in-photosynthesis-with-diagram/52269
IV. PROCEDURES
A. Preparatory ACTIVIT 1: ENCIRCLE
Activity
Let the students copy the photosynthesis equation in their
notebooks or any piece of paper:
Based on the previous lesson on light-dependent reaction, let
them encircle the raw materials and products produced during
the light-dependent reaction.
B. Motivation Q1. Which molecules have you not encircled in the equation?
- CO2 and Sugar(Glucose)
Q2.Why?
- These molecules are not used/produced during the
light-dependent reaction.
Prepared by: LYN-NO A. REGALADO(T-I)
FROILAN A. ALANANO MHS
Q3. Since they are not used in the light-dependent reaction, in
which step of photosynthesis will these molecules be
used/produced?
- During the Calvin cycle or light-independent reaction.
C. Activity ACTVITY 2: STARCH IN PLANTS
Refer to Attachment A for the materials and steps of this
activity.
D. Analysis Q1. After dropping some iodine into the samples, what color
appeared?
- Bluish/dark blue coloration
Q2. What does a dark-blue or black color indicate?
- The dark color indicates presence of starch.
Now we knew that starch is produced in plants, let us discuss
how starch is made during the light-independent reaction
E. Abstraction Option 1: If you have an internet connection in your school or a
capacity to have a video presentation in the class, you can use
this video.
Video link: https://www.youtube.com/watch?
v=l12GClqoI10&list=PLI1XjFOSo4gPnFD37G9R-
fiQMtBiLXs8m&index=6
Option 2: If you don’t have internet connection in your room
and do not have an audio-video equipment available, refer to
Attachment B for the pictures of the process.
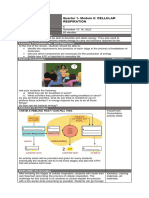
The Calvin cycle happens in the stroma of the chloroplast. It is
also known as the light-independent reaction/dark reaction
since light is not needed in this step of photosynthesis.
However, the products from the light-dependent reaction,
namely NADPH and ATP, are used in this process.
The Calvin cycle has three stages/phases: 1)Fixation,
2)Reduction, 3)Regeneration
THE EVENTS IN CALVIN CYCLE
Phase 1: Fixation
- Three(3) molecules of carbon dioxide(CO2)
combines with three(3) molecules of RuBP to form
six(6) molecules of 3-PGA. The combining of carbon
Prepared by: LYN-NO A. REGALADO(T-I)
FROILAN A. ALANANO MHS
dioxide and RuBP is carried out by the enzyme
Rubisco.
Phase 2: Reduction
- The six(6) molecules of 3-PGA uses the energy from
six(6) molecules of ATP and six(6) molecules of
NADPH to form six(6) molecules of G3P. One out of
the six molecules of G3P will exit the Calvin Cycle and
will be used to make other compounds such as glucose
or starch (these are the sugars). The other five(5)
molecules of G3P will continue the cycle.
Phase 3: Regeneration:
- The remaining five molecules of G3P will undergo
some series of reactions to regenerate three (3)
molecules of RuBP which is again used in Phase 1 of
the Calvin cycle. For this to happen, three (3)
molecules of ATP will again be used.
F. Application We have encountered the three phases of the Calvin Cycle.
Now let us trace again the cycle by doing this activity.
(This can be done by group, by pair or individually).
ACTIVITY 3: FILL IN THE MOLECULE
Please refer to attachment C for this activity
G. Practical Q1. Photosynthesis allows plants to make their own food. We,
Applications of animals, are also benefited by this process since we eat plants
Concepts and and photosynthesis produce oxygen. Aside from these things,
Skills in Daily what other benefit is photosynthesis giving us and our planet?
Living - Photosynthesis uses carbon dioxide. This process
absorbs the carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. If there
will be more plants/trees, more carbon dioxide can be
absorbed.
H. Generalization The Calvin cycle or light-independent reaction is the second
and last step of photosynthesis. This is the step where sugar is
produced. It has three phases: Fixation, reduction, and
regeneration.
I. Evaluation Please see Attachment D for the evaluation
J. Additional activities
for application or
remediation
(assignment)
V. REMARKS
Prepared by: LYN-NO A. REGALADO(T-I)
FROILAN A. ALANANO MHS
VI. REFLECTION
No. of learners who
earned 80% in the
evaluation
No. of learners who
continue to require
remediation
Did the remedial
lesson work? No. of
learners who caught
up the lesson
No. of learners who
require remediation
Which of my teaching
strategies worked
well? Why did these
work?
What difficulties did I
encounter which
principal and
supervisor can help or
solve?
What innovation or
localized did I
use/discover which I
wish to share?
Prepared by: LYN-NO A. REGALADO(T-I)
FROILAN A. ALANANO MHS
ATTACHMENT A
(Attachment for Activity 2: STARCH IN PLANTS)
Objective: To see the presence of starch in plants.
Materials: Iodine solution, small amount of rice (or corn grits), banana or any root crop, petri dish or
saucer (if petri dish is not available), dropper.
Steps:
1. Prepare three petri dishes.
2. One petri dish will be placed with rice/corn grits; the other will be with banana; and the last
one will be with root crop.
3. Put a few drops of iodine solution to each sample.
4. Wait for about two-three minutes.
5. Record your observations. If the sample turned dark or bluish in color, it indicates the
presence of starch in the sample.
ATTACHMENT B
Attachment for Abstraction)
Prepared by: LYN-NO A. REGALADO(T-I)
FROILAN A. ALANANO MHS
Prepared by: LYN-NO A. REGALADO(T-I)
FROILAN A. ALANANO MHS
ATTACHMENT C
(Attachment for Application)
ACTIVITY 3: FILL IN THE MOLECULES
Directions: Fill in the blanks with the molecules and the number of molecules required or produced
during the different phases of the Calvin Cycle.
Phase 1: Fixation
Example : 3 molecules of CO2 + 3 molecules of RuBP 6 molecules of 3-PGA
Phase 2: Reduction
6 molecules of 3-PGA + __ molecules of NADPH + 6 molecules of _____ ____ molecules of G3P
Phase 3: Regeneration
___ molecules of G3P + ___ molecules of ATP __ molecules of _______
Answers:
Phase 1: Fixation
3 molecules of CO2 + 3 molecules of RuBP 6 molecules of 3-PGA
Phase 2: Reduction
6 molecules of 3-PGA + 6 molecules of NADPH + 6 molecules of ATP 6 molecules of G3P
Phase 3: Regeneration
5 molecules of G3P + 3 molecules of ATP 3 molecules of RuBP
Prepared by: LYN-NO A. REGALADO(T-I)
FROILAN A. ALANANO MHS
ATTACHMENT D
(Attachment for Evaluation)
Directions: Match Column A and Column B. Write the letter of your answer before the
number.
Column A Column B
___1. The phase of Calvin cycle where NADPH a.Rubisco
is used.
___2. The phase of Calvin cycle where CO2 is b. Regeneration
used
___3. In this phase of Calvin cycle, RuBP is c. 1
produced again
___4. The enzyme that combines RuBP and d. 5
carbon dioxide
___5. Number of G3P molecule that exits the e. Fixation
cycle to form larger sugar molecules
___6. Number of G3P molecule used to f. 3-PGA
reproduce RuBP
___7. Number of ATP molecules used in the g.
regeneration phase
___8. Produced after RuBP and CO2 combines h. Reduction
i.3
Answers.
1. H
2. E
3. B
4. A
5. C
6. D
7. I
8. F
Prepared by: LYN-NO A. REGALADO(T-I)
FROILAN A. ALANANO MHS
You might also like
- Photosynthesis NotesDocument10 pagesPhotosynthesis Notesapi-544344393100% (2)
- Daily Lesson PlanDocument7 pagesDaily Lesson PlanErmieGraceEllorando80% (5)
- SHS STEM Bio1 Q2 Week 2 Module 3 - Patterns of Electron FlowDocument17 pagesSHS STEM Bio1 Q2 Week 2 Module 3 - Patterns of Electron FlowRomel Bayaban80% (5)
- Quarter 2 - W E E K 2 - : GradeDocument9 pagesQuarter 2 - W E E K 2 - : GradeShennieNo ratings yet
- GB1 Q2 Week-3Document7 pagesGB1 Q2 Week-3Ian JamesNo ratings yet
- Module 11 Calvin CycleDocument14 pagesModule 11 Calvin CycleCandice LopezNo ratings yet
- Bio 12 AModule 7Document7 pagesBio 12 AModule 7Ivan RamirezNo ratings yet
- Specific Objectives: Marjoriechiong001@deped - Gov.phDocument7 pagesSpecific Objectives: Marjoriechiong001@deped - Gov.phAnnejhel Mae PoralanNo ratings yet
- Light Independent PhotosynthesisDocument13 pagesLight Independent PhotosynthesismaddoxNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1: Quarter 2 - Module 3: When Cells BreatheDocument26 pagesGeneral Biology 1: Quarter 2 - Module 3: When Cells BreathePLS help me get 1k subsNo ratings yet
- 15 Quarter 1 Module 15-light-INDEPENDENT-reactionsDocument19 pages15 Quarter 1 Module 15-light-INDEPENDENT-reactionsMah Jane Divina0% (1)
- Self-Instructional ModuleDocument19 pagesSelf-Instructional ModuleMarlon S. BarangganNo ratings yet
- Biology 1 - 12 - Q2 - M11PSPCDocument16 pagesBiology 1 - 12 - Q2 - M11PSPCHera VictrixNo ratings yet
- Biology - Module 5Document11 pagesBiology - Module 5ASHLEY MONICA PLATANo ratings yet
- Biology 1 12 Q2 M10Document17 pagesBiology 1 12 Q2 M10Jimboy AmadNo ratings yet
- GENERAL BIOLOGY Q2 WEEK 3 Calvin CycleDocument11 pagesGENERAL BIOLOGY Q2 WEEK 3 Calvin CycleAryan Jovic DomingoNo ratings yet
- Q2 STEM General Biology 1 Week 2Document4 pagesQ2 STEM General Biology 1 Week 2MarkElijah ObelNo ratings yet
- Gen Biology 1 q2 Wk1Document33 pagesGen Biology 1 q2 Wk1kai lifurnitureNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio1 Module 9Document23 pagesGen Bio1 Module 9Anjhiene Camba100% (2)
- A GENERAL BIOLOGY I 12 Q2M4 Teacher Copy Final LayoutDocument18 pagesA GENERAL BIOLOGY I 12 Q2M4 Teacher Copy Final LayoutmariaNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE-9 Q1 W6-W7 Mod5 ADM-1-photosythesisDocument42 pagesSCIENCE-9 Q1 W6-W7 Mod5 ADM-1-photosythesisJB Dar100% (1)
- Earth and Life Science SHS 16.2 PhotosynthesisDocument15 pagesEarth and Life Science SHS 16.2 PhotosynthesisPamela MalihanNo ratings yet
- Lesson Guide in Earth and Life Science I. Objectives: The Learners Demonstrate An Understanding ofDocument4 pagesLesson Guide in Earth and Life Science I. Objectives: The Learners Demonstrate An Understanding ofJT SaguinNo ratings yet
- Q2W2 General Biology ModuleDocument10 pagesQ2W2 General Biology ModuleBatman Of monstadtNo ratings yet
- Activity 10 Answer KeyDocument8 pagesActivity 10 Answer KeyRyan LeeNo ratings yet
- General Biology - Q2 - Week 5Document14 pagesGeneral Biology - Q2 - Week 5Renard JaenNo ratings yet
- The Photosynthesis Equation 6CO + 6H O - C H O + 6ODocument4 pagesThe Photosynthesis Equation 6CO + 6H O - C H O + 6OMicaela SuarezNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science SHS 16.2 PhotosynthesisDocument15 pagesEarth and Life Science SHS 16.2 PhotosynthesisWinsear VardeNo ratings yet
- PDG CH 8 - PhotosynthesisDocument2 pagesPDG CH 8 - PhotosynthesisSkillzBeast -Minecraft,PUBG,and MoreNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis: A Level Biology 2016-17Document27 pagesPhotosynthesis: A Level Biology 2016-17sabaNo ratings yet
- Metabolism Is The Sum Total of All Chemical Processes Taking Place Within A Living SystemDocument5 pagesMetabolism Is The Sum Total of All Chemical Processes Taking Place Within A Living SystemFerdinand Arcangel Ebalo IiNo ratings yet
- Q2 Lesson Plan 6Document17 pagesQ2 Lesson Plan 6NOVA LESLIE AGAPAYNo ratings yet
- 7e's - Cellular RespirationDocument5 pages7e's - Cellular RespirationVea Patricia AngeloNo ratings yet
- Biology 1 - 12 - Q2 - M8Document17 pagesBiology 1 - 12 - Q2 - M8Satomi SamsonNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1 Q2 Wk3 QADocument30 pagesGeneral Biology 1 Q2 Wk3 QAEdreyan Adong Cortez LimbagaNo ratings yet
- Arcebido, GwynnDocument4 pagesArcebido, GwynnGwynnNo ratings yet
- Cellular Energy Resp PhotoDocument85 pagesCellular Energy Resp Photomuhra khaeld salim al abo aldariiNo ratings yet
- Self Assessment 2b Part 2Document2 pagesSelf Assessment 2b Part 2Darlene KrizianNo ratings yet
- Science11 q2 Mod1 Generalbiology1-Aquino, Paul Reagan P.Document17 pagesScience11 q2 Mod1 Generalbiology1-Aquino, Paul Reagan P.Lyka Mae BenitoNo ratings yet
- BIO 1-FinalDocument23 pagesBIO 1-FinalThessa Vee Capuno RioNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio1 2ND Q.module 2Document9 pagesGen Bio1 2ND Q.module 2Lara FloresNo ratings yet
- Division of Cebu Lilo-An National High School - Senior High: Department of Education (Deped)Document5 pagesDivision of Cebu Lilo-An National High School - Senior High: Department of Education (Deped)Jeston Mar BayogNo ratings yet
- GENERAL BIOLOGY 1 Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration - 084809Document18 pagesGENERAL BIOLOGY 1 Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration - 084809James KamfoliNo ratings yet
- Gen BioDocument5 pagesGen Bionmaningo338No ratings yet
- Semi-Detailed Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesSemi-Detailed Lesson Planjoselyn bergonia100% (1)
- Photosynthesis and Cellular RespirationDocument18 pagesPhotosynthesis and Cellular Respirationmaria genio100% (2)
- Lesson Plan in Biology 1 2 Quarter I. Learning ObjectivesDocument2 pagesLesson Plan in Biology 1 2 Quarter I. Learning ObjectivesLieshaNo ratings yet
- Biology CH 8 and 9Document31 pagesBiology CH 8 and 9Ann QuiranteNo ratings yet
- Second Quarterly Examination in General Biology 1 SY 2022-2023Document10 pagesSecond Quarterly Examination in General Biology 1 SY 2022-2023Ruby Uriarte100% (1)
- Biology 9 Unit 7 - PhotosynthesisDocument28 pagesBiology 9 Unit 7 - PhotosynthesisLo ViNo ratings yet
- GENBIODocument5 pagesGENBIOTyro PaulNo ratings yet
- Q2W3 General Biology ModuleDocument10 pagesQ2W3 General Biology ModuleBatman Of monstadtNo ratings yet
- GB - 1st Quarter - wk9 - PDFDocument10 pagesGB - 1st Quarter - wk9 - PDFHeaven LeighNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Learning Activity Worksheets (LAW) General Biology 1 Grade 12Document4 pagesDepartment of Education: Learning Activity Worksheets (LAW) General Biology 1 Grade 12Maria Bettina DizonNo ratings yet
- Ap Biology PhotosynthesisDocument7 pagesAp Biology PhotosynthesisMinh Triet LyNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration 2 UpdatedDocument17 pagesPhotosynthesis and Cellular Respiration 2 Updatedharold carbonelNo ratings yet
- Student Module 2 Genbio1Document5 pagesStudent Module 2 Genbio1Lezel LaracasNo ratings yet
- Hotosynthesis: Big PictureDocument3 pagesHotosynthesis: Big Picturehomamunfat100% (1)
- Sustainable synthesis of ciclopentene derivatives through multicomponent reactions in continuous flow regimeFrom EverandSustainable synthesis of ciclopentene derivatives through multicomponent reactions in continuous flow regimeNo ratings yet
- Qar Form 1 7 10Document10 pagesQar Form 1 7 10MARIANNE OPADANo ratings yet
- Science Lab FormsDocument6 pagesScience Lab FormsMARIANNE OPADANo ratings yet
- TARPAPEL ScienceDocument25 pagesTARPAPEL ScienceMARIANNE OPADANo ratings yet
- Biology G9 Q1 W8 D2Document11 pagesBiology G9 Q1 W8 D2MARIANNE OPADANo ratings yet
- Missile Technology Control Regime - HandbookDocument267 pagesMissile Technology Control Regime - HandbookHector VillarrealNo ratings yet
- Best Rosin Press of 2020 PDFDocument4 pagesBest Rosin Press of 2020 PDFdannie gaoNo ratings yet
- Ford Focus Mk3 SpecifikacijeDocument14 pagesFord Focus Mk3 Specifikacijemisterno27No ratings yet
- Mother Tongue DLPDocument10 pagesMother Tongue DLPmaricrispigangNo ratings yet
- BHIR121 102 Bussiness Comm Assignment 1Document7 pagesBHIR121 102 Bussiness Comm Assignment 1nncptp7nsbNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Urban Heat Island IntensityDocument14 pagesAnalysis of Urban Heat Island IntensityItishree RanaNo ratings yet
- Science 5Document6 pagesScience 5Edlyn KayNo ratings yet
- TM Meeting Roles HBDDocument4 pagesTM Meeting Roles HBDHB DayaratneNo ratings yet
- Planning and Organizing The Housekeeping PDFDocument16 pagesPlanning and Organizing The Housekeeping PDFclaudiaweiNo ratings yet
- 2013 Rotary Index Drives Manual1Document16 pages2013 Rotary Index Drives Manual1Manoj TiwariNo ratings yet
- Consumer Behavior and Pricing Strategy: Mcgraw-Hill/IrwinDocument32 pagesConsumer Behavior and Pricing Strategy: Mcgraw-Hill/IrwinNg. Minh ThảoNo ratings yet
- Legacy of Wisdom Academy Dasmariñas Inc. Golden City, Salawag, Dasmariñas CityDocument3 pagesLegacy of Wisdom Academy Dasmariñas Inc. Golden City, Salawag, Dasmariñas Citynancy cruzNo ratings yet
- Spanning Space, Horizontal-Span Building Structures, Wolfgang SchuellerDocument752 pagesSpanning Space, Horizontal-Span Building Structures, Wolfgang Schuellerwolfschueller91% (11)
- Project 4Document6 pagesProject 4Trai TranNo ratings yet
- Assignment - 02 - 8609Document10 pagesAssignment - 02 - 8609Tariq NaseerNo ratings yet
- Dan-Fuel Rod Heat ConductionDocument7 pagesDan-Fuel Rod Heat ConductionMahmoud EidNo ratings yet
- Zentraldoku-Jade - FV Am GGW-EDocument165 pagesZentraldoku-Jade - FV Am GGW-Emahmoud alraoushNo ratings yet
- KB00194 - DCOM Settings For The OPC Interface That Cause The Following Errors - Advise Returns Error 8004020 - or PIPCDocument1 pageKB00194 - DCOM Settings For The OPC Interface That Cause The Following Errors - Advise Returns Error 8004020 - or PIPCJunior PassosNo ratings yet
- Phoenix Contact PT 2-PES-230AC-STDocument6 pagesPhoenix Contact PT 2-PES-230AC-STblitz301No ratings yet
- EchoAndReverberation PDFDocument19 pagesEchoAndReverberation PDFSlavita JarcovNo ratings yet
- How To Draw and Read Line Diagrams Onboard Ships?: ShareDocument9 pagesHow To Draw and Read Line Diagrams Onboard Ships?: ShareShaif uddin rifatNo ratings yet
- Language Revival and RevitalizationDocument2 pagesLanguage Revival and RevitalizationEstrella Janirol Humoc PiccioNo ratings yet
- Devlibrary - in-NIOS Class 12 Sociology Chapter 39 Impact of Media and CultureDocument6 pagesDevlibrary - in-NIOS Class 12 Sociology Chapter 39 Impact of Media and CultureAnushkaNo ratings yet
- Crowding Risk in Smart Beta StrategiesDocument32 pagesCrowding Risk in Smart Beta StrategiesRogerio Monaco SimõesNo ratings yet
- S5-1-2 - Typical Steel Beam DetailsDocument1 pageS5-1-2 - Typical Steel Beam DetailsTony PedaNo ratings yet
- Lady Macbeth - Infirm of PurposeDocument7 pagesLady Macbeth - Infirm of PurposeBen TaylorNo ratings yet
- Guide Card: Casa Del Niño Montessori School Guinatan, City of Ilagan, IsabelaDocument5 pagesGuide Card: Casa Del Niño Montessori School Guinatan, City of Ilagan, IsabelaManAsseh EustaceNo ratings yet
- Name: Period: DateDocument3 pagesName: Period: DateCarolina RozoNo ratings yet
- Ainscow, Farrell y Tweddle IJIE - 00 Developing Policies For Inclusive EducationDocument19 pagesAinscow, Farrell y Tweddle IJIE - 00 Developing Policies For Inclusive EducationMatías Reviriego RomeroNo ratings yet
- E38 DSC System PDFDocument32 pagesE38 DSC System PDFjoker63000No ratings yet